Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Tests
Chemical Tests
Uploaded by
Chal WijeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Tests
Chemical Tests
Uploaded by
Chal WijeCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical tests
Inorganic Chemistry
Testing for gases
1. Hydrogen gas – colourless, odourless, neutral, flammable, lighter than air
Test : Hold a lighted splint to the mouth of the tube containing the gas.
Observation : Hydrogen gas explodes with a squeaky pop.
Reaction:
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) -> 2H2O (g)
2. Oxygen gas – colourless, odourless, neutral, feeds fire, same weight as atmospheric air
Test : Hold a glowing splint to the mouth of the tube containing the gas.
Observation : Oxygen gas relights relights the glowing splint.
3. Carbon dioxide gas – colourless, odourless, acidic, extinguishes fire, heavier than air
Test : Bubble through limewater(calcium hydroxide solution).
Observation : Carbon dioxide gas turns limewater milky.
Reaction : As limewater is calcium hydroxide solution, carbon dioxide reacts with it to form a
white precipitate of calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) -> CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l)
4. Chlorine gas – greenish, highly toxic, acidic, bleaching, heavier than air
Test : Hold a damp litmus paper or universal indicator paper to the gas.
Observation : Chlorine gas bleaches(decolourises) the damp litmus/ universal indicator paper.
5. Sulphur dioxide gas – colourless, pungent, acidic, bleaching, heavier than air
Same as Chlorine gas
Carbon dioxide, Sulphur dioxide and Chlorine gases are acidic.
6. Ammonia gas – colourless, pungent, alkaline, lighter than air
Test : Hold a damp red litmus paper to the gas.
Observation : Turn damp red litmus paper blue.
(Ammonia is the only alkaline gas that you will meet at international GCSE)
Other gases in GCSE syllabus but not necessary in identification
Carbon monoxide – colourless, odourless, toxic(binds haemoglobin and deprives oxygen
transport), neutral, lighter than air
Sulphur trioxide – Colourless, acidic(forms sulphuric acid with water), heavier than air
Nitrogen – colourless, odourless, neutral, coolant gas, pretty much inert, makes up most of
atmospheric air
Nitrogen dioxide – Brownish, pungent, acidic, toxic, heavier than air
Testing for water
Test 1 : Use anhydrous copper(II) sulphate crystals.
Observation : Water turns white anhydrous copper(II) sulphate blue by converting it to hydrated
copper(II) sulphate.
Anhydrous copper(II) sulphate + Water -> Hydrated copper(II) sulphate
CuSO4 (s) + 5 H2O (l) -> CuSO4. 5H2O (s)
Anhydrous copper(II) sulphate lacks water of crystallisation and is white. Dropping water on to it
replaces the water of crystallisation and turns it blue.
Testing for ions
Testing for cations ( positive ions ) using flame test.
Flame test
Different Metal Ions produce different flame colours when they are heated strongly. This is the
basis of flame test.
Dip a clean wire loop into conc. H2SO4
Dip the loop back into a solution of metal salt being tested
Hold the loop into the edge of the blue flame from a Bunsen burner
Observe and record the flame colour produced
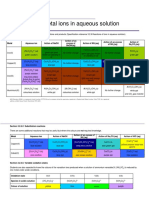
Testing for cations using NaOH solution
Ion Colou On In excess of On In excess of
r addition NaOH(aq) addition NH3(aq)
of of
NaOH NH3(aq)
(aq)
Ca2+ White White No change No -
ppt visible
ppt
Al3+ White White Dissolves to White No
ppt a colourless ppt change(white
solution(as ppt remains)
Al(OH)3 is
amphoteric)
Zn2+ White White Dissolves to White Dissolves to a
ppt a colourless ppt colourless
solution(as solution(as
Zn(OH)2 is Zn forms an
amphoteric) ammonium
complex)
Cu2+ Blue Light No Light Dissolves to a
blue change(ppt blue ppt deep blue
ppt remains) solution
Fe2+ Green Green No Green No
ppt change(ppt ppt change(ppt
remains) remains)
Cr3+ Green Green Dissolves to Green No
ppt a green ppt change(ppt
solution remains)
Fe3+ Brown Brown No Brown No
ppt change(ppt ppt change(ppt
remains) remains)
Testing for anions ( negative ions )
Tests for halides
Halide ion With AgNO3 and HNO3 acid With Pb(NO3)2 and HNO3 acid
Cl- AgCl White ppt PbCl2
White ppt
Br- AgBr PbBr2
Cream ppt Cream ppt
I- AgI PbI2
Yellow ppt Yellow
Tests for polyatomic anions
CO3 2- Carbonate ion
Test : Add a small amount of dil.HCl acid
Observation : if a gas is given off that turns limewater milky, it is the CO3 2- ions.
SO3 2- Sulphite ion
Test : Add a small amount of dil. HCl acid and heat
Observation : if a gas is given off that turns acidified potassium permanganate soaked paper
from purple to colourless, it is sulphite ions.
SO3 2-(aq) + 2H+ (aq) -> H2O(l) + SO2(g)
SO4 2- Sulphate ion
Test : Add a small amount of dil. HCl and BaNO3 solution
Observation : A white precipitate forms.
Ba2+(aq) + SO4 2-(aq) -> BaSO4(s)
NO3 - Nitrate ion
Test : Add NaOH(aq), small pieces of Al foil and gently heat.
Observation : if a gas is given off that turns damp red litmus blue, it is NO3 – ion.
NH4 +Ammonium ion
Test : Add NaOH(aq) and heat.
Observation : if a gas is given off that turns damp red litmus blue, it is NH4 + ion.
You might also like
- Wastewater Treatment Technologies Design Consideration by MritunjayDocument259 pagesWastewater Treatment Technologies Design Consideration by MritunjayThetti TunNo ratings yet
- ZIMSEC O-Level Physical ScienceDocument44 pagesZIMSEC O-Level Physical ScienceBluebelgian100% (1)
- Bs 2654-1989 - Vertical TanksDocument102 pagesBs 2654-1989 - Vertical TanksMohanadNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument65 pagesChemistrybilalNo ratings yet
- CP 07 & CP 15 - Analysis of Unknown CompoundsDocument5 pagesCP 07 & CP 15 - Analysis of Unknown Compoundsdameesh9No ratings yet
- AS Level Qualitative AnalysisDocument8 pagesAS Level Qualitative AnalysismahahajNo ratings yet
- Y4 ChemDocument7 pagesY4 Chembendadick cloneNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument5 pagesQualitative AnalysisAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Test Observation Conclusion: The City School, Ravi Campus (Johar Town Lahore) O Level ChemistryDocument3 pagesTest Observation Conclusion: The City School, Ravi Campus (Johar Town Lahore) O Level ChemistryTayyabaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 NotesDocument3 pagesTopic 9 Notesmarin tamNo ratings yet
- CP 8 - Analysis of Some Inorganic and Organic UnknownsDocument6 pagesCP 8 - Analysis of Some Inorganic and Organic UnknownsPOPNo ratings yet
- Y4 ChemDocument7 pagesY4 Chembendadick cloneNo ratings yet
- Testing Liquids For PolarityDocument17 pagesTesting Liquids For PolarityRaniaKaliNo ratings yet
- Comparative Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide GroupDocument5 pagesComparative Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide GroupPATRICIA ROSE SORIANO100% (1)
- Edexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Document7 pagesEdexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Ibrahim BtNo ratings yet
- Identification of Ions and GasesDocument9 pagesIdentification of Ions and GasesAbdullah BilalNo ratings yet
- 0 - Organic and Inorganic Tests For AS PDFDocument8 pages0 - Organic and Inorganic Tests For AS PDFAbed AymanNo ratings yet
- Identification of Unknown Ionic Compounds - Flame Tests, Halide Tests and Sulphates, Carbonates (Autoguardado)Document59 pagesIdentification of Unknown Ionic Compounds - Flame Tests, Halide Tests and Sulphates, Carbonates (Autoguardado)nicole100% (1)
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument4 pagesQualitative AnalysisVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Some IonsDocument42 pagesQualitative Analysis of Some IonsShaina Mae ContilloNo ratings yet
- Comparative Reactions of The Ammonium Sulfide GroupDocument2 pagesComparative Reactions of The Ammonium Sulfide GroupPharmaNo ratings yet
- Anion and Cation TestsDocument2 pagesAnion and Cation TestsTanvir Ahmed MazumderNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) Chapter 1.3 - Qualitative AnalysisDocument11 pages(CHEM) Chapter 1.3 - Qualitative AnalysisVijay Kumar NatteyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ChemistryDocument25 pagesIGCSE ChemistryLiliana DamocNo ratings yet
- Practical ChemistryDocument5 pagesPractical Chemistrysara bajajNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 2 NotesDocument19 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 2 Notesaminata13536No ratings yet
- Final Practical RevisionDocument32 pagesFinal Practical RevisionReverse ClanNo ratings yet
- Ion / Gas Test Observation: Add To Anhydrous Copper Sulfate (White in Colour) Will Turn Blue in Presence ofDocument1 pageIon / Gas Test Observation: Add To Anhydrous Copper Sulfate (White in Colour) Will Turn Blue in Presence oftayowilliams23No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis: Basic Radicals Group Determination Experiments Observation InferenceDocument5 pagesSalt Analysis: Basic Radicals Group Determination Experiments Observation InferenceFouzul Mobin KhanNo ratings yet
- Anion AnalysisDocument1 pageAnion AnalysisSarah LouieNo ratings yet
- Anion AnalysisDocument1 pageAnion Analysisaafaf.sdfddfaNo ratings yet
- Manual Fo AnalysisDocument2 pagesManual Fo AnalysisSabeeha MansoorNo ratings yet
- Cation AnalysisDocument8 pagesCation AnalysisKushagra Kun.No ratings yet
- C12 Chemical Analysis and InvestigationDocument10 pagesC12 Chemical Analysis and InvestigationSarah PendNo ratings yet
- 4th Form Qualitative Analysis Sheet Summary SheetDocument2 pages4th Form Qualitative Analysis Sheet Summary SheetFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Notes For Use in Qualitative Analysis-1Document2 pagesNotes For Use in Qualitative Analysis-1Nehara FernandoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Qualitative AnalysisDocument2 pagesChemistry - Qualitative AnalysisAditya SenthilNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis 3Document17 pagesQualitative Analysis 3Joseph UdoudoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis For A LevelDocument17 pagesQualitative Analysis For A LevelTim KarmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Qualitative Analysis NotesDocument9 pagesChemistry Qualitative Analysis NotesLim Yan Peng GaryNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Reaction and Analysis of Group Iii Cations Ions NH OH Excess NH OH NH CI and NH OH (NH) S Naoh Excess Naoh Na O or H O ZNDocument4 pagesExperiment 6 Reaction and Analysis of Group Iii Cations Ions NH OH Excess NH OH NH CI and NH OH (NH) S Naoh Excess Naoh Na O or H O ZNJamille SucalditoNo ratings yet
- ATP Notes For Chemistry o LevelDocument25 pagesATP Notes For Chemistry o LevelSaad Arsalan100% (4)
- Qualitative Analysis NotesDocument2 pagesQualitative Analysis NotesFaiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Identification of Ions and GasesDocument4 pagesIdentification of Ions and GasesMuqaddas FatimaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideDocument5 pagesQualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideJeremy TehNo ratings yet
- C12 AnalysisDocument21 pagesC12 AnalysiskhôiNo ratings yet
- Test For Hydrogen GasDocument6 pagesTest For Hydrogen Gasb52352986No ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument5 pagesSalt Analysisnifty.vedNo ratings yet
- Experimental Techniques - Summary Notes PreviewDocument8 pagesExperimental Techniques - Summary Notes Previewchong56No ratings yet
- CH 1 Identification Ions and Gases For StudentDocument4 pagesCH 1 Identification Ions and Gases For StudentAli r24No ratings yet
- TestsDocument1 pageTestsJo StandleyNo ratings yet
- 2024 - 6092 - Notes of Qualitative AnalysisDocument1 page2024 - 6092 - Notes of Qualitative Analysisaleesya1302No ratings yet
- Rivera Experiment-6Document5 pagesRivera Experiment-6Ma Angelica RiveraNo ratings yet
- CSEC Qualitative Analysis CATIONSDocument7 pagesCSEC Qualitative Analysis CATIONS-Sabiraaa -No ratings yet
- Reactions of Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution: Chemistry A-Level (7405)Document2 pagesReactions of Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution: Chemistry A-Level (7405)SAMANNo ratings yet
- Identification of Cations, Anions and GasesDocument2 pagesIdentification of Cations, Anions and GasesMustufa FerozNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document1 pageWa0003.Sarim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Test For Gases: Gas Test and Test ResultsDocument2 pagesTest For Gases: Gas Test and Test ResultsKhim YangNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument3 pagesQualitative AnalysisYukeling TayNo ratings yet
- Substance Physical Appearance and State at Room Temperature Chemical Test Observation Explanation Video LinkDocument3 pagesSubstance Physical Appearance and State at Room Temperature Chemical Test Observation Explanation Video LinkOindri MandalNo ratings yet
- TestsDocument2 pagesTestsayeshaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2nd Term 2021 9 HealthDocument5 pages2nd Term 2021 9 HealthChal WijeNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument5 pagesCoordination and ResponseChal WijeNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical ReactionsDocument17 pagesBalancing Chemical ReactionsChal WijeNo ratings yet
- F3 Aluminium ExtractionDocument9 pagesF3 Aluminium ExtractionChal WijeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Organisms Bio 5090 Notes Chalani WijesuterendraDocument19 pagesClassification of Organisms Bio 5090 Notes Chalani WijesuterendraChal WijeNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument13 pagesReactivity SeriesChal WijeNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis - Biology NotesDocument4 pagesHomeostasis - Biology NotesChal WijeNo ratings yet
- MicroencapsulationDocument10 pagesMicroencapsulationprinceamitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Aromatic HydrocarbonsAbdirashid Adam IsakNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Idoia Arribas, Amaia Santamaría, Estela Ruiz, Vanesa Ortega-López, Juan M. MansoDocument12 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Idoia Arribas, Amaia Santamaría, Estela Ruiz, Vanesa Ortega-López, Juan M. MansoLaura Michelle Rodriguez AriasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument30 pagesChapter 4 PDFAram Nasih MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chlor Alkali Engineering ServicesDocument27 pagesChlor Alkali Engineering ServicesvasucristalNo ratings yet
- VSD Program Guide v2Document43 pagesVSD Program Guide v2David BEN HAIMNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper III (Nuclear Physics)Document6 pagesPhysics Paper III (Nuclear Physics)YocobSamandrewsNo ratings yet
- Manual St3100 OhausDocument19 pagesManual St3100 OhausDaniloSripNo ratings yet
- Denim Dry ProcessDocument9 pagesDenim Dry ProcessZaman Parvez0% (1)
- Coe Comfort Powder MSDS011509Document2 pagesCoe Comfort Powder MSDS011509Deepak RajendranNo ratings yet
- 2-Physical Chemical and Bact. Characteristics of WastewaterDocument6 pages2-Physical Chemical and Bact. Characteristics of WastewatermarkhanNo ratings yet
- Batch No: Wurth SR No: 1 Date: 2/1/2018 Tested For: PAHARPUR Test Type: Tensile - Rod/Tube Basic Load/Displacement GraphDocument7 pagesBatch No: Wurth SR No: 1 Date: 2/1/2018 Tested For: PAHARPUR Test Type: Tensile - Rod/Tube Basic Load/Displacement GraphkasvikrajNo ratings yet
- Teknik Eksplorasi-Eksplorasi GeokimiaDocument27 pagesTeknik Eksplorasi-Eksplorasi GeokimiaAndry FerdianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint PresentationDocument54 pagesChapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint PresentationEsther SparksNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Determination of Sulfur Trioxide in A Soluble Sulfate SaltDocument6 pagesGravimetric Determination of Sulfur Trioxide in A Soluble Sulfate SaltWendell Kim Llaneta100% (1)
- 01-50-911 en Soldadura MIG y TIGDocument24 pages01-50-911 en Soldadura MIG y TIGjuliae194No ratings yet
- Pithecellobium Dulce Medicinal Plant Traditional Knowledge Nutritional and Therapeutic Potential Sulekha Et Al 2021Document10 pagesPithecellobium Dulce Medicinal Plant Traditional Knowledge Nutritional and Therapeutic Potential Sulekha Et Al 2021María José TorallaNo ratings yet
- Transient Flow in Natural Gas PipelineDocument24 pagesTransient Flow in Natural Gas Pipelineaen 010No ratings yet
- Pipework SpecificationDocument111 pagesPipework Specificationwentroprem100% (2)
- A266A266M-13 Standard Specification For Carbon Steel Forgings For Pressure Vessel Components PDFDocument5 pagesA266A266M-13 Standard Specification For Carbon Steel Forgings For Pressure Vessel Components PDFManuel Antonio Santos VargasNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Liquid Petroleum Meters For Custody Transfer MeasurementDocument12 pagesA Comparison of Liquid Petroleum Meters For Custody Transfer MeasurementAmr Guenena100% (2)
- Owl Online Homework Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesOwl Online Homework Organic Chemistrycffm80at100% (1)
- Quantitative Models For Microscopic To Macroscopic Biological Macromolecules and TissuesDocument234 pagesQuantitative Models For Microscopic To Macroscopic Biological Macromolecules and TissuesfitoscribdNo ratings yet
- Estimation of CO2 Emissions From IncineratorsDocument9 pagesEstimation of CO2 Emissions From IncineratorsMustafa AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dequest® 2060S - MSDSDocument9 pagesDequest® 2060S - MSDSDangnoi Shih Tzu DongNo ratings yet
- Msds Benzoate de MetiloDocument5 pagesMsds Benzoate de MetiloCristobal ValdebenitoNo ratings yet
- 23-01-2023 - SR - Super60 - (NUCLEUS, STERLING) & LIIT - BT - Jee-Main-GTM-13 - Q.PAPERDocument21 pages23-01-2023 - SR - Super60 - (NUCLEUS, STERLING) & LIIT - BT - Jee-Main-GTM-13 - Q.PAPERmanasa settipalliNo ratings yet