Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factsheet - Enzymes
Factsheet - Enzymes
Uploaded by
Andy DlobelaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factsheet - Enzymes
Factsheet - Enzymes
Uploaded by
Andy DlobelaCopyright:
Available Formats
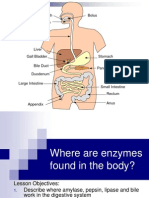
Enzy
Enzymes are special proteins that can break large molecules into small molecules; they act as
mes
biological catalysts. Different types of enzymes can break down different nutrients. (Amylase is an
example of a carbohydrase)
enzyme reaction catalysed enzyme where produced
amylase starch → sugars amylase salivary glands, pancreas, small intestine
protease proteins → amino acids proteas stomach, pancreas, small intestine
e
lipase lipids → fatty acids + glycerol
lipase pancreas, small intestine
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are digested in the mouth, stomach and small intestine. Carbohydrase enzymes
break down starch into sugars.
The saliva in your mouth contains amylase, which is another starch digesting enzyme. If you
chew a piece of bread for long enough, the starch it contains is digested to sugar, and it begins to
taste sweet.
Proteins
Proteins are digested in the stomach and small intestine. Protease enzymes break down
proteins into amino acids. Digestion of proteins in the stomach is helped by stomach acid, which
is strong hydrochloric acid. This also kills harmful micro-organisms that may be in the food.
Fats
Lipase enzymes break down fat into fatty acids and glycerol. Digestion of fat in the small
intestine is helped by bile, made in the liver. Bile breaks the fat into small droplets that are easier
for the lipase enzymes to work on.
You might also like
- The Digestive Enzyme of The BodyDocument12 pagesThe Digestive Enzyme of The BodyClarisse WongNo ratings yet
- Biology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestionDocument3 pagesBiology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestiontahamidNo ratings yet
- CHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 4Document8 pagesCHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 4Ysa DienteNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemafssmowNo ratings yet
- Digestive EnzymesDocument1 pageDigestive EnzymesAaishahNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: DigestionDocument5 pagesEnzyme: Digestion24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Digestive Form 4Document43 pagesDigestive Form 4miraazizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Answer KeyzakiyaNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument3 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionCapriceNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: VitaminsDocument29 pagesNutrition: Vitaminsrv5bcgywkpNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaNo ratings yet
- Nurition in Mammals - 2Document3 pagesNurition in Mammals - 2Farzan ButtNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bio 1Document2 pagesTugas Bio 1Made SetiadjiNo ratings yet
- Digestive Enzymes & BacteriaDocument13 pagesDigestive Enzymes & BacteriaEsraa BahaaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Human BeingsDocument28 pagesNutrition in Human Beingssarrah asgarNo ratings yet
- N2 Digestive System AnswersDocument4 pagesN2 Digestive System AnswersitziarccNo ratings yet
- Kuliah II - Digestive EnzymesDocument22 pagesKuliah II - Digestive EnzymesHastomo Nur HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Applications of EnzymesDocument11 pagesApplications of EnzymesNadish Namish BhradwajNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Educational Video in Red Pink Illustrative StyleDocument15 pagesDigestive System Educational Video in Red Pink Illustrative Stylefarrahfahad72No ratings yet
- Digestive System: Structure FunctionDocument7 pagesDigestive System: Structure Functionreeta ramNo ratings yet
- Alimentary Canal 3rd YearDocument19 pagesAlimentary Canal 3rd Yearsamson aslamNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Digestive SystemDocument5 pages2.3 Digestive SystemsalNo ratings yet
- Digestion-Food Is BrokenDocument32 pagesDigestion-Food Is Brokenaerell manuelNo ratings yet
- Biology - Course - Haidar RahhalDocument36 pagesBiology - Course - Haidar RahhalFatima SlimNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Digestion 1Document28 pagesAbsorption and Digestion 1InaraNo ratings yet
- Revision Lesson On EnzymesDocument14 pagesRevision Lesson On EnzymesPiper McleanNo ratings yet
- Macronutrient Project FinalDocument6 pagesMacronutrient Project Finalapi-259363834No ratings yet
- Digestive Enzymes by JajaDocument12 pagesDigestive Enzymes by JajaYvonne Alonzo De BelenNo ratings yet
- Digestive Enzymes WorksheetDocument2 pagesDigestive Enzymes WorksheetSaima UsmanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Notes On Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesIGCSE Biology Notes On Digestive SystemTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of MacronutrientsDocument3 pagesDigestion and Absorption of MacronutrientsMuhammad Usman FastNUNo ratings yet
- Lecture On: Digestive EnzymesDocument21 pagesLecture On: Digestive EnzymesFaith G. FloresNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionDocument26 pagesDigestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionTemz HlubyNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and DigestionDocument24 pagesEnzymes and DigestionAndy DlobelaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes in DigestionDocument14 pagesEnzymes in Digestionapi-188431847No ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument46 pagesNutrition in AnimalsFreshNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Document9 pagesDigestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Monojit DharNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Digestive Systemvidur_talrejaNo ratings yet
- 06 Nutrition in Humans NoteDocument12 pages06 Nutrition in Humans Notetarankaur401No ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Teeth To Digestion Handout' With YouDocument12 pagesI Am Sharing 'Teeth To Digestion Handout' With YouAthena CrooksNo ratings yet
- The Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemJeanAnzurezNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism - EnzymesDocument14 pagesMicrobial Metabolism - EnzymesSaint TzyNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Enzymes in DigestionDocument16 pagesBacteria Enzymes in Digestionroselam226No ratings yet
- Digestion NotesDocument3 pagesDigestion NoteskuluNo ratings yet
- Food and Digestion BWDocument16 pagesFood and Digestion BWJaymee GonzalesNo ratings yet
- The Small IntestineDocument16 pagesThe Small IntestineMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument25 pagesDigestive Systemshayn budihardjoNo ratings yet
- Food DigestionDocument36 pagesFood Digestionthiruchelvam1No ratings yet
- Amylase WorksheetDocument2 pagesAmylase WorksheetG Meera Prem KumarNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument38 pagesDigestive SystemeriNo ratings yet
- Digestion NoteDocument5 pagesDigestion Notebob burgersNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive Sysytem Icse BoardDocument40 pagesHuman Digestive Sysytem Icse BoardJagrity SinghNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 (3.3 Human Digestive System)Document10 pagesScience Form 2 (3.3 Human Digestive System)sivanesshniNo ratings yet
- B2.5.1 Proteins - B2.5.2 Enzymes: No Higher Tier ContentDocument3 pagesB2.5.1 Proteins - B2.5.2 Enzymes: No Higher Tier ContentRekaNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Group 5Document16 pagesPost Lab Group 5Charie May Antipasado CallanoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesDigestive SystemDainalissa SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Food and DigestionDocument8 pagesFood and Digestionharoonadnan196No ratings yet
- 9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroDocument51 pages9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroPratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet