Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calibration of Wattmeter Directloading
Calibration of Wattmeter Directloading
Uploaded by
Murugan RCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- EEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalDocument29 pagesEEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalImokhai Abdullah50% (2)
- Voltmeter Loading EffectsDocument4 pagesVoltmeter Loading EffectsIan BagunasNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Wattmeter Phantom LoadingDocument15 pagesCalibration of Wattmeter Phantom LoadingMurugan RNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Energy MeterDocument4 pagesCalibration of Energy MeterKalyana Sundaram M.SNo ratings yet
- EMSL Cycle 2 ExptsDocument25 pagesEMSL Cycle 2 ExptsVarun ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Calibration WattmeterDocument2 pagesCalibration WattmeterVARAPRASADNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits 6 SibuloDocument9 pagesDC Circuits 6 Sibulonoah.sibulo2014No ratings yet
- Viva PDFDocument50 pagesViva PDFkimerlyNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronics Measurement (EEMMI) Subject Code: 303Document31 pagesElectrical & Electronics Measurement (EEMMI) Subject Code: 303Blue eyes India kiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 - Calibration of Wattmeter by Phantom LoadingDocument2 pagesExperiment 10 - Calibration of Wattmeter by Phantom LoadingFALSERNo ratings yet
- Mi Exp 1Document3 pagesMi Exp 1Dr. Tapas Kumar MajiNo ratings yet
- EEE Department Electrical Measurements Lab ManualDocument47 pagesEEE Department Electrical Measurements Lab ManualZer ZENITHNo ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument7 pagesBee Labanitha paramasivamNo ratings yet
- A Study On Multimeter: Engineering DepartmentDocument50 pagesA Study On Multimeter: Engineering DepartmentMazin Rashid Salim Al AamriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Lab Practice 1Document37 pagesElectrical Lab Practice 1JUDHISTHIRA BEHERANo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements Lab ManualDocument56 pagesElectrical Measurements Lab Manualpoornak47No ratings yet
- Energy MeterDocument3 pagesEnergy MeterkishorebabNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementDocument30 pagesLab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementEngr Haseena JabbarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engg Laboratory ManualDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical Engg Laboratory ManualDheerenNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL (Instrument and Measure)Document42 pagesLAB MANUAL (Instrument and Measure)Abaad AliNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Three Phase Reactive Power.Document5 pagesMeasurement of Three Phase Reactive Power.Murugan RNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementDocument28 pagesLab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementEngr Haseena Jabbar0% (1)
- Expt 2Document8 pagesExpt 2bkthejaswini2013No ratings yet
- Module 2 Testing InstrumentDocument8 pagesModule 2 Testing Instrumentnelson ijeboimenNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Power MetersDocument39 pagesTopic 5 Power MetersAsmairie MatNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Physical Lab #2Document10 pagesElectrical Circuit Physical Lab #2josephNo ratings yet
- Measurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Document6 pagesMeasurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Mohd IskandarNo ratings yet
- Measurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Document6 pagesMeasurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Mohd IskandarNo ratings yet
- 14697Document35 pages14697Akhileshkumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument11 pagesStrain Gaugemontaser.nalawiNo ratings yet
- I 1251-Electrical Measurements and InstrumentationDocument11 pagesI 1251-Electrical Measurements and Instrumentationsatishcoimbatore2No ratings yet
- Electrical MeasurementsDocument47 pagesElectrical MeasurementsManikantaNo ratings yet
- Analysis Exp 1 Version 2Document3 pagesAnalysis Exp 1 Version 2Erwin CabangalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Workshop ReportDocument16 pagesEngineering Workshop ReportAmanda Elizabeth SeniorNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 3: Use Measuring Instruments: Ammeter, Voltmeter, and WattmeterDocument4 pagesPractical No. 3: Use Measuring Instruments: Ammeter, Voltmeter, and Wattmeter166CMYashvardhan Shinde100% (1)
- Ei 34Document24 pagesEi 34Md. Mahmud Hasan SumonNo ratings yet
- 21BEC0361 Exp9 (PowerMeasurement)Document5 pages21BEC0361 Exp9 (PowerMeasurement)Ministry of PianoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 06, 2024Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 06, 2024Mohd Naif FirozNo ratings yet
- Measurement ElectricityDocument4 pagesMeasurement ElectricityMd HamzaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurement Lab ManualDocument57 pagesElectrical Measurement Lab Manualckrishna625100% (1)
- Topic 5Document39 pagesTopic 5Nazatul ZalianNo ratings yet
- Swin Burns ARUNDocument6 pagesSwin Burns ARUNArun TezNo ratings yet
- Measurement and InstrumentationDocument4 pagesMeasurement and InstrumentationAbirami RajendranNo ratings yet
- .NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1Document29 pages.NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1archibong dominicNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 6 Single Phase Energymeter-I Aim:: ApparatusDocument3 pagesExperiment No: 6 Single Phase Energymeter-I Aim:: ApparatusAswin RâjNo ratings yet
- EMDocument18 pagesEMSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurement Et-314Document57 pagesInstrumentation and Measurement Et-314ammarshahzad501No ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements and InstrumentationDocument6 pagesElectrical Measurements and InstrumentationPratik PathareNo ratings yet
- EMMI LAB MANUAL - Correct PDFDocument41 pagesEMMI LAB MANUAL - Correct PDFAryaNo ratings yet
- Mi Exp 2Document3 pagesMi Exp 2Dr. Tapas Kumar MajiNo ratings yet
- Govt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabDocument6 pagesGovt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabAnkit0% (1)
- لقطة شاشة 2021-06-21 في 11.09.14 مDocument10 pagesلقطة شاشة 2021-06-21 في 11.09.14 مnanimohammed240No ratings yet
- Measurement of Voltage in Engineering Practices LabDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Voltage in Engineering Practices LabSenthil IlangovanNo ratings yet
- AN4993Document10 pagesAN4993iskandarn_el5735No ratings yet
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology FY B.Tech: S.D.Gavarskar Ect DeptDocument14 pagesElectrical Technology FY B.Tech: S.D.Gavarskar Ect DeptAniket PatilNo ratings yet
- ORA LM Vol. IV Section 15 Drug and Device MicrobiologyDocument83 pagesORA LM Vol. IV Section 15 Drug and Device MicrobiologyDO KHNo ratings yet
- JstackDocument69 pagesJstackMike TNo ratings yet
- The Story of The Aral Sea: Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesThe Story of The Aral Sea: Reading ComprehensionGreceanu AlinaNo ratings yet
- Specification For Offshore Pipeline InstDocument28 pagesSpecification For Offshore Pipeline InstChandra WisnuNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server Operating Systems - Red HatDocument4 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux Server Operating Systems - Red HatBramanto MarthaNo ratings yet
- Skoog Química Analítica cCh8 InglésDocument6 pagesSkoog Química Analítica cCh8 InglésDavid DualNo ratings yet
- Mete AggiesDocument16 pagesMete AggiesJohn Renzel RiveraNo ratings yet
- BetaBeat Reviews:Is It Best Soultion For Diabetes?Document6 pagesBetaBeat Reviews:Is It Best Soultion For Diabetes?bohigg popixNo ratings yet
- LeafletDocument2 pagesLeafletCarlos Jose Sanchez EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Rancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Koperasi Xyz Menggunakan Framework Laravel Dan Vue - JsDocument10 pagesRancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Koperasi Xyz Menggunakan Framework Laravel Dan Vue - JsRifky LanaNo ratings yet
- Trine Natasja Sindahl PSYKphd MAR2019 B5Document169 pagesTrine Natasja Sindahl PSYKphd MAR2019 B5Maira Espinoza LabraNo ratings yet
- Canon SX130 SpecsDocument3 pagesCanon SX130 SpecsAtul WaikulNo ratings yet
- 500AMPDocument4 pages500AMPEsteban Quezada NeriNo ratings yet
- Flexible CableDocument48 pagesFlexible CableAhmed H. HassanNo ratings yet
- Efl Learners' Perception On Different AccentsDocument26 pagesEfl Learners' Perception On Different AccentsLydiaNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Triple Diffused: ApplicationDocument6 pagesSilicon NPN Triple Diffused: ApplicationDidi ConanNo ratings yet
- Ethical-Dilemma PresentationDocument4 pagesEthical-Dilemma PresentationNaymau SuarezNo ratings yet
- Fabric v2.4 AppDevDocument27 pagesFabric v2.4 AppDevBilgehan SavguNo ratings yet
- Dispersal of Modern Homo Sapiens: Known H. Sapiens Migration Routes in The PleistoceneDocument2 pagesDispersal of Modern Homo Sapiens: Known H. Sapiens Migration Routes in The Pleistocenenikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- What Are The Signs of An Impending Geologic HazardDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Signs of An Impending Geologic HazardANTON GABRIEL PRECIOSONo ratings yet
- Proton Arena Engine Cooling 1.5 1.8 Service ManualDocument16 pagesProton Arena Engine Cooling 1.5 1.8 Service ManualchipestNo ratings yet
- Read The Following Text and Answer Questions 1-3Document5 pagesRead The Following Text and Answer Questions 1-3Anonymous AKr7hWjBiNo ratings yet
- Counseling Pro Inv - SKDocument13 pagesCounseling Pro Inv - SKPadam PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Class: VIII English Literature: What Makes Me IndianDocument6 pagesClass: VIII English Literature: What Makes Me IndianHarshit RajNo ratings yet
- Condensing Unit Vertical Discharge 60 HZ R410A: 36KBTU Model Has A Different GrillDocument1 pageCondensing Unit Vertical Discharge 60 HZ R410A: 36KBTU Model Has A Different GrilljuanNo ratings yet
- Orientation On The Manual For The Evaluation (Autosaved)Document31 pagesOrientation On The Manual For The Evaluation (Autosaved)Em Boquiren CarreonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Disassembly of Basic EngineDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Disassembly of Basic EnginePurnama AbhieNo ratings yet
- U Sai Aung Tun - The Tai Ethnic MigrationDocument15 pagesU Sai Aung Tun - The Tai Ethnic MigrationDuran ThiyamNo ratings yet
- sgpnr001 enDocument70 pagessgpnr001 enAli AlmukhtarNo ratings yet
- EX - NO 3 (A) Applications Using TCP Sockets Like Echo Client and Echo Server AimDocument4 pagesEX - NO 3 (A) Applications Using TCP Sockets Like Echo Client and Echo Server AimHaru HarshuNo ratings yet
Calibration of Wattmeter Directloading
Calibration of Wattmeter Directloading
Uploaded by
Murugan RCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calibration of Wattmeter Directloading
Calibration of Wattmeter Directloading
Uploaded by
Murugan RCopyright:
Available Formats
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY
DIRECT LOADING
User Manual
Version 1.0
Technical Clarification /Suggestion :
N/F
Technical Support Division,
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
Plot No :75, Electronics Estate,
Perungudi, Chennai - 600 096, INDIA.
Ph: 91- 44-2496 3142, 91-44-2496 1852
Mail : service@vimicrosystems.com,
Web : www.vimicrosystem
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION 1
2. THEORETICAL CONCEPT 3
2.1 Calibration 4
2.2 Wattmeter 4
3. EXPERIMENTAL SECTION 6
EXP 1: To calibrate the single phase wattmeter by using direct loading 7
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
Chapter-1
Introduction
Vi Microsystems Pvt.Ltd., [1]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
INTRODUCTION:
Measurements involve the use of instruments as physical means of determining quantities or
variables. An instrument consists of a single unit which gives an output reading or signal
according to the unknown variable applied to it. Instruments can be classified as Mechanical,
Electrical and Electronic instruments. In a much broad sense, instruments are classified as,
1. Absolute Instruments
2. Secondary Instruments.
Absolute Instruments:
Absolute instruments are those which give the value of the quantity to be measured,in terms
of the constants of the instrument and their deflection only.
Eg.
Tangent Galvanometer, which gives the values of current, in terms of tangent of deflection
produced by the count,radius,and number of turns of wire used and the horizontal components
of earth's surface.
Secondary Instruments:
Secondary instruments are so constructed that the quantity being measured can be measured only
by observing the output indicated by the instrument. These instruments are calibrated by
comparison with an absolute instrument. Without calibration the deflection if such instruments
is meaningless. These secondary instruments are usually used in routine works.
Eg:
Voltmeter, Glass Thermometer, Pressure Gauge, etc,
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [2]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
Chapter-2
Theoretical Concept
(This section is solely to explain the theoretical details of Calibration of Energy meter by
considering the ideal conditions which may vary for practical conditions. So some
difference may be seen between the ideal responses to the practical responses of our
trainer.)
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [3]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
2.1 CALIBRATION:
Calibration is process in which the instrument to be calibrated is checked against a known
standard to find its error and determine its accuracy. The calibration procedure involves the
comparison of the particular instruments with either (i) a primary standard, or (ii) a secondary
standard with a higher accuracy than the instrument to be Calibrated (or) (iii) an instrument of
known accuracy.It is essential that any measurement made must ultimately be acceptable to the
relevant primary standards.
Error Calibration Curve:
Error calibration curve is a curve obtained by a set of static error points,with respect to measured
variable.Static error is defined as the difference between the measured value and true value of
the measuring vatiable. A typical error calibration curve is as shown in fig:(1) The formula for
calculating % Error is given by,
2.2 WATTMETER:
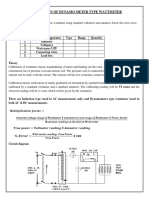
Wattmeter is an instrument which gives direct indication of the power in the circuit in which it
is connected . Based on their design and construction, wattmeter are classified as Dynamometer
type and induction type wattmeters. Let us discuss in the brief the basic construction and
working of dynamometer type wattmeter. The basic construction of dynamometer type wattmeter
is shown in fig.2. The dynamometer wattmeter consists of two coils fixed coil and moving coil.
The fixed coils are connected in series with the load and they carry the current the circuit. Hence,
they form the current coil (CC) of the wattmeter. The moving coil is connected across the voltage
and so carry a current proportional to the voltage, and hence forms the voltage coil or pressure
coil(P.C.) of the wattmeter. A high non-inductive resistance is connected in series with the
moving coil to limits the current to a small value. Spring control and air friction damping as used
in this type of wattmeter. The instrument is equipped with mirror type scales and knife edge
points. The circuit of dynamometer wattmeter is as shown in fig:2.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [4]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
Fig.2 Dynamometer type Wattmeter
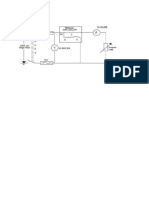
Fig.3 Simple Connection diagram of dynamometer type wattmeter.
The various errors in the wattmeter:
are: i) Error due to different connections.
ii) Error due to voltage coil (p.c.) inductance
iii) Error due to voltage coil capacitance.
iv) Error due to stray magnetic fields.
v) Error due to Eddy currents.
vi) Error due to vibration of moving system.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [5]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
Chapter-3
Experimental Section
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [6]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
AIM
To calibrate the single phase wattmeter using direct Loading.
APPARATUS REQUIRED
1. Voltmeter- (0-300V) MI.
2. Single phase variac.
3. Ammeter- (0-10A) MI.
4. Power factor meter.
5. Wattmeter.
6. R load
CONNECTION PROCEDURE
1. Connect the single phase variac to 230VAC supply.
2 Connect the voltmeter across the single phase variac.
3 Connect the Ammeter one end to the voltmeter and another end of the Power factor meter
terminal M.
4 Connect the power factor meter terminal L to the wattmeter terminal M
5 Connect the power factor terminal V and wattmeter terminal V to single phase variac.
6 Connect the wattmeter terminal L to the R load.
7. Connect the R load to single phase variac.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [7]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
1. Make the connection as per connection diagram.
2. Initially the load should be at zero.
3. Vary the autotransformer and keep the input voltage at 230VAC.
4. Add load in steps upto 5A and note down the readings of ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter
and power factor and tabulate it.
5. The appropriate multiplication factor for should be selected for Power factor meter and
wattmeter.
6. Calculate the Wcalculated and percentage error using the formulas.
TABULAR COLUMN :
M.F.=............
S.NO V I Power factor W calculated W measured
(Volts) (Amps) (CosN) VIcosN M. F×W
(Watts) (Watts)
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [8]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
3.2 CONNECTION DIAGRAM
3.3 SAMPLE CALCULATION
For unity power factor
Sample Readings:
Pressure coil voltage = 220V
current flow in current coil = 2A
Power factor =1
where,
Actual watt - Power calculated using the formula
measured watt - Reading shown by the wattmeter.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [9]
CALIBRATION OF WATTMETER BY USING DIRECT LOADING
For lagging power factor
Sample Readings
Pressure coil voltage = 220V
current flow in current coil = 2A
Power factor = 0.7
For leading power factor
Sample Readings:
Pressure coil voltage = 220V
current flow in current coil = 2A
Power factor = 0.7
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd. [10]
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- EEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalDocument29 pagesEEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalImokhai Abdullah50% (2)
- Voltmeter Loading EffectsDocument4 pagesVoltmeter Loading EffectsIan BagunasNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Wattmeter Phantom LoadingDocument15 pagesCalibration of Wattmeter Phantom LoadingMurugan RNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Energy MeterDocument4 pagesCalibration of Energy MeterKalyana Sundaram M.SNo ratings yet
- EMSL Cycle 2 ExptsDocument25 pagesEMSL Cycle 2 ExptsVarun ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Calibration WattmeterDocument2 pagesCalibration WattmeterVARAPRASADNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits 6 SibuloDocument9 pagesDC Circuits 6 Sibulonoah.sibulo2014No ratings yet
- Viva PDFDocument50 pagesViva PDFkimerlyNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronics Measurement (EEMMI) Subject Code: 303Document31 pagesElectrical & Electronics Measurement (EEMMI) Subject Code: 303Blue eyes India kiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 - Calibration of Wattmeter by Phantom LoadingDocument2 pagesExperiment 10 - Calibration of Wattmeter by Phantom LoadingFALSERNo ratings yet
- Mi Exp 1Document3 pagesMi Exp 1Dr. Tapas Kumar MajiNo ratings yet
- EEE Department Electrical Measurements Lab ManualDocument47 pagesEEE Department Electrical Measurements Lab ManualZer ZENITHNo ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument7 pagesBee Labanitha paramasivamNo ratings yet
- A Study On Multimeter: Engineering DepartmentDocument50 pagesA Study On Multimeter: Engineering DepartmentMazin Rashid Salim Al AamriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Lab Practice 1Document37 pagesElectrical Lab Practice 1JUDHISTHIRA BEHERANo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements Lab ManualDocument56 pagesElectrical Measurements Lab Manualpoornak47No ratings yet
- Energy MeterDocument3 pagesEnergy MeterkishorebabNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementDocument30 pagesLab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementEngr Haseena JabbarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engg Laboratory ManualDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical Engg Laboratory ManualDheerenNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL (Instrument and Measure)Document42 pagesLAB MANUAL (Instrument and Measure)Abaad AliNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Three Phase Reactive Power.Document5 pagesMeasurement of Three Phase Reactive Power.Murugan RNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementDocument28 pagesLab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementEngr Haseena Jabbar0% (1)
- Expt 2Document8 pagesExpt 2bkthejaswini2013No ratings yet
- Module 2 Testing InstrumentDocument8 pagesModule 2 Testing Instrumentnelson ijeboimenNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Power MetersDocument39 pagesTopic 5 Power MetersAsmairie MatNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Physical Lab #2Document10 pagesElectrical Circuit Physical Lab #2josephNo ratings yet
- Measurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Document6 pagesMeasurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Mohd IskandarNo ratings yet
- Measurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Document6 pagesMeasurement (Dee10013) Experiment 6: Title: Introduction To Power Meter (CLO 2)Mohd IskandarNo ratings yet
- 14697Document35 pages14697Akhileshkumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument11 pagesStrain Gaugemontaser.nalawiNo ratings yet
- I 1251-Electrical Measurements and InstrumentationDocument11 pagesI 1251-Electrical Measurements and Instrumentationsatishcoimbatore2No ratings yet
- Electrical MeasurementsDocument47 pagesElectrical MeasurementsManikantaNo ratings yet
- Analysis Exp 1 Version 2Document3 pagesAnalysis Exp 1 Version 2Erwin CabangalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Workshop ReportDocument16 pagesEngineering Workshop ReportAmanda Elizabeth SeniorNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 3: Use Measuring Instruments: Ammeter, Voltmeter, and WattmeterDocument4 pagesPractical No. 3: Use Measuring Instruments: Ammeter, Voltmeter, and Wattmeter166CMYashvardhan Shinde100% (1)
- Ei 34Document24 pagesEi 34Md. Mahmud Hasan SumonNo ratings yet
- 21BEC0361 Exp9 (PowerMeasurement)Document5 pages21BEC0361 Exp9 (PowerMeasurement)Ministry of PianoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 06, 2024Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 06, 2024Mohd Naif FirozNo ratings yet
- Measurement ElectricityDocument4 pagesMeasurement ElectricityMd HamzaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurement Lab ManualDocument57 pagesElectrical Measurement Lab Manualckrishna625100% (1)
- Topic 5Document39 pagesTopic 5Nazatul ZalianNo ratings yet
- Swin Burns ARUNDocument6 pagesSwin Burns ARUNArun TezNo ratings yet
- Measurement and InstrumentationDocument4 pagesMeasurement and InstrumentationAbirami RajendranNo ratings yet
- .NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1Document29 pages.NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1archibong dominicNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 6 Single Phase Energymeter-I Aim:: ApparatusDocument3 pagesExperiment No: 6 Single Phase Energymeter-I Aim:: ApparatusAswin RâjNo ratings yet
- EMDocument18 pagesEMSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurement Et-314Document57 pagesInstrumentation and Measurement Et-314ammarshahzad501No ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements and InstrumentationDocument6 pagesElectrical Measurements and InstrumentationPratik PathareNo ratings yet
- EMMI LAB MANUAL - Correct PDFDocument41 pagesEMMI LAB MANUAL - Correct PDFAryaNo ratings yet
- Mi Exp 2Document3 pagesMi Exp 2Dr. Tapas Kumar MajiNo ratings yet
- Govt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabDocument6 pagesGovt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabAnkit0% (1)
- لقطة شاشة 2021-06-21 في 11.09.14 مDocument10 pagesلقطة شاشة 2021-06-21 في 11.09.14 مnanimohammed240No ratings yet
- Measurement of Voltage in Engineering Practices LabDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Voltage in Engineering Practices LabSenthil IlangovanNo ratings yet
- AN4993Document10 pagesAN4993iskandarn_el5735No ratings yet
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology FY B.Tech: S.D.Gavarskar Ect DeptDocument14 pagesElectrical Technology FY B.Tech: S.D.Gavarskar Ect DeptAniket PatilNo ratings yet
- ORA LM Vol. IV Section 15 Drug and Device MicrobiologyDocument83 pagesORA LM Vol. IV Section 15 Drug and Device MicrobiologyDO KHNo ratings yet
- JstackDocument69 pagesJstackMike TNo ratings yet
- The Story of The Aral Sea: Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesThe Story of The Aral Sea: Reading ComprehensionGreceanu AlinaNo ratings yet
- Specification For Offshore Pipeline InstDocument28 pagesSpecification For Offshore Pipeline InstChandra WisnuNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server Operating Systems - Red HatDocument4 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux Server Operating Systems - Red HatBramanto MarthaNo ratings yet
- Skoog Química Analítica cCh8 InglésDocument6 pagesSkoog Química Analítica cCh8 InglésDavid DualNo ratings yet
- Mete AggiesDocument16 pagesMete AggiesJohn Renzel RiveraNo ratings yet
- BetaBeat Reviews:Is It Best Soultion For Diabetes?Document6 pagesBetaBeat Reviews:Is It Best Soultion For Diabetes?bohigg popixNo ratings yet
- LeafletDocument2 pagesLeafletCarlos Jose Sanchez EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Rancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Koperasi Xyz Menggunakan Framework Laravel Dan Vue - JsDocument10 pagesRancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Koperasi Xyz Menggunakan Framework Laravel Dan Vue - JsRifky LanaNo ratings yet
- Trine Natasja Sindahl PSYKphd MAR2019 B5Document169 pagesTrine Natasja Sindahl PSYKphd MAR2019 B5Maira Espinoza LabraNo ratings yet
- Canon SX130 SpecsDocument3 pagesCanon SX130 SpecsAtul WaikulNo ratings yet
- 500AMPDocument4 pages500AMPEsteban Quezada NeriNo ratings yet
- Flexible CableDocument48 pagesFlexible CableAhmed H. HassanNo ratings yet
- Efl Learners' Perception On Different AccentsDocument26 pagesEfl Learners' Perception On Different AccentsLydiaNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Triple Diffused: ApplicationDocument6 pagesSilicon NPN Triple Diffused: ApplicationDidi ConanNo ratings yet
- Ethical-Dilemma PresentationDocument4 pagesEthical-Dilemma PresentationNaymau SuarezNo ratings yet
- Fabric v2.4 AppDevDocument27 pagesFabric v2.4 AppDevBilgehan SavguNo ratings yet
- Dispersal of Modern Homo Sapiens: Known H. Sapiens Migration Routes in The PleistoceneDocument2 pagesDispersal of Modern Homo Sapiens: Known H. Sapiens Migration Routes in The Pleistocenenikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- What Are The Signs of An Impending Geologic HazardDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Signs of An Impending Geologic HazardANTON GABRIEL PRECIOSONo ratings yet
- Proton Arena Engine Cooling 1.5 1.8 Service ManualDocument16 pagesProton Arena Engine Cooling 1.5 1.8 Service ManualchipestNo ratings yet
- Read The Following Text and Answer Questions 1-3Document5 pagesRead The Following Text and Answer Questions 1-3Anonymous AKr7hWjBiNo ratings yet
- Counseling Pro Inv - SKDocument13 pagesCounseling Pro Inv - SKPadam PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Class: VIII English Literature: What Makes Me IndianDocument6 pagesClass: VIII English Literature: What Makes Me IndianHarshit RajNo ratings yet
- Condensing Unit Vertical Discharge 60 HZ R410A: 36KBTU Model Has A Different GrillDocument1 pageCondensing Unit Vertical Discharge 60 HZ R410A: 36KBTU Model Has A Different GrilljuanNo ratings yet
- Orientation On The Manual For The Evaluation (Autosaved)Document31 pagesOrientation On The Manual For The Evaluation (Autosaved)Em Boquiren CarreonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Disassembly of Basic EngineDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Disassembly of Basic EnginePurnama AbhieNo ratings yet
- U Sai Aung Tun - The Tai Ethnic MigrationDocument15 pagesU Sai Aung Tun - The Tai Ethnic MigrationDuran ThiyamNo ratings yet
- sgpnr001 enDocument70 pagessgpnr001 enAli AlmukhtarNo ratings yet
- EX - NO 3 (A) Applications Using TCP Sockets Like Echo Client and Echo Server AimDocument4 pagesEX - NO 3 (A) Applications Using TCP Sockets Like Echo Client and Echo Server AimHaru HarshuNo ratings yet