Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document 28
Document 28
Uploaded by
sattwik.christnaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Document 28
Document 28
Uploaded by
sattwik.christnaCopyright:
Available Formats
Stereotypes associated with an ethnic group/culture in South-east Asia, and its relevance for their
identity
Southeast Asia is a diverse and culturally rich region, with a wide range of ethnic groups, languages, and
traditions. Unfortunately, many of these groups are subject to stereotypes and negative assumptions,
which can have a significant impact on their identity and sense of self.
One of the most common stereotypes in Southeast Asia is the idea that Chinese people are wealthy and
business-savvy. While it's true that many Chinese people have been successful in business, this
stereotype ignores the diversity of Chinese experiences and the challenges faced by many members of
the community. For example, many Chinese people have faced discrimination and violence throughout
Southeast Asia, particularly during periods of political turmoil.
Similarly, Malays are often stereotyped as lazy and not as hardworking as other groups. This stereotype
is harmful and ignores the many contributions made by Malays to Southeast Asian society. Like all
groups, Malays are diverse, and their experiences and achievements cannot be reduced to a single
stereotype.
Filipinos are often stereotyped as domestic helpers or working in service industries. While it's true that
many Filipinos work in these fields, this stereotype ignores the many other contributions made by
Filipinos to Southeast Asian society, including in fields like medicine, engineering, and technology.
Thais are often stereotyped as friendly and hospitable, but also willing to engage in unethical behavior
to get ahead. While it's true that Thais are known for their hospitality and friendliness, this stereotype is
harmful and ignores the many positive contributions made by Thai people to Southeast Asian society.
Vietnamese are often stereotyped as frugal and hardworking but lacking in creativity. This stereotype
ignores the many contributions made by Vietnamese people to Southeast Asian culture and history,
including in fields like literature, music, and art.
These stereotypes can have a significant impact on how people from these ethnic groups see
themselves and their identity. For example, someone who is Chinese may feel pressure to live up to the
stereotype of being wealthy and successful, and may feel shame or embarrassment if they are not.
Similarly, someone who is Malay may feel frustrated or discouraged if they are constantly viewed as lazy
or unproductive.
At the same time, these stereotypes can also be a source of pride and connection to one's cultural
heritage. For example, someone who is Thai may feel a strong sense of identity and belonging when
they are praised for their hospitality and friendliness.
It's important to note that these stereotypes are often oversimplified and do not accurately reflect the
diversity and complexity of Southeast Asian cultures and ethnic groups. They can also be harmful and
perpetuate discrimination and inequality. As such, it's important to challenge these stereotypes and
recognize individuals for who they are, rather than making assumptions based on their ethnicity or
culture.
You might also like
- Ed Soja ThirdspaceDocument193 pagesEd Soja Thirdspacepoemadelsol69% (13)
- Human Face of Big Data - Teachers Guide PDFDocument7 pagesHuman Face of Big Data - Teachers Guide PDFim247blackNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Thailand: Monarchy, War and Resilience: The Fascinating Story of the Gilded Kingdom at the Heart of AsiaFrom EverandBrief History of Thailand: Monarchy, War and Resilience: The Fascinating Story of the Gilded Kingdom at the Heart of AsiaRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Proof of Cash ProblemDocument3 pagesProof of Cash ProblemKathleen Frondozo71% (7)
- How Does Culture Matter - SenDocument6 pagesHow Does Culture Matter - SenKrithika GanesanNo ratings yet
- Abn ExtractionDocument2 pagesAbn Extractionuttamkumar_mondol_5No ratings yet
- Core Concepts Nina Evason 2016Document5 pagesCore Concepts Nina Evason 2016Nur FarihaNo ratings yet
- GTVHDocument10 pagesGTVHQuyết Thắng Lê VõNo ratings yet
- Eastern and WesternDocument5 pagesEastern and WesternCatherine EllabaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Cultural Heritage EssayDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Cultural Heritage EssayAbdul QodirtNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two CulturesDocument3 pagesA Tale of Two CulturesApril RondinaNo ratings yet
- Lang and CultDocument4 pagesLang and CultElba Aurora Diana DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Research Report DIV001Document10 pagesResearch Report DIV001samridhi.bansal89No ratings yet
- HANDOUT - Cultural Diversity: Examples of Personal CulturesDocument2 pagesHANDOUT - Cultural Diversity: Examples of Personal Culturesapi-364338283No ratings yet
- SocioautobiographyDocument4 pagesSocioautobiographyAmeer HamzaNo ratings yet
- About People From Asia and AfricaDocument5 pagesAbout People From Asia and AfricaCatherine RoseosNo ratings yet
- RJ Kristine C. Daque Bsa - Iii: Diversity in Philippine CultureDocument3 pagesRJ Kristine C. Daque Bsa - Iii: Diversity in Philippine CultureRJ Kristine DaqueNo ratings yet
- ASEAN at 50 4A.2 Acharya FinalDocument14 pagesASEAN at 50 4A.2 Acharya Finalronan.villagonzaloNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument3 pagesCultureanastasiia.yerhanNo ratings yet
- Communication and Globalization G1 Purposive CommunicationDocument14 pagesCommunication and Globalization G1 Purposive CommunicationLotchie Mae VencerNo ratings yet
- An Ambiguous Juncture Racism and The Formation of Asian FemininityDocument14 pagesAn Ambiguous Juncture Racism and The Formation of Asian Femininity7zyhn4czz8No ratings yet
- RPH Activity Midterm Tejada 2Document3 pagesRPH Activity Midterm Tejada 2deanyangg25No ratings yet
- MULTICULTURAL3Document3 pagesMULTICULTURAL3VENA LANDERONo ratings yet
- Name: Krishna Ayu Wigati NPM: 211003792020255 Class: S1 Bahasa Inggris (Morning) Summary "Asian-American: What Teachers Should Know"Document2 pagesName: Krishna Ayu Wigati NPM: 211003792020255 Class: S1 Bahasa Inggris (Morning) Summary "Asian-American: What Teachers Should Know"Instagram BeautyNo ratings yet
- Demystifying DiasporasDocument1 pageDemystifying DiasporasCentre for Poverty AnalysisNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Ethnic Identity: Primordial Versus SituationalDocument7 pagesThe Fundamentals of Ethnic Identity: Primordial Versus SituationalFayyaz AliNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Soregov - Bsba - Salem, Aaliyah Joy E. - RectoDocument1 pageActivity 1 - Soregov - Bsba - Salem, Aaliyah Joy E. - RectoLiyah SalemNo ratings yet
- Sociology Autobio ExampleDocument3 pagesSociology Autobio ExampleElu pipNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Essay ExampleDocument4 pagesDescriptive Essay ExampleAngry BirdNo ratings yet
- English Oral Migrants To Australia, Skills NeededDocument1 pageEnglish Oral Migrants To Australia, Skills Neededzicheng wangNo ratings yet
- Cultural BiographyDocument6 pagesCultural Biographyapi-301063740No ratings yet
- Yellow and Confused: Born in Taiwan, raised in South Africa and making sense of it allFrom EverandYellow and Confused: Born in Taiwan, raised in South Africa and making sense of it allNo ratings yet
- Essay Draft 2Document7 pagesEssay Draft 2api-427948812No ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument1 pageConclusionMuanlian Hatlang YTNo ratings yet
- Essay IBCDocument2 pagesEssay IBCVu Ngoc Cuong RamboNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Australian Immigration: 1. Serenity That's Beyond ImaginationDocument20 pagesBenefits of Australian Immigration: 1. Serenity That's Beyond ImaginationGeraldine NambioNo ratings yet
- Cultural Differences Influence On Language: 2.1 Geographic SituationsDocument4 pagesCultural Differences Influence On Language: 2.1 Geographic SituationsAlan LeeNo ratings yet
- The Definition of SelfDocument3 pagesThe Definition of Selfmaryanncabansag029No ratings yet
- Vietnamese ValuesDocument3 pagesVietnamese ValuesNguyễn Kiều TrangNo ratings yet
- To What Extent, Is History The Primary Influence in One's Individual Identity and Culture?Document2 pagesTo What Extent, Is History The Primary Influence in One's Individual Identity and Culture?Cj MwaleNo ratings yet
- Faiz On Problems of Cultural Planning in Asia, PakistanDocument9 pagesFaiz On Problems of Cultural Planning in Asia, PakistanSajjad IdreesNo ratings yet
- ThailandDocument2 pagesThailandTican SimonaNo ratings yet
- It's All Chinese To Me: An Overview of Chinese Culture, Travel & Etiquette (Fully Revised and Expanded)From EverandIt's All Chinese To Me: An Overview of Chinese Culture, Travel & Etiquette (Fully Revised and Expanded)No ratings yet
- Câu hỏi ôn tập VHMDocument18 pagesCâu hỏi ôn tập VHMBắp ChiênnNo ratings yet
- Importance of Phillipine CultureDocument1 pageImportance of Phillipine CultureMary Rose Ygonia CañoNo ratings yet
- StereotypesDocument23 pagesStereotypescaironsalamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Subcultures and Consumer BehaviorDocument19 pagesChapter 5. Subcultures and Consumer BehaviorMichelle Danika MarquezNo ratings yet
- Tribals in The NortheastDocument1 pageTribals in The Northeasttaran4gaNo ratings yet
- Asean Lit.Document4 pagesAsean Lit.Hazel HazeNo ratings yet
- Identity and Social FormationDocument9 pagesIdentity and Social Formationqzvcxmh9k9No ratings yet
- Overcoming Cross-Cultural Communication Barriers: Blande E. Corpuz-TullaoDocument41 pagesOvercoming Cross-Cultural Communication Barriers: Blande E. Corpuz-TullaoPSSg Sadang Sheryl DNo ratings yet
- Thai Culture and EtiquetteDocument6 pagesThai Culture and EtiquetteBoranNo ratings yet
- 11F - 747 - Dilara İpek Acar - Essay On Minorities Living in Their Own CommunityDocument2 pages11F - 747 - Dilara İpek Acar - Essay On Minorities Living in Their Own CommunityhjaskdNo ratings yet
- Forum LifelongDocument2 pagesForum LifelongNisha ShanmuganathanNo ratings yet
- How Does Geography Affect CultureDocument4 pagesHow Does Geography Affect CultureDaniel S. SantosNo ratings yet
- Cultural System ReportDocument6 pagesCultural System ReportMulat, Catherine Nicole R.No ratings yet
- An Egalitarian SocietyDocument4 pagesAn Egalitarian SocietyAndreea HizanuNo ratings yet
- Oriental & OccidentalDocument10 pagesOriental & OccidentalFaruque FerdowsNo ratings yet
- Popular IssuesDocument5 pagesPopular Issuesn2sn8ngmcdNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Cultural Diversity and Why Does It MatterDocument2 pagesAn Analysis of Cultural Diversity and Why Does It MatterMeisyita QothrunnadaNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Melc 3Document4 pagesUcsp Melc 3Joseph Magallanes GrulloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document10 pagesChapter 5jentitularNo ratings yet
- Agilent Dual Directional Coupler 778D 100 To 2000 MHZ: Data SheetDocument4 pagesAgilent Dual Directional Coupler 778D 100 To 2000 MHZ: Data Sheetdanilo espinozaNo ratings yet
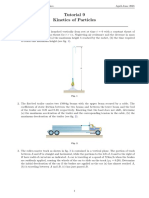
- AM Assignment 9 1,3,5,8Document3 pagesAM Assignment 9 1,3,5,8Thami kpNo ratings yet
- Enfriadores Oilair, Modelos OAIDocument6 pagesEnfriadores Oilair, Modelos OAISergioAbdonNo ratings yet
- Smart Dustbin Report PaperDocument9 pagesSmart Dustbin Report PaperAbhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- The Bug Shop: Ben Nagy & The GrugqDocument47 pagesThe Bug Shop: Ben Nagy & The Grugqtimtom123No ratings yet
- RICS Qualification BrochureDocument8 pagesRICS Qualification BrochureManikNo ratings yet
- 7585102-Yamaha Teos Xn125 Xn150 Workshop Repair Manual DownloadDocument259 pages7585102-Yamaha Teos Xn125 Xn150 Workshop Repair Manual Downloadwww1234maxcom67% (3)
- Lte-A Resource Allocation Scheme Using Chicken Swarm OptimizationDocument26 pagesLte-A Resource Allocation Scheme Using Chicken Swarm OptimizationVIGNESH SNo ratings yet
- Ôn DLKTDocument21 pagesÔn DLKTLinh DoanNo ratings yet
- Milnor ManualDocument94 pagesMilnor ManualMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Models of Interactions For Piano and Live ElectronicsDocument97 pagesModels of Interactions For Piano and Live ElectronicsLucas Quínamo Furtado de MendonçaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligences InventoryDocument4 pagesMultiple Intelligences Inventorylape darwelNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 q3 Mod1 Introductiontoaccounting FinalDocument20 pagesFabm1 q3 Mod1 Introductiontoaccounting FinalJomark RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Key Performance Indicators Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesKey Performance Indicators Literature Reviewdowxgtbnd100% (1)
- 0f097aee82afecba7907e84ecc3efa03Document3 pages0f097aee82afecba7907e84ecc3efa03swa9saws89awNo ratings yet
- Test Bank, Solutions Manual, Ebooks - List 9Document7 pagesTest Bank, Solutions Manual, Ebooks - List 9smtbportal0% (2)
- M.SC Math PDFDocument42 pagesM.SC Math PDFgollakotiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure of PRDocument127 pagesOrganizational Structure of PRgopalmeb6368No ratings yet
- Module 6 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument29 pagesModule 6 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarkhill Veran TiosanNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Ulf 600 Pro2Document3 pagesData Sheet Ulf 600 Pro2Salman ZaheerNo ratings yet
- GeeCee VenturesDocument1 pageGeeCee VenturesNaveen kishore100% (1)
- MANUAL - Part 1 PN 101328780Document370 pagesMANUAL - Part 1 PN 101328780AlessonNo ratings yet
- Doctor and Society Relationship-HIMA - PPTX 20231016 130902 0000-1Document20 pagesDoctor and Society Relationship-HIMA - PPTX 20231016 130902 0000-1Madhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 - Arts ActivitiesDocument7 pagesGrade 5 - Arts ActivitiesMarcus Sayson DabonNo ratings yet
- SCMPE Edition Four Additions Part TwoDocument42 pagesSCMPE Edition Four Additions Part TwoGiriNo ratings yet
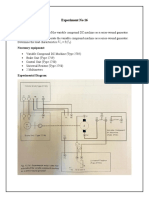
- Experiment No 16Document3 pagesExperiment No 16Usama MughalNo ratings yet