Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math p1 2019
Math p1 2019
Uploaded by
yingwuenchanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math p1 2019
Math p1 2019
Uploaded by
yingwuenchanCopyright:
Available Formats
4
2 (a) Ali and Mo share a sum of money in the ratio Ali : Mo = 9 : 7.
Ali receives $600 more than Mo.
Calculate how much each receives.
Ali $ ...................................................
Mo $ ................................................... [3]
(b) In a sale, Ali buys a television for $195.80 .
The original price was $220.
Calculate the percentage reduction on the original price.
................................................ % [3]
(c) In the sale, Mo buys a jacket for $63.
The original price was reduced by 25%.
Calculate the original price of the jacket.
$ ................................................... [3]
© UCLES 2019 0580/41/O/N/19
5
3 (a) Dina invests $600 for 5 years at a rate of 2% per year compound interest.
Calculate the value of this investment at the end of the 5 years.
$ ................................................... [2]
(b) The value of a gold ring increases exponentially at a rate of 5% per year.
The value is now $882.
(i) Calculate the value of the ring 2 years ago.
$ ................................................... [2]
(ii) Find the number of complete years it takes for the ring’s value of $882 to increase to a value
greater than $1100.
.................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2019 0580/41/O/N/19 [Turn over
6
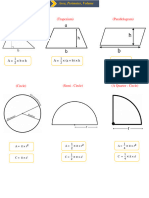
4 (a) (i) Calculate the external curved surface area of a cylinder with radius 8 m and height 19 m.
............................................... m2 [2]
(ii) This surface is painted at a cost of $0.85 per square metre.
Calculate the cost of painting this surface.
$ ................................................... [2]
(b) A solid metal sphere with radius 6 cm is melted down and all of the metal is used to make a solid cone
with radius 8 cm and height h cm.
(i) Show that h = 13.5 .
4
[The volume, V, of a sphere with radius r is V = rr 3 .]
3
1
[The volume, V, of a cone with radius r and height h is V = rr 2 h .]
3
[2]
(ii) Calculate the slant height of the cone.
.............................................. cm [2]
(iii) Calculate the curved surface area of the cone.
[The curved surface area, A, of a cone with radius r and slant height l is A = rrl .]
............................................. cm2 [1]
© UCLES 2019 0580/41/O/N/19
7
(c) Two cones are mathematically similar.
The total surface area of the smaller cone is 80 cm2.
The total surface area of the larger cone is 180 cm2.
The volume of the smaller cone is 168 cm3.
Calculate the volume of the larger cone.
............................................. cm3 [3]
(d) The diagram shows a pyramid with a P
square base ABCD.
DB = 8 cm. NOT TO
P is vertically above the centre, X, of SCALE
the base and PX = 5 cm.
D C
A B
Calculate the angle between PB and the base ABCD.
.................................................... [3]
© UCLES 2019 0580/41/O/N/19 [Turn over
12
7 (a) Oranges cost 21 cents each.
Alex buys x oranges and Bobbie buys (x + 2) oranges.
The total cost of these oranges is $4.20 .
Find the value of x.
x = ................................................... [3]
(b) The cost of one ruler is r cents.
The cost of one protractor is p cents.
The total cost of 5 rulers and 1 protractor is 245 cents.
The total cost of 2 rulers and 3 protractors is 215 cents.
Write down two equations in terms of r and p and solve these equations to find the cost of one
protractor.
........................................... cents [5]
© UCLES 2019 0580/41/O/N/19
13
(c) Carol walks 12 km at x km/h and then a further 6 km at (x - 1) km/h.
The total time taken is 5 hours.
(i) Write an equation, in terms of x, and show that it simplifies to 5x 2 - 23x + 12 = 0 .
[3]
(ii) Factorise 5x 2 - 23x + 12 .
.................................................... [2]
(iii) Solve the equation 5x 2 - 23x + 12 = 0 .
x = .................... or x = ................... [1]
(iv) Write down Carol’s walking speed during the final 6 km.
........................................... km/h [1]
© UCLES 2019 0580/41/O/N/19 [Turn over
16
10 (a) Complete the table for the 5th term and the nth term of each sequence.
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th
nth term
term term term term term
9 5 1 -3
4 9 16 25
1 8 27 64
8 16 32 64
[11]
(b) 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, …
This sequence is a Fibonacci sequence.
After the first two terms, the rule to find the next term is “add the two previous terms”.
For example, 5 + 8 = 13.
Use this rule to complete each of the following Fibonacci sequences.
2 4 ............ ............ ............
1 ............ ............ ............ 11
............ -1 ............ ............ 1
[3]
1 3 4 7 11
(c) , , , , , …
3 4 7 11 18
p
(i) One term of this sequence is .
q
Find, in terms of p and q, the next term in this sequence.
.................................................... [1]
(ii) Find the 6th term of this sequence.
.................................................... [1]
Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every
reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the
publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity.
To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced online in the Cambridge
Assessment International Education Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download
at www.cambridgeinternational.org after the live examination series.
Cambridge Assessment International Education is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group. Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of the University of
Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which itself is a department of the University of Cambridge.
© UCLES 2019 0580/41/O/N/19
You might also like
- Prediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024Document21 pagesPrediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024Shlok And gauransh legend100% (3)
- Chapter 1 Functions - Thomas Calculus 12th EditionDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Functions - Thomas Calculus 12th Editionfudge5391% (11)
- Chapter 3: Linear Inequalities: (Sec 3 Express)Document24 pagesChapter 3: Linear Inequalities: (Sec 3 Express)KalNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 1Document16 pagesScheme of Work Mathematics Form 1Cikgu SaripahNo ratings yet
- Math p4 2019 2Document9 pagesMath p4 2019 2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Paper 42 2022Document6 pagesPaper 42 2022yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Math P4 3Document9 pagesMath P4 3yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Paper 3Document10 pagesPaper 3yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Paper 41 2022Document9 pagesPaper 41 2022yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 - MENSURATION REVISION WSDocument6 pagesYr 11 - MENSURATION REVISION WSHaseeb BadrNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument12 pagesMy TestDigilib Cambridge TazkiaNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document7 pagesMath 1yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 - 2Document18 pagesPaper 4 - 2andryNo ratings yet
- Predicted Paper 2 and 4 Version 2 and SolutionsDocument96 pagesPredicted Paper 2 and 4 Version 2 and SolutionsMaisaa NajiNo ratings yet
- Paper-4Document19 pagesPaper-4visionaryheights.intNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE 0580 2019 Hardest QuestionsDocument72 pagesCIE IGCSE 0580 2019 Hardest QuestionsAnisha Bushra AkondNo ratings yet
- Tpole Paper 32 2024Document15 pagesTpole Paper 32 2024Ahmed SamahNo ratings yet
- 0580 Practice Test 3 2024 (Paper 4)Document22 pages0580 Practice Test 3 2024 (Paper 4)AFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 - Sample 1_QPDocument20 pagesPaper 4 - Sample 1_QPHaider ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Homework P4Document7 pagesHomework P4yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Bgcse Mathematics Pp2Document12 pagesBgcse Mathematics Pp2tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAhmed AmanNo ratings yet
- Class 11C - Maths P2Document20 pagesClass 11C - Maths P2St. Andrew's High School KarachiNo ratings yet
- Exam - 1 - IG 2022-2023Document10 pagesExam - 1 - IG 2022-2023algerocaineNo ratings yet
- 0580_s22_qp_22 (1)Document10 pages0580_s22_qp_22 (1)Yash KolvekarNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam Review Pack 2Document15 pagesMock Exam Review Pack 2Aman WaniyaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics O1p1Document10 pagesMathematics O1p1Umar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Prediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024Document21 pagesPrediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024Hamna BilalNo ratings yet
- Prediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024 SolutionsDocument21 pagesPrediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024 SolutionsHamna BilalNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Saya p1Document14 pagesAhmed Saya p1Demon trioNo ratings yet
- Weekend Assignment 2 0580Document9 pagesWeekend Assignment 2 0580prathamkumar8374No ratings yet
- MensurationDocument28 pagesMensurationpillboxsesame0sNo ratings yet
- Paper IVDocument9 pagesPaper IVWates SoluNo ratings yet
- Prediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024 SolutionsDocument21 pagesPrediction Paper 4 0580 May 2024 SolutionsAlyrNo ratings yet
- Calculations Involving Compound Shapes P4Document5 pagesCalculations Involving Compound Shapes P4Ucok PandapotanNo ratings yet
- 0580 m19 QP 22Document12 pages0580 m19 QP 22Richie TangNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Final - Review Pack-2Document132 pagesTerm 2 Final - Review Pack-2OmarNo ratings yet
- 0580_m18_qp_22Document11 pages0580_m18_qp_224dznhz88zjNo ratings yet
- 2 1 "We Eat More Ice Cream As The Temperature Rises."Document11 pages2 1 "We Eat More Ice Cream As The Temperature Rises."andryNo ratings yet
- 8 Igcse Physics Sa-2 Paper 4Document8 pages8 Igcse Physics Sa-2 Paper 4chandrshannuNo ratings yet
- ERC 2018 O Level Math P1 - v4 Final PDFDocument15 pagesERC 2018 O Level Math P1 - v4 Final PDFLim Kew ChongNo ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 1Document12 pages2020 Specimen Paper 1Haya DanishNo ratings yet
- 2023 Mock Exam Paper 2 QP - DraftDocument14 pages2023 Mock Exam Paper 2 QP - DraftMaya SombradoNo ratings yet
- G10 Final Mid Term Oct 22Document11 pagesG10 Final Mid Term Oct 22Mai khue NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSEDocument23 pagesCambridge IGCSEshayan sheikhNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Class 9 - PagenumberDocument41 pagesMid Term Class 9 - PagenumberAnay PatelNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42spotifysubs250No ratings yet
- Tafadzwa WorkDocument5 pagesTafadzwa WorkffgfgfgffgNo ratings yet
- IG 1 (A) Math (Core) S1T1 2023 - P2Document17 pagesIG 1 (A) Math (Core) S1T1 2023 - P2Su YongshengNo ratings yet
- Updated Specimen-CE-13-Additional-Mathematics-2022Document12 pagesUpdated Specimen-CE-13-Additional-Mathematics-2022Praneewan TunwattanaNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and Area of Shapes P4Document7 pagesPerimeter and Area of Shapes P4Ucok PandapotanNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test (April) - Igcse Maths: Marks %Document6 pagesMonthly Test (April) - Igcse Maths: Marks %Aqilah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41Majd Sharaf AldinNo ratings yet
- Mensuration HardestDocument39 pagesMensuration HardestBasma Emad Eddin ObajiNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document10 pagesHW 3Leyla NamazovaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration New 23 CombineDocument24 pagesMensuration New 23 CombineAshbeela rashdiNo ratings yet
- Maths Rcis Sem 2 Full PortionDocument13 pagesMaths Rcis Sem 2 Full PortionKavyaNo ratings yet
- A Plus 03.02 fm20 - 22 - 42Document17 pagesA Plus 03.02 fm20 - 22 - 42chinkhuslen1225No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Nikhil MenonNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Trig PracticeDocument9 pagesYear 10 Trig Practice이규민No ratings yet
- Gcse Maths 0580 Practice QuestionsDocument398 pagesGcse Maths 0580 Practice Questionsshalinta tyagiNo ratings yet
- Mock Test - Paper 4 - 0580Document17 pagesMock Test - Paper 4 - 0580bdb6wxhyxfNo ratings yet
- Molarity 4Document1 pageMolarity 4yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Heat 1Document1 pageHeat 1yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming p2Document16 pagesLinear Programming p2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Simulataneous EQDocument2 pagesSimulataneous EQyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Functions (H)Document7 pagesTransformation of Functions (H)yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- InequalitiesDocument30 pagesInequalitiesyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- LCM HCFDocument9 pagesLCM HCFyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Heat 13Document1 pageHeat 13yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Ratio & PercentageDocument35 pagesRatio & PercentageyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document7 pagesHomework 2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Paper 3Document10 pagesPaper 3yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListDocument11 pagesAx bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListDocument11 pagesAx bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 CheckpointDocument16 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 CheckpointDương Ngọc CườngNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 6 MathsDocument10 pagesCBSE Sample Paper For Class 6 MathsBhavana ShindeNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Unit 7Document9 pagesAlgebra: Unit 7ShilpaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Sendari NoviaNo ratings yet
- June 2017 MathsDocument24 pagesJune 2017 MathsEva Risueño0% (1)
- Maths & Mech FormulasDocument19 pagesMaths & Mech FormulasgunasekaranNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Question Paper Set B PDFDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 9 Mathematics Question Paper Set B PDFRaj TokasNo ratings yet
- Math Practice Problems Module 4Document9 pagesMath Practice Problems Module 4Peejay OllabracNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (Class-Vii) Major Test # 01: Section-ADocument4 pagesMathematics (Class-Vii) Major Test # 01: Section-ASandeep SomaiyaNo ratings yet
- Sohcahtoa Worksheet 1Document6 pagesSohcahtoa Worksheet 1Daffa Guevara RaushanfikriNo ratings yet
- 9.7 Small Changes and ApproximationsDocument1 page9.7 Small Changes and ApproximationsJiajia LauNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface Area AnswersDocument5 pagesVolume and Surface Area AnswersArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Math Paper2 Jun 99 PDFDocument11 pagesIgcse Math Paper2 Jun 99 PDFResearcher75% (4)
- Program:: Student Marksheet ReportDocument9 pagesProgram:: Student Marksheet ReportSHARVESH SNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Application of DifferentiationDocument11 pages4.0 Application of DifferentiationShafiqa ShafiraNo ratings yet
- Formatted Quantitative Aptitude For RRB NTPC 1 1 1 PDFDocument6 pagesFormatted Quantitative Aptitude For RRB NTPC 1 1 1 PDFRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Fractal Geometry and Dynamical Systems Yakov Pesin and Vaughn Climenhaga PDFDocument334 pagesLectures On Fractal Geometry and Dynamical Systems Yakov Pesin and Vaughn Climenhaga PDFYau Stein100% (2)
- APMOPS 2018 SolutionDocument11 pagesAPMOPS 2018 SolutionMarilyn Citadel100% (1)
- PS - CBSE - IX - Math - Heron's FormulaDocument4 pagesPS - CBSE - IX - Math - Heron's FormulaR.R.Rathod'sNo ratings yet
- Math 5thDocument4 pagesMath 5thMohib AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To Problem Solving: Math Foundations IDocument4 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Problem Solving: Math Foundations IAne MattNo ratings yet
- Math10 WorkbookFullDocument222 pagesMath10 WorkbookFullTuyếnĐặng100% (1)
- 1984 AIME Problems/Problem 3Document1 page1984 AIME Problems/Problem 3Abdullapoor RamReddyNo ratings yet
- Ozobots Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesOzobots Lesson Planapi-497020000No ratings yet
- GRE Math QuestionsDocument23 pagesGRE Math QuestionsratnaNo ratings yet
- Python Excercises With SolutionsDocument37 pagesPython Excercises With SolutionsAnonymous gqSpNAmlW100% (2)
- NSM Enhanced 7 CBDocument530 pagesNSM Enhanced 7 CBRenee Ng0% (8)
- A1704153589 - 17906 - 22 - 2019 - Dimensions 1and Scale1Document42 pagesA1704153589 - 17906 - 22 - 2019 - Dimensions 1and Scale1JfudNo ratings yet