Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction of Control System (Complete)
Introduction of Control System (Complete)
Uploaded by
Tanvir Mahatab NadimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction of Control System (Complete)
Introduction of Control System (Complete)
Uploaded by
Tanvir Mahatab NadimCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |1
Question: Define control system. Discuss the types of control system.
Answer:
Control System: A control system is a system or device or set of device which
control the output of main system to get desire output.
Types of Control System: There are two types of control system:
1. Open loop system: In an open loop system, the control action is
independent of the desired output. In other words, when the output
quantity of the control system is not feedback to the input quantity, the
control system is called an open loop system. For example: Washing
machine, traffic control etc.
2. Closed loop system: In the closed loop control system, the control
action is dependent on the desired output, where the output quantity is
considerably controlled by sending a command signal to input quantity.
For example: Air conditioner (AC), Cooling system in car.
Question: Write down some practical example of open loop system and closed
loop system.
Answer:
Practical example of open loop system:
1. Electrical hand driver
2. Washing machine
3. Bread toaster
4. Coffee maker
5. Timer based cloth driver
6. Light switch
7. Stereo system
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |2
Practical examples of closed loop system:
1. Servo voltage stabilizer
2. Water level indicator
3. Missile launcher and auto tracked by radar
4. Air conditioner
5. Cooling system in car
Question: Differentiate between open loop system and closed loop system.
Answer:
Open loop system Closed loop system
1. The feedback element is absent. 1. The feedback element is present.
2. An error detector is absent. 2. An error detector is present.
3. It is stable one. 3. It may become unstable.
4. It is easy to construct. 4. Complicated construction.
5. It is economical. 5. It is costly.
6. It is inaccurate. 6. It is accurate.
7. Maintenance cost is less. 7. Maintenance cost is high.
8. It is unreliable. 8. It is reliable.
9. Example: Coffee maker. 9. Example: Air conditioner.
Question: Define: (a) System (b) Controlled variable (c) Controller (d) Plant (e)
Disturbance (f) Feedback (g) Feedback control (h) Actuating signal/Error
signal.
Answer:
a) System: A system is a combination of component that work together and
perform certain objective.
b) Controlled variable: It is the quantity or condition that is measured and
controlled. Example: In case of air conditioner, controlled variable is
temperature.
c) Controller: Controller measures the value of the controlled variable of
the system and applies necessary steps or commends to get desire result.
Example: Switch, regulator etc.
d) Plant: A plant is a piece of equipment which is a set of machine parts
functioning together. The purpose of which is to perform a particular
operation. Example: Furnace, space craft etc.
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |3
e) Disturbance: A disturbance is a signal that tends to affect the value of
the output of a system. If a disturbance is created inside the system, it is
called internal disturbance. If it is created outside the system, it is called
external disturbance.
f) Feedback: The portion of an output signal which is retransmitted as an
input signal is called feedback. Normally the feedback signal has the
opposite polarity to the input signal. That is why it is called negative
feedback.
g) Feedback control: Feedback control is an operation that in the presence
of disturbance tends to reduce the difference between the output of a
system and some reference input.
h) Actuating signal/Error signal: The signal found from the difference of
reference input and feedback signal is smaller in magnitude. So, it is
easier to handle. It is called actuating signal [E(s)]. Sometimes the value
of actuating signal becomes zero when desire output is acquired.
Question: Write down the classification of feedback system/closed loop system.
Answer: The classification of feedback system/closed loop system is given
below:
1. Linear vs. non-linear feedback system
2. Time variant vs. time invariant system
3. Continuous vs. discontinuous system
4. Position vs. velocity feedback system
Question: Write down some names of industrial controller.
Answer: The name of some industrial controller is given below:
1. PID controller (Proportionality, Derivatives, Integral constroller)
2. ON and OFF controller
3. PD controller (Proportionality, Derivative controller)
4. Optimal controller
5. Adaptive controller
6. Neural controller
7. Fuzzy logic controller
8. Servomechanism controller etc.
Question: What is block diagram? What is the necessity of block diagram
representation?
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |4
Answer:
Block diagram: A block diagram of a system is a pictorial representation of the
functions performed by each component ad of the flow of signals.
Necessity of block diagram representation:
A system can be described in a number of different ways. For example, it can be
described mathematically by a set of differential equations or it can be
represented by a detailed schematic diagram which shows all the components
and their interconnections. However, when the system is fairly complicated,
neither of these two methods of representation is particularly satisfactory. The
purely mathematical representation tends to convert an engineering problem
into a mathematical exercise; it is difficult to acquire from the equations and
their manipulation a physical insight of the effect of the individual components
and their interconnections on the over-all system response. On the other hand,
detailed schematic diagrams are hard to draw and they do not give quantitative
relationships unless equations are also written. The block diagram method of
describing a system is a combination of the two methods i.e. it uses blocks to
indicate mathematical operations on the various physical quantities. Block
diagram of a system consists of unidirectional, operational blocks; they show
the direction of flow and the operations on the system variables in such a way
that a relationship is established between the input and the output as the path is
traced through the diagram. Each block is completely characterized by a transfer
function.
Question: Define open loop transfer function and feed-forward transfer
function.
Answer:
Open loop transfer function: The ratio of the feedback signal B(s) to the
actuating error signal E(s) is called open loop transfer function.
( )
Open loop transfer function = ( )
= G(s) H(s)
Feed-forward transfer function: The ratio of the output signal C(s) to the
actuating error signal E(s) is called feed-forward transfer function.
( )
Feed-forward transfer function = ( )
= G(s)
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |5
Question: Explain the result of sudden load on close loop and open loop system.
Answer:
In case of closed loop system when a sudden load is applied, the system
becomes unstable for a moment and it creates an error signal which is fed back
to the input. The system then automatically tries to recover the error and
eventually it gets back to its previous state or gains system stability.
On the other hand, when a sudden load is applied to an open loop system, the
system becomes unstable. As there is no feedback path, the system cannot
compensate this error and so it can never recover its previous state or stability.
Problem 1: Draw a block diagram for the R-C circuit where Vi and Vo are the
input and output variables respectively.
Solution:
Two transformed equations can be written for the two elements in the circuit:
For R: I(s) = [Vi(s) Vo(s)]
For C: Vo(s) = I(s)
Vi(s) 1 I(s) 1 Vo(s)
𝑅 𝐶𝑠
Vo(s)
Problem 2: Draw the block diagram for the two section R-C circuit.
Solution:
The four transformed equations are:
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |6
For R1: I(s) = [Vi(s) V1(s)]
For C1: V1(s) = [I (s)
( ) 1
I2(s)]
For R2: I2(s) = [V1(s) Vo(s)]
For C2: Vo(s) = I (s)
( ) 2
I2(s)
Vi(s) 1 I1(s) 1 V1(s) 1 1 Vo(s)
𝑅 𝐶 (𝑠) 𝑅2 𝐶2 (𝑠)
V1(s) Vo(s)
Question: Prove that, open loop transfer function = Feed-forward transfer
function = G(s).
Answer:
We know,
( )
Open loop transfer function = ( )
= G(s) H(s)
( )
And Feed-forward transfer function = ( )
= G(s)
If the feedback transfer function H(s) is unity i.e. 1, then open loop transfer
function = G(s)
So, Open loop transfer function = Feed-forward transfer function = G(s).
Question: Derive the transfer function of closed loop system.
Answer:
Here,
R(s) = Input signal
C(s) = Output signal
E(s) = Error signal/Actuating signal
B(s) = Feedback signal
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |7
G(s) = Feed-forward transfer function
H(s) = Feedback transfer function
From the figure,
C(s) = G(s) E(s) -------------- (i)
And, E(s) = R(s) B(s)
⇒ E(s) = R(s) C(s) H(s) [∵ B(s) = C(s) H(s)]
Putting the value of E(s) in equation (i),
C(s) = G(s)[R(s) C(s) H(s)]
⇒ C(s) = G(s) R(s) – G(s) C(s) H(s)
⇒ C(s) + G(s) C(s) H(s) = G(s) R(s)
⇒ C(s)[1+G(s) H(s)] = G(s) R(s)
( ) ( )
⇒ ( )
= ( ) ( )
This is the transfer function of closed loop system.
Question: Define close loop transfer function.
Answer:
Close loop transfer function: The ratio of the output signal C(s) to the input
signal R(s) is called closed loop transfer function.
( ) ( )
Closed loop transfer function = ( )
= ( ) ( )
Question: Show that the transfer function of closed loop system is [1+G(s) H(s)]
times less than open loop system.
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |8
Answer: We know, the ratio of the feedback signal B(s) to the actuating error
signal E(s) is called open loop transfer function.
Figure (a): Open loop system
( )
Open loop transfer function = ( )
= G(s) H(s)
If the feedback transfer function H(s) is unity i.e. 1; then open loop transfer
function = G(s)
Now in the case of closed loop system from the figure (b),
C(s) = G(s) E(s) -------------- (i)
And, E(s) = R(s) B(s)
⇒ E(s) = R(s) C(s) H(s) [∵ B(s) = C(s) H(s)]
Figure (b): Closed loop system
Putting the value of E(s) in equation (i),
C(s) = G(s)[R(s) C(s) H(s)]
⇒ C(s) = G(s) R(s) – G(s) C(s) H(s)
⇒ C(s) + G(s) C(s) H(s) = G(s) R(s)
⇒ C(s)[1+G(s) H(s)] = G(s) R(s)
( ) ( )
⇒ ( )
= ( ) ( )
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
INTRODUCTION OF CONTROL SYSTEM |9
It is the closed loop transfer function. If the value of [1+G(s) H(s)] is gradually
increased, the transfer function of closed loop system will be decreased. So, we
can say that, the transfer function of closed loop system is [1+G(s) H(s)] times
less than open loop system.
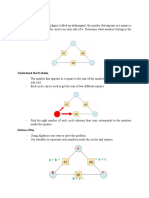
Question: Discuss the rule of block diagram simplification.
Answer:
1. Blocks in cascade/series:
2. Combining blocks in parallel:
3. Eliminating a feedback loop:
4. Moving a take-off point beyond a block:
5. Moving a take-off point ahead of a block:
Question: Simplify the following block diagram and find the transfer function:
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
I N T R O D U C T I O N O F C O N T R O L S Y S T E M | 10
Solution: By eliminating the feedback paths we get,
( )
∴ Transfer function, TF = ( )
=( )( )
Problem: Simplify the following block diagram and find the transfer
function:
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
I N T R O D U C T I O N O F C O N T R O L S Y S T E M | 11
Solution:
1. Taking the take-off beyond the block ‘G3’, we get,
2. Combining G2 and G3,
3. Eliminating H3 (feedback path)
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
I N T R O D U C T I O N O F C O N T R O L S Y S T E M | 12
4. Eliminating the feedback path H2/G3, we get,
5. Combining blocks in series
6. Eliminating the feedback path H1/G3 we get,
( )
∴ Transfer function, TF = ( )
=
Problem: Simplify the following block diagram and find the transfer function:
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
I N T R O D U C T I O N O F C O N T R O L S Y S T E M | 13
Solution:
1. Rearranging the block diagram we get,
2. Eliminating H2 loop, we get,
3. Combining the blocks in series,
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
I N T R O D U C T I O N O F C O N T R O L S Y S T E M | 14
4. Eliminating feedback loop H3, we get,
5. Eliminating feedback loop H1H2, we get,
( )
∴ Transfer function, TF = ( )
=
Prepared By: Hasan Bin Firoz (533)
Control System-I (EEE 703)
You might also like
- FeedCon (Unit 1) PDFDocument17 pagesFeedCon (Unit 1) PDFAbby MacallaNo ratings yet
- EEN 407 Sample QuestionsDocument41 pagesEEN 407 Sample QuestionsAbu SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- ECE - Control System 1 AprDocument9 pagesECE - Control System 1 Aprmukesh soniNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument7 pagesUnit IanandhNo ratings yet
- 1 Class (04-02-2021) : 1. What Is Block Diagram? 2. What Is Summing Junction?Document25 pages1 Class (04-02-2021) : 1. What Is Block Diagram? 2. What Is Summing Junction?Md.Atikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Take Home Examprocess Control1Document4 pagesTake Home Examprocess Control1Gehad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 NotesDocument43 pagesUnit-1 NotesMD SHAHRIARMAHMUDNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument96 pagesControl SystemsDr. Gollapalli NareshNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Introduction 1Document36 pagesControl Systems Introduction 1mary mutungaNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument11 pagesControl Systembalaji1986No ratings yet
- Biological Control Systems: Biomedical Engineering - Bcs - Short Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesBiological Control Systems: Biomedical Engineering - Bcs - Short Questions and AnswersNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Fundamentals of Control System: Lecturer: D. R. PardeshiDocument18 pagesUnit I: Fundamentals of Control System: Lecturer: D. R. PardeshiDnyaneshwar RajputNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Presentation - 1Document30 pagesControl Systems Presentation - 1soumikchatterjee1912No ratings yet
- Control System Engineering (15A02303) : Lecture Note B.TechDocument126 pagesControl System Engineering (15A02303) : Lecture Note B.TechNAZMUS SAKIBNo ratings yet
- Control Systems NotesDocument152 pagesControl Systems Notesdarlachantisaideepthi450No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document28 pagesPresentation 1Sithy JuhaniyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminologies in Control System SystemDocument8 pagesBasic Terminologies in Control System SystemPandimadevi GanesanNo ratings yet
- Control Systems NotesDocument74 pagesControl Systems NotesNirjal RanipaNo ratings yet
- Unit No - II: Block Diagram RepresentationDocument56 pagesUnit No - II: Block Diagram RepresentationNamrta DeokateNo ratings yet
- Control System Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesControl System Engineering Questions and AnswersYassir OwangeNo ratings yet
- II EceDocument16 pagesII EceAruna ChandranNo ratings yet
- EE2253 CS 2marks 2013Document14 pagesEE2253 CS 2marks 2013selvi0412100% (1)
- Control SystemDocument20 pagesControl Systembiswasmoumita981No ratings yet
- Lab 6-CSDocument8 pagesLab 6-CSAmir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Unit I System and Representation Part A: Open Loop System Closed Loop SystemDocument9 pagesUnit I System and Representation Part A: Open Loop System Closed Loop SystemPRABAKARANNo ratings yet
- Ec2255 - Control SystemDocument42 pagesEc2255 - Control Systemselvi0412No ratings yet
- Control Systems - PART - ADocument12 pagesControl Systems - PART - Aaarthir88100% (1)
- Control System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2Document109 pagesControl System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2KejeindrranNo ratings yet
- Control Systems NotesDocument135 pagesControl Systems Notessugunasri UNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Controls and Feedback: BackgroundDocument6 pagesLab 5 - Controls and Feedback: BackgroundABamisheNo ratings yet
- Control System Unit 1 (5 TH Sem.)Document61 pagesControl System Unit 1 (5 TH Sem.)kishan guptaNo ratings yet
- Dept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)Document9 pagesDept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)DeepakLingamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Sub. Name: Ae6505 Control Engineering Answer Key Semester/Year: V / Iii Cat-1 Part-ADocument12 pagesSub. Name: Ae6505 Control Engineering Answer Key Semester/Year: V / Iii Cat-1 Part-AgallantprakashNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering: 2 Marks Questions & AnswersDocument16 pagesControl Engineering: 2 Marks Questions & AnswersLakshumaiah MajjariNo ratings yet
- ECE 331 Complete NotesDocument129 pagesECE 331 Complete NotespolygatoneoderaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering 5Document5 pagesControl Systems Engineering 5ANo ratings yet
- Unit I NotesDocument43 pagesUnit I Notesaravinth69601No ratings yet
- Control Systems Laboratory Experiment 4 Open-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Control SystemsDocument6 pagesControl Systems Laboratory Experiment 4 Open-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Control SystemsAli MoustafaNo ratings yet
- Open-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Control SystemDocument6 pagesOpen-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Control SystemJaveria AfzalNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument72 pagesNotes026Himani GautamNo ratings yet
- LabExercise 9 - Dynamic Systems SimulationDocument16 pagesLabExercise 9 - Dynamic Systems SimulationQueenie Rose PercilNo ratings yet
- Lab 6-CSDocument8 pagesLab 6-CSkashafNo ratings yet
- Control Systems 12 Marks PDFDocument20 pagesControl Systems 12 Marks PDFSwathiNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument356 pagesControl System21ee017No ratings yet
- Contyrol Systems Revision-1-1Document33 pagesContyrol Systems Revision-1-1generaliemmanuel1No ratings yet
- Ec2255 - Control SystemDocument42 pagesEc2255 - Control SystemK.RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction Review of Laplace TransformsDocument35 pagesIntroduction Review of Laplace TransformsVeilNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionHARISHNo ratings yet
- LESSON1 IntroToControlSystemDocument10 pagesLESSON1 IntroToControlSystemalexancog456No ratings yet
- Adaptive Control Theory: IntroductionDocument19 pagesAdaptive Control Theory: IntroductionThanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cpe 315 Feedback Control System LessonsDocument28 pagesCpe 315 Feedback Control System Lessonskeny amigableNo ratings yet
- CS Two MarksDocument7 pagesCS Two MarkssivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- Control System Guess PaperDocument35 pagesControl System Guess PaperSonu BairwaNo ratings yet
- AUTOMATIC - CONTROL - SYSTEM - UNIT - 1 - For MergeDocument45 pagesAUTOMATIC - CONTROL - SYSTEM - UNIT - 1 - For MergemanishaNo ratings yet
- EC2255 Controls Systems 2marks With Answers (Sem4)Document39 pagesEC2255 Controls Systems 2marks With Answers (Sem4)lvrevathiNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Journal For: Control System Engineering (2150909)Document37 pagesA Laboratory Journal For: Control System Engineering (2150909)Bhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 309 Mechatronics MCQDocument27 pages309 Mechatronics MCQMr.G.Chandrasekar mechanicalstaffNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlFrom EverandNonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlNo ratings yet
- Jackel, Kawai - The Future Is Convex - Wilmott Magazine - Feb 2005Document12 pagesJackel, Kawai - The Future Is Convex - Wilmott Magazine - Feb 2005levine_simonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Deep Learning Using R: A Step-by-Step Guide To Learning and Implementing Deep Learning Models Using R Taweh Beysolow IiDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Deep Learning Using R: A Step-by-Step Guide To Learning and Implementing Deep Learning Models Using R Taweh Beysolow Iimarguerite.sansotta786100% (9)
- Hatdog 1.2Document18 pagesHatdog 1.2Jonafe PiamonteNo ratings yet
- Number BashingDocument5 pagesNumber BashingWithoon ChinchalongpornNo ratings yet
- Storace (2004) - Piecewise-Linear Approximation of Nonlinear Dynamical SystemsDocument13 pagesStorace (2004) - Piecewise-Linear Approximation of Nonlinear Dynamical SystemsSohibul HajahNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Tutorial 1Document4 pagesLinear Programming Tutorial 1Thaya IdhyomaticNo ratings yet
- Turing Computability: Robert I. SoareDocument289 pagesTuring Computability: Robert I. SoareJune KangNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Infinite Impulse Response FiltersDocument41 pagesUnit Ii Infinite Impulse Response FiltersPavithra ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document33 pagesUnit 2iamutkarshdubeNo ratings yet
- Fast and Numerically Stable Circle Fit: H. Abdul-Rahman and N. ChernovDocument16 pagesFast and Numerically Stable Circle Fit: H. Abdul-Rahman and N. ChernovParitoshNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression Using PythonDocument15 pagesLinear Regression Using PythonGnanarajNo ratings yet
- Needham-Schroeder ProtocolDocument4 pagesNeedham-Schroeder ProtocolCynthia Prasanna100% (1)
- Kas 3Document2 pagesKas 3yaredNo ratings yet
- Unit 4&5Document108 pagesUnit 4&5chirag suresh chiruNo ratings yet
- Backtracking: General MethodDocument68 pagesBacktracking: General Methodsantosh.parsaNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document21 pagesCH 10MuhammadImranNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 Solutions Ex 10 2 Method Umer AsgharDocument17 pagesChap 10 Solutions Ex 10 2 Method Umer AsgharSikandar Khan100% (3)
- Modeling Simulation and Control of A Methanol Synthesis Fixed Bed ReactorDocument13 pagesModeling Simulation and Control of A Methanol Synthesis Fixed Bed ReactorAbdullaNo ratings yet
- M2A1: Double Taylor Series & The Jacobian Matrix 1 Double Taylor SeriesDocument2 pagesM2A1: Double Taylor Series & The Jacobian Matrix 1 Double Taylor SeriessompongtNo ratings yet
- Binary Search (BS) : Md. Mehedi HassanDocument8 pagesBinary Search (BS) : Md. Mehedi HassanMehedi HassanNo ratings yet
- WWW: Jingli/teach Email: Jingli@ece - Lehigh.edu: ECE 342 Communication Theory Fall 2005, Midterm 1Document7 pagesWWW: Jingli/teach Email: Jingli@ece - Lehigh.edu: ECE 342 Communication Theory Fall 2005, Midterm 1WaleedWaelNo ratings yet
- Project Management A Managerial Approach 9th Edition Meredith Test BankDocument15 pagesProject Management A Managerial Approach 9th Edition Meredith Test Bankhoangsang9my43100% (25)
- TMP 46 C6Document5 pagesTMP 46 C6FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Niko Busch - Time Frequency Analysis of EEG Data PDFDocument30 pagesNiko Busch - Time Frequency Analysis of EEG Data PDFsaikat2No ratings yet
- Number 7 (Solution 1) : A+b A + CDocument6 pagesNumber 7 (Solution 1) : A+b A + Cnaze grace dulnuanNo ratings yet
- Variables Aleatorias 2Document34 pagesVariables Aleatorias 2XSonicplay XNo ratings yet
- Micromachines 13 00947Document12 pagesMicromachines 13 00947Đỗ QuảngNo ratings yet
- EE-232 Signals & Systems: Fourier Series & Fourier TransformsDocument17 pagesEE-232 Signals & Systems: Fourier Series & Fourier TransformsHaris AsifNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Computer Engineering Machine Learning SUBJECT CODE: 3710216Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Computer Engineering Machine Learning SUBJECT CODE: 3710216Er Umesh ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - SolutionsDocument8 pagesChapter 12 - SolutionsShahariar RiasatNo ratings yet