Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pmls2-Module 6
Pmls2-Module 6
Uploaded by
Cherold RoldanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Oncology Skills ChecklistDocument7 pagesOncology Skills Checklistnorthweststaffing100% (2)
- Guidelines For Managing Substance Withdrawal in JailsDocument128 pagesGuidelines For Managing Substance Withdrawal in JailsepraetorianNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Date of Dx. Exam: Aug 22, 2017Document4 pagesLaboratory: Date of Dx. Exam: Aug 22, 2017Chris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryDocument5 pagesLESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryAlthea EspirituNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryDocument5 pagesLESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryAlthea EspirituNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFDocument6 pagesLaboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Pre-Analytical Considerations in PhlebotomyDocument56 pagesPre-Analytical Considerations in PhlebotomyAngel joyce ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Pre-Analytical Variables-1Document25 pagesLesson 6 Pre-Analytical Variables-1Allen ChristianNo ratings yet
- Blood Specimen Collection: Elaine M. KeohaneDocument15 pagesBlood Specimen Collection: Elaine M. KeohanePrince Guevara100% (1)
- Pre AnalyticalDocument8 pagesPre AnalyticalIvy RhonneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Principles of Mls2Document14 pagesLesson 6 Principles of Mls2macugaynylorweenNo ratings yet
- Oncology 3rd NotesDocument10 pagesOncology 3rd Notesmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Transe 5Document17 pagesTranse 5lija.medija.swuNo ratings yet
- Haemostatic AgentsDocument3 pagesHaemostatic Agentsmeenalairan100% (1)
- Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionDocument10 pagesHemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionCarl Earvin L. FavoritoNo ratings yet
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) : Posted: 05 Sep 2010 10:11 PM PDTDocument9 pagesBlood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) : Posted: 05 Sep 2010 10:11 PM PDTLanie Reyes de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Type of Cancer SuspectedDocument20 pagesThe Type of Cancer SuspectedkdfhjfhfNo ratings yet
- DIABETES Nursing ManagementDocument11 pagesDIABETES Nursing ManagementKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Left Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDocument9 pagesLeft Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDominic BristolNo ratings yet
- Preanalytic Variables in Laboratory TestingDocument6 pagesPreanalytic Variables in Laboratory TestingYasin ArafatNo ratings yet
- Vet Record Case Reports - 2022 - Bondel - Treatment of An Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt by Placement of A HydraulicDocument6 pagesVet Record Case Reports - 2022 - Bondel - Treatment of An Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt by Placement of A HydraulicQueijo MinasNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument64 pagesDiabetes MellitusCris Tine67% (6)
- Jerash University Faculty of Nursing Critical Care Nursing Practicum Case StudyDocument9 pagesJerash University Faculty of Nursing Critical Care Nursing Practicum Case StudytasneemNo ratings yet
- Hema TFST MergedDocument94 pagesHema TFST MergedMICHAEL RYAN T. BAANo ratings yet
- Extramedullary Relapse of Multiple Myeloma PresentDocument4 pagesExtramedullary Relapse of Multiple Myeloma Presentnisya rafikohNo ratings yet
- Rot 2 Darunday Surgical Instruments Used Als 4Document11 pagesRot 2 Darunday Surgical Instruments Used Als 4Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- AnaesthesiaDocument163 pagesAnaesthesiappp683823No ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument15 pagesThyroid CancerA. Lizette PabloNo ratings yet
- Terms/ Choices/questions Given by Other Students With The Same RecallDocument27 pagesTerms/ Choices/questions Given by Other Students With The Same RecallchippaiqweqweNo ratings yet
- Referensi Nilai KritisDocument9 pagesReferensi Nilai KritisFaiz AchmadNo ratings yet
- Labs - Case ConDocument7 pagesLabs - Case ConDara Sophia EncarguezNo ratings yet
- Altered LocDocument19 pagesAltered Locgeeeelzy07No ratings yet
- An Unique Encounter With ParaprotenemiaDocument3 pagesAn Unique Encounter With ParaprotenemiaramazankocabasNo ratings yet
- Pre-Analytical Consideration in PhlebotomyDocument3 pagesPre-Analytical Consideration in PhlebotomyJacinta Malamion100% (1)
- Lesson 8 Special Collections and Point-of-Care Testing: Principles of Medical Laboratory Science 2Document19 pagesLesson 8 Special Collections and Point-of-Care Testing: Principles of Medical Laboratory Science 2nwgcyrb8v9No ratings yet
- Special Technique On CytohistologyDocument36 pagesSpecial Technique On CytohistologyKecil DekNo ratings yet
- Current Diagnostic Tests For Colorectal Cancer: Evlina Suzanna, MD, PathDocument87 pagesCurrent Diagnostic Tests For Colorectal Cancer: Evlina Suzanna, MD, PathFaulina Yosia PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Answers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: 4. It Is Important For The Nurse To RecognizeDocument10 pagesAnswers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: 4. It Is Important For The Nurse To RecognizeNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Neoplastic Disorders: Pathogenesis of CancerDocument37 pagesNeoplastic Disorders: Pathogenesis of CancerEn ConejosNo ratings yet
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDocument27 pagesLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Book-for - A دوسية من دكتور المقاصدDocument63 pagesBook-for - A دوسية من دكتور المقاصدAli Toma HmedatNo ratings yet
- RLE Case Study (Katty)Document12 pagesRLE Case Study (Katty)Johanna Danica VillaricaNo ratings yet
- Hematological DisordersDocument9 pagesHematological DisordersFoxtrot NursingNo ratings yet
- English Lingo SurgicalDocument36 pagesEnglish Lingo SurgicalObydaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Apheresis of Acute Renal Failure: V.A.VoinovDocument19 pagesTherapeutic Apheresis of Acute Renal Failure: V.A.VoinovMaryNo ratings yet
- General ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesGeneral ConsiderationsAudree BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Chem123 Lab Phlebotomy-FinalsDocument6 pagesChem123 Lab Phlebotomy-Finalssaculala0291pamNo ratings yet
- A Manual of Laboratory Techniques in Clinical Hematology 1Document15 pagesA Manual of Laboratory Techniques in Clinical Hematology 1Jaycel Mae Ba-ay (Gaikokujinn)No ratings yet
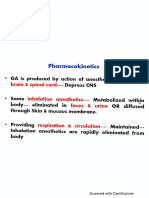
- BARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSDocument4 pagesBARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- Clinical BiochemistryDocument25 pagesClinical Biochemistrymirzafahad82005No ratings yet
- Precautions in Handling, Acceptance and Fixation of SpecimenDocument5 pagesPrecautions in Handling, Acceptance and Fixation of SpecimenMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug Study NCM 112Document15 pages8 Drug Study NCM 112Marie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- JIFCC Lab Tests Interpretation 2018Document8 pagesJIFCC Lab Tests Interpretation 2018Abdul Sattar100% (1)
- Cushings SyndromeDocument2 pagesCushings SyndromeCourtney HammonsNo ratings yet
- Sample Management For Clinical Biochemistry Assays: Are Serum and Plasma Interchangeable Specimens?Document22 pagesSample Management For Clinical Biochemistry Assays: Are Serum and Plasma Interchangeable Specimens?Jessica Asitimbay ZuritaNo ratings yet
- MEIR Scenario 1 Acute Dose of RadiationDocument2 pagesMEIR Scenario 1 Acute Dose of RadiationRADIOACTIVENo ratings yet
- CC1-PRELIM-ACTIVITY AnsweredDocument6 pagesCC1-PRELIM-ACTIVITY AnsweredSky Angel RasonableNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document5 pagesLec 1Jasarine CabigasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory & DiagnosticsDocument11 pagesLaboratory & DiagnosticsPandesal with EggNo ratings yet
- Labs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeFrom EverandLabs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeNo ratings yet
- Wound Healing: Stem Cells Repair and Restorations, Basic and Clinical AspectsFrom EverandWound Healing: Stem Cells Repair and Restorations, Basic and Clinical AspectsNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 10Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 10Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 5Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 5Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document6 pagesModule 2Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 1Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 1Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 3Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 3Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 4Document4 pagesPmls2-Module 4Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Answersheet Anatomy 21Document3 pagesModule 13 Answersheet Anatomy 21Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Purposive Comm - Module 8 EvaluationDocument2 pagesPurposive Comm - Module 8 EvaluationCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES LectureDocument10 pagesCARBOHYDRATES LectureCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- M 7-WorksheetDocument2 pagesM 7-WorksheetCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Saq Module 10Document3 pagesSaq Module 10Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- M 8-WorksheetDocument2 pagesM 8-WorksheetCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Original Nursing Theories of Florence Nightingale: by Mary B. Knutson, RN, BSN, FCP MSN Student Viterbo UniversityDocument23 pagesOriginal Nursing Theories of Florence Nightingale: by Mary B. Knutson, RN, BSN, FCP MSN Student Viterbo UniversityGlorie Anne AniscoNo ratings yet
- Theo 289 - 2016 - Class 1 - Overview + Nature of CounselingDocument62 pagesTheo 289 - 2016 - Class 1 - Overview + Nature of CounselingJuanmiguel Ocampo Dion SchpNo ratings yet
- Philippine Heart Center, East Ave Quezon City Telephone Number 441 1049 or 9252401 Loc 3903 Mobile Number: 09166459979Document9 pagesPhilippine Heart Center, East Ave Quezon City Telephone Number 441 1049 or 9252401 Loc 3903 Mobile Number: 09166459979HarbyNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy - Knowledge For Medical Students and PhysiciansDocument6 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy - Knowledge For Medical Students and PhysiciansNafiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Working From Home PowerPoint TemplatesDocument14 pagesWorking From Home PowerPoint TemplatesDiana HermidaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Developmen1Document2 pagesInternational Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Developmen1aihuutran51No ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument26 pagesStress Managementjune jaguarNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument25 pagesRESEARCHjillianeNo ratings yet
- Divyamrutayurcare ComDocument2 pagesDivyamrutayurcare ComKothariTech WorkNo ratings yet
- Fishermen's Perceptions and Attitudes Toward Risk Diving and Management Issues in Small-Scale FisheriesDocument10 pagesFishermen's Perceptions and Attitudes Toward Risk Diving and Management Issues in Small-Scale FisheriesIpehNo ratings yet
- DPM 70 - Sanitary (R1)Document1 pageDPM 70 - Sanitary (R1)rofik uddinNo ratings yet
- Initial TemplateDocument8 pagesInitial TemplateZuj PayNo ratings yet
- Rapport: What Is It and Why Is ImportantDocument14 pagesRapport: What Is It and Why Is ImportantGisse Mardini100% (1)
- Narayan Hredyalaya SummaryDocument3 pagesNarayan Hredyalaya SummaryVarun JainNo ratings yet
- Pocket CRT en PDFDocument1 pagePocket CRT en PDFjanNo ratings yet
- SF2 by TeacherTechDocument3 pagesSF2 by TeacherTechJONATHAN GARGANERA100% (1)
- ADHD Pathway Booklet1 PDFDocument28 pagesADHD Pathway Booklet1 PDFFreditya Mahendra Putra100% (1)
- Organisasi Perawat Indonesia Dan Dunia PDFDocument35 pagesOrganisasi Perawat Indonesia Dan Dunia PDFRosalina LubisNo ratings yet
- UNDP Issue Brief - Universal Health Coverage For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument16 pagesUNDP Issue Brief - Universal Health Coverage For Sustainable DevelopmentbabubvNo ratings yet
- High Priority Site Update - 72519 - 0Document8 pagesHigh Priority Site Update - 72519 - 0Masud HasanNo ratings yet
- Approach To Nursing Assessment 1Document5 pagesApproach To Nursing Assessment 1Taiye OkondoNo ratings yet
- Qatar Foundation Construction Safety Standard For Contractors Final VersionDocument119 pagesQatar Foundation Construction Safety Standard For Contractors Final VersionAnosh1978100% (3)
- FPCN Contract - 2017 COHN6Document36 pagesFPCN Contract - 2017 COHN6Teddy WilsonNo ratings yet
- PHIH - SOP - Glucose Tolerance TestDocument4 pagesPHIH - SOP - Glucose Tolerance TestMyoNo ratings yet
- Apilarnil Improving Reproductive Qualities of Pigs Using The Drone Brood HomogenateDocument4 pagesApilarnil Improving Reproductive Qualities of Pigs Using The Drone Brood HomogenateFundatia AnaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Assessment of The Kudz Ze Kayah ProjectDocument310 pagesEnvironmental Assessment of The Kudz Ze Kayah ProjectThe NarwhalNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument2 pagesMineralsgnana deepNo ratings yet
- Neubauer2015 Article TheYalePharyngealResidueSeveriDocument8 pagesNeubauer2015 Article TheYalePharyngealResidueSeveriGisele DiasNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: A Goal-Planning Approach: Barbara A. Wilson, PHDDocument14 pagesCognitive Rehabilitation: A Goal-Planning Approach: Barbara A. Wilson, PHDMiguelySusy Ramos-RojasNo ratings yet
Pmls2-Module 6
Pmls2-Module 6
Uploaded by
Cherold RoldanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pmls2-Module 6
Pmls2-Module 6
Uploaded by
Cherold RoldanCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 6.
PRE-ANALYTICAL CONSIDERATION Variable Blood Composition Affected
Age Red blood cells, white blood cells,
IN PHLEBOTOMY creatinine clearance
Attitude Red blood cells
-Introduction- Dehydration Hemoconcentration, red blood cells.
enzymes, iron, calcium, sodium
The pre-analytical testing phase includes procedures such Diet Glucose, lipids, electrolytes
as laboratory handling, and identification, which take place Diurnal Thyroid-stimulating hormone, cortisol,
prior to any laboratory testing. In this phase proper control variation iron
measures are placed to avoid subsequent issues. It starts Drug Therapy Enzymes, hormones
when the doctor’s order is given and ends when the Exercise/ Potential of hydrogen (pH), carbon
laboratory testing has officially commenced. lM injection dioxide partial pressure (PCO2), creatine
kinase (CK), lactic acid dehydrogenase
During this phase, the phlebotomist must not only be able (LDH), glucose
to draw blood from the patient but must also be able to
Fever Hormones, cortisol
identify factors that affect the process and address them .as
Gender Red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit
needed.
Jaundice Yellow color interfaces due to increased
bilirubin
-objectives- Intramuscular Creatine kinase and the skeletal muscle
injection fraction of LDH
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: Position Protein, potassium
1. enumerate the physiological variables that Pregnancy Red blood cells
influence laboratory test results and identify the Smoking Cholesterol, cortisol, glucose, growth
tests most affected by each one; hormones, triglyceride, white blood cells
2. identify problem areas to avoid in site selection, Stress White blood cells, iron,
give causes for concern, and describe the adrenocorticotropic hormone,
procedure to follow when a difficult situation occurs; catecholamine, cortisol
3. explain how to handle patient complications Temperature Hemoconcentration
associated with blood collection; and humidity
4. spell out how to avoid or handle procedural error
risks, and reasons for failure to draw blood; and PART 2. PROBLEM AREAS TO AVOID AND
5. discuss appropriate specimen quality. TROUBLESHOOTING IN THE SITE SELECTION
Definition of terms Phlebotomists should be aware of the following problem
areas when selecting the venipuncture site. They could
Term Definition (Meriam Webster Dictionary) choose an alternative site or perform the procedure under
Pre-analytical - is the testing phase that occurs first in special conditions.
the laboratory process. 1. Burns, Scars, and Tattoos – It is not advisable to
choose a site that has burns, scars, or tattoos
-discussion- because veins in the area may be difficult to examine
and blood circulation may be impaired. Burns may be
too painful to touch, and tattoos may also be
The laboratory test is used by physicians to diagnose and susceptible to infection due to the dyes used that
monitor the presence of a disease. The physicians compare may interfere with the process.
the results to a reference range or reference interval. This 2. Damaged Veins - Aside from being difficult to
range shows the high and low limits of result values as perform, puncturing damaged veins may also
compared to healthy individuals. Several factors are produce inaccurate results. Veins could be sclerosed
considered as part of the reference interval study or the or hardened or thrombosed or clotted.
interpretation of the data obtained. 3. Edema - Edema, also known as oedema, is an
abnormal swelling caused by the accumulation of
In phlebotomy, the basal state is ideal in establishing fluid in the tissues. The tissues become fragile,
reference range since it represents the condition of the making the task of locating the veins harder. This
metabolism of the body early in the morning or after condition may be due to reactions from medications,
approximately 12 hours of fasting. This can be influenced pregnancy, infections, and other medical problems.
by age, gender, and conditions of the body. 4. Hematoma - Hematoma is a solid swelling or mass
of blood in the tissues caused by the leakage of blood
PART 1. PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES THAT from the vessels during venipuncture. Selecting a
INFLUENCE LABORATORY TEST RESULTS venipuncture site with hematoma will be painful for
the patient because it will obstruct the blood flow. It
Listed below are some of the factors that affect blood could also lead to the contamination of blood sample.
collection.
better or until the feeling subsides. An emesis basin
or wastebasket should be provided, and a cold
damp washcloth should be applied to the forehead.
5. Pain
The patient should be warned before the needle
insertion, and the phlebotomist should avoid
redirection of the needle. If the patient complains of
extreme pain or numbness, remove the needle and
apply ice to the site because this could indicate
nerve involvement. The phlebotomist needs to
document the incident if the condition persists.
Figure 6.1 Hematoma
6. Petechiae
5. Mastectomy - This procedure, often done to breast This condition involves the appearance of small red
cancer patients, refers to the removJ of the breast or purple spots that look like rashes, which appear
through surgery. Blood drawing from patients who on the arm when tourniquet is applied.
had undergone this procedure becomes a Figure 6.2 Petechiae
challenge since the lymph flow is obstructed, and
there may be swelling and infection after the
surgery. In addition, tourniquet cannot be applied
because it can cause injury. It could also change
the blood composition.
6. Obesity- This is the condition in which the
individual is grossly overweight. Patients who are
obese have veins that are deep and difficult to
locate. A solution is using a longer tourniquet or
locating the cephalic of cubital vein.
PART 3. HANDLING PATIENT COMPLICATIONS 7. Seizures or convulsions
ASSOCIATED WITH BLOOD COLLECTION When seizures or convulsions occur, the blood
draw should be discontinued quickly. There must
1. Allergies to Equipment and Supplies be pressure held over the site but it must be made
When the patient has adhesive allergy, a gauze certain that movement is not restricted; the mouth
should be placed over the site and should be is free from any obstruction and the patient 1s
removed after 15 minutes. The alternative is to ask protected from self-injury. The first-aid personnel
the patient to apply pressure for five minutes. When must be notified immediately.
the patient has antiseptic allergy, simply use a
different antiseptic. When the patient has latex PART 4. AVOIDING AND HANDLING PROCEDURAL
allergy, look for a sign to indicate the allergy and ERROR RISKS AND FAILURE TO DRAW BLOOD
use a non-latex alternative for gloves, tourniquet,
and bandages. 1. Hematoma Formation
The phlebotomist should hold pressure over the
2. Excessive Bleeding site immediately after discontinuing the draw. A
When a patient is on aspirin or anticoagulant, the cold compress or ice pack may be offered to help
bleeding may take a longer time. The pressure address the swelling. The following are conditions
should be applied to the site until the bleeding that trigger hematoma:
stops. The attention of the authorized personnel • There is excessive or blind probing.
should be called when the bleeding continues after • There is inadvertent arterial puncture.
five minutes. • The size of the vein is too small.
• The needle penetration has gone all
3. Fainting through the vein.
Fainting is a temporary loss of consciousness • Needle is not completely ·inserted.
which is caused by the insufficient flow of blood to • Tourniquet is still on when the needle was
the. brain. Patients prone to fajnting during removed.
venipuncture are asked to lie down during the • The pressure is not adequate.
procedure.
2. Iatrogenic Anemia
4. Nausea and Vomiting This results from blood loss due to blood draw to
When the patient feels nauseous and has the blood draw. It is important to ensure that only the
tendency to vomit, the phlebotomist has to required specimen volume is collected because if
discontinue the procedure until the patient feels 10% of the blood volume is removed at once from
the body, the patient could face a threat.
MODULE 6 –PRE-ANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IN PHLEBOTOMY 2
5) Wrong or expired collection tube should not be used
3. Inadvertent Arterial Puncture because the manufacturer could not warrant the
This happens when blood is filling up the tube quality of the seal and the pressure after the
rapidly and there is a rapid formation of hematoma expiration date indicated in the tube.
on the site.
PART 6. TROUBLESHOOTING FAILED
4. Infection VENIPUNCTURE
Infection can be avoided by making sure that tapes
or bandages are not opened ahead of time; Venipuncture attempts could fail due to improper setting of
needles are not preloaded into the rube holders, the tube and failure of the needle to go through the stopper.
insertion site of the needle is not touched after The phlebotomist must be aware and must take measures
sterilization; cap is removed just before to ensure that the proper procedures are followed.
venipuncture; and the patients are advised to keep
the bandage on the site for at least 15 minutes. The needle position is critical to the success of the
venipuncture. The phlebotomist should ensure that the
5. Nerve Injury following do not happen.
Nerve injuries happen when there is improper site 1. Needle not inserted far enough
selection, rapid needle insertion, excessive 2. Bevel partially out of skin
redirection of the needle, and blind probing. 3. Bevel partially into vein
If the initial attempt is unsuccessful, the 4. Bevel partially through vein
phlebotomist should try to redirect the needle by 5. Bevel completely through vein
using a slightly forward or backward movement. 6. Bevel against vein wall
The next step is to remove the needle and look for 7. Needle beside vein
an alternative site. 8. Undetermined position
6. Reflux of Anticoagulant A. Collapsed Vein
Blood that has already been drawn flowing back
into the vein from the collection tube may cause The collapsed veins usually occur when conditions are less
adverse reaction because of the presence of tube than ideal, which leads to the veins being blocked, resulting
additives. To avoid this, make sure that the arm of in insufficient blood flow. This happens when there is a
the patient is in a downward position and the tube strong pressure in the vacuum of the tube or plunger; the
is just below the venipuncture site. tourniquet is too close to the site or it is too tight; or when
the tourniquet has been removed during the draw.
7. Vein Damage
Damaging the vein could be avoided by following B. Tube Vacuum
the proper technique and avoiding blind probing.
To avoid failure due to loss of vacuum, the phlebotomist
PART 5. SPECIMEN QUALITY should make sure that the bevel is not partially out of skin
and the tube itself is not damaged.
1) Hemoconcentration is a decrease in the fluid content
or plasma volume which is usually caused by
tourniquet that stagnates the normal flow of blood Figure 6.3 Correct
Angle of the Bevel
leading to the increase in concentration of red blood (15-30o)
cells and other non-filterable large molecules.
2) Hemolysis, which is also called haemolysis, refers to
the rupture of the red blood cells. The hemoglobin is
then released into the surrounding fluid.
3) Partially filled tube or short draw, happens when the
phlebotomist pulls a tube before reaching the
required volume. This may lead to the incorrect Figure 6.4 Failed
blood-to-additive ratio. Venipuncture
4) Specimen contamination means that the specimen is
due to incorrect handling, which involves allowing
alcohol, powder or other materials into the sample.
Getting glove powder or perspiration into films and
specimens; using the wrong antiseptic; or simply not
following the proper antiseptic procedure could
interfere with the results.
MODULE 6 –PRE-ANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IN PHLEBOTOMY 3
Student assessment question 1:
A patient blood sample looked normal without any
hemolysis, but the following critical values were obtained
and flagged:
Initial test Repeated Test
Ca2+ 0.6 mmol/L 0.7mmol/L
K+ 15.5mmol/L 15.5mmol/L
ALK 5 U/L 4 U/L
These abnormal data were not consistent with the
patient’s medical history. As a result, the medical
laboratory scientist communicated this to the
phlebotomist and learned this patient serum sample was
contaminated by EDTA-K2 because the tested sample
was a combination of his blood from a purple top tube
(with EDTA-K2 as coagulant) and a red top tube.
Case Study Questions:
1. Do you think this is considered as a Pre-analytical
error? Explain your answer. (10 pts)
2. What was the effect of combining blood from a purple
top tube and a red top tube. Make sure to support your
answer. (20 pts)
3. What would be your next step after knowing what
happened? (10 pts)
-SUMMARY-
A professional Medical Laboratory Scientist knows that the
pre-analytical phase – when a specimen is collected,
transported, and processed – is a crucial part of the lab
testing process. Over 40% of lab errors happen during the
pre-analytical stage, while a mere 7% occur during the
actual testing. These errors result in added medical costs
when tests have to be re-issued and can sometimes lead to
patient misdiagnosis and in extreme cases they can be the
cause of serious patient illness. Pre-analytical errors can
occur at any point during the specimen collection process.
-reference-
• Learning Guide for Principles of Medical
Laboratory Sciences 2
Copyright 2020 by C&E Publishing Inc.,
Bernard U. Ebuen, Nini F. Lim, Edliberto P.
Manahan, Jose Jurel M. Nuevo, Maria Luisa R.
Olano, and Aileen C. Patron
Prepared by:
Ruth Abigail S. Contante, RMT, LPT
Instructor
MODULE 6 –PRE-ANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IN PHLEBOTOMY 4
You might also like
- Oncology Skills ChecklistDocument7 pagesOncology Skills Checklistnorthweststaffing100% (2)
- Guidelines For Managing Substance Withdrawal in JailsDocument128 pagesGuidelines For Managing Substance Withdrawal in JailsepraetorianNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Date of Dx. Exam: Aug 22, 2017Document4 pagesLaboratory: Date of Dx. Exam: Aug 22, 2017Chris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryDocument5 pagesLESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryAlthea EspirituNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryDocument5 pagesLESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryAlthea EspirituNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFDocument6 pagesLaboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Pre-Analytical Considerations in PhlebotomyDocument56 pagesPre-Analytical Considerations in PhlebotomyAngel joyce ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Pre-Analytical Variables-1Document25 pagesLesson 6 Pre-Analytical Variables-1Allen ChristianNo ratings yet
- Blood Specimen Collection: Elaine M. KeohaneDocument15 pagesBlood Specimen Collection: Elaine M. KeohanePrince Guevara100% (1)
- Pre AnalyticalDocument8 pagesPre AnalyticalIvy RhonneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Principles of Mls2Document14 pagesLesson 6 Principles of Mls2macugaynylorweenNo ratings yet
- Oncology 3rd NotesDocument10 pagesOncology 3rd Notesmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Transe 5Document17 pagesTranse 5lija.medija.swuNo ratings yet
- Haemostatic AgentsDocument3 pagesHaemostatic Agentsmeenalairan100% (1)
- Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionDocument10 pagesHemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionCarl Earvin L. FavoritoNo ratings yet
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) : Posted: 05 Sep 2010 10:11 PM PDTDocument9 pagesBlood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) : Posted: 05 Sep 2010 10:11 PM PDTLanie Reyes de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Type of Cancer SuspectedDocument20 pagesThe Type of Cancer SuspectedkdfhjfhfNo ratings yet
- DIABETES Nursing ManagementDocument11 pagesDIABETES Nursing ManagementKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Left Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDocument9 pagesLeft Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDominic BristolNo ratings yet
- Preanalytic Variables in Laboratory TestingDocument6 pagesPreanalytic Variables in Laboratory TestingYasin ArafatNo ratings yet
- Vet Record Case Reports - 2022 - Bondel - Treatment of An Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt by Placement of A HydraulicDocument6 pagesVet Record Case Reports - 2022 - Bondel - Treatment of An Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt by Placement of A HydraulicQueijo MinasNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument64 pagesDiabetes MellitusCris Tine67% (6)
- Jerash University Faculty of Nursing Critical Care Nursing Practicum Case StudyDocument9 pagesJerash University Faculty of Nursing Critical Care Nursing Practicum Case StudytasneemNo ratings yet
- Hema TFST MergedDocument94 pagesHema TFST MergedMICHAEL RYAN T. BAANo ratings yet
- Extramedullary Relapse of Multiple Myeloma PresentDocument4 pagesExtramedullary Relapse of Multiple Myeloma Presentnisya rafikohNo ratings yet
- Rot 2 Darunday Surgical Instruments Used Als 4Document11 pagesRot 2 Darunday Surgical Instruments Used Als 4Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- AnaesthesiaDocument163 pagesAnaesthesiappp683823No ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument15 pagesThyroid CancerA. Lizette PabloNo ratings yet
- Terms/ Choices/questions Given by Other Students With The Same RecallDocument27 pagesTerms/ Choices/questions Given by Other Students With The Same RecallchippaiqweqweNo ratings yet
- Referensi Nilai KritisDocument9 pagesReferensi Nilai KritisFaiz AchmadNo ratings yet
- Labs - Case ConDocument7 pagesLabs - Case ConDara Sophia EncarguezNo ratings yet
- Altered LocDocument19 pagesAltered Locgeeeelzy07No ratings yet
- An Unique Encounter With ParaprotenemiaDocument3 pagesAn Unique Encounter With ParaprotenemiaramazankocabasNo ratings yet
- Pre-Analytical Consideration in PhlebotomyDocument3 pagesPre-Analytical Consideration in PhlebotomyJacinta Malamion100% (1)
- Lesson 8 Special Collections and Point-of-Care Testing: Principles of Medical Laboratory Science 2Document19 pagesLesson 8 Special Collections and Point-of-Care Testing: Principles of Medical Laboratory Science 2nwgcyrb8v9No ratings yet
- Special Technique On CytohistologyDocument36 pagesSpecial Technique On CytohistologyKecil DekNo ratings yet
- Current Diagnostic Tests For Colorectal Cancer: Evlina Suzanna, MD, PathDocument87 pagesCurrent Diagnostic Tests For Colorectal Cancer: Evlina Suzanna, MD, PathFaulina Yosia PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Answers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: 4. It Is Important For The Nurse To RecognizeDocument10 pagesAnswers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: 4. It Is Important For The Nurse To RecognizeNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Neoplastic Disorders: Pathogenesis of CancerDocument37 pagesNeoplastic Disorders: Pathogenesis of CancerEn ConejosNo ratings yet
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDocument27 pagesLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Book-for - A دوسية من دكتور المقاصدDocument63 pagesBook-for - A دوسية من دكتور المقاصدAli Toma HmedatNo ratings yet
- RLE Case Study (Katty)Document12 pagesRLE Case Study (Katty)Johanna Danica VillaricaNo ratings yet
- Hematological DisordersDocument9 pagesHematological DisordersFoxtrot NursingNo ratings yet
- English Lingo SurgicalDocument36 pagesEnglish Lingo SurgicalObydaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Apheresis of Acute Renal Failure: V.A.VoinovDocument19 pagesTherapeutic Apheresis of Acute Renal Failure: V.A.VoinovMaryNo ratings yet
- General ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesGeneral ConsiderationsAudree BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Chem123 Lab Phlebotomy-FinalsDocument6 pagesChem123 Lab Phlebotomy-Finalssaculala0291pamNo ratings yet
- A Manual of Laboratory Techniques in Clinical Hematology 1Document15 pagesA Manual of Laboratory Techniques in Clinical Hematology 1Jaycel Mae Ba-ay (Gaikokujinn)No ratings yet
- BARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSDocument4 pagesBARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- Clinical BiochemistryDocument25 pagesClinical Biochemistrymirzafahad82005No ratings yet
- Precautions in Handling, Acceptance and Fixation of SpecimenDocument5 pagesPrecautions in Handling, Acceptance and Fixation of SpecimenMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug Study NCM 112Document15 pages8 Drug Study NCM 112Marie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- JIFCC Lab Tests Interpretation 2018Document8 pagesJIFCC Lab Tests Interpretation 2018Abdul Sattar100% (1)
- Cushings SyndromeDocument2 pagesCushings SyndromeCourtney HammonsNo ratings yet
- Sample Management For Clinical Biochemistry Assays: Are Serum and Plasma Interchangeable Specimens?Document22 pagesSample Management For Clinical Biochemistry Assays: Are Serum and Plasma Interchangeable Specimens?Jessica Asitimbay ZuritaNo ratings yet
- MEIR Scenario 1 Acute Dose of RadiationDocument2 pagesMEIR Scenario 1 Acute Dose of RadiationRADIOACTIVENo ratings yet
- CC1-PRELIM-ACTIVITY AnsweredDocument6 pagesCC1-PRELIM-ACTIVITY AnsweredSky Angel RasonableNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document5 pagesLec 1Jasarine CabigasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory & DiagnosticsDocument11 pagesLaboratory & DiagnosticsPandesal with EggNo ratings yet
- Labs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeFrom EverandLabs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeNo ratings yet
- Wound Healing: Stem Cells Repair and Restorations, Basic and Clinical AspectsFrom EverandWound Healing: Stem Cells Repair and Restorations, Basic and Clinical AspectsNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 10Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 10Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 5Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 5Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document6 pagesModule 2Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 1Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 1Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 3Document5 pagesPmls2-Module 3Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Pmls2-Module 4Document4 pagesPmls2-Module 4Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Answersheet Anatomy 21Document3 pagesModule 13 Answersheet Anatomy 21Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Purposive Comm - Module 8 EvaluationDocument2 pagesPurposive Comm - Module 8 EvaluationCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES LectureDocument10 pagesCARBOHYDRATES LectureCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- M 7-WorksheetDocument2 pagesM 7-WorksheetCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Saq Module 10Document3 pagesSaq Module 10Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- M 8-WorksheetDocument2 pagesM 8-WorksheetCherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- Original Nursing Theories of Florence Nightingale: by Mary B. Knutson, RN, BSN, FCP MSN Student Viterbo UniversityDocument23 pagesOriginal Nursing Theories of Florence Nightingale: by Mary B. Knutson, RN, BSN, FCP MSN Student Viterbo UniversityGlorie Anne AniscoNo ratings yet
- Theo 289 - 2016 - Class 1 - Overview + Nature of CounselingDocument62 pagesTheo 289 - 2016 - Class 1 - Overview + Nature of CounselingJuanmiguel Ocampo Dion SchpNo ratings yet
- Philippine Heart Center, East Ave Quezon City Telephone Number 441 1049 or 9252401 Loc 3903 Mobile Number: 09166459979Document9 pagesPhilippine Heart Center, East Ave Quezon City Telephone Number 441 1049 or 9252401 Loc 3903 Mobile Number: 09166459979HarbyNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy - Knowledge For Medical Students and PhysiciansDocument6 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy - Knowledge For Medical Students and PhysiciansNafiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Working From Home PowerPoint TemplatesDocument14 pagesWorking From Home PowerPoint TemplatesDiana HermidaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Developmen1Document2 pagesInternational Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Developmen1aihuutran51No ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument26 pagesStress Managementjune jaguarNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument25 pagesRESEARCHjillianeNo ratings yet
- Divyamrutayurcare ComDocument2 pagesDivyamrutayurcare ComKothariTech WorkNo ratings yet
- Fishermen's Perceptions and Attitudes Toward Risk Diving and Management Issues in Small-Scale FisheriesDocument10 pagesFishermen's Perceptions and Attitudes Toward Risk Diving and Management Issues in Small-Scale FisheriesIpehNo ratings yet
- DPM 70 - Sanitary (R1)Document1 pageDPM 70 - Sanitary (R1)rofik uddinNo ratings yet
- Initial TemplateDocument8 pagesInitial TemplateZuj PayNo ratings yet
- Rapport: What Is It and Why Is ImportantDocument14 pagesRapport: What Is It and Why Is ImportantGisse Mardini100% (1)
- Narayan Hredyalaya SummaryDocument3 pagesNarayan Hredyalaya SummaryVarun JainNo ratings yet
- Pocket CRT en PDFDocument1 pagePocket CRT en PDFjanNo ratings yet
- SF2 by TeacherTechDocument3 pagesSF2 by TeacherTechJONATHAN GARGANERA100% (1)
- ADHD Pathway Booklet1 PDFDocument28 pagesADHD Pathway Booklet1 PDFFreditya Mahendra Putra100% (1)
- Organisasi Perawat Indonesia Dan Dunia PDFDocument35 pagesOrganisasi Perawat Indonesia Dan Dunia PDFRosalina LubisNo ratings yet
- UNDP Issue Brief - Universal Health Coverage For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument16 pagesUNDP Issue Brief - Universal Health Coverage For Sustainable DevelopmentbabubvNo ratings yet
- High Priority Site Update - 72519 - 0Document8 pagesHigh Priority Site Update - 72519 - 0Masud HasanNo ratings yet
- Approach To Nursing Assessment 1Document5 pagesApproach To Nursing Assessment 1Taiye OkondoNo ratings yet
- Qatar Foundation Construction Safety Standard For Contractors Final VersionDocument119 pagesQatar Foundation Construction Safety Standard For Contractors Final VersionAnosh1978100% (3)
- FPCN Contract - 2017 COHN6Document36 pagesFPCN Contract - 2017 COHN6Teddy WilsonNo ratings yet
- PHIH - SOP - Glucose Tolerance TestDocument4 pagesPHIH - SOP - Glucose Tolerance TestMyoNo ratings yet
- Apilarnil Improving Reproductive Qualities of Pigs Using The Drone Brood HomogenateDocument4 pagesApilarnil Improving Reproductive Qualities of Pigs Using The Drone Brood HomogenateFundatia AnaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Assessment of The Kudz Ze Kayah ProjectDocument310 pagesEnvironmental Assessment of The Kudz Ze Kayah ProjectThe NarwhalNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument2 pagesMineralsgnana deepNo ratings yet
- Neubauer2015 Article TheYalePharyngealResidueSeveriDocument8 pagesNeubauer2015 Article TheYalePharyngealResidueSeveriGisele DiasNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: A Goal-Planning Approach: Barbara A. Wilson, PHDDocument14 pagesCognitive Rehabilitation: A Goal-Planning Approach: Barbara A. Wilson, PHDMiguelySusy Ramos-RojasNo ratings yet