Professional Documents
Culture Documents
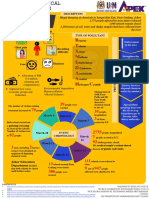
Intro To Toxicology
Intro To Toxicology
Uploaded by
kiarabravo1226Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro To Toxicology
Intro To Toxicology
Uploaded by
kiarabravo1226Copyright:
Available Formats
The Great
Smog of London Compound PEL2(ppm)
Anthracosis accumulation of carbon in the lungs Benzene 1 0
·
-
.
Minamata Disease carbon monoxide 50
caused Carbon retrachloride
by Mercury 10
·
↑
ingestion of contaminated seafood Chloroform 50
Chemoby' Nitrogen dioxide (
0 1
Explosion of nuclear powerplant Ozone
·
.
·
still radioactive Sulfur dioxide -
100
Tetrachloroethylene
GENERALITIES Toluene 200
Exposure
:
environment/occupational 1 ,
1 ,
1 -
Trichloroethane 350
·
Most common chemicals -
used in household ,
personal care
,
consumer products , Trichloroethylene 100
agriculture ,
a
industry
Effects ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY
Dose
Ecotoxicology
·
·
Duration of Impact of environment
exposure chemical pollutants in the a
living organisms
· ·
of individuals Air , soil
Vulnerability or water
·
Affect ·
Product of industrialization ,
technological development , a Urbanization
Central nervous system
Liver & kidneys HAZARD
Reproductive system
·
Ability of a chemical agent to cause injury/disease
·
Potential to cause harm
OCCUPATIONAL TOXICOLOGY
·
Found in the workplace RISK
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) ·
Expected frequency of the occurrence of an undesirable effect
·
"safe" chemical exposure limits for workers arising from exposure to a chemical/physical agent
Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) ·
Likelihood of harm taking place
standards for specific materials of particularly toxicity
serious
·
Lower PEL :
more toxic ROUTES OF EXPOSURE
Threshold limit values (TLVS) ·
Industrial : inhalation ,
transdermal ,
oral
Minimum concentration in the blood to indicate safe zone
QUANTITY , DURATION
,
A INTENSITY OF EXPOSURE
Acute exposure
-
single/multiple exposure over a brief period of time
·
Chronic exposure -
single/multiple exposure over a
long period of time
HEIRARCHY OF CONTROLS
tachycardia tachypnea , , syncope ,
coma
Elimination physically remove the nazard deep convulsions shock failure
coma
respiratory
· -
, , ,
:
substitution replace the hazard Aggravated by heavy labor
-
·
Engineering controls isolate people from the hazard high altitude
· -
Administrative controls change the way people work high ambient temperature
-
·
PPE-protect the worker with Personal Protective Equipment smoking exposure
cardiorespiratory diseases
ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS Treatment : remove from source
Degradability ,
bioaccumulation , transport biomagnification
, Oxygen-specific antagonist for CO
Poorly degraded chemicals environmental persistence accumulate high concentrations of oxygen for a short amount of time
=
a can
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) ,
polychlorinated biphenyls dioxins , ,
furans hypothermic therapy
·
can
easily accumulate in the environment Side effects :
neuropsychological o motor dysfunction
Methyl Mercury discharges neurotoxic
·
-
Lipophilic substances -
bioaccumulate in body fat Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
·
Endocrine disruption , neurological disorders , carcinogenesis Characteristics : colorless ,
irritant
Biomagnification concentrates the chemical in organisms higher the food chain Source : combustion of sulfur-containing fossil fuel
-
on
·
Bioaccumulation pollutants with the widest environmental impact poorly burning of coal domestic heating high-sulfur transportation
-
·
& , ,
degradable Mechanism of action :
high solubility of SO2 in moist membranes
severe irritant on the eyes , mucous membranes ,
AIR POLLUTANTS respiratory tract a skin
,
Carbon Monoxide (20) 90% (inhaled form) absorbed in upper
respiratory
characteristics : colorless ,
tasteless
,
odorless , non-irritating track (Acute Irritant Asthma
Source : of incomplete combustion adapting to irritating concentrations in workers
by product
Found in :
gas stores generator , gasoline powered equipment ,
automobile Clinical effects :
eye ,
nose ,
a throat irritation
,
exhaust
,
tobacco smoke reflex broncho constriction
of action bronchial secretions
Mechanism :
tightly but
combines reversibly with Ith increased
Carboxyhemoglobin initiate/exacerbate bronchial asthma
220x affinity delayed onset pulmonary edema
reduced oxygen transfers to tissues Treatment : supportive , non-specific
organs with highest oxygen demand are affected
brain ,
heart , kidneys
Clinical effects : of hypoxia
symptoms
Psychomotor impairment
headache
& rightness in the temporal area
confusion a loss of visual acuity
Nitrogen Oxide (NO2) SOLVENTS
characteristics : irritank Halogenated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
·
brownish ,
source : fires Aromatic Hydrocarbons
fresh silage /farmers) Halohydrocarbon
diesel equipment /miners) Examples : Carbon tetrachloride ,
trichloroethylene , chloroform ,
automobile a truck traffic emissions Tetrachloroethylene , 1, 1 ,) -trichlowethane
Mechanism of action :
relatively insoluble deep lung irritant Source : industrial solvents
damages lung infrastructure that produces the degreasing agents
surfactant to allow smooth a low effort cleaning agents
necessary
lung alveolar expansion Clinical effects : human carcinogens
-
renal , prostate , testicular cancer
Clinical effects : Silo-Filler's disease CNS depression
non-allergic asthma kidney a liver injury
Twitchy-airway disease cardiotoxicity
Acute-irritation of eyes & nose , cough , mucoid/frothy arrythmia
sputum production chest pain Chronic impaired memory , peripheral neuropathy
-
, dyspnea a
,
pulmonary
edema ,
fibrotic destruction of terminal bronchioles Treatment :
supportive , non-specific
Chronic emphysematous changes Most are classified known/probable human carcinogens
-
as
Treatment :
supportive non-specific Freon (Aluorinated aliphatic) causes severe damage in the ozone layer
-
·
Ozone (03) & Other Oxides AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS
characteristics Earth's Benzene
bluish irritant naturally found
: in the
,
, atmosphere
Source : burning of fossil fuel source : component of gasoline
emitted from powerplants ,
motor vehicles ,
a other high heat compounds Clinical effects : Acute-CN) depression ,
nausea , euphoria ,
locomotor
high-voltage electrical equipmenta air and water purification systems problems a coma , vertigo , drowsiness , headache
agriculture Chronic -
bone marrow injury
Mechanism of action : irritant of mucous membranes Mechanism of action : pluripotent bone marrow stem cells
produces upper respiratory tract irritation to deep lung Potent clastogen
irritation with pulmonary edema Treatment : supportive , non-specific
formation of reactive fre radicals
Clinical effects :
rapid breathing
shallow , ,
decrease in pulmonary compliance
Acute-irritation a dryness to throat , changes to visual acuity ,
substemal pain o
dyspnea ,
ARDS
Chronic-chronic bronchitis , bronchiolitis , emphysema
Treatment : supportive , non-specific
Toluene Clinical effects : miosis
Methylbenzene Urination
No myelotoxic properties diarrhea
·
Found in :
paint thinners ,
nail polish remover , glues , correction fluid , explosives diaphoresis
Clinical effects : CNS depressant ,
a eye irritant
skin ,
fetotoxic lacrimation
rapid loss of consciousness ,
severe fatigue , ataxia excitation of CNS
salivation
Xylene if not reversed , patients will develop neuromuscular
Dimethylbenzene transmission failure cardiorespiratory failure , weakness
·
substitute for benzene in solvent degreasing operations of respiratory muscles , a death
No myelotoxic properties Treatment :
physostigmine , pralidoximine
Clinical effects : CN) depressant
skin irritant ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTANTS
Polychlorinated &
Polybrominated Biphenyls
PESTICIDES
Highly halogenated biphenyl compounds
Organochlorine Pesticides Used for insulation ,
fire retardancy
Amyl Carbocyclic/heterocyclic compounds w/ chlorine substituents Food-major source of PCB residues in humans
·
·
Four classes : DDT/Chlorphenothane) & analogs MOA :
potent endocrine disruptor
Benzenehexachlorides Clinical effects : reproductive a teratogenic effects on animal studies
Cyclodienes
Toxaphenes perfluorinated
Compounds (PFCs)
Endocrine disruptors in humans & animals coolant materials in air-conditioning systems
DDT domestic mosquito elimination malaria-infested regions in Africa used as materials in clinical studies
in
oxygen-carrying
-
Mechanism of action : interfere with inactivation of the sodium channel in excitable
·
Used as heat ,
stain ,
& stick-resistant coatings for cookware ,
fabrics
Membranes
a cause rapid repetitive firing in most neurons
·
Deletrious effects in the Ozone layer
Calcium ion transport is inhibited ROE : Ingestion & inhalation
Clinical effects : DDT-tremov Half-life : 3 years
Carcinogenic potential MOA :
Potent endocrine disruptor
Clinical effects : long-term adverse effect on reproductive function ,
Organophosphorous Pesticides cellular proliferation , a other cellular homeostatic mechanisms
Used against large variety of pests proliferation of breast cancer cells ,
renal , ovarian ,
Either via direct contact or via plant systemics prostate , & Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
·
·
Based on warfare chemicals like Savin ,
soman ,
a tabun Cholesterol & vvic acid abnormalities
ROE : absorbed via the skin , respiratory , & GI track Polymer Fume Fever
MOA : inhibition of acetylcholinesterase through phosphorylation of esteratic state
Asbestos ENDOCRINE DISRUPTORS
Widely used in for Mimic inhibit hormonal
industry over 100 years ,
enhance , or action
Causes progressive fibrotic
lung diseases ,
lung cancer ,
mesothelioma ·
Estrogen-like/autiandrogenic effects , thyroid functions
synergistic effect with cigarette smoking a exposure to rador daughters Includes
·
plant constituents
Mechanism for cancer is not well-defined Phytoestrogens
·
Many countries banned Asbestos Mycoestrogens
Synthetic forms : industrial chemicals
·
METALS persistent organochlorine agents (DDT)
(Be)
Beryllium PCBs
Light alkaline metal Brominated flame retardants
Used in ceramics a alloys
·
Increasing concerns mainly due to bioaccumulation , toxicity , a
increasing
ROE : Inhalation contamination in the environment
Clinical effects : Acuted Chronic Beryllium Disease
Progressive pulmonary Fibrosis INTERNATIONAL AGENCY FOR RESEARCH ON CANCER CLASSIFICATION
IARG
Cadmium ((d) ·
Group 1
-
carcinogenic to humans
Transition metal Cadmium
-
Beryllium
·
·
Found in nickel cadmium batteries
-
sufficient evidence in humans , casual relationship
ROE : Inhalation a ingestion Group 2 A-probably carcinogenic to humans
Clinical effects : Cadmium Fume Fever limited : humans ; sufficient : animals
-
Chronic-progressive pulmonary fibrosis renal failure Group 21
possibly carcinogenic to humans
-
limited : humans
; insufficient : animals
Nanomaterials Group 3
Carcinogenicity not classifiable
-
·
Any material bearing size of at least one dimension that lies bet 1-100 nm inadequate evidence
-
Group 4
Toxicology profile fairly novel probably not carcinogenic
-
is
·
Increasing production environmental contamination
carcinogenicity
-
·
led to no
ROE : inhalation ,
oral , deal , parenteral
MOA : can cross cellular membranes
penetrate nuclear material &
genetic information
Clinical effects : Silica-kidney toxicity
Zinc Oxide
hepatocellular damage
-
Multiwalled carbon nanotubes cytotoxic in humans
-
Titanium dioxide toxic to lungs & other organs
-
You might also like
- Devlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsDocument1,241 pagesDevlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsJorge100% (5)
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell: © 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Principles of EngineeringDocument23 pagesHydrogen Fuel Cell: © 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Principles of Engineeringharpr jackNo ratings yet
- IHS Light Linear Alpha Olefin Prospectus PDFDocument23 pagesIHS Light Linear Alpha Olefin Prospectus PDFAnonymous 0doDAL1No ratings yet
- PUB Drinking Water Quality StandardsDocument4 pagesPUB Drinking Water Quality StandardsongNo ratings yet
- OrganicDocument1 pageOrganicAiman Hakim LimNo ratings yet
- It Is More Real Than What You Think: HalogenoalkanesDocument1 pageIt Is More Real Than What You Think: HalogenoalkanesDaryl John LibianoNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Boards 2024 by Bharat PanchalDocument37 pagesShort Notes Boards 2024 by Bharat PanchalatulithdfNo ratings yet
- 2 Magnetic SusceptibilityDocument33 pages2 Magnetic SusceptibilityJaneth ChambiNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Periodic Table - Annotated 2023Document1 pageAQA GCSE Periodic Table - Annotated 2023Ash SmithNo ratings yet
- Material Flowsheet CHEMPARK DOR: Polyether H2-CleaningDocument1 pageMaterial Flowsheet CHEMPARK DOR: Polyether H2-CleaningtotpityiNo ratings yet
- Tips To Stop Smoking Your Family and Loved Ones: Quit Smoking - If You Don't Love YourselfDocument2 pagesTips To Stop Smoking Your Family and Loved Ones: Quit Smoking - If You Don't Love YourselfKelvin YipNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics..Document5 pagesChemical Kinetics..Limetless GamingNo ratings yet
- VOC Emissions ControlsDocument8 pagesVOC Emissions ControlsLisbeth Roos RoosNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument21 pagesCarbon CompoundNur UmairahNo ratings yet
- Incomplete: Organic CompleteDocument2 pagesIncomplete: Organic CompletesabinaNo ratings yet
- On-Line Analyzer Systems For Safety and Control of EDC Production PlantsDocument1 pageOn-Line Analyzer Systems For Safety and Control of EDC Production Plantslaoying qdNo ratings yet
- Study of CompoundsDocument17 pagesStudy of CompoundsGodhuliNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis Reaction Pathways - A Level ChemistryDocument15 pagesOrganic Synthesis Reaction Pathways - A Level ChemistryremesanmeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Organic GOC Short RevisionDocument7 pagesOrganic GOC Short Revisionmohitjain0076No ratings yet
- Global Warming UMS POSTERDocument1 pageGlobal Warming UMS POSTERByron KadumNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AS Notes 4Document1 pageChemistry AS Notes 4cassandra.on134No ratings yet
- Treatment of Emuents From Ammonia Plants - Part III Ozonation of Amines in An Emuent From A Reforming Plant Serving An Ammonia ComplexDocument8 pagesTreatment of Emuents From Ammonia Plants - Part III Ozonation of Amines in An Emuent From A Reforming Plant Serving An Ammonia ComplexMiguelNo ratings yet
- E. Annex A: Quality Control Guidance For Analytical Test Data - Supporting ZDHC MRSL V2.0 ConformanceDocument11 pagesE. Annex A: Quality Control Guidance For Analytical Test Data - Supporting ZDHC MRSL V2.0 ConformanceVIJAYAKUMAR K ANo ratings yet
- Reducing Dioxin Emissions in Electric Steel Mills PDFDocument4 pagesReducing Dioxin Emissions in Electric Steel Mills PDFJames DuNo ratings yet
- 15NRM03 D3Document14 pages15NRM03 D3Anonymous y3tPCbVrNo ratings yet
- Default FolderDocument6 pagesDefault FolderAtharva SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Relative Contributions of IMF To Haloalkane Boiling Points (Pui Wah 2016)Document11 pagesRelative Contributions of IMF To Haloalkane Boiling Points (Pui Wah 2016)Axel HimawanNo ratings yet
- MSA 08 Portable-Instruments Application-Guide ENDocument9 pagesMSA 08 Portable-Instruments Application-Guide ENArdito CaesarNo ratings yet
- Poster Ex2Document1 pagePoster Ex2jim0410168No ratings yet
- Chemistry A Level - Nitrogen - SulfurDocument2 pagesChemistry A Level - Nitrogen - SulfurKeanan WongsoNo ratings yet
- Revision Mindmap For Unit 9H - Using ChemistryDocument1 pageRevision Mindmap For Unit 9H - Using Chemistrysam mirisonNo ratings yet
- Biomass For H&P - GasificationDocument42 pagesBiomass For H&P - GasificationAhmad Sederhna AdjaNo ratings yet
- Tire Safety: Lesson From PetrochemicalDocument11 pagesTire Safety: Lesson From PetrochemicalIwan AkurNo ratings yet
- CPVC ModelDocument1 pageCPVC ModelZhu Chen ChuanNo ratings yet
- OCOC-1 Live Class-3 Teacher NotesDocument41 pagesOCOC-1 Live Class-3 Teacher Notesmardarchod 123No ratings yet
- Specification - Perklone EXT™ Catalyst Grade BannerChemicals-meets UOP-Refinery - Irwan PtrisDocument1 pageSpecification - Perklone EXT™ Catalyst Grade BannerChemicals-meets UOP-Refinery - Irwan PtrisfajaradityadarmaNo ratings yet
- Benezokain SzintézisDocument6 pagesBenezokain SzintézisZelei ÁgostonNo ratings yet
- Siemens GTDocument8 pagesSiemens GThbalu007No ratings yet
- Chemistry DataDocument7 pagesChemistry DataJ LevinsNo ratings yet
- Master Plan of Chemistry Versi 1Document1 pageMaster Plan of Chemistry Versi 1bensudinNo ratings yet
- Oxidation AllenDocument10 pagesOxidation AllenAditi KharatNo ratings yet
- Infographic Plant SafetyDocument1 pageInfographic Plant SafetySri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Flow Uerdingen KrefeldDocument1 pageFlow Uerdingen KrefeldtotpityiNo ratings yet
- DS Og Carbomax Ac 191105Document2 pagesDS Og Carbomax Ac 191105Delarenus SianiparNo ratings yet
- Extremely Advantageous Amino-Protecting Group: Vitamin Derivative NovelDocument2 pagesExtremely Advantageous Amino-Protecting Group: Vitamin Derivative NovelAlexander ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundDocument15 pagesAromatic Compoundgadhavidhyey5No ratings yet
- Production of Aromatic Hydrocarbons On A Petrochemical BasisDocument8 pagesProduction of Aromatic Hydrocarbons On A Petrochemical Basisstephanie lazarteNo ratings yet
- Scientific & Technical Report: Separations Technologies To Improve Amine System Reliability: A Case StudyDocument10 pagesScientific & Technical Report: Separations Technologies To Improve Amine System Reliability: A Case StudyMarcelo García FacalNo ratings yet
- Group II Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument17 pagesGroup II Alkaline Earth MetalsIftitahur Rohmah -No ratings yet
- Poster Ashish FinalDocument1 pagePoster Ashish Finalapi-637394043No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 PDFDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 PDFKami TazuNo ratings yet
- 1.A.1 Energy Industries 2019Document116 pages1.A.1 Energy Industries 2019izudindNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument1 pageReferencesfaatu85No ratings yet
- AQA-GCSE-Periodic-table - Name 4Document1 pageAQA-GCSE-Periodic-table - Name 4aneyarajaNo ratings yet
- Poster KSIEC&KIChe Fall 2016Document2 pagesPoster KSIEC&KIChe Fall 2016ArtimurnandariNo ratings yet
- INTER CAT FCC Gasoline Sulphur Reduction Using Catalyst Additives Mechanisms and Commercial ExperiencesDocument10 pagesINTER CAT FCC Gasoline Sulphur Reduction Using Catalyst Additives Mechanisms and Commercial ExperiencesKumaresan LoganathanNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Short Notes Nitesh DevnaniDocument4 pagesIUPAC Short Notes Nitesh Devnaniunderprocess786No ratings yet
- Overview of Real Time Monitoring Technologies and Case Studies of The ApplicationsDocument12 pagesOverview of Real Time Monitoring Technologies and Case Studies of The Applicationssafira143No ratings yet
- Tipical Solvent For Cementing ThermoplasticsDocument1 pageTipical Solvent For Cementing ThermoplasticsDamiano CrestanNo ratings yet
- Investigating+Pollution UNESCODocument10 pagesInvestigating+Pollution UNESCOmidhundasNo ratings yet
- Fixed Oils and Fats: Group 3Document19 pagesFixed Oils and Fats: Group 3Addis MémñøňNo ratings yet
- Bildschirmfoto 2022-05-20 Um 17.52.39Document8 pagesBildschirmfoto 2022-05-20 Um 17.52.39s.wNo ratings yet
- Microbes in Human Welfare ProjectDocument36 pagesMicrobes in Human Welfare ProjectMonika S100% (2)
- Industrial Crops & Products: Ulmoides Oliver Branches Under Different Refining Methods andDocument14 pagesIndustrial Crops & Products: Ulmoides Oliver Branches Under Different Refining Methods andAbeer El ShahawyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Exam Reviewer (Carbohydrates and Lipids)Document5 pagesBiochemistry Lab Exam Reviewer (Carbohydrates and Lipids)Kimberly EspaldonNo ratings yet
- Ch-3-Organic ChemDocument3 pagesCh-3-Organic Chemzia khanNo ratings yet
- NRC - Chem - M15 - ChemSimplified - Acidity of Carboxylic AcidsDocument10 pagesNRC - Chem - M15 - ChemSimplified - Acidity of Carboxylic AcidsTirtha Mukerjee ChemistryNo ratings yet
- MANAS VIDYALAYA Practical 2021-22 SyllabusDocument9 pagesMANAS VIDYALAYA Practical 2021-22 SyllabusAditya RajNo ratings yet
- Sepuran NG Membranes Natural Gas ProcessingDocument6 pagesSepuran NG Membranes Natural Gas ProcessingTran Cong BinhNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Consists of Chemicals or Particles in The Atmosphere That Pose Serious Health and Environmental ThreatsDocument4 pagesAir Pollution Consists of Chemicals or Particles in The Atmosphere That Pose Serious Health and Environmental ThreatsKen TubungbanuaNo ratings yet
- Proceeding 1 (Cellulolytic and Proteolytic Yeast)Document6 pagesProceeding 1 (Cellulolytic and Proteolytic Yeast)Syifa AuliaNo ratings yet
- LKPD TATA NAMA KimiaDocument9 pagesLKPD TATA NAMA Kimiagabriel.dominggo 192010013No ratings yet
- Agriculture, The Frontier Man Made Environment - Copy (Autosaved)Document33 pagesAgriculture, The Frontier Man Made Environment - Copy (Autosaved)Sekar PramestiNo ratings yet
- Comp LabellingDocument42 pagesComp Labellingpitambari pitambariNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility Status in Taluks of Chitradurga District Under Zero Budget Natural Farming of KarnatakaDocument4 pagesSoil Fertility Status in Taluks of Chitradurga District Under Zero Budget Natural Farming of KarnatakaMadhu G ReddyNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds c1 To c57 Part 1 PDFDocument98 pagesOrganic Compounds c1 To c57 Part 1 PDFUmar OmarNo ratings yet
- Application of Docking and Active Site Analysis For Enzyme Linked Biodegradation of Textile DyesDocument10 pagesApplication of Docking and Active Site Analysis For Enzyme Linked Biodegradation of Textile DyesAngie BedoyaNo ratings yet
- Rankem 2014-2015Document168 pagesRankem 2014-2015Chetan Joshi0% (1)
- Ijacs M155Document5 pagesIjacs M155Dr. Ranjan BeraNo ratings yet
- Detergent (Group 1,2)Document29 pagesDetergent (Group 1,2)Sourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Functional Group InterconversionDocument7 pagesFunctional Group InterconversionSUBHASISH DASHNo ratings yet
- TTTV 4 Plant InsectsDocument54 pagesTTTV 4 Plant InsectsNhật TriềuNo ratings yet
- Produk KamiDocument4 pagesProduk KamiChristin AgapeNo ratings yet
- Volumetric SolutionsDocument14 pagesVolumetric Solutionsfazza medikaNo ratings yet
- MJ Accessories: Glands, Gaskets, Bolts & NutsDocument7 pagesMJ Accessories: Glands, Gaskets, Bolts & Nutsgabriel240371No ratings yet
- Progress of Bio-Calcium Carbonate Waste Eggshell and Seashell Fillers in Polymer Composites: A ReviewDocument22 pagesProgress of Bio-Calcium Carbonate Waste Eggshell and Seashell Fillers in Polymer Composites: A Reviewachmad nandangNo ratings yet
- GAS-Technical Data-G3516H-HR-v1Document5 pagesGAS-Technical Data-G3516H-HR-v196791359No ratings yet
- Using Cilantro Leaves....Document92 pagesUsing Cilantro Leaves....Lakshmipriya GopinathNo ratings yet