Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IHP Report
IHP Report
Uploaded by
prasadbhoite711Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IHP Report
IHP Report
Uploaded by
prasadbhoite711Copyright:
Available Formats
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF
TECHNICAL EDUCATION (MUMBAI)
A
Project Report
On
Prepare report on Reciprocating positive Displacement pumps.
Submitted by,
Jadhav Abhishek Jitendra (1916740101)
Jadhav Harsh Santosh (1916740102)
Mulik Yuvraj Sandip (1916740103)
Chavan Samarth Nagesh (1916740104)
Under the guidance of
Mr. Y. V. Shinde
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Phaltan Education Society’s
College of Engineering, Phaltan
[2021-22]
Certificate
This is to certify that
Jadhav Abhishek Jitendra (1916740101)
Jadhav Harsh Santosh (1916740102)
Mulik Yuvraj Sandip (1916740103)
Chavan Samarth Nagesh (1916740104)
Students of TY Diploma Mechanical has successfully Completed this Micro Project
of Subject – Industrial hydraulics & Pneumatics (22655) under I Scheme for the
fulfillment of TY Diploma in Mechanical Engineering.
Subject Teacher HOD Principal
1. Title of Micro-Project: Prepare report on Reciprocating positive Displacement
pumps.
2. Rational : Reciprocating pumps are constant volume pumps. Variations in
discharge pressure do not affect flow rate. Since these pumps continue to deliver the
same capacity, any attempt to throttle the discharge flow may overpressure the
pump casing and/or discharge piping.
3. Aim/Benefits of the Micro-project:
To learn about Reciprocating positive Displacement pumps& it’s types or
applications.
4. Course Outcomes Achieved:
Select the pump & actuators for given fluid operated system.
5. Literature review:
i. Name of Pdf :- Reciprocating Pumps
Jayesh Patel, The working of the reciprocating pump is very simple and just
like an I.C engine. First of all the piston has the function of providing the
suction force, so that the liquid can be lift up and can be sucked in with great
force. After that comes the compression part which will bring the required
pressure energy to the fluids.
ii. Google link :- https://www.theengineerspost.com/reciprocating-pump/
6. Actual methodology:
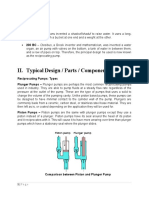
Working Principle/ Working
A Reciprocating Positive Displacement pump works by the repeated back-and-forth
movement (strokes) of either a piston, plunger or diaphragm . These cycles are
called reciprocation.
In a piston pump, the first stroke of the piston creates a vacuum, opens an inlet valve,
closes the outlet valve and draws fluid into the piston chamber (the suction phase). As
the motion of the piston reverses, the inlet valve, now under pressure, is closed and
the outlet valve opens allowing the fluid contained in the piston chamber to be
discharged (the compression phase).
The bicycle pump is a simple example. Piston pumps can also be double acting with
inlet and outlet valves on both sides of the piston. While the piston is in suction on
one side, it is in compression on the other. More complex, radial versions are often
used in industrial applications.
Classification or Types:-
1. Axial piston pump
i. In line axial piston pump
ii. Bent axis piston pump
2. Radial piston pump
i. Radial piston pump with stationary cylinder block.
ii. Radial piston pump with rotating cylinder block.
1.Axial piston pump
Axial piston pumps are positive displacement pumps which converts rotary motion of the
input shaft into an axial reciprocating motion of the pistons.These pumps have a number of
pistons (usually an odd number) in a Circular array Within a housing which is commonly
referred to as a cylinder block.
These pumps have sub-types as:
a. In Line axial Piston Pump
b. Bent Axis Piston Pump.
a. In Line axial Piston Pump
A swash plate is device that translates the rotary motion of a shaft into the reciprocating
motion .
An axial piston pump is a positive displacement pump that has a number of pistons
in a circular array within a cylinder block. It can be used as a stand-alone pump, a hydraulic
motor or an automotive air conditioning compressor.
b. Bent Axis piston pump
In these pumps the reciprocating action of the pistons is obtained by bending the
axis of the cylinder block. The cylinder block rotates at an angle which is inclined to the
drive shaft. The cylinder block is turned by the drive shaft through a universal link. The
cylinder block is set at an offset angle with the drive shaft. The cylinder block contains a
number of pistons along its periphery. These piston rods are connected with the drive shat
flange by ball-and-socket joints. These pistons are forced in and out of their bores as the
distance between the drive shaft flange and the cylinder block changes. A universal link
connects the block to the drive shaft, to provide alignment and a positive drive.
2. Radial piston pump
A radial piston pump is a type of hydraulic piston pump. The working pistons extend in a
radial direction symmetrically around the shaft, marking the main difference between them
and another piston pump, the axial piston pump, which has axially rotating pistons.
Radial piston pumps arrange a series of pistons radially in a cylindrical block around a rotor
hub. The block consists of a pantile, a cylinder barrel with pistons, and a rotor. The pantile
directs the fluid in and out of the cylinder. The rotor, mounted eccentrically in the pump
housing, forces the pistons in and out of cylinders as it rotates, which cause hydraulic fluid
to be sucked into the cylinder cavity and then be discharged from it. Inlets and outlets for
the pump are located in a valve in a central hub. Each piston is connected to inlet port when
it starts extending while it is connected to the outlet port when start retracting.
These pump have sub-types as:
i. Radial piston pump with stationary cylinder block.
ii. Radial piston pump with rotating cylinder block.
Radial piston pump with stationary cylinder block.
In a stationary block type radial piston pump. the cylinder block is kept
stationary: Reciprocating motion is imparted to the piston by rotating track ring. The
Cylinder block & the pump housing with track ring are positioned eccentric which allows
the radially placed pistons to make To & fro movement.
Radial Piston Pump with rotating Cylinder Block
In radial piston pump with rotating cylinder block. Cylinder block is connected
to drive shaft & outer ring is fixed. As the cylinder block & outer ring are eccentrically
placed. The pistons are thrown out by centrifugal force and pushed back because of
eccentricity between Track ring & cylinder block.
7. Actual Resources used:-
Sr. No Name of Specifications Quality Remark
resources/material
1. IHP Textbook C. P. 01 -
Murgudkar
2. Google Mobile Data - -
8. Outputs of micro project:
We learn about Reciprocating positive Displacement pumps &it’s types.
We learn about applications of Reciprocating positive Displacement pumps.
9. Skill Developed / Learning outcomes of this Micro-Project:
Team work.
Management of time.
knowledge increased about pumps.
10.Applications of Micro-project :
Water – high pressure washing; other low viscosity liquids; oil production; paint
spraying.
You might also like
- C-15, C-16, C-18 Dissassembly - Assembly 2008 PDFDocument144 pagesC-15, C-16, C-18 Dissassembly - Assembly 2008 PDFJose Pichinte89% (18)
- Introduction To Internal Combustion Engines, 2nd Edition by Richard StoneDocument295 pagesIntroduction To Internal Combustion Engines, 2nd Edition by Richard StoneChukwunonso Arinze50% (2)
- Donny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionFrom EverandDonny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CVO Paper PDFDocument10 pagesCVO Paper PDFvigneshwaran100% (1)
- cfm567b Training Manual Component Identification PDFDocument120 pagescfm567b Training Manual Component Identification PDFyura100% (2)
- Project Report On For The Course Industrial Hydraulics and Pneumatics (Mechanical Engineering) by 2200440226 2200440225 Under The Guidance ofDocument13 pagesProject Report On For The Course Industrial Hydraulics and Pneumatics (Mechanical Engineering) by 2200440226 2200440225 Under The Guidance ofAfaque KhatriNo ratings yet
- Design, Installation and Fabrication of Reciprocating PumpDocument40 pagesDesign, Installation and Fabrication of Reciprocating PumpMehdi Baghaie78% (9)
- Lab ReportDocument8 pagesLab ReportNurMd NabilNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Melab - Exp 3Document10 pagesGroup 6 - Melab - Exp 3Loy Joseph De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Figure: Centrifugal PumpDocument5 pagesFigure: Centrifugal PumpDhruv BagadeNo ratings yet
- Jet, Submersible and Rotary PumpsDocument15 pagesJet, Submersible and Rotary Pumpsmssant100% (1)
- Final ReportDocument118 pagesFinal Reportdivmech1988No ratings yet
- Study of A Centrifugal Pump, Pipe Fittings and Valves - Ch.E 206Document30 pagesStudy of A Centrifugal Pump, Pipe Fittings and Valves - Ch.E 206Synthia100% (1)
- Marine Auxiliary Machinery: 4 Positive Displacement PumpsDocument36 pagesMarine Auxiliary Machinery: 4 Positive Displacement PumpsJoshua Hicks100% (1)
- I. History: II. Typical Design / Parts / ComponentsDocument16 pagesI. History: II. Typical Design / Parts / ComponentsAriel GamboaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pump: Presented ByDocument10 pagesReciprocating Pump: Presented ByNikhil ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Pump - WikipediaDocument89 pagesPump - WikipediaMuhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Based On The Online Classes Session: 2020-21 B. Tech. VII SemesterDocument10 pagesBased On The Online Classes Session: 2020-21 B. Tech. VII SemesterHemant KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Generation Using Speed BreakerDocument36 pagesCompressed Air Generation Using Speed BreakerRaja ManeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pump & Its ClassificationDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Pump & Its ClassificationsenaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pumping System: in The Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocument49 pagesReciprocating Pumping System: in The Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofWjahvs GahahNo ratings yet
- Hyd Micro ProjectDocument20 pagesHyd Micro ProjectOmkar Moze CE - J1 - 88No ratings yet
- pumpالسيمنرDocument15 pagespumpالسيمنرعبد الرحمن قاسم البناءNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PumpsDocument11 pagesUnit 2 PumpsThuy TranNo ratings yet
- Radial Piston PumpDocument4 pagesRadial Piston PumpSamuel TanNo ratings yet
- PumpssssssDocument19 pagesPumpssssssJedz Tuluan Maslang IIINo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:-Reciprocating Pump 2.1: IntroducationDocument7 pagesChapter 2:-Reciprocating Pump 2.1: IntroducationParth VyasNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: Fluid MechanicsDocument13 pagesTerm Paper: Fluid Mechanicsdharmendrarj_3No ratings yet
- Artigo 1Document6 pagesArtigo 1Daniel Garutti EidNo ratings yet
- Pump Definition:: Plant Maintenance and Work Service - PracticeDocument9 pagesPump Definition:: Plant Maintenance and Work Service - PracticeTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNo ratings yet
- Types of Pumps and Centrifugal PumpDocument23 pagesTypes of Pumps and Centrifugal PumpRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Steering in ShipDocument34 pagesEmergency Steering in ShipMayilai AshokNo ratings yet
- PumpsDocument39 pagesPumpsneo_nitin100% (1)
- 4th Sem Hydraulic MICROPROJECTDocument16 pages4th Sem Hydraulic MICROPROJECTOmkar Jambhale100% (1)
- HM LAB Study & Experiments ManualDocument55 pagesHM LAB Study & Experiments Manualalanboss129No ratings yet
- All ChaptersDocument38 pagesAll ChaptersMalliKarjun ReddyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic MachineryDocument15 pagesHydraulic MachineryRichardNo ratings yet
- Pump - DisambiguationDocument6 pagesPump - DisambiguationsundaramNo ratings yet
- Presentation by Mr. Kalu Charan Sia Sr. Maintenance Engineer The Supreme Industries Limited Kharagpur - PPDDocument54 pagesPresentation by Mr. Kalu Charan Sia Sr. Maintenance Engineer The Supreme Industries Limited Kharagpur - PPDAnimesh Jana100% (1)
- Pump - TypeDocument16 pagesPump - Typeslam12125No ratings yet
- PumpDocument13 pagesPumpDomagoj ButumovićNo ratings yet
- Ivan-Mac Ivan MagbatocDocument16 pagesIvan-Mac Ivan MagbatocJayjay MonterdeNo ratings yet
- Chap3 - Positive Displacement Hydraulic PumpsDocument22 pagesChap3 - Positive Displacement Hydraulic PumpsMohamed GhareebNo ratings yet
- CF Pump Study 1stageDocument7 pagesCF Pump Study 1stageHa M ZaNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump: PrincipleDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Pump: Principle962943415xNo ratings yet
- Types of Pumps: Working Principle of PumpDocument12 pagesTypes of Pumps: Working Principle of PumpFe CaprichoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - PumpDocument50 pagesChapter 6 - Pumpa9157272235No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Pumps PDFDocument13 pagesHydraulic Pumps PDFtonylyfNo ratings yet
- MICRO-PROGECT - Hydraulics (22401)Document18 pagesMICRO-PROGECT - Hydraulics (22401)hemant sakhareNo ratings yet
- Types of Pumps On ShipDocument4 pagesTypes of Pumps On ShipchristianNo ratings yet
- Pumps: Applications, Components, Types, WorkingDocument19 pagesPumps: Applications, Components, Types, WorkingHassan KafilNo ratings yet
- Pump - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesPump - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 - Theory SMEDocument28 pagesUnit-6 - Theory SMEpratikpdhakateNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery - Centrifugal PumpsDocument33 pagesFluid Machinery - Centrifugal PumpsDaniel Paul67% (3)
- On Hydraulic Pumps: Design GuideDocument16 pagesOn Hydraulic Pumps: Design Guideali morisy100% (2)
- PEOP1009 - Pumps-1 PDFDocument17 pagesPEOP1009 - Pumps-1 PDFShazeem HoseinNo ratings yet
- Report On Reciprocating PumpDocument22 pagesReport On Reciprocating PumpAshokNo ratings yet
- Design of Impeller of Centrifugal Pump by Using Analytical and Numerical MethodDocument10 pagesDesign of Impeller of Centrifugal Pump by Using Analytical and Numerical MethodVSNo ratings yet
- Aniket Parise-Converted-MergedDocument10 pagesAniket Parise-Converted-Merged39 - Deep MandokarNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Operated Water PumpDocument42 pagesPendulum Operated Water PumpSRL MECH100% (1)
- For Other Uses of "Pump" or "Pumps", SeeDocument26 pagesFor Other Uses of "Pump" or "Pumps", Seekhalil zahaniNo ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Selwood EngineDocument5 pagesSelwood EngineramjoceNo ratings yet
- Volvo Overhaul KitsDocument96 pagesVolvo Overhaul KitswaleedNo ratings yet
- Error Codes 1 4 MultiAir Published v1Document48 pagesError Codes 1 4 MultiAir Published v1JuanNo ratings yet
- Engines+Lc1p88f 1、Lc1p90f 1、Lc1p92f 1+Part+ListDocument24 pagesEngines+Lc1p88f 1、Lc1p90f 1、Lc1p92f 1+Part+ListAndrewNo ratings yet
- Engine ParametersDocument27 pagesEngine ParametersahmedNo ratings yet
- Engine Mass Elastic DataDocument35 pagesEngine Mass Elastic Datamartin.rubenNo ratings yet
- Damping of Torsional Vibrations of Ship Engine Crankshafts - General Selection Methods of Viscous Vibration DamperDocument5 pagesDamping of Torsional Vibrations of Ship Engine Crankshafts - General Selection Methods of Viscous Vibration Dampersuhas110No ratings yet
- SENR1013 Cнятие клапанов 3408ЕDocument7 pagesSENR1013 Cнятие клапанов 3408ЕAminadavNo ratings yet
- 03aiv. DFP4 2012 C10 Technical Data PDFDocument2 pages03aiv. DFP4 2012 C10 Technical Data PDFcchristt2584No ratings yet
- Finding Top Center Position For No. 1 Piston: Testing and AdjustingDocument3 pagesFinding Top Center Position For No. 1 Piston: Testing and AdjustingDiego CatariNo ratings yet
- Dellorto X Series Needle Di..Document2 pagesDellorto X Series Needle Di..Carlos Bajo FNo ratings yet
- Maxx Force DTusaDocument1 pageMaxx Force DTusaffralbertoNo ratings yet
- WORKSHOP MANUAL MAXX FORCE 4.8-7.2 Parte 2Document119 pagesWORKSHOP MANUAL MAXX FORCE 4.8-7.2 Parte 2Daniel Graterol0% (1)
- The Crankcase: Construction and Design Crankcases Are of Many Sixe and Shapes and Konstruksi Dan DesainDocument5 pagesThe Crankcase: Construction and Design Crankcases Are of Many Sixe and Shapes and Konstruksi Dan DesainDhimas AdiNo ratings yet
- NOx Reduction MethodsDocument2 pagesNOx Reduction MethodsMadhu NarayananNo ratings yet
- Piston Engine ConstructionDocument150 pagesPiston Engine ConstructionHastian SuryaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Service Tool 2020C v1.0 Product Status ReportDocument6 pagesElectronic Service Tool 2020C v1.0 Product Status ReportHakim GOURAIANo ratings yet
- Service Bulletins: To Request A Service BulletinDocument1 pageService Bulletins: To Request A Service BulletinJeff LangleyNo ratings yet
- Online Adaptive Fuzzy Neural Network Automotive Engine Control by Keith JamesDocument267 pagesOnline Adaptive Fuzzy Neural Network Automotive Engine Control by Keith JamesFelipe SilvaNo ratings yet
- Cummins Isde245 30 So40149 Parts CatalogueDocument10 pagesCummins Isde245 30 So40149 Parts CatalogueChen Caroline100% (1)
- CUMMINS - b3.9-c116 Parts Catalog cpl2351 DynapacDocument83 pagesCUMMINS - b3.9-c116 Parts Catalog cpl2351 DynapacLord Eskar100% (1)
- Alpina 070-ServiceDocument5 pagesAlpina 070-Servicefrancesco.accinni.onlineNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones de Biela CaterpillarDocument2 pagesEspecificaciones de Biela CaterpillarYubiangel Celeste Perugini Parababith100% (1)
- CG20 25 30 33 35NXP Stage V (Xsb1801e)Document695 pagesCG20 25 30 33 35NXP Stage V (Xsb1801e)vitrinetecnicaNo ratings yet
- V12-2000 EN WebDocument2 pagesV12-2000 EN WebElshan jalilzadeh100% (1)
- Bosch Nozzle Injectors Cross References PDF List PDFDocument11 pagesBosch Nozzle Injectors Cross References PDF List PDFGustampa TampaNo ratings yet