Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Wireless and Mobile Gen
3 Wireless and Mobile Gen
Uploaded by
ingawalemadhura57220 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pagesOriginal Title
3-wireless-and-mobile-gen
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pages3 Wireless and Mobile Gen
3 Wireless and Mobile Gen
Uploaded by
ingawalemadhura5722Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
CHAPTER 3
Error Detection and Correction
and wireless Communication
MARKS 12
WIRELESS LAN 802.11
➢ IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards that defines wireless LAN
(WLAN) technologies.
➢ It is commonly known as Wi-Fi.
➢ It uses radio waves to transmit data between devices over
short distances.
➢ Wi-Fi is simply a trademarked phrase that means IEEE
802.11.
➢ IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN:
➢ The 802.11 architecture define two types of services and three
different types of stations.
➢ 802.11 services: The two types of services are
➢ 1) Basic services set (BSS)
➢ 2) Extended services set (ESS)
Basic services set
❑ The basic services set contain stationary or mobile
wireless station and central base station=>access
point (AP)
❑ The use of access point is optimal.
❑ If the access point is not present, it is known as
standalone network. These types of architecture is
known as adhoc architecture.
❑ The BSS in which an access point is present is known
as infrastructure network.
WIRELESS LAN 802.11
➢ If no access point =>adhoc architecture.
➢ The BSS with access point =>infrastructure network.
Extended services set
➢ An extended service set is created by initializing two or
more basic services set (BSS) having access points(AP)
➢ These extended networks are created by joining the
access points of basic station set through a wired LAN
=>distribution system.
➢ The distribution system can be any IEEE LAN.
➢ There are two types of station in ESS.
➢ Mobile Station: These are normal station inside a BSS
➢ Stationary Station: these are AP station that are part of a wired LAN
➢ Communication between two stations in two different BSS usually
occurs via two AP’S. A mobile Station can belong to more than
one BSS at the same time.
WIRELESS LAN 802.11
WI-MAX 802.16
➢ Wi-Max- Wi- Max is worldwide interoperability for Microwave
Access.
➢ It is a wireless communication standard which can provide data
rates up to 1Gbps:
➢ It is refers to interoperable implementation of IEEE 802.16
family of standards.
➢ Uses and Application:
➢ Portable mobile broadband connectivity.
➢ It can be used as an alternative to cable, digital subscriber line
(DSL) for providing a broad band access.
➢ To provide services such as voice on IP (VOIP)
➢ For providing a source of internet connectivity.
WI-MAX 802.16
➢ Wi-Max is capable of providing at home or mobile
internet access across the whole city or country.
➢ It is cheap to use Wi-Max to provide Internet Access to
the remote locator.
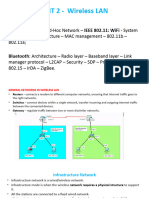
BLUETOOTH ARCH
BLUETOOTH ARCH
❖Bluetooth is short range wireless technology.
❖Range of Bluetooth is 10 meters.
❖Bluetooth Architecture defines 2 types of
networks.
1. Piconet
2. Scatternet
BLUETOOTH ARCH
P
✓ Piconet S
❖ It consists of 1 master node and 7 slave nodes.
S M SB
❖ Piconet have 8 active nodes (7+1) in the range of 10
meters. SB
S
❖ There can be only 1 master station in each piconet.
P
❖ Communication is between master and slave
❖ Slave to slave communication is not possible.
❖ Piconet can have 255 parked nodes, that cannot take
part in communication
❖ There will be 7 slaves in active state and 255 nodes in
parked state.
Scatternet
❖ It is formed by combining various piconets.
❖ Slave in one piconet can act as master in other
piconet.
❖ Such a node can receive message from the master in
the first piconet and deliver the message in second
piconet.
❖ Station can be member of two piconets.
❖ Station cannot be master of two piconet.
Mobile Generatio-1G
• 1G or (1-G) refers to the first generation of wireless
telephone technology (mobile telecommunications).
• These were the analog telecommunications standards that
were introduced in 1979 and the early to mid-1980s and
continued until being replaced by 2G digital
telecommunications.
• The main difference between the two mobile telephone
systems (1G and 2G), is that the radio signals used by 1G
network are analog, while 2G networks are digital.
Mobile Generation-2G
• 2G (or 2-G) provides three primary benefits over their
predecessors:
– phone conversations are digitally encrypted;
– 2G systems are significantly more efficient on the spectrum
allowing for far greater mobile phone penetration levels;
– and 2G introduced data services for mobile, starting with SMS
(Short Message Service) plain text-based messages.
• 2G technologies enable services such as text messages,
picture messages and MMS (Multimedia Message Service).
• It has 3 main services: Bearer services is one of them which
is also known as data services and communication.
• Second generation 2G cellular telecom networks were
commercially launched on the GSM standard in 1991.
Mobile Generation-3G
• 3G refers to the third generation of wireless mobile
communication technology.
• It was introduced in the early 2000s(1998) and used digital radio
signals for voice and data communication.
• It had higher capacity, better quality, and introduced mobile
internet and video calling.
• 3G technology provides an information transfer rate of at least
200 kbit/s.
• CDMA2000 is a family of 3G mobile technology standards for
sending voice, data, and signaling data between mobile phones
and cell sites.
Mobile Generation-3.5G
• 3.5G is a grouping of disparate mobile telephony and data
technologies designed to provide better performance than 3G
systems, as an interim step towards the deployment of full 4G
capability. The technology includes:
• High-Speed Downlink Packet Access
• 3GPP Long Term Evolution, precursor of LTE Advanced
• Evolved HSPA
Mobile Generation-4G
• 4G refers to the fourth generation of wireless mobile
communication technology.
• It was introduced in the 2008s and used advanced digital radio
signals for voice and data communication.
• It had even higher capacity, better quality, and introduced
features such as mobile broadband, video streaming, and faster
data transfer speeds.
• Potential and current applications include amended mobile web
access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV,
video conferencing, 3D television, and cloud computing.
Mobile Generation-4.5G
• 4.5G provides better performance than 4G systems, as
a process step towards deployment of full 5G
capability.
• The technology includes:
• LTE Advanced Pro
• MIMO
Mobile Generation-5G
• 5G refers to the fifth generation of wireless mobile
communication technology.
• It was introduced in 2019 and uses advanced digital
radio signals for voice and data communication.
• It has extremely high capacity, low latency, and faster
data transfer speeds than 4G.
• It also introduces features such as massive machine-
type communication, ultra-reliable and low latency
communication, and network slicing.
You might also like
- MC870 Motor Control: Operating InstructionsDocument34 pagesMC870 Motor Control: Operating InstructionsСергей УспенскийNo ratings yet
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- OIC ReviewerDocument37 pagesOIC ReviewerJonieLachicaNo ratings yet
- BigMike's PH ManifestoDocument31 pagesBigMike's PH ManifestodalbanwaitNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Introduction To GrindingDocument5 pagesChapter1 Introduction To GrindingSwati GautamNo ratings yet
- By:-D.Siva Prasad Branch: - Ex Iii SemDocument18 pagesBy:-D.Siva Prasad Branch: - Ex Iii Semnaruto_3No ratings yet
- 2 Session-2 Advantages-Generations-Wireless LAN and WLLDocument20 pages2 Session-2 Advantages-Generations-Wireless LAN and WLLGizachew TesfaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Network Basics: Wireless TechnologiesDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Network Basics: Wireless Technologiesnishasaiyed2304No ratings yet
- Zigbee FinalDocument29 pagesZigbee FinalcvmgreatNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth: Seminar Report ForDocument16 pagesBluetooth: Seminar Report FortravelnagaNo ratings yet
- 20911A04B6Document19 pages20911A04B6gouraramnandiniNo ratings yet
- Mobile Telecommunication TechnologiesDocument3 pagesMobile Telecommunication TechnologiesChinmaya SahuNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument24 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication EngineeringVîshNo ratings yet
- 5 GDocument26 pages5 GRani ManugrahaniNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Wireless TechnologyDocument11 pagesBenefits of Wireless TechnologyAdemola AdesiyiNo ratings yet
- Presented BY:-Jafar ShahDocument26 pagesPresented BY:-Jafar Shahyekoyesew100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2anon_494993240No ratings yet
- Assi 01 Wireless CommDocument5 pagesAssi 01 Wireless CommUmar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Wifi Vs BluetoothDocument17 pagesWifi Vs BluetoothSIVA PRASADNo ratings yet
- NGN Notes of All UnitsDocument22 pagesNGN Notes of All Unitsbishtsunita2002No ratings yet
- Blah Blah VlamDocument15 pagesBlah Blah VlambikuttanNo ratings yet
- WNPPT2Document24 pagesWNPPT2namudajiyaNo ratings yet
- 3G vs. Wifi: Presented By:-DEEPAK GUPTA 0911HDSSD104Document36 pages3G vs. Wifi: Presented By:-DEEPAK GUPTA 0911HDSSD104Deepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- DCC Chapter 3Document5 pagesDCC Chapter 3Khan Rahil AhmedNo ratings yet
- mhdC8Vuv5Ntvq8MUqJCZI9Jo PDFDocument34 pagesmhdC8Vuv5Ntvq8MUqJCZI9Jo PDFAhmed58seribegawanNo ratings yet
- 02-Describing and Implementing Foundational Wireless TheoryDocument32 pages02-Describing and Implementing Foundational Wireless TheoryMiguel Angel MartínezNo ratings yet
- WLAN - 802.11 A, B, G and N: Wireless Standards White Paper SeriesDocument10 pagesWLAN - 802.11 A, B, G and N: Wireless Standards White Paper Seriessidsharma187No ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksDocument15 pagesWireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksSyed ShahidNo ratings yet
- MN - Unit 2Document50 pagesMN - Unit 212c04gokulsboaNo ratings yet
- WLAN NotesDocument14 pagesWLAN Notesriya vargheseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless TechnologyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Wireless TechnologyRatnesh KhainwarNo ratings yet
- History of WirelessDocument7 pagesHistory of WirelessHarshaNo ratings yet
- WCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Document40 pagesWCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Sushíl kanikeNo ratings yet
- Notes Satellite, Bluetooth, Wifi, CdmaDocument6 pagesNotes Satellite, Bluetooth, Wifi, Cdmaharshgrey888No ratings yet
- CH 2. Wireless LANDocument13 pagesCH 2. Wireless LANJessica LasariaNo ratings yet
- 5g Wireless TechnologyDocument26 pages5g Wireless TechnologyMadhu SaatwaduNo ratings yet
- BY Upasana GaikwadDocument30 pagesBY Upasana GaikwadRenu YadavNo ratings yet
- 2 Ch1broadbandDocument34 pages2 Ch1broadbandAbdullah HabibNo ratings yet
- CN Notes Unit 5Document13 pagesCN Notes Unit 5Shreya MankarNo ratings yet
- 8th Semester QuestionsDocument17 pages8th Semester QuestionsArkadeep RoyNo ratings yet
- 5gDocument36 pages5graelpogi4No ratings yet
- Experiment No 3Document5 pagesExperiment No 3Priti RumaoNo ratings yet
- IoT Course IoT Communications 25 10 2021Document63 pagesIoT Course IoT Communications 25 10 2021ESSADIKE ZAITANo ratings yet
- 4g Wireless System DocumentationDocument9 pages4g Wireless System DocumentationSuni SuneethaNo ratings yet
- CP4153 Unit 2 Network TechnologiesDocument27 pagesCP4153 Unit 2 Network Technologiesbhuvanesh.cse23No ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument32 pagesSeminar ReportsherrysherryNo ratings yet
- Bluetoothtechnology: Seminor OnDocument9 pagesBluetoothtechnology: Seminor OnNitturi VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- 4GDocument44 pages4G7semNo ratings yet
- 4G, 5G and Its Beyond Technology 6GDocument33 pages4G, 5G and Its Beyond Technology 6Gsaurabh_ezilozik57% (7)
- Latihan 28-09-21 Muhammad NaufalDocument3 pagesLatihan 28-09-21 Muhammad NaufalMuhamad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Reduced SpacingDocument6 pagesReduced SpacingabhiNo ratings yet
- Communication Networks: 2.2. Second-Generation Wireless CommunicationDocument6 pagesCommunication Networks: 2.2. Second-Generation Wireless CommunicationcvsueeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1GANAPATHY SUNDARAM G 21CA018No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Wireless NetworksDocument7 pagesCharacteristics of Wireless NetworksFilip ShramkoNo ratings yet
- 01 03 01 BluetoothDocument12 pages01 03 01 BluetoothMuhammad HattaNo ratings yet
- Local Multipoint Distribution Service (LMDS)Document21 pagesLocal Multipoint Distribution Service (LMDS)Bibin PuthiyathNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Technology in Wireless Communications: Paper Presentation OnDocument11 pagesBluetooth Technology in Wireless Communications: Paper Presentation Onpraveen_449100% (2)
- 4G TechnologyDocument21 pages4G TechnologyvigneshknNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Jafar ShahDocument26 pagesPresented By:-Jafar ShahLokeshNo ratings yet
- Network Communication ProtocolDocument12 pagesNetwork Communication ProtocolKohinoor BegumNo ratings yet
- Mod Overlay DesignDocument33 pagesMod Overlay DesignDevarajNo ratings yet
- List of ContentsDocument13 pagesList of ContentsBedigi SridharNo ratings yet
- Architecture of An ISPDocument8 pagesArchitecture of An ISPSajad AliNo ratings yet
- DbmsproposalpdfDocument5 pagesDbmsproposalpdfingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- DBMSFINALREPORTDocument9 pagesDBMSFINALREPORTingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical EducationDocument13 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Educationingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- DCC Proposal FinalDocument6 pagesDCC Proposal Finalingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- EvaluDocument1 pageEvaluingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- 4 4 1 P 603a0fa9ead7a FileDocument14 pages4 4 1 P 603a0fa9ead7a Fileingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- Alamine 304 052523Document7 pagesAlamine 304 052523Loisse GrimaldoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decisions Using An Article About Prognosis: Noel L. Espallardo, MD, MSCDocument38 pagesClinical Decisions Using An Article About Prognosis: Noel L. Espallardo, MD, MSCjustinryanNo ratings yet
- Applications of EigenvalueDocument16 pagesApplications of EigenvalueLiaquat Ali PanhwerNo ratings yet
- GC4000+ Auto Super Charge Station User Manual-V1.3 EN202107151155Document14 pagesGC4000+ Auto Super Charge Station User Manual-V1.3 EN202107151155lyfar.markNo ratings yet
- Structures ThesisDocument25 pagesStructures ThesisAbhijith SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sony Playstation 3 Cecha00 Cecha01 Sm-Ps3-0013e-02Document45 pagesSony Playstation 3 Cecha00 Cecha01 Sm-Ps3-0013e-02naoyakatsu100% (2)
- "The Tropic of Cancer Rule Book" Science Fiction: Tim Cedewall, Roshan Patel & Tamati Turnbull 2010Document9 pages"The Tropic of Cancer Rule Book" Science Fiction: Tim Cedewall, Roshan Patel & Tamati Turnbull 2010api-26623930No ratings yet
- Concrete Road Surface With The Use of Cement Concrete - Selected ResultsDocument8 pagesConcrete Road Surface With The Use of Cement Concrete - Selected ResultsElber Cuya PillacaNo ratings yet
- Final Week For Brewers To Enter AIBADocument2 pagesFinal Week For Brewers To Enter AIBAWrightsPRNo ratings yet
- CoffeemakerDocument25 pagesCoffeemakersunilsainiNo ratings yet
- Optimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDocument9 pagesOptimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDanaNo ratings yet
- Cirrus 5 Oxygen Concentrator Manual: Important: Make Sure You Read and Understand All of The InformationDocument21 pagesCirrus 5 Oxygen Concentrator Manual: Important: Make Sure You Read and Understand All of The Informationmario pulido benitezNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Studies and Physico Chemical Analysis of Potable Water From Rural Areas of West Godavari District, Andhrapradesh.Document9 pagesWater Quality Studies and Physico Chemical Analysis of Potable Water From Rural Areas of West Godavari District, Andhrapradesh.IJAMTESNo ratings yet
- UnconsciousnessDocument6 pagesUnconsciousnessSeema RahulNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Science (သိပ္ပံ)Document160 pagesGrade 6 - Science (သိပ္ပံ)Khin Nyein100% (9)
- GU-501 - Guidelines For Excavating and Working Around Live PipelinesDocument22 pagesGU-501 - Guidelines For Excavating and Working Around Live PipelinesDhameemAnsari0% (1)
- Activity Selection ProblemDocument24 pagesActivity Selection ProblemKrisha DavdaNo ratings yet
- 18bondingcalc 2Document10 pages18bondingcalc 2Dundi Kumar BevaraNo ratings yet
- (RSC Analytical Spectroscopy Momographs) M. J. Adams-Chemometrics in Analytical Spectroscopy - Royal Society of Chemistry (1995)Document225 pages(RSC Analytical Spectroscopy Momographs) M. J. Adams-Chemometrics in Analytical Spectroscopy - Royal Society of Chemistry (1995)ciborg1978No ratings yet
- Harmonic Analysis of A Welding ProcessDocument5 pagesHarmonic Analysis of A Welding ProcessUMA AKANDU UCHENo ratings yet
- 5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesDocument96 pages5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesMauricio SantosNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis For SubmissionDocument6 pagesSwot Analysis For Submissionapi-502888276No ratings yet
- Aggregation Level and PDCCHDocument2 pagesAggregation Level and PDCCHMuhammad RizkiNo ratings yet
- J28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengDocument17 pagesJ28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengLeeLowersNo ratings yet
- Cafco ® Fendolite Mii: Application GuideDocument27 pagesCafco ® Fendolite Mii: Application GuideAhmed LepdaNo ratings yet
- 2 Condenser 3: CompressorDocument16 pages2 Condenser 3: CompressorLeslie CatindigNo ratings yet