Professional Documents
Culture Documents
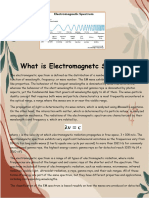
EM Radiation Summary
EM Radiation Summary
Uploaded by
yhenembiadoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EM Radiation Summary
EM Radiation Summary
Uploaded by
yhenembiadoCopyright:
Available Formats
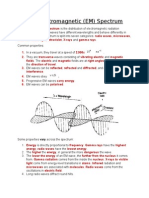
EM Radiation
describes in terms of a stream of particles, each travelling in a wave-like pattern and moving at
the speed of light
makes EM waves transverse waves
EM Wave
arrange in electromagnetic spectrum based on their frequency, wavelength, and photon energy
an electrical and magnetic disturbance that moves through space at the speed of light
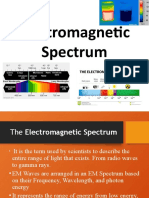
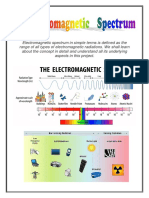
Types of Electromagnetic Radiation
Radio Waves
have longest wavelengths and electromagnetic spectrum
have wavelengths that range from less than a centimeter or tens or even hundreds of meters.
can be used to transmit radio and television signal, mobile phones, magnetic resonance
Microwaves
have very short wavelengths ranging from approximately one millimeter to 30 centimeters
they are made by various types of transmitters an electronic device which, with the aid of an
antenna, produces radio waves
can be used in telecommunication, such as mobile phones, fixed traffic speed camera, oven
cooking, radar, aircraft, navigation, terrain mapping, molecular research, long distance
communication
Infrared
William Herschel discovered the existence of infrared by passing sunlight through a prism.
sometimes called heat or thermal energy
they can be used in heating and drying, night vision cameras, satellite remote sensing, remote
controls
Visible Light
the portion of EM radiation that is visible to human eye
given off by anything that is not enough to glow (light waves can be seen as the colors of
rainbow)
red is the longest wavelength and violet is the shortest
used as what the typical eye and film can see like visible light photography, lasers emitting visible
light like laser pointers, laser surgery and cutting of metals
Ultraviolet
an EM radiation with a wavelength shorter than visible light but longer than x-ray
produced by high-temperature surfaces, such as the sun
can be used in photochemical and photo electric effects, hardening cast in medicines
X-rays
high-energy waves which have great penetrating power and are used extensively in medical
applications like examination of bones, teeth, and vital organs, treatment for types of cancer;
crystallography, astrophysics.
Overexposure to x-rays may lead to cancer such as leukemia
Gamma Rays
these are more penetrating than x-rays
generated by radioactive atoms and in nuclear explosions, and are used in many medical
applications like treatment for types of cancer, food irradiation.
these can be used also in nuclear research, geophysics and mineral exploration.
Photon – particles contain a bundle of energy
Thermography – infrared radiation used to remote and determine the temperature of objects
You might also like
- VLF-CR 60 Hp.Document61 pagesVLF-CR 60 Hp.Gabriel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Em Wave and em SpectrumDocument22 pagesEm Wave and em Spectrummilk teaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pages3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesDocument4 pagesConcept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesLunaNo ratings yet
- General Informatio NDocument15 pagesGeneral Informatio NJenny RoblesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum:: Common Properties of em WavesDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum:: Common Properties of em Wavesgwen_frenz2500No ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesYippeNo ratings yet
- What Are Electromagnetic Waves?Document8 pagesWhat Are Electromagnetic Waves?Jay Marie OcampoNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument15 pages3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum, The Entire Distribution ofDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum, The Entire Distribution ofHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Document7 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Nur-shima SakilinNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTamayo KivsNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pages1 - Electromagnetic Spectrumbinyang lalaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument43 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumRin Kiyoshi Hazumi-FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic WavesArisa LopezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDanae Forrester100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic WavesShazira Ally100% (1)
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumFOODHEALTHNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave HandoutDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Wave HandoutARLENE POMBONo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument34 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumShinpay doodles100% (1)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrummuddasarhussain739No ratings yet
- Name Wavelength : Gamma Ray E KeDocument3 pagesName Wavelength : Gamma Ray E KeJose Andrei Dalisay PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- Document (4) - 1Document9 pagesDocument (4) - 1Justin DugangNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum of RadiationDocument4 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum of RadiationGanaka KodithuwakkuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumamyrulerzNo ratings yet
- EM SpectrumDocument6 pagesEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum 20232024Document15 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum 20232024WowNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationAyman BashirNo ratings yet
- C12 Electromagnetic WavesDocument48 pagesC12 Electromagnetic WavesRosemarie Cabanilla50% (2)
- Science 10Document13 pagesScience 10Joel De LeonNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience ReviewerAphrodite UnderwoodNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Applications of EM WavesDocument28 pagesModule 2 - Applications of EM WavesMariane HinanibanNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument2 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumMegan CabahugNo ratings yet
- Radio WavesDocument4 pagesRadio WavesSophia Nicole ZaraNo ratings yet
- 10 2 - EmsDocument15 pages10 2 - Emsapi-262219273No ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Applications of MicrowavesDocument6 pagesApplications of MicrowavesorculloNo ratings yet
- Nature of LightDocument25 pagesNature of LightPremnath KrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: by Chandra Prakash B.Tech (CS) 07ECICS021Document13 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: by Chandra Prakash B.Tech (CS) 07ECICS021Indrajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- Spectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveDocument10 pagesSpectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveJabez Edwin SivaNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document38 pagesScience 10Angelo LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumDenise Marie Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument43 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumxunxhineNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumJohn Bernie RevillaNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pages7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesAbigail Domingo100% (1)
- Elctronic RadiationDocument4 pagesElctronic RadiationTia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Essay 300 Words Orig.Document1 pageEssay 300 Words Orig.Yeddah Marie TanezaNo ratings yet
- Vibration and Waves: Electromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument43 pagesVibration and Waves: Electromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumrancesNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1. Electromagnetic Sgypectrum NOTESDocument38 pagesLESSON 1. Electromagnetic Sgypectrum NOTESRyan Aint simpNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- Alziya Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesAlziya Physics ProjectMohammad AyanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesririkgopeNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of LightDocument21 pagesDispersion of Lightshafqat hussainNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumKC KayeNo ratings yet
- Speed and Position Sensors HandoutDocument16 pagesSpeed and Position Sensors HandoutJose Ramón Orenes ClementeNo ratings yet
- Tile Testing Basics: ASTM C370: Moisture ExpansionDocument4 pagesTile Testing Basics: ASTM C370: Moisture ExpansionLucky KhanNo ratings yet
- Arduino Micro Controller Processing For Everyone Part 1Document114 pagesArduino Micro Controller Processing For Everyone Part 1fashazee6750100% (1)
- Cisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Document54 pagesCisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Paul100% (2)
- Topic 1 - Fundamental of Electrical System in BuildingDocument25 pagesTopic 1 - Fundamental of Electrical System in BuildingsyakirohNo ratings yet
- NVG Cockpit Lighting For Sikorsky Helicopter S-76Document4 pagesNVG Cockpit Lighting For Sikorsky Helicopter S-76Jacob MillerNo ratings yet
- Alternator Part I Eac ReviewDocument15 pagesAlternator Part I Eac ReviewKevin MaramagNo ratings yet
- PFD Asam Benzoat - Noor Wahyu & NurulDocument1 pagePFD Asam Benzoat - Noor Wahyu & NurulFahmi ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document63 pagesLecture 4InfragNo ratings yet
- How To Create Alphanumeric Auto Increment in ASPDocument4 pagesHow To Create Alphanumeric Auto Increment in ASPPinaki Ranjan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Globalcad Landscape: Expert Software For Landscape Design and Land PlanningDocument2 pagesGlobalcad Landscape: Expert Software For Landscape Design and Land PlanningsmstefNo ratings yet
- AGMA 9002A-86 Square Keyway Tolerances PDFDocument6 pagesAGMA 9002A-86 Square Keyway Tolerances PDFKriztopher UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Barriers in Relation To The Crash Testing Standards: Wasim QADIRDocument8 pagesBridge Barriers in Relation To The Crash Testing Standards: Wasim QADIR정주호No ratings yet
- Engineering Proporties of Komice (Pumice) SoilDocument19 pagesEngineering Proporties of Komice (Pumice) SoilLiyu GudissaNo ratings yet
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Pavushetti Abhilash, Raghavan Nanda Kumar, Raparthi Praveen KumarDocument5 pagesMaterials Today: Proceedings: Pavushetti Abhilash, Raghavan Nanda Kumar, Raparthi Praveen Kumarmuntasir antuNo ratings yet
- Zoom Timetable BFC KahutaDocument5 pagesZoom Timetable BFC KahutaYumna ArOojNo ratings yet
- Extrautils 2Document3 pagesExtrautils 2Илья СемёновNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Q3 COTDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics V Q3 COTBRENDA SUBAANNo ratings yet
- Beirut Arab University: CVLE 210 StaticsDocument3 pagesBeirut Arab University: CVLE 210 StaticsbassamNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Joen 2018 11 006 PDFDocument5 pages10 1016@j Joen 2018 11 006 PDFVijithNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Computer Skills (CT 101) Book ActivitiesDocument10 pagesAnswer Key Computer Skills (CT 101) Book ActivitiesMOKHALLAD GHAWASNo ratings yet
- Isometric View: SLA Product Variables Part Id Nominal Size ID OD MFG WT Mass (KG)Document2 pagesIsometric View: SLA Product Variables Part Id Nominal Size ID OD MFG WT Mass (KG)leizel dacuNo ratings yet
- Intro To QPDocument30 pagesIntro To QPdkffgufxxaybfhqzizNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Smarajit MishraNo ratings yet
- Envelope Theorem and Identities (Good)Document17 pagesEnvelope Theorem and Identities (Good)sadatnfsNo ratings yet
- Dkrci - Py.fn0.b2.02 Fia InsertsDocument1 pageDkrci - Py.fn0.b2.02 Fia Insertsyoye1968No ratings yet
- Earthing ReportDocument8 pagesEarthing ReportkhandelwalaNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification Part-1Document380 pagesTechnical Specification Part-1Jayashree GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- 10 PhysicsDocument4 pages10 PhysicsNicka Asereht MinaNo ratings yet