Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C1 Atomic Structure
C1 Atomic Structure
Uploaded by
OblizinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C1 Atomic Structure
C1 Atomic Structure
Uploaded by
OblizinCopyright:
Available Formats
C1 Atomic Structure
Knowledge Organiser
Atom—Smallest part of an element that can exist. Mixture—Two or more chemicals not chemically bonded.
Molecule—Two or more atoms chemically bonded. Separation Techniques—Used to separate mixtures:
Filtration—get an insoluble solid from a liquid.
Element—Only one type of atom present. Can be single atoms or molecules. Crystallisation—get a soluble solid from a liquid by evaporating liquid off.
Distillation—get a pure liquid from a mixture of liquids.
Compound—Two or more different elements chemically bonded. Chromatography—separate mixtures of coloured compounds.
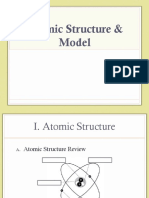
Nuclear Atom Model—Electrons orbit. Protons & neutrons in Electron energy levels—Where electrons are found. The shells
nucleus. Number of protons = number of electrons. each hold this many electrons maximum: 2, 8, 8.
Nucleus—The center of the atom. Contains neutrons & protons. Periodic Table—A list of all the elements in order of atomic
number. Columns called groups. Rows called periods.
Proton—Charge of +1. Mass of 1. Found inside the nucleus.
Conservation of Mass—In a chemical reaction the total mass of
reactants = total mass of products.
Neutron—Charge of 0. Mass of 1. Found inside the nucleus.
Mass Number—number of neutrons + protons.
Electron—Charge of –1. Mass of almost 0. Found orbiting the nucleus.
Atomic Number—Number of protons.
Isotope—same number of protons, different number of neutrons.
Plum Pudding Atomic Model—Early model. Ball of positive
Ion—Atom where number of protons is not equal to electrons. charge with electrons in it.
You might also like
- Chapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Document17 pagesChapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Kayte Middleton100% (1)
- Price 2022-D - 1669879424Document19 pagesPrice 2022-D - 1669879424Moses SilvaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 1: Structure, Bonding and Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 1: Structure, Bonding and Introduction To Organic ChemistryDefaults rulezNo ratings yet
- Post-Reaction WorkupDocument19 pagesPost-Reaction Workupwasa100% (1)
- 2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument6 pages2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chemistry Igcse SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Chemistry Igcse Summarytaliaamjad771No ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Chapter 2BrigitteNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics - 1Document61 pagesNuclear Physics - 1Rose MusariraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Document5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Chris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Campbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeDocument42 pagesCampbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeSophia Andrei VillalunaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Chemistry of Life EditedDocument68 pages2.1 The Chemistry of Life EditedPatricia Jayshree Samuel Jacob100% (1)
- Basic ChemistryDocument14 pagesBasic ChemistryPitherNo ratings yet
- CHEM (No Formula)Document4 pagesCHEM (No Formula)palacioaya28No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PartialDocument11 pagesChapter 2 PartialcrystalghayleparrasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2Document24 pagesChemistry Unit 2Auvan HilarioNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chemistry of LifeDocument55 pages1 - Chemistry of LifeDaniel KipnisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Atomic StructureDocument14 pagesChemistry Atomic StructureProDyut ChakraBortyNo ratings yet
- Rebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamDocument5 pagesRebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamjoshuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1 Formulae, Equations and Amounts of Substances: He Foundations of HemistryDocument9 pagesChapter 1.1 Formulae, Equations and Amounts of Substances: He Foundations of HemistryRawdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gen ChemDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Gen ChemJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- Atoms: 1. Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesAtoms: 1. Atomic Structurecherry shane abanesNo ratings yet
- 1.1 CchemDocument1 page1.1 CchemcallumNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Nuclear Medicine - Edited Version)Document65 pagesLecture Notes in Nuclear Medicine - Edited Version)Jestia Lyn EngracialNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Atomic Theory Part 1: Recall: NotesDocument11 pagesTopic 3: Atomic Theory Part 1: Recall: NotesniloNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument9 pagesChemistryJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- Elements PHSA Notes TV 09Document15 pagesElements PHSA Notes TV 09FFFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Atomic StructureDocument1 pageChapter 5 - Atomic StructureKayla WNo ratings yet
- Chemi Try Review: A. Elements (Chapter 2)Document7 pagesChemi Try Review: A. Elements (Chapter 2)Valentina RumhizhaNo ratings yet
- C2-Chemical Basis of LifeDocument2 pagesC2-Chemical Basis of LifeLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms MoleculesDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms Moleculesonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- HUBS1403 - Biomedical Science 1 - Lecture 2. Organisation of MatterDocument30 pagesHUBS1403 - Biomedical Science 1 - Lecture 2. Organisation of MatterEvelyn YongNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryKent RosimaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 2 Chemical Foundations For CellDocument2 pagesAP Biology Chapter 2 Chemical Foundations For Cellwrenet1231503No ratings yet
- All Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsDocument11 pagesAll Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsmNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: Class ObjectivesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: Class ObjectivesSebastian VillegasNo ratings yet
- 01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDocument4 pages01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDaniel Angelo MiradorNo ratings yet
- AtomicStructure 1Document41 pagesAtomicStructure 1Juned AlamNo ratings yet
- 1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFDocument4 pages1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument70 pagesCHEMISTRYF E R N A NNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Topics (1-3)Document22 pagesChemistry - Topics (1-3)shyannNo ratings yet
- A. Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument40 pagesA. Atoms and Atomic StructurewasimsabriNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesAtomic Structureyahvip07No ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureCağdaş AydınNo ratings yet
- FUNCHEM.2 2021 Slides 2021 2Document27 pagesFUNCHEM.2 2021 Slides 2021 2shabanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer PrelimsDocument4 pagesBiology Reviewer PrelimsOROZCO, Almira MaeNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument3 pagesSCIENCE - 3rd Quarter Reviewerdanvenice194No ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Module 1 Notes 2023Document30 pagesCape Chemistry Unit 1 Module 1 Notes 2023chelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Principles: The Structure of AtomsDocument11 pagesChemical Principles: The Structure of AtomsApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument57 pagesAtomic StructureMary Rose JasminNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserNaveen ChebroluNo ratings yet
- Eastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Document3 pagesEastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Isaac PiaoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 y 4 ATOMSDocument3 pagesUNIT 3 y 4 ATOMSLucia OrtegaNo ratings yet
- OCR Chemistry Module 2 AS LevelDocument9 pagesOCR Chemistry Module 2 AS LevelDarshan MistryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes - Matter & AtomsDocument5 pagesChemistry Notes - Matter & AtomsMikaela Fien Demecillo CorroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaDocument75 pagesChemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaJESPHER GARCIANo ratings yet
- Chem11e Group 02 Nuclear ChemistryDocument36 pagesChem11e Group 02 Nuclear ChemistryArdent BautistaNo ratings yet
- Marieb - CH - 02 - Lecture - Doc (Edited)Document5 pagesMarieb - CH - 02 - Lecture - Doc (Edited)Dustin RamosNo ratings yet
- Llogers - General Chemistry m1-m6Document18 pagesLlogers - General Chemistry m1-m6api-639087356No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Consituents of An Atom GSNDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Consituents of An Atom GSNhello3850No ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument5 pagesAtoms and MoleculesPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- RC Notes by Engr. GREGDocument49 pagesRC Notes by Engr. GREGMichael SuanNo ratings yet
- Viscosity Measuring DeviceDocument54 pagesViscosity Measuring DeviceShubhankur Mishra100% (1)
- TumsDocument2 pagesTumsAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Air Cleaners For Particulate Contaminants: Aerosol CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesAir Cleaners For Particulate Contaminants: Aerosol CharacteristicsImran AzizNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower ChlorinationDocument1 pageCooling Tower ChlorinationdeejayroxNo ratings yet
- Know Your Cooling SystemDocument122 pagesKnow Your Cooling SystemGustavo Adolfo Royero LopezNo ratings yet
- Utah Medical Cannabis ActDocument28 pagesUtah Medical Cannabis ActLarryDCurtisNo ratings yet
- Morphotropic Phase Boundary in BNT-BZT Solid Solution: A Study by Raman Spectroscopy and Electromechanical ParametersDocument7 pagesMorphotropic Phase Boundary in BNT-BZT Solid Solution: A Study by Raman Spectroscopy and Electromechanical Parametersrahma rahmaNo ratings yet
- AASHTO Designation T 290-95 (2012)Document9 pagesAASHTO Designation T 290-95 (2012)Mosa Talebi100% (1)
- The Effect of Light On Silver Halides: ExperimentDocument3 pagesThe Effect of Light On Silver Halides: ExperimentGerman CarleNo ratings yet
- Lab # 2Document7 pagesLab # 2Santos CocNo ratings yet
- ALS Metallurgy - Mineral Sands Process DevelopmentDocument8 pagesALS Metallurgy - Mineral Sands Process DevelopmentaghilifNo ratings yet
- Entech ControlsDocument12 pagesEntech Controlsmanmohansingh1999No ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of A Pressure Swing Adsorption PDFDocument12 pagesNumerical Simulation of A Pressure Swing Adsorption PDFGustavo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- 1 - Appendix 2 Escort Overtime FormDocument4 pages1 - Appendix 2 Escort Overtime FormAde TriefNo ratings yet
- Brittle Coating TheoryDocument24 pagesBrittle Coating TheorySaad Afzal50% (2)
- Chapter.5 MethodologyDocument14 pagesChapter.5 MethodologyUmesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- GMP and Preparation in Hospital Pharmacies - Bouwman and Andersen 19 (5) - 469 - European Journal of Hospital Pharmacy - Science and PracticeDocument4 pagesGMP and Preparation in Hospital Pharmacies - Bouwman and Andersen 19 (5) - 469 - European Journal of Hospital Pharmacy - Science and Practicecarbou0% (1)
- Final Chap 1 2 Group 2Document11 pagesFinal Chap 1 2 Group 2Franshel CaldozaNo ratings yet
- Accredited Consultants PDFDocument142 pagesAccredited Consultants PDFShantanu EksambekarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4:5 Lab ReportDocument6 pagesExperiment 4:5 Lab ReportHannah GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 2013-3-11 - ThinkaboutwhatyoudrinkDocument10 pages2013-3-11 - ThinkaboutwhatyoudrinkmistermaximNo ratings yet
- Narela Defaulters List As On 31.3.16Document182 pagesNarela Defaulters List As On 31.3.16dharmender singhNo ratings yet
- Coconut Shell Ash CHBDocument29 pagesCoconut Shell Ash CHBRBT BoysNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY: Rocephin - Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY: Rocephin - Ceftriaxone SodiumYum C100% (1)
- Lectures Biological MethodsDocument44 pagesLectures Biological MethodsAlpha PlacardNo ratings yet
- Effects of Textile Dyes On Health and The Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living OrganismsDocument17 pagesEffects of Textile Dyes On Health and The Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living OrganismsfikaNo ratings yet
- Bulletin 60 AFQRJOS Issue 27 Feb 2013 PDFDocument6 pagesBulletin 60 AFQRJOS Issue 27 Feb 2013 PDFpersadanusantaraNo ratings yet