Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
Uploaded by
julia.caballero01070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesPharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
Uploaded by
julia.caballero0107Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
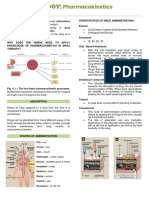
Pharmacokinetics PHARMACOLOGY
It refers to the study of effects of drugs on
It refers to the study of the absorption, living organism
distribution, metabolism and excretion of MEDICATION MANAGEMENT
drugs to determine the relationship between
1. HALF LIFE – Refers to the time it takes the
the dose of a drug and the drugs concentration
body to eliminate half of the blood
in biological fluids
concentration level of the original drug dose
ABSORPTION 2. ONSET OF ACTION – it is the time it takes
Oral preparations such as tablets and capsules the body to responds to a drug after
must first disintegrate into smaller particles for administration
gastric juices to dissolve and prepare the drugs 3. PEAK PLASMA LEVEL – it is the highest
for absorption in the small intestine blood concentration of a single drug dose
FACTORS AFFECTION ABSORPTION before the elimination rate equals the rate of
1. Blood flow to the administration site – a rich absorption
blood supply facilities good absorption, where 4. TROUGH – lowest blood serum
a poor blood supply will slow absorption. concentration of a drug in a person’s system
2. Solubility of the drug – drugs in liquid from 5. DURATION – is the time a drug remains in
are easier to absorbed the system in a concentration great enough to
3. pH of the drug – a drug that is acidic can be have a therapeutic effect
more easily to absorbed in an acidic PREPARATION AND ROUTE
environment such as gastric content Special consideration regarding administration…
4. Ingestion of food before taking oral 1. Chewable tablets are designed to be
medication – some medication interacts with chewed before swallowing because
foods. chewing enhances gastric absorption
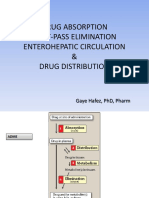
DISTRIBUTION 2. Buccal and Sublingual medications must
It refers to the movement of drugs from the be allowed to dissolve completely before
blood into various body fluids and tissues. the client can or drink
FACTORS AFFECTING DISTRIBUTION 3. Suspension and Emulsion should be
1. Blood flow – how fast the drug releases the administered immediately after shaking
orans and tissues depends on the cardiac and pouring the bottle
output (blood flow) of the person ORAL ROUTE
2. Cell membrane permeability – to be Safest
distributed to the tissue- the drug must cross Most convenient
the cell membrane; some membrane act as Least expensive
barrier to distribution of medication. Disadvantage of oral route is slower acting
3. Protein – binding capacity of the medication, than another route
once the drug enters the circulations, it may It should be given on client’s under NPO
become attached top protein mostly albumins, Oral drugs should be given with caution to
this protein binding decreases the amount the client who have had CVA (stroke)
free drug available to reach the site of action BUCCAL
(cheek) – designed to be place in the buccal
pocket (superior-posterior aspect of the
internal cheek next to the molars) for
absorption by the mucous membrane of the
METABOLISM mouth
Known as biotransformation, which refers to SUBLINGUAL
the physical and chemical processing of the Medication is designed to dissolve quickly
drug. when placed under the tongue
Liver is the primary source of PARENTAL ROUTE
biotransformation Introduction of medication by injecting into the body
EXCRETION 1. Intradermal (ID) – injection to the
Process in which drugs are eliminated from dermis
the body 2. Subcutaneous (SC, SQ) – injection into
Kidney is the organ involved in excretion the subcutaneous tissues
3. Intramuscular (IM) – injection into the irritating, no viscous and water-soluble
muscle medications
4. Intravenous (IV) – injection into the vein Subcutaneous injections place the medication
OTHER ROUTE into the subcutaneous tissues between the
1. Topical – drugs directly apply to the skin and dermis and the muscle
are absorbed into the bloodstream Common sites: abdomen, lateral and anterior
2. Transdermal patches aspect of the upper arm or thigh, scapular area
3. Suppositories at the back
4. Eye and Nasal Drops INTRAMUSCULAR
5. Inhalation – Nasal inhaler, Metered-dose
Used to promote rapid drug absorption and to
inhaler
provide an alternate route when the drug is
6. Intraocular
irritating to subcutaneous tissue
RIGHTS IN GIVING MEDICATION
Sites: ventrogluteal, dorsolateral, vastus
FIVE basic RIGHTS
lateralis, deltoid
1. Right Drug
2. Right Dose Angle of insertion is 90°
3. Right Client Placed the patient in the prone position
4. Right Route Z tract injection (zigzag technique)
5. Right Time INTRAVENOUS
PARTS OF THE DRUGS ORDER It is the administration of fluids, electrolytes,
1. Name of the client nutrients or medication by the venous routes
2. Date and when the order is written
3. Name of the drug to be administered CENTRAL LINES
4. Dosage It refers to a venous catheter inserted into the
5. Route by which is to be administered and superior vena cava through the subclavian,
special directives about its administration internal or external jugular vein
SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE REACTION CAPILLARY PUNCTURE
Adverse reaction – drug effect other than
A skin puncture performed when small
those that are therapeutically intended and
qualities of capillary blood are needed for
expected; unexpected and potentially
analysis (blood glucose analysis)
hazardous
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS (ABS)
Side effects – Nontherapeutic effect maybe
mild and predictable Revels the ability of the lungs to exchange
gases by measuring the partial pressure of 02
TYPES OF ADVERSE REACTON
(PO2) and carbon dioxide (PCO2) and
1. Drug allergy
evaluates the pH of the arterial blood
2. Drug tolerance
3. Toxic effects BLOOD GASES ARE ORDERED TO
4. Idiosyncratic reaction EVALUATE:
TYPES OF MEDICATION ORDERS 1. Oxygenation
1. STAT Orders 2. Ventilation and the effectiveness of respiratory
2. Single-dose Orders therapy
3. Standing Orders 3. Acid base level of the blood
4. PRN Orders VENIPUNCTURE
INTRADERMAL Puncturing of a vein with a needle to aspirate
It is generally used to diagnose tuberculosis blood.
PPD – purified protein derivatives or PLEBOTOMIST
MANTOUX test An individual who performs venipuncture
Identify allergens (ANST) NONINVASIVE PROCEDURES
Administer local anesthetics The body is not entered with any type of
instruments; the skin and other body tissues,
Common site is the inner aspect of the forearm
organs, and cavities remain intact.
3-4 width below the antecubital space
INVASIVE PROCEDURES
SUBCUTANEOUS
Means accessing the body’s tissue, organs or
Commonly used is the administration of small cavity through some type of instrumentation
amount/dose (0.5-1 ml) pf isotonic, non- procedure
TWO MAJOR COMPONENTS OF ROUTINE ECHOCARDIOGRAMS
ANALYSIS: Ultrasonographic procedures used to reveal
1. Random Collection abnormal structure of the heart wall.
Macroscopic Analysis – Includes color, DOPPLER ULTRASONOGRAPHY
appearance, odor, specific gravity, pH, protein, Doppler (a handled transducer) transmit high
glucose, ketones, blood, bilirubin and frequency sound waves to the artery or vein
urobilinogen, nitrite and leukocytes. being examined. Doppler ultrasonography
Microscopic Analysis – Includes RBC, WBC, reveals blood clots and peripheral vascular
epithelial cells, casts and crystals and other disease.
substance such as bacteria, yeast, mucus ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
spermatozoa and parasites. An electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) is a
2. Timed Collection graphic recording of the heart's electrical
3. Collection from a Closed Drainage activity.
Stool analysis HOLSTER MONITOR
It is used to determine the various constituents A portable cardiac monitor is a device that
of the stool for diagnostic purpose. records the heart electrical activity.
OCCULT BLOOD ENDOSCOPY
It is said to be occult when blood is invisible Endoscopy is the visualization cavity through
on inspection; blood can be detected only a scope.
through a microscopic or by chemical means. ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY
Culture and Sensitivity Test (C&S) Electroencephalography (EEG) is the graphic
Performed to identify both the mature invading recording of the brain’s electrical activity.
organism and their susceptibility to commonly ASPIRATIONS and BIOPSY
used antibiotics. Aspiration is performed to withdraw fluid that
PAPANICOLAOU TEST (Pap Smear) has abnormally collected or to obtain a
Done to evaluate the cell maturity, metabolic specimen.
activity and morphologic variations of the BIOPSY
cervical tissue. Excision of a small amount of tissue.
MAMMOGRAPHY AMNIOCENTESIS
A lose dose radiographic study of breast tissue It is the withdrawal of amniotic fluids to obtain
to reveal congenital abnormalities and lesions. a sample for specimen examination
ANGIOGRAPHY PARACENTESIS
Allows visualization of the vascular structure Aspiration of fluids from the abdominal cavity.
through the use of fluoroscopy with a contrast THORACENTESIS
medium into the vessel or vascular system;
Is the aspiration of fluids from the pleural
also need used in diagnosing aneurism.
cavity.
ANGIOGRAMS
PNEUMOTHORAX
Are serial radiographs of blood vessels that are
(Collection of air or gas in the pleural space
used to evaluate the size, shape and potency of
causing the lungs to collapse.
the veins.
LUMBAR PUNCTURE (Spinal Tap)
CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
It is the aspiration of CSF from the
Reveals defects in the heart chambers, valves
subarachnoid space.
and coronary arteries.
ANEURYSM
Weakness in the wall of a blood vessel
CONTRAST MEDIUM
Any substance that is used to improve the
visibility of structures during radiography
ULTRASONOGRAPHY
Ultrasounds (echogram) is a noninvasive study
that uses high frequency sound waves to
visualize deep body structure; doesn't need
contrast medium; the client is instructed to lie
still during the procedure.
You might also like
- Lab Report 10Document6 pagesLab Report 10api-301352285No ratings yet
- Pharmacology 3 PDFDocument10 pagesPharmacology 3 PDFJASMINE VERGANo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Pharma LecDocument11 pagesWeek 4 - Pharma LecJayla MarieNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Drugs and The BodyDocument18 pagesWeek 2 - Drugs and The BodyDino MicaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology LecturesDocument7 pagesPharmacology LecturesMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: How Drugs Are Administered?Document4 pagesPharmacology: How Drugs Are Administered?Monica Melchor DoriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology, 10 R's To Drugs, Nursing ProcessDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology, 10 R's To Drugs, Nursing ProcessJasmin AdoraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics and Drug MetabolismDocument54 pagesPharmacokinetics and Drug MetabolismDeirdreNo ratings yet
- Respon Obat: Faktor Fisiologis Dan PatologisDocument27 pagesRespon Obat: Faktor Fisiologis Dan Patologisfauziah qurrota a'yuniNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Routes of Drug ADM: Terminologi PenjelasanDocument6 pagesIntroduction and Routes of Drug ADM: Terminologi PenjelasanAmirah AnfNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument136 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacologycathlynjoy.marsamoloNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument35 pagesPharmacokineticsBandita DattaNo ratings yet
- Share Pharmacology Book 1Document101 pagesShare Pharmacology Book 1Jmcle AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Summary NotesDocument11 pagesPharmacology Summary Notesnurhana faudziNo ratings yet
- L1_Pharmacokinetic and BiopharmaceuticsDocument8 pagesL1_Pharmacokinetic and BiopharmaceuticsKalea Elsher MintzNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument8 pagesPharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsAnonymous vKjGGgNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (Lesson 1)Document11 pagesModule 1 (Lesson 1)Jovencio Jr. Milo MilanNo ratings yet
- Buccal Drug Delivery SystemDocument35 pagesBuccal Drug Delivery Systemshamma shahulhameedNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic, Absorption and Ionisation of DrugsDocument31 pagesPharmacokinetic, Absorption and Ionisation of DrugsAli ElmehdawiNo ratings yet
- Onset VS, Duration of Action Onset: The Time Required For The Drug Before A Duration of Action: The Span of Time WhereDocument4 pagesOnset VS, Duration of Action Onset: The Time Required For The Drug Before A Duration of Action: The Span of Time WhereAmaetenNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes #1 DRUG ACTIONDocument4 pagesPharmacology Notes #1 DRUG ACTIONAyumi StarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Alo AquinoDocument54 pagesPharmacology: Alo AquinotychynNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes #1Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes #1JUSTINE ALLYSA MAY CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes #1Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes #1Ayumi StarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesPharmacokinetics Lecture Notesbmhsh100% (4)
- Oral (PO) - Per Os Latin Phrase Meaning by Way of Mouth: HarmacokineticsDocument10 pagesOral (PO) - Per Os Latin Phrase Meaning by Way of Mouth: Harmacokineticsdlneisha61No ratings yet
- Pilapil PharmacologyDocument6 pagesPilapil PharmacologyIza FaboresNo ratings yet
- Pharma Sub Part Unit 2Document6 pagesPharma Sub Part Unit 2Beverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Principle of Drug ActionDocument4 pagesPrinciple of Drug ActionChristopher jan Legaspi100% (1)
- 1 - C PharmacokineticDocument14 pages1 - C PharmacokineticMaoth AhmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology: Katzung, Bertram G, Susan B. Masters, and Anthony J. Trevor. Basic & ClinicalDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology: Katzung, Bertram G, Susan B. Masters, and Anthony J. Trevor. Basic & Clinicaljamila ilNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument4 pagesPharmaAngel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Pharma - 2020 General Principles of Drug ActionDocument163 pagesPharma - 2020 General Principles of Drug Actiongelean payodNo ratings yet
- CR PharmaDocument16 pagesCR Pharmainlyzgol45 PassiveNo ratings yet
- 2.principles of Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamic SlidesDocument13 pages2.principles of Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamic Slidesran8384080No ratings yet
- PHBP Prelims - ReviewerDocument39 pagesPHBP Prelims - ReviewerAia RohaNo ratings yet
- BiopharmaceuticsDocument9 pagesBiopharmaceuticsAbigail OreelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - PsychopharmacologyDocument11 pagesChapter 4 - Psychopharmacologymanilyn dacoNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOKINETICSDocument4 pagesPHARMACOKINETICSMichiko CiriacoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Lesson 2Document5 pagesPharma Lesson 2BabyJane GRomeroNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Principles Part 1Document43 pagesPharmacologic Principles Part 1studentme annNo ratings yet
- FNP - Oral Medication NotesDocument23 pagesFNP - Oral Medication NotesOliver DiamaeNo ratings yet
- 2 Drug AdministrationDocument93 pages2 Drug AdministrationNajib HPNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document9 pagesDocument 2zoha fatimaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport: 1. Passive DiffusionDocument12 pagesCellular Transport: 1. Passive DiffusionDaniel MontesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ModuleDocument31 pagesPharmacology ModuleIm jungkook JUSTIN SEAGULL A.K.A jungshookNo ratings yet
- Pharmababy Reviewer-1Document6 pagesPharmababy Reviewer-1Erika Mae Deleña MarcoNo ratings yet
- Module 4. NotesDocument40 pagesModule 4. NotesEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Nlreader - dll@BookID 114778&FileName Page 3Document1 pageNlreader - dll@BookID 114778&FileName Page 3minh thếNo ratings yet
- PRELIMSDocument6 pagesPRELIMSAzalee WillowNo ratings yet
- TMDR PharmaChapter3Document8 pagesTMDR PharmaChapter3JkimNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Transes - Unit 1Document13 pagesPharmacology Transes - Unit 1venturaphoenixNo ratings yet
- Absorption NotesDocument1 pageAbsorption NotesHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drug Absorption-DistributionDocument60 pagesDrug Absorption-DistributionRuqayya AdamuNo ratings yet
- (1M) TO Pharmacology: Al-Hamad, Rawan CDocument7 pages(1M) TO Pharmacology: Al-Hamad, Rawan CLowell Jay Narciso LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Routes of AdministrationDocument3 pagesRoutes of AdministrationNathaliaVegaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems: PharmaceuticsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems: PharmaceuticsJelight Faith Salero GachoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology: Dr. Zaid Al-AttarDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology: Dr. Zaid Al-Attarعلي حميد فريحNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology- The Molecular Dance: Understanding Drug Interactions: Harmony and Chaos: The Symphony of Drug InteractionsFrom EverandPharmacology- The Molecular Dance: Understanding Drug Interactions: Harmony and Chaos: The Symphony of Drug InteractionsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- November 2014 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument16 pagesNovember 2014 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFmanan damaniNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledPaul Wendy DasilvaNo ratings yet
- Periosteal Pocket Flap For Horizontal Bone RegenerDocument10 pagesPeriosteal Pocket Flap For Horizontal Bone RegenerViorel Ion100% (1)
- Cell Organelles 2Document13 pagesCell Organelles 2Sadeeq ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cvs BP Monitor 271245 Wrong UmDocument31 pagesCvs BP Monitor 271245 Wrong UmDarlaNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Rauwolfia TetraphyllaDocument8 pagesA Review of The Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Rauwolfia TetraphyllaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- VitellogeninDocument1 pageVitellogeninQuinnee VallejosNo ratings yet
- Grgs Fhym Grgs - 2023 11 10 - 10214384 - 7087Document3 pagesGrgs Fhym Grgs - 2023 11 10 - 10214384 - 7087hanygrs2011No ratings yet
- Repertorium UniversaleDocument13 pagesRepertorium Universaleatuguesp100% (1)
- 26-Oxidative Phosphorylation-Qp Alevel-Edexcel-Biology UpdatedDocument12 pages26-Oxidative Phosphorylation-Qp Alevel-Edexcel-Biology UpdatedFatma ZorluNo ratings yet
- Extracellular Matrix ScafoldDocument16 pagesExtracellular Matrix ScafoldmanishNo ratings yet
- Serum and Urine Biomarkers of Kidney Disease.Document8 pagesSerum and Urine Biomarkers of Kidney Disease.Andronic GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Gundelia 2012cDocument8 pagesGundelia 2012cIsmail Bazly ZarirNo ratings yet
- Marine Life and The Marine EnvironmentDocument69 pagesMarine Life and The Marine EnvironmentCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Cheliceriformes PDFDocument17 pagesCheliceriformes PDFAtin FifaNo ratings yet
- Lethal GenesDocument27 pagesLethal GenesBikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Bioc 2580 MnemonicsDocument3 pagesBioc 2580 MnemonicsChanceNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation Protocol For Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum L.) Using Embryogenic Mass As ExplantDocument8 pagesAn Efficient Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation Protocol For Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum L.) Using Embryogenic Mass As ExplantIman Fadhul HadiNo ratings yet
- Truth About TestosteroneDocument34 pagesTruth About TestosteroneNaturalBioHealthNo ratings yet
- (1905) A Vine On A House (Ambrose Bierce)Document2 pages(1905) A Vine On A House (Ambrose Bierce)StelioPassarisNo ratings yet
- Introduction 1 Esoteric HealingDocument20 pagesIntroduction 1 Esoteric HealingEdgardo Musi100% (1)
- VBAC Doula Certification Manual v2 April 2019Document111 pagesVBAC Doula Certification Manual v2 April 2019The VBAC Link100% (3)
- Cinnamon Water: Preparation Category Synonyms Description of Final Product Use/s IngredientsDocument6 pagesCinnamon Water: Preparation Category Synonyms Description of Final Product Use/s IngredientsMaan EspirituNo ratings yet
- Fate Core Vampire 5 - Mechanics - UnfinishedDocument1 pageFate Core Vampire 5 - Mechanics - UnfinishedbobyNo ratings yet
- Biotech Note 2Document7 pagesBiotech Note 2bedant_sapNo ratings yet
- 100 Years of ZsiDocument5 pages100 Years of ZsiAshutoshkumar jhaNo ratings yet
- Biology The Essentials 2nd Edition by Marielle Hoefnagels ISBN Solution ManualDocument10 pagesBiology The Essentials 2nd Edition by Marielle Hoefnagels ISBN Solution Manualmichael100% (31)
- Reparian ZoneDocument12 pagesReparian ZoneMohammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Sunbeam Instructor Manual Interactive PDFDocument34 pagesSunbeam Instructor Manual Interactive PDFcarlene haynesNo ratings yet