Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measurements and Instrumentation Question Bank
Measurements and Instrumentation Question Bank
Uploaded by
Surya SekaranOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measurements and Instrumentation Question Bank
Measurements and Instrumentation Question Bank
Uploaded by
Surya SekaranCopyright:
Available Formats
Measurements and instrumentation Question Bank
07:00 Srini
Question Bank
2 Marks and 16 Marks
UNIT-1
1. List out the dynamic characteristics oI any measurement system.
2. What are the types oI error measurement system?
3. What are the static characteristics important?
4. What is standard? What are the diIIerent types oI standard?
5. What is the Iunction oI manipulation element in a measurement system?
6. What are the primary standards? Where are they used?
7. What is primary sensing element?
8. What is calibration?
9. DeIine the terms precision and sensitivity?
10. DeIine static error.
11. Distinguish re-productibility and repeatability.
12. Show the block diagram indicating Iunctional elements oI measurement system.
13. Distinguish between zero driIt and span driIt.
14. DeIine a dynamic response oI an instrument.
15. What are the diIIerent calibration methodologies?
16. DeIine limiting errors and instrumental errors.
17. Mention any Iour static characteristics oI measuring instruments.
18. Distinguish between direct and indirect methods oI measurements.
19. What is the signiIicance oI calibration?
20. What is meant by accuracy and precision oI an instrument?
21. List the diIIerent types oI possible errors in measurements.
22. What is the diIIerence between analog and digital instrument?
23. What are absolute instruments?
24. What is a secondary instrument?
25. How are secondary instruments classiIied?
16 Marks
1. Draw the block diagram showing the basic Iunctional elements oI an instrument and explain the Iunctions oI each.
2. DeIine limiting errors. Derive the expression Ior relative limiting errors.
3. Explain in detail calibration techniques and draw the calibration curve in general.
4. Give the methods oI using any three standard inputs being used Ior analyzing the dynamic response oI system with neat
sketches.
5. Explain on the static and dynamic characteristics oI a measurement system.
6. Describe in detail the diIIerent types oI dynamic errors in a measurement system.
7. By using a micro meter screw the Iollowing readings were taken oI a certain physical length
UNIT -II
2 Marks
1. What is creeping and how it is prevented?
2. What is the working principle oI wattmeter employed in measuring instruments?
3. How are the analog instruments classiIied on the basis oI method used Ior comparing the unknown quantity?
4. Give the advantages oI moving iron meters.
5. What are diIIerent methods oI measurement oI Irequency in the power Irequency range?
6. Explain why it is necessary to make the potential coil circuit purely resistive in wattmeters.
7. What are the advantages oI digital instruments over analog instruments?
8. How are resistors are checked using digital multimeters?
9. What is auto ranging?
10. DeIine resolution oI DVM.
11. What are volt-ampere hour and watt-hour?
12. What is the purpose oI instrument transIormers?
13. What are the various principles oI analog type electrical instruments?
14. Give the importance oI iron loss measurements.
15. What is the reason Ior using MI on both A.C and D.C?
16. What is the precaution to be Iollowed while using current transIormer?
17. What is transIer instrument?
18. Why the PMMC instrument is not used Ior a.c measurements?
19. What is the principle oI ramp type digital voltmeter?
20. Which torque is absent in energy meter? Why?
21. Explain the purpose oI Schmitt trigger in digital Irequency meter.
22. What are the essential parts oI a ramp type digital voltmeter?
23. DeIine nominal rate oI instrument transIormer.
24. Explain the Iollowing term as applied to digital displays 3 digit and 4- digit display.
25. Explain the principle oI digital phase meter.
16 Marks
1. Derive the torque equation oI electrodynamometer type instrument.
2. Explain with neat circuit diagram the working oI successive approximation type DVM.
3. Draw the circuit diagram oI digital phase meter and explain its working.
4. Give the construction and principle oI operation oI single phase induction type energy meter.
5. Describe the construction and Iunctioning oI mechanical type Irequency meter.
6. Explain the Iunctioning oI Ferro-dynamic type electrical resonance Irequency meter.
7. Describe the construction and working oI PMMC instrument. Derive the equation Ior deIlection iI the instruments are spring
controlled.
8. Derive the torque equation Ior an electro dynamometer type oI wattmeter.
9. Write brieIly with neat Iigures on (i) Principle oI operation oI a current transIormer (ii) B-H curve analysis oI a magnetic
circuit.
10. Explain the working oI moving iron instruments.
11. Explain the Iunction oI 3 phase energy meter and wattmeter.
12. How the range oI d.c. Ammeter and d.c voltmeter can be extended? Derive the expressions to calculate shunt resistance and
multiplier resistance.
13. Draw and explain the circuit diagram oI digital Irequency meter.
14. Explain the working oI a digital multimeter with a schematic block diagram.
15. Explain the construction, working principle oI a three-phase wattmeter. What is the importance oI deIlecting torque in these
analog instruments?
UNIT-3
2 Marks
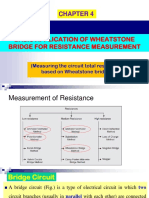
1. State the advantages oI using the bridge circuits Ior the measurement.
2. What is the sensitivity oI Wheat stone bridge?
3. What are the sources oI errors in Wheat stone bridge?
4. Give the application and limitations oI Wheat stone bridge.
5. Which measurement can be carried out by Maxwell bridge?
6. List the advantages oI using standard capacitor in Maxwell bridge.
7. Give the advantage and limitations oI Maxwell bridge.
8. What is Hay`s bridge?
9. Compare Hay`s bridge with Maxwell bridge.
10. What is Wien`s bridge?
11. Give the classiIication oI external interIerence signals.
12. What is capacitance interIerence?
13. What is electrostatic shielding?
14. What is inductive interIerence?
15. State the method oI reducing inductive interIerence.
16. What is electromagnetic interIerence?
17. State the sources oI EM waves, which can cause interIerence.
18. State the method oI reducing ground loop interIerence.
19. What is the standardization oI potentiometer?
20. Write the application oI d.c. Potentiometers.
21. Write the application oI a.c. potentiometers.
16 Marks
1. Derive the bridge balance condition Ior the Maxwell bridge and Schering bridge
2. Explain in detail about the laboratory type DC potentio meter.
3. Describe about the multiple earth and earth loops.
4. Explain the diIIerent techniques oI grounding.
5. Describe the circuit oI Kelvin double bridge used Ior measurement oI low resistance.
6. Explain how the inductance is measured in terms oI known capacitance using Maxwell`s bridge.
7. Explain the working oI Schering bridge.
8. Which bridge is used to measure Irequency and explain the measurement procedure?
9. With neat diagram explain in detail about Hay bridge.
10. Explain about the Anderson bridge.
UNIT-4
2 Marks
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages oI FM method oI magnetic tape recording?
2. What are the diIIerent types oI ampliIiers used Ior CRO`s?
3. Give the principle oI LCD type display device.
4. Draw a neat diagram on X-Y recorder.
5. Write two advantages oI LED on electronic displays.
6. What are the advantages oI magnetic tape recorder?
7. What is isolation probe?
8. State the Ieatures oI ink-jet printers.
9. What are the various methods oI recording data?
10. In what way line printers are advantages over dot matrix printer?
11. What are the diIIerent types oI magnetic recording?
12. What are the diIIerent materials used on LED?
13. What are data loggers?
14. What are the Iunctions oI data loggers?
15. What are the basic components oI data loggers?
16. List the advantages oI LCD.
17. What is the sweeper in oscilloscope?
18. List the controllers normally Iound on XY recorder.
19. What is a recorder? How are the classiIied?
20. DeIine the deIlection sensitivity oI CRT.
21. List the main parts oI cathode ray tube.
22. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages oI PDM recording.
23. What is the basic operating principle oI digital tape recording?
24. What are the basic components oI a tape recorder?
25. What are the advantages oI LCD over LED?
16 Marks
1. Explain the FM method oI magnetic tape recording and explain its advantages and disadvantages.
2. Describe the principle oI working and circuit diagram oI a digital oscilloscope.
3. With neat Iigure explain the working principle oI a digital CRO. What are its advantages oI analog CRO.
4. Explain in detail how the data stored in magnetic disk and tape.
5. Describe the construction and working oI LCD`s , mention the diIIerence between light scattering and Iield eIIect types oI
LCD`s also explain the advantages oI LCDs.
6. Discuss in detail about various types oI recorders.
7. Discuss in detail about dot matrix displays.
8. Explain the various methods oI magnetic recording.
9. Describe the pulse duration modulation (PDM) as used in magnetic tape recording and explain its merits and demerits.
10. With neat Iigure explain the construction and working principle oI a digital storage oscilloscope. Compare its advantages over
an analog CRO.
UNIT-5
1.) 2 Marks
1. DeIine transducer.
2. Mention some advantages oI electrical transducers.
3. Mention some basic requirements oI a transducer.
4. What are the classiIications oI transducers?
5. What is primary transducer?
6. What is secondary transducer?
7. What is active transducer? Mention some example.
8. What is passive transducer? Mention some example.
9. What is analog and digital transducers?
10. What is inverse transducer?
11. What are the types oI potentiometers?
12. What are the advantages and disadvantages oI potentiometers?
13. DeIine strain gauges.
14. DeIine gauge Iactor.
15. Mention types oI strain gauge.
16. What is resistance thermometer?
17. What are the advantages and disadvantages oI resistance thermometers?
18. What is thermistor? State the advantage and disadvantages.
19. What is inductive transducer?
20. Mention some advantages and disadvantages oI LVDT.
21. Mention the applications oI LVDT.
22. What is the basic principle oI capacitive transducer?
23. Mention some advantages and disadvantages oI capacitive transducer.
24. What is piezo electric eIIect?
25. What are the materials used Ior piezo electric transducer?
26. What are the types oI DAS? State the applications also.
27. What are the essential Iunctions oI digital DAC?
28. What are the types oI ADC?
29. What are the types oI DAC?
30. What is smart sensor? Mention some applications.
2.) 16 Marks
1. How the transducers are classiIied on the basis oI principle oI operation?
2. Explain the generalized diagram oI a digital data acquisition system?
3. Describe the diIIerent modes oI operation oI piezo electric transducers.
4. Describe in details the successive approximation method oI ADC.
5. Describe the diIIerent principles oI working oI capacitive transducers.
6. Explain the construction and principle oI working oI a LVDT.
7. Explain about the thermistor and thermocouples.
8. Discuss R-2R ladder type DAC.
9. Explain the resistive transducer with respective potentiometer.
10. Explain the principle oI operation oI piezo electric transducer.
11. Discuss in detail about optical encoder, Resistive encoder and shaIt encoder.
12. Explain in detail about ADC and DAC converters.
3.) 16 Marks
1. How the transducers are classiIied on the basis oI principle oI operation?
2. Explain the generalized diagram oI a digital data acquisition system?
3. Describe the diIIerent modes oI operation oI piezo electric transducers.
4. Describe in details the successive approximation method oI ADC.
5. Describe the diIIerent principles oI working oI capacitive transducers.
6. Explain the construction and principle oI working oI a LVDT.
7. Explain about the thermistor and thermocouples.
8. Discuss R-2R ladder type DAC.
9. Explain the resistive transducer with respective potentiometer.
10. Explain the principle oI operation oI piezo electric transducer.
11. Discuss in detail about optical encoder, Resistive encoder and shaIt encoder.
12. Explain in detail about ADC and DAC converters.
You might also like
- Ch13 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument10 pagesCh13 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Solid State DevicesDocument42 pagesSolid State Devicesmonirba48No ratings yet
- Measurements and Instrumentation Ec2351 Model Question PaperDocument11 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation Ec2351 Model Question PaperSathish BalaNo ratings yet
- 16 Mark Questions: Unit I Basic Measurement ConceptsDocument3 pages16 Mark Questions: Unit I Basic Measurement ConceptsRohini SanthanakumarNo ratings yet
- Lagos City Polytechnic, IkejaDocument1 pageLagos City Polytechnic, IkejaDobgima LangsiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3 - Transistor As A SwitchDocument5 pagesLab Report 3 - Transistor As A Switchアベルジョン パランNo ratings yet
- Form 4 END of Year 2012 SPVDocument9 pagesForm 4 END of Year 2012 SPVkesnaNo ratings yet
- AakashDocument8 pagesAakashshawn mendisNo ratings yet
- Form 4 END of Year 2011 AGODocument7 pagesForm 4 END of Year 2011 AGOkesnaNo ratings yet
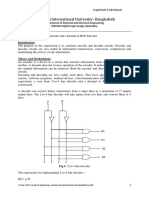
- B 7 Segment Display DecoderDocument8 pagesB 7 Segment Display Decoderlokesh krapaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits &electronics Device Question PaperDocument5 pagesElectric Circuits &electronics Device Question PaperSalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- Cusat Ec 6th Sem Question PaperDocument16 pagesCusat Ec 6th Sem Question PaperJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- CTE 235 Instrumentation and Measurement IIDocument7 pagesCTE 235 Instrumentation and Measurement IIMac world TrustNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Ece 213 PDFDocument15 pagesDigital Electronics Ece 213 PDFAlisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Typical Questions and AnswersDocument158 pagesTypical Questions and Answersiragire viateurNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Useful Theorems in Circuit AnalysisDocument53 pagesQuestions & Answers On Useful Theorems in Circuit Analysiskibrom atsbha100% (1)
- Wheatstone Bridge ProblemsDocument10 pagesWheatstone Bridge ProblemsMadhavan KNo ratings yet
- Voltage-Level Detectors Using Op-AmpDocument7 pagesVoltage-Level Detectors Using Op-AmpMatt Imri0% (1)
- SBA PORTFOLIO ASSESSMENT - ElectricalDocument6 pagesSBA PORTFOLIO ASSESSMENT - ElectricalSolomon ThomasNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics LabDocument34 pagesPower Electronics LabanaatmandarthiNo ratings yet
- Ecl 203 MCQDocument3 pagesEcl 203 MCQresham k vNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of Power System - Circuit GlobeDocument7 pagesSingle Line Diagram of Power System - Circuit GlobeMohammad HamamdNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 6Document20 pagesDigital Electronics 6Kshitij SalaveNo ratings yet
- ELE 1003 Elect Workshop Tutorial 01 Feb 2006Document8 pagesELE 1003 Elect Workshop Tutorial 01 Feb 2006Courtney 'Jackworld' JackNo ratings yet
- Digital Design-Digital Electronics Question BankDocument1 pageDigital Design-Digital Electronics Question BankPaweceNo ratings yet
- Ac Servo Motor LabDocument23 pagesAc Servo Motor LabHardik SharmaNo ratings yet
- DcsDocument50 pagesDcskartikNo ratings yet
- EC6411 Circuit & Devices Lab ManualDocument93 pagesEC6411 Circuit & Devices Lab ManualKALAIMATHINo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 3-Phase MeasurementDocument10 pagesExperiment 2 3-Phase MeasurementSaraha AloNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Skills, Syllabus, Kashmir UniversityDocument1 pageElectrical Circuits Skills, Syllabus, Kashmir UniversitySS S0% (2)
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument51 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualAnand ShankarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions On Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On Bipolar Junction TransistorAnuradha SahaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Industrial MeasurementsDocument4 pagesSample Question Paper Industrial MeasurementsRajNo ratings yet
- Dual ConvertersDocument5 pagesDual ConvertersAmit ParchakeNo ratings yet
- Questions On SCR, Diac and Triac: Q1. An SCR Has .. PN JunctionsDocument6 pagesQuestions On SCR, Diac and Triac: Q1. An SCR Has .. PN JunctionsArathi SuryaramananNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 28wheatstonebridge 29Document26 pagesChapter4 28wheatstonebridge 29Amirul SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Electronics LAB MANUAL Exp-2Document6 pagesElectronics LAB MANUAL Exp-2Dulce DeNo ratings yet
- Csec E&ET TestDocument5 pagesCsec E&ET TestkesnaNo ratings yet
- EEE121 - Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesEEE121 - Electric Circuit Analysisrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Question Bank S&TDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank S&Tarvind r0% (1)
- Brushless DC MotorDocument3 pagesBrushless DC MotorSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions. Topic: Number System and CodesDocument56 pagesObjective Questions. Topic: Number System and Codesthejareddy14No ratings yet
- Experiment No. - 5 EXPERIMENT NAME: To Determine Accurate Quality Factor of An Unknown Coil. TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment No. - 5 EXPERIMENT NAME: To Determine Accurate Quality Factor of An Unknown Coil. TheoryDibyajit SenNo ratings yet
- EE8261-Electric Circuits Lab Manual PDFDocument91 pagesEE8261-Electric Circuits Lab Manual PDFPraveen Kumar50% (2)
- EE8711-Power System Simulation Lab ManualDocument155 pagesEE8711-Power System Simulation Lab ManualNagarajan MunusamyNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik BJTDocument35 pagesKarakteristik BJTKrisna Adji SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Ec8361 Adc Lab SyllabusDocument2 pagesEc8361 Adc Lab SyllabusNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- American International University-Bangladesh: Title: Design of A 2 To 4 Decoder and A Decimal To BCD EncoderDocument4 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Title: Design of A 2 To 4 Decoder and A Decimal To BCD EncoderAbid ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Elec Workshop Mid 2016 TestDocument6 pagesElec Workshop Mid 2016 TestJermain PeartNo ratings yet
- Open-Circuit or No-Load TestDocument13 pagesOpen-Circuit or No-Load TestNANDHAKUMAR ANo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring Devices and MeasurementDocument62 pagesElectrical Measuring Devices and MeasurementDanelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Breadboard ImplementationDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 Breadboard ImplementationJeremy Lorenzo Teodoro VirataNo ratings yet
- Worked Example No.1: (Answer 7.394 MV)Document1 pageWorked Example No.1: (Answer 7.394 MV)renvNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 DC BridgesDocument7 pagesTopic 4 DC BridgesReeta DuttaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Ohm MetersDocument24 pagesLecture 5 Ohm MetersAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 and 6 McqsDocument4 pagesUnit 5 and 6 McqsAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- EI1202 M& IDocument7 pagesEI1202 M& IBaskar RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Ec 2351 Measurements and Instrumentation Question BankDocument5 pagesEc 2351 Measurements and Instrumentation Question BankMathiyazhagan RajendranNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Instrumentation-QbDocument11 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation-Qbnavi1234No ratings yet
- Unit - V: Sensors and Transducers: 8. Define Strain Gauge. Define Gauge FactorDocument4 pagesUnit - V: Sensors and Transducers: 8. Define Strain Gauge. Define Gauge FactorJayaram KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Fire Awareness PresentationDocument37 pagesFire Awareness Presentationshailu178No ratings yet
- Future Trends in European Public Administration and Management: An Outside-In PerspectiveDocument45 pagesFuture Trends in European Public Administration and Management: An Outside-In PerspectivevickyNo ratings yet
- Stay Where You Are' For 21 Days: Modi Puts India Under LockdownDocument8 pagesStay Where You Are' For 21 Days: Modi Puts India Under LockdownshivendrakumarNo ratings yet
- House Beautiful 2010 Spring SummerDocument124 pagesHouse Beautiful 2010 Spring SummerAnnabel Lee100% (2)
- Portable Fire ExtinguisherDocument44 pagesPortable Fire ExtinguisherjohainaNo ratings yet
- PAPERSDocument5 pagesPAPERSAlfia AlfiNo ratings yet
- DEMONSTRATION TEACHING in MATHEMATICS VIDocument17 pagesDEMONSTRATION TEACHING in MATHEMATICS VIHyacinth Eiram AmahanCarumba LagahidNo ratings yet
- Training Staff IDDocument14 pagesTraining Staff IDRS DulayNo ratings yet
- Internship PosterDocument1 pageInternship PosterJanice YizingNo ratings yet
- Passing Package PDFDocument10 pagesPassing Package PDFAddds Muhammmed100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocational High SchoolsDocument14 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Public Technical - Vocational High SchoolsWendy Arnido100% (4)
- MBA Programme: Wayamba University of Sri Lanka Faculty of Business Studies and FinanceDocument44 pagesMBA Programme: Wayamba University of Sri Lanka Faculty of Business Studies and FinanceTommba TommyNo ratings yet
- ELEN 3018 - Macro Test - 2013 - ADocument1 pageELEN 3018 - Macro Test - 2013 - AsirlordbookwormNo ratings yet
- UnivibeDocument1 pageUnivibePablo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Creating Delivering: MagnificenceDocument51 pagesCreating Delivering: MagnificencesharmarahulhemantNo ratings yet
- Specifications For Lime Slurry Injection For Ground ImprovementDocument5 pagesSpecifications For Lime Slurry Injection For Ground ImprovementSrini BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Applications MC1802-Software Project Management Question BankDocument9 pagesDepartment of Computer Applications MC1802-Software Project Management Question BankSuhin Vimal RajNo ratings yet
- QM ZG528 Ec-2r Second Sem 2021-2022Document1 pageQM ZG528 Ec-2r Second Sem 2021-2022shahul hameedNo ratings yet
- What's New in NX 12: NX Product Marketing Team October 2017Document120 pagesWhat's New in NX 12: NX Product Marketing Team October 2017parthifirelookNo ratings yet
- Sem - 2 AEC - 25329 - Speaking & Writing Skills of Communication 2023-24Document2 pagesSem - 2 AEC - 25329 - Speaking & Writing Skills of Communication 2023-24kanakparikh3No ratings yet
- Bien Prononcer L'anglais: Corrigés Et ScriptsDocument43 pagesBien Prononcer L'anglais: Corrigés Et ScriptsThierry HarmannNo ratings yet
- SternMed Xenox C400 LeafletDocument10 pagesSternMed Xenox C400 LeafletrelfathaliNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For TlsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan For TlsAini NordinNo ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS NB-AMR Rate Control Feature GuideDocument63 pagesZTE UMTS NB-AMR Rate Control Feature GuideArturoNo ratings yet
- DTU EE 4th Sem Midsem SyllabusDocument5 pagesDTU EE 4th Sem Midsem SyllabusHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- CRM # 4044662347 (Zpec # 5)Document1 pageCRM # 4044662347 (Zpec # 5)Mohammad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Wired Dynamic Vocal Mic With CableDocument2 pagesWired Dynamic Vocal Mic With CableMarius DanielNo ratings yet
- Website Comprehensibility Research DesignDocument14 pagesWebsite Comprehensibility Research DesignRay Garcia100% (1)
- English 8 Third Quarter Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesEnglish 8 Third Quarter Curriculum MapAgnes Gebone TaneoNo ratings yet