Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MP and MC
MP and MC
Uploaded by
MC Meconzy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesMicrocontroller and microprocessor
Original Title
MP AND MC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMicrocontroller and microprocessor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesMP and MC
MP and MC
Uploaded by
MC MeconzyMicrocontroller and microprocessor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
METTAH CONRAD BAMEH
CT21A160
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC
TOPIC: ANALOGUE TO DIGITAL ONVERTER (ADC)
Definition: An ADC is a data converter which allows digital circuits (e.g. an Arduino) to
interface with the real world by encoding an analogue signal into a binary code. There exist two
main types of ADC, Unipolar and bipolar ADC.
UNIPOLAR ADC
A unipolar ADC is that whose input can only receive signals with either zero or positive polarity.
For example, given that the signal is a voltage, a unipolar ADC can only support 0 - to - +5V or
whatever the maximum value may be. The input signal looks like that in the figure below.
The pulse rise time is faster while the fall time is slower.
The formula to calculate the digital output of a unipolar ADC is the following.
Where: is the input voltage, is the reference voltage, n is the
number of bits and is the digital output.
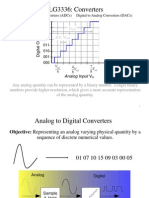
TRANSFER FUNCTION: The transfer function of an ADC is a plot of the input signal to the
ADC versus the output signals or codes from the ADC. The transfer function for unipolar ADC
is the following
BIPOLAR ADC
This is an ADC in which the input signal can swing between positive and negative. For example
U = ±10V.
The rise and fall times are both fast. The input signal is the following.
TRANSFER FUNCTION
The transfer functions of a bipolar ADC if given below.
The formula for the digital output is the following
You might also like
- Digital Electronics-10 PDFDocument8 pagesDigital Electronics-10 PDFTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- integratedelectronicsUNIT 3convertersDocument11 pagesintegratedelectronicsUNIT 3convertersYogeshwaranNo ratings yet
- Analogue To Digital Converter: By: Vishnu Raj R S BDocument18 pagesAnalogue To Digital Converter: By: Vishnu Raj R S Bvishnurajrajesh2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4Tejan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- ADC Unit 5Document36 pagesADC Unit 5Nine ToNo ratings yet
- BScPhysics 4sem MrrajeshKumarDocument20 pagesBScPhysics 4sem MrrajeshKumarchaudhuriabhinaba1No ratings yet
- Using A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowDocument10 pagesUsing A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowPrakhar BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterRavi Patel100% (1)
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterPratyay DharNo ratings yet
- Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC) Interfacing With MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Converter (ADC) Interfacing With MicrocontrollerSridhar DineshNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter - Block Diagram, Types Its ApplicationsDocument10 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter - Block Diagram, Types Its ApplicationsNikka Hernandez FloresNo ratings yet
- ADC FinalDocument35 pagesADC FinalAmit BarNo ratings yet
- Adc and Dac Converters: BY:-PULKIT PARASHAR (17BEE080), Pritam Yaduvanshi (17bee079) Guide:-Prof. Akhilesh NimjeDocument9 pagesAdc and Dac Converters: BY:-PULKIT PARASHAR (17BEE080), Pritam Yaduvanshi (17bee079) Guide:-Prof. Akhilesh NimjePritam YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 D A ConvertorDocument60 pagesUnit 4 D A Convertorneverinstall86No ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument4 pagesAnalog To Digital Converterzero kimochiNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Data Converters: Types of Analog To Digital ConvertersDocument3 pagesUnit Iv Data Converters: Types of Analog To Digital ConvertersAshrith LadiNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument4 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertermuzamiru Kahise sayumweNo ratings yet
- An Analog To Digital ConverterDocument5 pagesAn Analog To Digital ConverterDINESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- ON ADC'sDocument24 pagesON ADC'sRavi BellubbiNo ratings yet
- Dac Adc FileDocument66 pagesDac Adc FileKhushbu JoshiNo ratings yet
- Module Data Converters (ADC and DAC)Document10 pagesModule Data Converters (ADC and DAC)Johnlester Maggay100% (1)
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument41 pagesAnalog To Digital Converterkhushbubansal100% (1)
- Pras DEDocument27 pagesPras DEprasnthsmNo ratings yet
- 6 Adc0804Document5 pages6 Adc0804esther_kakani919No ratings yet
- DAC, ADC, Sensor, Interfacing DevicesDocument36 pagesDAC, ADC, Sensor, Interfacing DevicesSimranSiMmy100% (1)
- Communications Lab. Experiment 6: Adc / DacDocument2 pagesCommunications Lab. Experiment 6: Adc / DacSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Analog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIIDocument50 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIILisa BhagatNo ratings yet
- Analogue To Digital Converter (ADC) BasicsDocument7 pagesAnalogue To Digital Converter (ADC) Basicsdiether.gozumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Part Ni Solo)Document10 pagesChapter 10 (Part Ni Solo)edward solomonNo ratings yet
- Mbed Course Notes - Analog Input and OutputDocument24 pagesMbed Course Notes - Analog Input and OutputBelkhiri MohammedNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument66 pagesAnalog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersSai Krishna Kodali100% (1)
- Teknik Konversi Data (Data Conversion) : Pendidikan Vokasional Mekatronika FT UnmDocument40 pagesTeknik Konversi Data (Data Conversion) : Pendidikan Vokasional Mekatronika FT UnmYuli Adhaning TyasNo ratings yet
- Ece3430 Lecture 18Document24 pagesEce3430 Lecture 18kuser5506No ratings yet
- Nama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCDocument4 pagesNama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCRifky Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- ADC and DACDocument16 pagesADC and DACThota Indra MohanNo ratings yet
- 4-Digital and AnalogDocument26 pages4-Digital and Analogteklaykibrom3No ratings yet
- Lecture 21 PDFDocument15 pagesLecture 21 PDFAjmal YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Electronic ConvertersDocument18 pagesElectronic ConvertersKairredin Mahamed HusenNo ratings yet
- Electronic ConvertersDocument18 pagesElectronic ConvertersKairredin Mahamed HusenNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusNioNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 ADCDocument8 pagesUnit-5 ADCDr. M Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument12 pagesAdc DacSonu SauravNo ratings yet
- Adc ConversionDocument20 pagesAdc Conversionhemantec100% (1)
- Sar AdcDocument13 pagesSar AdcHunZilah ShEikhNo ratings yet
- Analog To DigitalDocument46 pagesAnalog To DigitalSaleem HaddadNo ratings yet
- Document On Interfacing ADC With 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesDocument On Interfacing ADC With 8051 MicrocontrollerSrideviKumaresanNo ratings yet
- Interfacing - ADC & DAC: ADC (Analog To Digital Converter)Document8 pagesInterfacing - ADC & DAC: ADC (Analog To Digital Converter)Jagan VNo ratings yet
- EE 120 - Interfacing With The Analog WorldDocument8 pagesEE 120 - Interfacing With The Analog WorldAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Digital To Analog Converters (DACs)Document7 pagesDigital To Analog Converters (DACs)Lentera RuhNo ratings yet
- Tim Eric 1Document21 pagesTim Eric 1Ljay_LoNo ratings yet
- Jadavpur University: PptonDocument39 pagesJadavpur University: PptonAmit BarNo ratings yet
- AVR120: Characterization and Calibration of The Adc On An AvrDocument15 pagesAVR120: Characterization and Calibration of The Adc On An AvrjmgandiaNo ratings yet
- EEN11, Finals CombinedDocument105 pagesEEN11, Finals CombinedlavadiajhonNo ratings yet
- Een 11 Finals Lec1Document46 pagesEen 11 Finals Lec1lavadiajhonNo ratings yet
- Clap Switch Using ArduinoDocument7 pagesClap Switch Using Arduinohamed razaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document40 pagesChapter 8UMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMNo ratings yet
- ADCsDocument12 pagesADCswalidNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)