Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 1.0 Interfaces & Interworking
Module 1.0 Interfaces & Interworking
Uploaded by
ahad siddiquiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- LTE Handover OptimizationDocument33 pagesLTE Handover Optimizationthang_1986dh100% (3)
- LTE Network Issue Analysis Guideline V1Document29 pagesLTE Network Issue Analysis Guideline V1Amir Miftahudin100% (1)
- LTE INTER Frequency Handover Trouble Shooting CaseDocument15 pagesLTE INTER Frequency Handover Trouble Shooting Casenoriaz100% (1)
- 3G3JZ Manual BasicDocument21 pages3G3JZ Manual BasicTran Le83% (6)
- l3gw Vmto Evpn Vxlan MplsDocument24 pagesl3gw Vmto Evpn Vxlan MplsVijay BhargavNo ratings yet
- LTE Trial: - EPC Testing NotesDocument9 pagesLTE Trial: - EPC Testing NotesVincent Teck Chai TanNo ratings yet
- 2 LTE ERAN6.0 Access Fault DiagnsisDocument66 pages2 LTE ERAN6.0 Access Fault Diagnsisfaysal137152.storageNo ratings yet
- 5g Nsa Access Trouble ShootingDocument10 pages5g Nsa Access Trouble ShootingPsi Factors100% (1)
- LTE Access Fault DiagnsisDocument71 pagesLTE Access Fault DiagnsisStanislas Arthur Lishu100% (2)
- ENDC & 5G AttachDocument10 pagesENDC & 5G Attachaslam_326580186No ratings yet
- Useful Drop IndicatorsDocument11 pagesUseful Drop IndicatorsRafiq mikNo ratings yet
- LTE N CNTRDocument4 pagesLTE N CNTRtkchauhan1No ratings yet
- CiscoDataCenterCertificatione Guide 2017Document40 pagesCiscoDataCenterCertificatione Guide 2017Fayyaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 EPC Interface Protocol AnalysisDocument41 pages1 EPC Interface Protocol AnalysisEdwin MurciaNo ratings yet
- 06 LTE Access Analysis and Counters - 31PDocument31 pages06 LTE Access Analysis and Counters - 31PBoualem AmineNo ratings yet
- Nokia RAN KPIs Part 2 RABDocument31 pagesNokia RAN KPIs Part 2 RABSABER1980No ratings yet
- 03 LTE Access Fault Diagnosis ISSUE1.02 cvb2 PDFDocument85 pages03 LTE Access Fault Diagnosis ISSUE1.02 cvb2 PDFČärlös Lemös FlörezNo ratings yet
- B Nid Controller Book Chapter 01111Document28 pagesB Nid Controller Book Chapter 01111Sameer KauraNo ratings yet
- 08ltekpi PDF FreeDocument15 pages08ltekpi PDF FreeJUCARLCNo ratings yet
- CQT Troubleshoooting V1.0Document10 pagesCQT Troubleshoooting V1.0KhangTranNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Analysis and Optimization of The LTE Call Completion RateDocument21 pagesCH-3 Analysis and Optimization of The LTE Call Completion Ratenaseem AhamdNo ratings yet
- Lacp With STP Sim PDFDocument8 pagesLacp With STP Sim PDFKang Mas PaijhoNo ratings yet
- Call Setup Analysis Exercise: FilesDocument3 pagesCall Setup Analysis Exercise: FilesABHISHEK AGARWALNo ratings yet
- A.2 Receive Message Function (MSG-RCV)Document8 pagesA.2 Receive Message Function (MSG-RCV)White TigerNo ratings yet
- FDD LTE Handover OptimizationDocument35 pagesFDD LTE Handover OptimizationmunzewNo ratings yet
- Consul As A Monitoring Service PresentationDocument85 pagesConsul As A Monitoring Service PresentationAnonymous ryDGv1No ratings yet
- 02 LTE KPI ArchitectureDocument104 pages02 LTE KPI ArchitectureVahid ZibakalamNo ratings yet
- LTE S1 Interface: Satish Kumar S, Val&FS2, Date: 22 Sep, 2021Document29 pagesLTE S1 Interface: Satish Kumar S, Val&FS2, Date: 22 Sep, 2021sandhya24No ratings yet
- KMPL-2143 - EVPN Migration From Legacy To Modern ArchDocument32 pagesKMPL-2143 - EVPN Migration From Legacy To Modern ArchquintaNo ratings yet
- Nokian Capacitor NC12 Controller InstructionsDocument44 pagesNokian Capacitor NC12 Controller InstructionsRiswan FrdmNo ratings yet
- Xrdocs Io ncs5500 Tutorials srv6 Transport On Ncs Part 6Document9 pagesXrdocs Io ncs5500 Tutorials srv6 Transport On Ncs Part 6Konstantinos DimitriouNo ratings yet
- FDD LTE Handover Optimization - 切换Document35 pagesFDD LTE Handover Optimization - 切换Ahmad FauzaniNo ratings yet
- Packt Lin Nov 2015 ISBN 1785284444Document16 pagesPackt Lin Nov 2015 ISBN 1785284444suraj singhNo ratings yet
- BRKMPL 2333Document102 pagesBRKMPL 2333alfagemeoNo ratings yet
- Day 2 - Module 1 - Lte SignallingDocument19 pagesDay 2 - Module 1 - Lte SignallingRahmatia SafitriNo ratings yet
- Ethernet VPN (Evpn) : Overlay Networks For Ethernet ServicesDocument34 pagesEthernet VPN (Evpn) : Overlay Networks For Ethernet ServicesaliaydemirNo ratings yet
- 04 - Co Core SW Re - Testing PlanDocument23 pages04 - Co Core SW Re - Testing PlanRomaNo ratings yet
- SDN & NFV IntroductionDocument72 pagesSDN & NFV Introductionmahmoud_shukur1447No ratings yet
- RG008608 Planning Differences Between EVDO and 1XDocument34 pagesRG008608 Planning Differences Between EVDO and 1XDeepak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Controller Area Network (CAN) Implementation: Hardware and Software PerspectiveDocument69 pagesController Area Network (CAN) Implementation: Hardware and Software PerspectiveAshokUmmadisettiNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lab: ACT-07T Data Conditioning Trainer KitDocument1 pageDigital Communication Lab: ACT-07T Data Conditioning Trainer KitFahim MunawarNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Controller NC-12 User'S ManualDocument44 pagesPower Factor Controller NC-12 User'S Manualgrigore mirceaNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Oam Tutorial Final v2 1362014627Document79 pagesEthernet Oam Tutorial Final v2 1362014627Mehmet DepoNo ratings yet
- 5g Non Standalone Access en DCDocument56 pages5g Non Standalone Access en DCNEO SinghNo ratings yet
- voLTE Call FlowDocument45 pagesvoLTE Call FlowSSCVT Technical TeamNo ratings yet
- Appendix3 - OTA105204 OptiX OSN 1500250035007500 Ethernet Services Configuration (Trail Configuration) ISSUE 1.21Document41 pagesAppendix3 - OTA105204 OptiX OSN 1500250035007500 Ethernet Services Configuration (Trail Configuration) ISSUE 1.21Huy LinhNo ratings yet
- Conventional Networks 2.4 GSM: Prof. JP HubauxDocument47 pagesConventional Networks 2.4 GSM: Prof. JP HubauxDedy MahaNo ratings yet
- 4G LTE Drive Test IntroductionDocument18 pages4G LTE Drive Test IntroductionHari MuklasNo ratings yet
- UMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFDocument63 pagesUMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFMahamadou Ousseini Barkiré100% (1)
- RECLOSERDocument39 pagesRECLOSER22142283No ratings yet
- Algorithm of 5G RAN1.0 Mobility ManagementDocument34 pagesAlgorithm of 5G RAN1.0 Mobility ManagementDuan Feng100% (3)
- Call Processing in Cdma: Mobile InitializationDocument28 pagesCall Processing in Cdma: Mobile InitializationVarun AdhikariNo ratings yet
- App BDocument14 pagesApp Babhayksparmar7157No ratings yet
- LTEPMCounter20150911140851 KPIDocument3,057 pagesLTEPMCounter20150911140851 KPIbalaNo ratings yet
- Banglalink Knowledge Sharing Part3-0423Document40 pagesBanglalink Knowledge Sharing Part3-0423Gazi Nazmul HoqNo ratings yet
- GVRP Protocol IntroductionDocument13 pagesGVRP Protocol IntroductionminhNo ratings yet
- En DCDocument37 pagesEn DCraj1978enatorNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Resume - Latest 1695029351432 Ahad Siddiqui-2Document3 pagesResume - Latest 1695029351432 Ahad Siddiqui-2ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - LTE Introduction Ver 1.0Document127 pagesModule 1 - LTE Introduction Ver 1.0ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Report 2402410522 1Document4 pagesReport 2402410522 1ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Gur 0324 CL 0004980 S01Document1 pageGur 0324 CL 0004980 S01ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Abdul Ahad MohammadDocument2 pagesAbdul Ahad Mohammadahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ahad Mohammad Farooque Siddiqui Abdul EAHAABD 2023 Annual Salary Review GlobalDocument1 pageAhad Mohammad Farooque Siddiqui Abdul EAHAABD 2023 Annual Salary Review Globalahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Resume - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEDocument5 pagesResume - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Resume - Ahad Siddiqui - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEDocument6 pagesResume - Ahad Siddiqui - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Resume - LatestDocument6 pagesResume - Latestahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Telia Project Library - 29 Nov 2021Document46 pagesTelia Project Library - 29 Nov 2021ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Initial SID - Telia Swap - Rev - ADocument15 pagesInitial SID - Telia Swap - Rev - Aahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Amaresh Update ResumeDocument10 pagesAmaresh Update Resumeahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Netshutdown Config ManualDocument16 pagesNetshutdown Config Manualkaleab eduictNo ratings yet
- Broken Authentication and Session Management Vulnerability: A Case Study of Web ApplicationDocument7 pagesBroken Authentication and Session Management Vulnerability: A Case Study of Web ApplicationgkpalokNo ratings yet
- Teenage PregnancyDocument19 pagesTeenage PregnancyJai-JaiAdalidNo ratings yet
- UCF CNT5805 - Fall2021 - SyllabusDocument46 pagesUCF CNT5805 - Fall2021 - SyllabusVictor KingbuilderNo ratings yet
- CCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingDocument8 pagesCCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkinghemachandranNo ratings yet
- 3gpp 29514-g70Document181 pages3gpp 29514-g70miniscribdloginNo ratings yet
- SX 52 BDDocument58 pagesSX 52 BDedson_rcNo ratings yet
- Using Spring Cloud Gateway With OAuth 2.0 Patterns - BaeldungDocument1 pageUsing Spring Cloud Gateway With OAuth 2.0 Patterns - Baeldungcarlos.h.cardoso140No ratings yet
- Lec1 BDocument29 pagesLec1 BHabtie TesfahunNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Multimedia Future NetworkingDocument9 pagesUnit 7 Multimedia Future Networkingnirjan ghimireNo ratings yet
- (ST Public) ZXR10 3900 Series Switches Running ZXROS - ST v1.5 PDFDocument53 pages(ST Public) ZXR10 3900 Series Switches Running ZXROS - ST v1.5 PDFyohannesNo ratings yet
- LTRT-31621 SBC Design GuideDocument32 pagesLTRT-31621 SBC Design GuidefanticelliNo ratings yet
- Anurag Singh Mini Project 2nd SemDocument43 pagesAnurag Singh Mini Project 2nd SemRitik100% (1)
- Content Matrix Release NotesDocument48 pagesContent Matrix Release NotesBrizaNo ratings yet
- Instalasi Dan Konfigurasi Squid Di Centos 7Document2 pagesInstalasi Dan Konfigurasi Squid Di Centos 7Habil Faleview BangeetNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument6 pagesNetwork DevicesDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Laj00440 PSRPT 2019-05-05 16.53.40Document21 pagesLaj00440 PSRPT 2019-05-05 16.53.40Darwin Herrera SalinasNo ratings yet
- SoloLearn (HTML)Document22 pagesSoloLearn (HTML)Md Tanvir MahtabNo ratings yet
- Lab ISCW: Cau Hinh Load Balancing Tren 2 Line ADSL Dùng SAA. I. Sơ Đ LabDocument4 pagesLab ISCW: Cau Hinh Load Balancing Tren 2 Line ADSL Dùng SAA. I. Sơ Đ LabLe Ngoc KhoaNo ratings yet
- 08 01 14 Verizon Response-20140804-153609979Document5 pages08 01 14 Verizon Response-20140804-153609979jbrodkin2000No ratings yet
- 8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer Lab 2Document6 pages8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer Lab 2darkbane00No ratings yet
- Mikrotik PBR GuideDocument10 pagesMikrotik PBR GuideIvoNo ratings yet
- Brand AwarenessDocument30 pagesBrand AwarenessKetan SonawaneNo ratings yet
- (Wellman) The Networked Nature of CommunityDocument15 pages(Wellman) The Networked Nature of Communityshi100% (1)
- Module-3: Device ConfigurationDocument22 pagesModule-3: Device ConfigurationNirabhra RayNo ratings yet
- Business Goldmine - 100 Profitable Business ModelsDocument23 pagesBusiness Goldmine - 100 Profitable Business Modelshimanshu_nazkaniNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint Security Gateway Gaia R77 InstallationDocument17 pagesCheckpoint Security Gateway Gaia R77 InstallationDave CullenNo ratings yet
- Tarjeta SNMP Del UPS Marca DeltaDocument2 pagesTarjeta SNMP Del UPS Marca DeltaJozé LuisNo ratings yet
- 3014 PreDocument95 pages3014 PreDinesh Raja MNo ratings yet
Module 1.0 Interfaces & Interworking
Module 1.0 Interfaces & Interworking
Uploaded by
ahad siddiquiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 1.0 Interfaces & Interworking
Module 1.0 Interfaces & Interworking
Uploaded by
ahad siddiquiCopyright:
Available Formats
Interfaces & Interworking with 3GPP& Non-3GPP
Network
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S1 Interface
• S1-AP protocol is designed for a single interface, namely the MME to eNodeB
interface. The protocol is named after the interface name (S1) and the addition of AP
(Application Part) which is the 3GPP term for signalling protocol between two
nodes.
• S1-AP supports all mechanisms necessary for the procedures between MME and
eNodeB and it also supports transparent transport for procedures that are executed
between the MME and the UE.
• S1-AP consists of Elementary Procedures. An Elementary Procedure is a unit of
interaction between the eNodeBs and the MME. These Elementary Procedures are
defined separately and are intended to be used to build up complete sequences in a
flexible manner.
• S1-AP relies on a reliable transport mechanism and is designed to run on top of
SCTP.
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S1 Interface
S1 Interface
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S1 Interface
S1AP Elementary Procedures, class 1
Elementary Initiating Message Successful Outcome Unsuccessful outcome
Response Message
Procedure, class 1 Response Message
Handover Preparation HANDOVER REQUIRED HANDOVER COMMAND HANDOVER PREPARATION
FAILURE
Handover Resource Allocation HANDOVER REQUEST HANDOVER REQUEST HANDOVER FAILURE
ACKNOWLEDGE
Path Switch Request PATH SWITCH REQUEST PATH SWITCH REQUEST PATH SWITCH REQUEST
ACKNOWLEDGE FAILURE
Handover Cancellation HANDOVER CANCEL HANDOVER CANCEL
ACKNOWLEDGE
E-RAB Setup E-RAB SETUP REQUEST E-RAB SETUP RESPONSE
E-RAB Modify E-RAB MODIFY REQUEST E-RAB MODIFY RESPONSE
E-RAB Release E-RAB RELEASE COMMAND E-RAB RELEASE RESPONSE
Initial Context Setup INITIAL CONTEXT SETUP INITIAL CONTEXT SETUP INITIAL CONTEXT SETUP
REQUEST RESPONSE FAILURE
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S1 Interface
S1AP Elementary Procedures, class 1
Elementary Initiating Message Successful Outcome Unsuccessful outcome
Response Message
Procedure, class 1 Response Message
Reset RESET RESET ACKNOWLEDGE
S1 Setup S1 SETUP REQUEST S1 SETUP RESPONSE S1 SETUP FAILURE
UE Context Release UE CONTEXT RELEASE UE CONTEXT RELEASE
COMMAND COMPLETE
UE Context Modification UE CONTEXT UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION
MODIFICATION REQUEST RESPONSE FAILURE
eNB Configuration Update ENB CONFIGURATION ENB CONFIGURATION ENB CONFIGURATION
UPDATE UPDATE ACKNOWLEDGE UPDATE FAILURE
MME Configuration Update MME CONFIGURATION MME CONFIGURATION MME CONFIGURATION
UPDATE UPDATE ACKNOWLEDGE UPDATE FAILURE
Write-Replace Warning WRITE-REPLACE WARNING WRITE-REPLACE WARNING
REQUEST RESPONSE
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S1 Interface
S1AP Elementary Procedures, Class 2
Elementary procedure, class 2 Initiating Message
Handover Notification HANDOVER NOTIFY
E-RAB Release Indication E-RAB RELEASE INDICATION
Paging PAGING
Initial UE Message INITIAL UE MESSAGE
Downlink NAS Transport DOWNLINK NAS TRANSPORT
Uplink NAS Transport UPLINK NAS TRANSPORT
NAS non delivery Indication NAS NON DELIVERY INDICATION
Error Indication ERROR INDICATION
UE Context Release Request UE CONTEXT RELEASE REQUEST
Downlink S1 CDMA 2000 Tunneling DOWNLINK S1 CDMA 2000 TUNNELING
Uplink S1 CDMA2000 Tunneling UPLINK S1 CDMA2000 TUNNELING
UE Capability Info Indication UE CAPABILITY INFO INDICATION
eNB Status Transfer ENB STATUS TRANSFER
MME Status Transfer MME STATUS TRANSFER
Deactivate Trace DEACTIVATE TRACE
Trace Start TRACE START
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
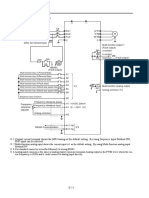
S1 Interface
S1 Handover
RRC
CONNECTED
RRC
CONNECTED
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
X2 Interface
• Inter-connection of eNodeBs supplied by different manufacturers;
• Support of continuation between eNodeBs of the E-UTRAN services offered via the
S1 interface;
• Separation of X2 interface Radio Network functionality and Transport Network
functionality to facilitate introduction of future technology
• The main purpose for X2 is to support the active mode UE mobility (Packet
Forwarding).
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
X2 Interface
X2 Protocol Model
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
X2 Interface
Functions of X2AP
• Setting up the X2
• Resetting the X2
• Mobility Management
• Load Management
• Reporting of General Error Situations
• eNodeB Configuration Update
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
X2 Interface
X2AP Elementary Procedures, class 1
Elementary Initiating Message Successful Outcome Unsuccessful outcome
Response Message
Procedure, class 1 Response Message
HANDOVER PREPARATION HANDOVER REQUEST HANDOVER REQUEST HANDOVER PREPARATION
ACKNOWLEDGE FAILURE
RESET RESET REQUEST RESET RESPONSE
X2 SETUP X2 SETUP REQUEST X2 SETUP RESPONSE X2 SETUP FAILURE
ENB CONFIGURATION UPDATE ENB CONFIGURATION ENB CONFIGURATION ENB CONFIGURATION
UPDATE UPDATE ACKNOWLEDGE UPDATE FAILURE
RESOURCE STATUS REPORTING RESOURCE STATUS RESOURCE STATUS RESOURCE STATUS
INITIATION REQUEST RESPONSE FAILURE
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
X2 Interface
X2AP Elementary Procedures, Class 2
Elementary procedure, class 2 Initiating Message
LOAD INDICATION LOAD INFORMATION
HANDOVER CANCEL HANDOVER CANCEL
SN STATUS TRANSFER SN STATUS TRANSFER
UE CONTEXT RELEASE UE CONTEXT RELEASE
RESOURCE STATUS REPORTING RESOURCE STATUS UPDATE
ERROR INDICATION ERROR INDICATION
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
X2 Interface
X2 Handover
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S11 Interface Procedure
• The S11 interface is defined between MME and the Serving GW. Due to the
separation of the control and user plane functions between MME and Serving GW,
the S11 interface is used to create a new session and then manage these sessions that
has established connection within EPS.
• The S11 interface is always triggered by some events either directly from the NAS
level signalling from the terminal or creating a connection towards a new PDN.
• In case of handover, the S11 interface is used to relocate the Serving GW when
appropriate, establish direct or indirect forwarding tunnel for user plane traffic and
manage the user data traffic flow.
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S5/S8 Interface Procedure
• The S5/S8 interface is defined between the Serving GW and the PDN GW. The S5
interface is used in non-roaming scenarios where as S8 interface is the roaming variant
of S5 and is used in roaming scenarios with the Serving GW in the visited network and
the PDN GW in the home network.
• When the GTP variant of the protocol is used, the S5/S8 interface provides the
functionality associated with creation/deletion/modification/change of bearers for
individual user connected to EPS.
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
S10 Interface Procedure
• The S10 interface is defined between two MMEs. The main function of this protocol
is to transfer the contexts for individual terminals attached to the EPC network and
thus sent on a per UE basis. This interface is primarily used when MME is relocated.
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
IMS & End to End Signaling
The IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) is a generic platform offering IP-based multimedia
services. IMS provides functions and common procedures for session control, bearer
control, policy and charging.
The CSCF (Call Session Control Function) plays a key role in IMS architecture, for
establishing, terminating or modifying IMS sessions. The CSCF is actually a specific
type of SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) server
SIP is the base protocol developed by the IETF for the management of IP-based
multimedia sessions and services
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
Inter-working with 3GPP systems
• The way of interworking basically requires a single subscription allowing the end-
user to attach over network.
• SGSN implements four new interfaces. Three of these(called S3, S4 and S16) rely on
an updated version of the GTP protocol.
• The fourth new interface is S6d which mimics the MME S6a interface towards the
HSS for retrieving subscriber data from the HSS.
• S3 is a signalling-only interface. It is used between the SGSN and the MME to
support inter-system mobility. S16 is the SGSN-SGSN interface, while S4 is
connecting the SGSN and the Serving GW.
• S12 is a direct connection between the Radio Network Controller (RNC) in the
WCDMA radio network and the Serving GW.
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
Inter-working with 3GPP systems
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
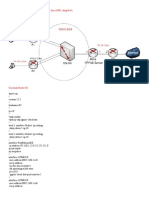
Inter-working with Non-3GPP systems
Besides the common and access-independent feature set for service treatment, the EPC
architecture allows for interworking between 3GPP technologies (i.e., GSM/GPRS,
WCDMA/HSPA and LTE) and non-3GPP technologies (e.g., CDMA , WLAN or a fixed
access technology).
Key interfaces for inter-working with non 3GPP accesses
Ø S2a : It provides the user plane with related control and mobility support between
trusted non 3GPP IP access and the Gateway.
Ø S2b : It provides the user plane with related control and mobility support between
ePDG and the Gateway.
Ø S2c : It provides the user plane with related control and mobility support between UE
and the Gateway.
Ø Gxa : It provides transfer of (QoS) policy information from PCRF to the Trusted Non-
3GPP accesses.
Ø Gxb : This interface is not specified within this release of the specification.
Ø Gxc : It provides transfer of (QoS) policy information from PCRF to the Serving
Gateway
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
Inter-working with Non-3GPP systems
There are two types of Non-3GPP system:
Ø Trusted non-3GPP accesses can be the one that is owned and operated by the LTE
HPLMN. It is secured.
Ø Untrusted non-3GPP accesses can be the one that is not owned and/or operated by
the LTE HPLMN.It is not secured.
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
Inter-working with Non-3GPP systems
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
Reference Points
Ø S1-MME: Reference point for the control plane protocol between E-UTRAN and MME.
Ø S1-U: Reference point between E-UTRAN and Serving GW for the per bearer user
plane tunnelling and inter eNodeB path switching during handover.
Ø S3: It enables user and bearer information exchange for inter 3GPP access network
mobility in idle and/or active state.
Ø S4:It provides related control and mobility support between GPRS Core and the 3GPP
Anchor function of Serving GW.
Ø S5: It provides user plane tunneling and tunnel management between Serving GW and
PDN GW.
Ø S6a: It enables transfer of subscription and authentication data for
authenticating/authorizing user access to the evolved system (AAA interface) between
MME and HSS.
Ø Gx: It provides transfer of (QoS) policy and charging rules from PCRF to Policy and
Charging Enforcement Function (PCEF) in the PDN GW.
Ø S8: Inter-PLMN reference point providing user and control plane between the Serving
GW in the VPLMN and the PDN GW in the HPLMN. S8 is the inter PLMN variant of S5.
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
Reference Points
Ø S9: It provides transfer of (QoS) policy and charging control information between the
Home PCRF and the Visited PCRF in order to support local breakout function.
Ø S10: Reference point between MMEs for MME relocation and MME to MME
information transfer.
Ø S11: Reference point between MME and Serving GW.
Ø S12: Reference point between UTRAN and Serving GW for user plane tunneling when
DirectTunnel is established.
Ø S13: It enables UE identity check procedure between MME and EIR.
Ø SGi: It is the reference point between the PDN GW and the packet data network.
Ø Rx The Rx reference point resides between the operator's IP Services and the PCRF .
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
Copyright © Nex-G | Skills , NESPL
You might also like
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- LTE Handover OptimizationDocument33 pagesLTE Handover Optimizationthang_1986dh100% (3)
- LTE Network Issue Analysis Guideline V1Document29 pagesLTE Network Issue Analysis Guideline V1Amir Miftahudin100% (1)
- LTE INTER Frequency Handover Trouble Shooting CaseDocument15 pagesLTE INTER Frequency Handover Trouble Shooting Casenoriaz100% (1)
- 3G3JZ Manual BasicDocument21 pages3G3JZ Manual BasicTran Le83% (6)
- l3gw Vmto Evpn Vxlan MplsDocument24 pagesl3gw Vmto Evpn Vxlan MplsVijay BhargavNo ratings yet
- LTE Trial: - EPC Testing NotesDocument9 pagesLTE Trial: - EPC Testing NotesVincent Teck Chai TanNo ratings yet
- 2 LTE ERAN6.0 Access Fault DiagnsisDocument66 pages2 LTE ERAN6.0 Access Fault Diagnsisfaysal137152.storageNo ratings yet
- 5g Nsa Access Trouble ShootingDocument10 pages5g Nsa Access Trouble ShootingPsi Factors100% (1)
- LTE Access Fault DiagnsisDocument71 pagesLTE Access Fault DiagnsisStanislas Arthur Lishu100% (2)
- ENDC & 5G AttachDocument10 pagesENDC & 5G Attachaslam_326580186No ratings yet
- Useful Drop IndicatorsDocument11 pagesUseful Drop IndicatorsRafiq mikNo ratings yet
- LTE N CNTRDocument4 pagesLTE N CNTRtkchauhan1No ratings yet
- CiscoDataCenterCertificatione Guide 2017Document40 pagesCiscoDataCenterCertificatione Guide 2017Fayyaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 EPC Interface Protocol AnalysisDocument41 pages1 EPC Interface Protocol AnalysisEdwin MurciaNo ratings yet
- 06 LTE Access Analysis and Counters - 31PDocument31 pages06 LTE Access Analysis and Counters - 31PBoualem AmineNo ratings yet
- Nokia RAN KPIs Part 2 RABDocument31 pagesNokia RAN KPIs Part 2 RABSABER1980No ratings yet
- 03 LTE Access Fault Diagnosis ISSUE1.02 cvb2 PDFDocument85 pages03 LTE Access Fault Diagnosis ISSUE1.02 cvb2 PDFČärlös Lemös FlörezNo ratings yet
- B Nid Controller Book Chapter 01111Document28 pagesB Nid Controller Book Chapter 01111Sameer KauraNo ratings yet
- 08ltekpi PDF FreeDocument15 pages08ltekpi PDF FreeJUCARLCNo ratings yet
- CQT Troubleshoooting V1.0Document10 pagesCQT Troubleshoooting V1.0KhangTranNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Analysis and Optimization of The LTE Call Completion RateDocument21 pagesCH-3 Analysis and Optimization of The LTE Call Completion Ratenaseem AhamdNo ratings yet
- Lacp With STP Sim PDFDocument8 pagesLacp With STP Sim PDFKang Mas PaijhoNo ratings yet
- Call Setup Analysis Exercise: FilesDocument3 pagesCall Setup Analysis Exercise: FilesABHISHEK AGARWALNo ratings yet
- A.2 Receive Message Function (MSG-RCV)Document8 pagesA.2 Receive Message Function (MSG-RCV)White TigerNo ratings yet
- FDD LTE Handover OptimizationDocument35 pagesFDD LTE Handover OptimizationmunzewNo ratings yet
- Consul As A Monitoring Service PresentationDocument85 pagesConsul As A Monitoring Service PresentationAnonymous ryDGv1No ratings yet
- 02 LTE KPI ArchitectureDocument104 pages02 LTE KPI ArchitectureVahid ZibakalamNo ratings yet
- LTE S1 Interface: Satish Kumar S, Val&FS2, Date: 22 Sep, 2021Document29 pagesLTE S1 Interface: Satish Kumar S, Val&FS2, Date: 22 Sep, 2021sandhya24No ratings yet
- KMPL-2143 - EVPN Migration From Legacy To Modern ArchDocument32 pagesKMPL-2143 - EVPN Migration From Legacy To Modern ArchquintaNo ratings yet
- Nokian Capacitor NC12 Controller InstructionsDocument44 pagesNokian Capacitor NC12 Controller InstructionsRiswan FrdmNo ratings yet
- Xrdocs Io ncs5500 Tutorials srv6 Transport On Ncs Part 6Document9 pagesXrdocs Io ncs5500 Tutorials srv6 Transport On Ncs Part 6Konstantinos DimitriouNo ratings yet
- FDD LTE Handover Optimization - 切换Document35 pagesFDD LTE Handover Optimization - 切换Ahmad FauzaniNo ratings yet
- Packt Lin Nov 2015 ISBN 1785284444Document16 pagesPackt Lin Nov 2015 ISBN 1785284444suraj singhNo ratings yet
- BRKMPL 2333Document102 pagesBRKMPL 2333alfagemeoNo ratings yet
- Day 2 - Module 1 - Lte SignallingDocument19 pagesDay 2 - Module 1 - Lte SignallingRahmatia SafitriNo ratings yet
- Ethernet VPN (Evpn) : Overlay Networks For Ethernet ServicesDocument34 pagesEthernet VPN (Evpn) : Overlay Networks For Ethernet ServicesaliaydemirNo ratings yet
- 04 - Co Core SW Re - Testing PlanDocument23 pages04 - Co Core SW Re - Testing PlanRomaNo ratings yet
- SDN & NFV IntroductionDocument72 pagesSDN & NFV Introductionmahmoud_shukur1447No ratings yet
- RG008608 Planning Differences Between EVDO and 1XDocument34 pagesRG008608 Planning Differences Between EVDO and 1XDeepak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Controller Area Network (CAN) Implementation: Hardware and Software PerspectiveDocument69 pagesController Area Network (CAN) Implementation: Hardware and Software PerspectiveAshokUmmadisettiNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lab: ACT-07T Data Conditioning Trainer KitDocument1 pageDigital Communication Lab: ACT-07T Data Conditioning Trainer KitFahim MunawarNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Controller NC-12 User'S ManualDocument44 pagesPower Factor Controller NC-12 User'S Manualgrigore mirceaNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Oam Tutorial Final v2 1362014627Document79 pagesEthernet Oam Tutorial Final v2 1362014627Mehmet DepoNo ratings yet
- 5g Non Standalone Access en DCDocument56 pages5g Non Standalone Access en DCNEO SinghNo ratings yet
- voLTE Call FlowDocument45 pagesvoLTE Call FlowSSCVT Technical TeamNo ratings yet
- Appendix3 - OTA105204 OptiX OSN 1500250035007500 Ethernet Services Configuration (Trail Configuration) ISSUE 1.21Document41 pagesAppendix3 - OTA105204 OptiX OSN 1500250035007500 Ethernet Services Configuration (Trail Configuration) ISSUE 1.21Huy LinhNo ratings yet
- Conventional Networks 2.4 GSM: Prof. JP HubauxDocument47 pagesConventional Networks 2.4 GSM: Prof. JP HubauxDedy MahaNo ratings yet
- 4G LTE Drive Test IntroductionDocument18 pages4G LTE Drive Test IntroductionHari MuklasNo ratings yet
- UMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFDocument63 pagesUMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFMahamadou Ousseini Barkiré100% (1)
- RECLOSERDocument39 pagesRECLOSER22142283No ratings yet
- Algorithm of 5G RAN1.0 Mobility ManagementDocument34 pagesAlgorithm of 5G RAN1.0 Mobility ManagementDuan Feng100% (3)
- Call Processing in Cdma: Mobile InitializationDocument28 pagesCall Processing in Cdma: Mobile InitializationVarun AdhikariNo ratings yet
- App BDocument14 pagesApp Babhayksparmar7157No ratings yet
- LTEPMCounter20150911140851 KPIDocument3,057 pagesLTEPMCounter20150911140851 KPIbalaNo ratings yet
- Banglalink Knowledge Sharing Part3-0423Document40 pagesBanglalink Knowledge Sharing Part3-0423Gazi Nazmul HoqNo ratings yet
- GVRP Protocol IntroductionDocument13 pagesGVRP Protocol IntroductionminhNo ratings yet
- En DCDocument37 pagesEn DCraj1978enatorNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Resume - Latest 1695029351432 Ahad Siddiqui-2Document3 pagesResume - Latest 1695029351432 Ahad Siddiqui-2ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - LTE Introduction Ver 1.0Document127 pagesModule 1 - LTE Introduction Ver 1.0ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Report 2402410522 1Document4 pagesReport 2402410522 1ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Gur 0324 CL 0004980 S01Document1 pageGur 0324 CL 0004980 S01ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Abdul Ahad MohammadDocument2 pagesAbdul Ahad Mohammadahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ahad Mohammad Farooque Siddiqui Abdul EAHAABD 2023 Annual Salary Review GlobalDocument1 pageAhad Mohammad Farooque Siddiqui Abdul EAHAABD 2023 Annual Salary Review Globalahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Resume - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEDocument5 pagesResume - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Resume - Ahad Siddiqui - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEDocument6 pagesResume - Ahad Siddiqui - Telecom Engg - 11+YOEahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Resume - LatestDocument6 pagesResume - Latestahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Telia Project Library - 29 Nov 2021Document46 pagesTelia Project Library - 29 Nov 2021ahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Initial SID - Telia Swap - Rev - ADocument15 pagesInitial SID - Telia Swap - Rev - Aahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Amaresh Update ResumeDocument10 pagesAmaresh Update Resumeahad siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Netshutdown Config ManualDocument16 pagesNetshutdown Config Manualkaleab eduictNo ratings yet
- Broken Authentication and Session Management Vulnerability: A Case Study of Web ApplicationDocument7 pagesBroken Authentication and Session Management Vulnerability: A Case Study of Web ApplicationgkpalokNo ratings yet
- Teenage PregnancyDocument19 pagesTeenage PregnancyJai-JaiAdalidNo ratings yet
- UCF CNT5805 - Fall2021 - SyllabusDocument46 pagesUCF CNT5805 - Fall2021 - SyllabusVictor KingbuilderNo ratings yet
- CCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingDocument8 pagesCCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkinghemachandranNo ratings yet
- 3gpp 29514-g70Document181 pages3gpp 29514-g70miniscribdloginNo ratings yet
- SX 52 BDDocument58 pagesSX 52 BDedson_rcNo ratings yet
- Using Spring Cloud Gateway With OAuth 2.0 Patterns - BaeldungDocument1 pageUsing Spring Cloud Gateway With OAuth 2.0 Patterns - Baeldungcarlos.h.cardoso140No ratings yet
- Lec1 BDocument29 pagesLec1 BHabtie TesfahunNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Multimedia Future NetworkingDocument9 pagesUnit 7 Multimedia Future Networkingnirjan ghimireNo ratings yet
- (ST Public) ZXR10 3900 Series Switches Running ZXROS - ST v1.5 PDFDocument53 pages(ST Public) ZXR10 3900 Series Switches Running ZXROS - ST v1.5 PDFyohannesNo ratings yet
- LTRT-31621 SBC Design GuideDocument32 pagesLTRT-31621 SBC Design GuidefanticelliNo ratings yet
- Anurag Singh Mini Project 2nd SemDocument43 pagesAnurag Singh Mini Project 2nd SemRitik100% (1)
- Content Matrix Release NotesDocument48 pagesContent Matrix Release NotesBrizaNo ratings yet
- Instalasi Dan Konfigurasi Squid Di Centos 7Document2 pagesInstalasi Dan Konfigurasi Squid Di Centos 7Habil Faleview BangeetNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument6 pagesNetwork DevicesDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Laj00440 PSRPT 2019-05-05 16.53.40Document21 pagesLaj00440 PSRPT 2019-05-05 16.53.40Darwin Herrera SalinasNo ratings yet
- SoloLearn (HTML)Document22 pagesSoloLearn (HTML)Md Tanvir MahtabNo ratings yet
- Lab ISCW: Cau Hinh Load Balancing Tren 2 Line ADSL Dùng SAA. I. Sơ Đ LabDocument4 pagesLab ISCW: Cau Hinh Load Balancing Tren 2 Line ADSL Dùng SAA. I. Sơ Đ LabLe Ngoc KhoaNo ratings yet
- 08 01 14 Verizon Response-20140804-153609979Document5 pages08 01 14 Verizon Response-20140804-153609979jbrodkin2000No ratings yet
- 8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer Lab 2Document6 pages8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer Lab 2darkbane00No ratings yet
- Mikrotik PBR GuideDocument10 pagesMikrotik PBR GuideIvoNo ratings yet
- Brand AwarenessDocument30 pagesBrand AwarenessKetan SonawaneNo ratings yet
- (Wellman) The Networked Nature of CommunityDocument15 pages(Wellman) The Networked Nature of Communityshi100% (1)
- Module-3: Device ConfigurationDocument22 pagesModule-3: Device ConfigurationNirabhra RayNo ratings yet
- Business Goldmine - 100 Profitable Business ModelsDocument23 pagesBusiness Goldmine - 100 Profitable Business Modelshimanshu_nazkaniNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint Security Gateway Gaia R77 InstallationDocument17 pagesCheckpoint Security Gateway Gaia R77 InstallationDave CullenNo ratings yet
- Tarjeta SNMP Del UPS Marca DeltaDocument2 pagesTarjeta SNMP Del UPS Marca DeltaJozé LuisNo ratings yet
- 3014 PreDocument95 pages3014 PreDinesh Raja MNo ratings yet