Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized Cot
Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized Cot
Uploaded by
Cris AlcalaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grade 5 Final History SS Lesson Plans Term 3Document10 pagesGrade 5 Final History SS Lesson Plans Term 3Tankiso Teekay MorotoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3rd Quarter MathDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 3rd Quarter MathAira Joyce Nepomuceno Cuaterno79% (19)
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 - contextualized-COTDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7 - contextualized-COTAzh Zel100% (12)
- Final Demo Feb 19 Circles Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFinal Demo Feb 19 Circles Lesson PlanClaudineGlenogo80% (5)
- Circle Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument4 pagesCircle Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsMark Paul Luna100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan - Distance and Midpoint Formula Grade 10Document4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan - Distance and Midpoint Formula Grade 10Rhadca Joy Santos80% (5)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Ed TechDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Ed TechJera Obsina100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotLeizel Samson100% (1)
- Department of Education: Division of General Santos CityDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Division of General Santos CityEdstreamx 08No ratings yet
- Classroom Observation 3rd Quarter Math 7 LPDocument3 pagesClassroom Observation 3rd Quarter Math 7 LPOdilio PilarcaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan MathDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan MathArlene SonNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanAira Joyce Nepomuceno CuaternoNo ratings yet
- Q3 W4 Mathematics 5Document90 pagesQ3 W4 Mathematics 5Michelle Ann DomagtoyNo ratings yet
- Circles Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCircles Lesson PlanReichelle FuaNo ratings yet
- 4as Lesson PlanDocument5 pages4as Lesson PlanEllajean Ojil100% (1)
- My Lesson plan for demo teachingDocument5 pagesMy Lesson plan for demo teachingconcharc1998No ratings yet
- CLASSROOM OBSERVATION LESSON PLAN - Mathematics VDocument3 pagesCLASSROOM OBSERVATION LESSON PLAN - Mathematics VMay Ann Somer-Maglahus Antiquisa67% (3)
- Circumference of A Circle Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesCircumference of A Circle Lesson PlanRhoda Mae CocjinNo ratings yet
- LUCERO - BEED2 1 - 5E Model Lesson Plan in Mathematics Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument2 pagesLUCERO - BEED2 1 - 5E Model Lesson Plan in Mathematics Technology For Teaching and LearningracelisjeahliemaeNo ratings yet
- Davao Oriental State UniversityDocument5 pagesDavao Oriental State UniversityMateo, Elijah Jonathan C.No ratings yet
- Math 10 LP4Document8 pagesMath 10 LP4Jara ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Mini - Task (AS) : Subject MatterDocument5 pagesMini - Task (AS) : Subject MatterTiffany Joy Lencioco GambalanNo ratings yet
- Final Demo BlueprintDocument2 pagesFinal Demo Blueprintjennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- Activity Tpack Output FormDocument8 pagesActivity Tpack Output FormJoni Czarina AmoraNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade School GeometryDocument53 pages8th Grade School Geometryعصام الشطناويNo ratings yet
- Aljun Pinaca 7 Doscst Mathematics Bsed-Mathematics 3rd AsynchronousDocument7 pagesAljun Pinaca 7 Doscst Mathematics Bsed-Mathematics 3rd Asynchronousgina bayateNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleKRISTINE JANE VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 - Q3 - Mod5 - Proving Theorems On The Different Kinds of Parallelogram - V3Document17 pagesMathematics 9 - Q3 - Mod5 - Proving Theorems On The Different Kinds of Parallelogram - V3alexablisss50% (2)
- Right TriangleDocument7 pagesRight TriangleMaine LegaspiNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN in MATH IV Parts ofDocument3 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN in MATH IV Parts ofaimeeNo ratings yet
- Math 105 Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMath 105 Lesson Planapi-250245193No ratings yet
- Area and Circumference of A CircleDocument2 pagesArea and Circumference of A CircleJovie Mae SabanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PlanningDocument2 pagesMathematics PlanningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Circumferenceofcircle 140708163044 Phpapp02Document5 pagesCircumferenceofcircle 140708163044 Phpapp02Donna Mae SuplagioNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry SimplifiedDocument60 pagesCircle Geometry Simplifiedcrass5469No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in SecantsDocument4 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Secantsmarygrace idananNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7 Quarter 3 Module 1Document25 pagesMathematics 7 Quarter 3 Module 1jun bonifacioNo ratings yet
- EdmathDocument3 pagesEdmaththanpinado21No ratings yet
- REVISION PAPER - IntermediateDocument7 pagesREVISION PAPER - Intermediatevongtranduykhoi020409v.tNo ratings yet
- Circle LPDocument8 pagesCircle LProse FrondaNo ratings yet
- Math5 Q3 Module9Document16 pagesMath5 Q3 Module9CyanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesDocument20 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesJennyNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q2 - Week 9Document16 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Week 9Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Equation of A CircleDocument7 pagesEquation of A CircleMellard JapsonNo ratings yet
- Math10 q2 Mod8of8 Graph of Circle and Other Geometric Figures v2Document15 pagesMath10 q2 Mod8of8 Graph of Circle and Other Geometric Figures v2Ledesma, Elijah O.No ratings yet
- Demo Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDemo Lesson Planjennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- CCA School, Gurugram (Session 2021-22) Holiday Homework (May - June) Class - IX A) EnglishDocument7 pagesCCA School, Gurugram (Session 2021-22) Holiday Homework (May - June) Class - IX A) EnglishJiya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Circle GeometryDocument4 pagesCircle GeometryJulius Fernan VegaNo ratings yet
- Stem Demo SampleDocument4 pagesStem Demo SampleEstacio B. Iraida JunaNo ratings yet
- 2nd COT The Equation of A CircleDocument5 pages2nd COT The Equation of A CircleDivina Dacalos-ClaroNo ratings yet
- TPC 5Document21 pagesTPC 5mukona199No ratings yet
- Techdrawg7 q2 w6 Las1Document1 pageTechdrawg7 q2 w6 Las1Van TotNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Section: - ScoreDocument8 pagesName: - Date: - Section: - ScoreDelaCruz Alburo DennisMark100% (1)
- Common Assessment 4 v4 FixDocument9 pagesCommon Assessment 4 v4 Fixdavidkw88No ratings yet
- LP CircleDocument7 pagesLP CircleJoan Grimpola SisonNo ratings yet
- Sim Math 8Document15 pagesSim Math 8May JavellanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Math7Document4 pagesLesson Plan Math7Annie Glen LovesParamore CanilaoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2 LPDocument6 pagesMathematics 2 LPRichell RueloNo ratings yet
- Cot Math 5 Q3Document9 pagesCot Math 5 Q3Roberto QuijanoNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson PlanJee Han100% (1)
- SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionFrom EverandSAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- W6las 4Document1 pageW6las 4Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- W7las 3Document1 pageW7las 3Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- W6las 2Document1 pageW6las 2Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ReadingDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in ReadingCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- M7-Q4-W5 - Las 4Document1 pageM7-Q4-W5 - Las 4Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- M7-Q4-W5 - Las-2Document1 pageM7-Q4-W5 - Las-2Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Catch-Up Fridays Teaching GuideDocument3 pagesCatch-Up Fridays Teaching GuideCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Teaching - Guide - Peace EducationDocument2 pagesTeaching - Guide - Peace EducationCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- 7cr CrackDocument12 pages7cr CracksniperiNo ratings yet
- Rencana Strategis Dinas Pekerjaan Umum Kabupaten Bengkulu Utara Tahun 2016-2021Document5 pagesRencana Strategis Dinas Pekerjaan Umum Kabupaten Bengkulu Utara Tahun 2016-2021Tendo SanNo ratings yet
- IMWA2016 Coetzee 66Document6 pagesIMWA2016 Coetzee 66Glenn NyirendaNo ratings yet
- Deped Naga City - Schools Division: Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Quarter 1, HEALTH 8Document4 pagesDeped Naga City - Schools Division: Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Quarter 1, HEALTH 8Jo DVera Gonzales IINo ratings yet
- MSI Algebra MemosDocument7 pagesMSI Algebra Memosmphodau92No ratings yet
- ACELEC 321 Module 2Document17 pagesACELEC 321 Module 2CAMILA RAFAELNo ratings yet
- Test - WASH PM Assistant - TemplateDocument6 pagesTest - WASH PM Assistant - Templatealgodami100% (6)
- CH 2 Summary The Disciplined Trader by Mark DouglasDocument2 pagesCH 2 Summary The Disciplined Trader by Mark Douglasdilipp_2No ratings yet
- Evaluation Form 1Document2 pagesEvaluation Form 1Cherissa Abay OmegaNo ratings yet
- Loch Ness Monster Research PaperDocument5 pagesLoch Ness Monster Research Paperegabnlrhf100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Biogas Production PDFDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Biogas Production PDFRosieNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 ArkhangelskiiDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 ArkhangelskiiEvgeniiNo ratings yet
- Zlib - Pub - Swarm Intelligence Methods For Statistical RegressionDocument137 pagesZlib - Pub - Swarm Intelligence Methods For Statistical RegressionASDSADNo ratings yet
- Patentable and Non Patentable InventionsDocument11 pagesPatentable and Non Patentable InventionsAniket SantraNo ratings yet
- Elgi LubricantsDocument1 pageElgi LubricantsANILNo ratings yet
- Review Chapter 2-PS-Fall2012Document4 pagesReview Chapter 2-PS-Fall2012Nguyễn DuyNo ratings yet
- Sara's Leadership StyleDocument5 pagesSara's Leadership StyleSara IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Kitcharao Central Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Kitcharao Central Elementary SchoolMalou EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Social Worker CV by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesSocial Worker CV by SlidesgoHadiNo ratings yet
- Reading Plus Houses and Homes Unit 7: Cambridge English Empower B1+Document2 pagesReading Plus Houses and Homes Unit 7: Cambridge English Empower B1+Sara AljoozNo ratings yet
- If You Steal From One Author - Quote InvestigatorDocument7 pagesIf You Steal From One Author - Quote InvestigatorhompfNo ratings yet
- ST202 NotesDocument52 pagesST202 NotesCharlieNo ratings yet
- Base Isolation - Seismic and WindsDocument2 pagesBase Isolation - Seismic and WindskamakshiNo ratings yet
- SUJ2 DatasheetDocument2 pagesSUJ2 DatasheetGyurmoooNo ratings yet
- USP 1228 DepyrogenationDocument5 pagesUSP 1228 Depyrogenationmustafa huseiny100% (1)
- Msme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: BatchDocument7 pagesMsme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: Batcharyan banchhorNo ratings yet
- Jobs To Be Done - JOB STATEMENT CANVAS - JOKULL - Helge Tenno - WlinkDocument1 pageJobs To Be Done - JOB STATEMENT CANVAS - JOKULL - Helge Tenno - WlinkbrisNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Drift AnalysisDocument2 pagesPreliminary Drift AnalysisNeil BeeraspatNo ratings yet
- Half Bridge Converter PaperDocument6 pagesHalf Bridge Converter PaperAryaNo ratings yet
Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized Cot
Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized Cot
Uploaded by
Cris AlcalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized Cot
Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized Cot
Uploaded by
Cris AlcalaCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|24696143
Lesson plan in mathematics 7 contextualized cot
General Mathematics (STI College)
Scan to open on Studocu
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Cher Cris (chercris1224@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|24696143
Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7
Teaching Date and Time: Feb. 19, 2020/ 8:30-9:30
Teacher: Ms. Azel D. Gantala
Grade Level: 7
Learning Area: Mathematics
Quarter: Fourth
I. OBJECTIVES
Content Standards:
The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of Geometry of shapes
and sizes, and geometric relationships.
Performance Standards:
The learner is able to create models of plan figures and formulate and solve
accurately authentic problems involving sides and angles of a polygon.
Learning Competencies/Objectives:
1. The learner illustrates a circle and the terms related to it: radius, diameter,
center, arc, chord, and central angle. (M7GE-IIIg-1)
The learner illustrates a circle and the terms related to it: radius, diameter,
center, arc, chord, and central angle with pictures of food products in
Southern Leyte. DLHTM VIII. Food and Local Products
2. Draw a circle with its parts correctly labelled.
3. Appreciate the importance of circles in our daily lives.
II. CONTENT
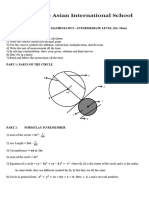
CIRCLES AND THE TERMS RELATED TO IT: RADIUS, DIAMETER, CHORD, AND CENTER
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide pages , pp. 286-289
2. Learner’s Materials pages, pp. 233-236
B. Other Learning Resources
Teacher-made test, TV, laptop, ruler, pencil
IV. PROCEDURES
1. Activity
Review
1. What is a polygon?
2. How are you going to determine the sum of the interior angles of a polygon?
3. How many sides are there in a decagon?
Downloaded by Cher Cris (chercris1224@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|24696143
Lesson Proper
Direction: Identify the following images.
(Group Activity)
Group 1 (Draw Me)
Directions: Draw a point somewhere in the middle of a sheet of a manila paper. Now,
using a ruler, mark 10 other points that are having a distance of 10 inches from the
first point.
Answer the following question:
a. What have you observed from your drawing?
Group 2 (Mark Me)
Directions: Fold the circle into 2 equal parts. Then mark the center with an X. Then
mark the fold A and B at both ends.
Answer the following question:
a. What did you notice?
Group 3 (Act Out)
Directions: Choose eight members of the group that will hold hands together;
choose one of the member of your group to stand at the center of the circle; then
the remaining members will form a line (first line) between the circle that passes to
the center; then half of the members who formed a line will leave (which creates a
second line).
Answer the following questions:
a. Compare the first line to the second line. Which is longer? Which is shorter?
Downloaded by Cher Cris (chercris1224@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|24696143
b. Do you have any idea of what part of the circle is the first line? How about the
second line?
2. Abstract
Presentation of the lesson and discussion using PowerPoint.
Circle is the set of all points that are the same distance from a fixed point. This fixed
point is called a center of the circle.
Note: A circle is named by its center. The circle here is called Circle O.
Radius- a segment drawn from any point on the circle to the center.
Chord- is a segment that connects any two points of a circle.
Diameter- is a chord that passes through the center of a circle.
Arc- is a part of the circumference between two points or a continuous piece of a
circle.
Central angle - is the angle that forms when two radii meet at the center of a circle a
Inscribed angle- is an angle whose vertex sits on the circumference of a circle. The
vertex is the common endpoint of the two sides of the angle. The two sides are
chords of the circle.
3. Analysis
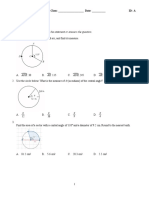
Determine whether each statement is TRUE or FALSE.
a. Two radii always have the same length. (TRUE)
b. Two chords always have the same length. (FALSE)
c. All chords are diameters. (FALSE)
d. All diameters are chords. (TRUE)
e. A radius is not a chord. (TRUE)
4. Generalization:
What is a circle?
What are the terms related to a circle?
5. Application
Identify each of the following related to the circle.
Downloaded by Cher Cris (chercris1224@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|24696143
1. O (center)
2. SN (diameter)
3. OM (radius)
4. PR (chord)
5. ST (chord)
IV. EVALUATION
A. Draw your own circle and illustrate the following:
1. chord QR
2. center A
3. diameter DE
4. radius AC
5. radius AP
B. The table below refers to radius and diameter of a circle. Complete the table.
Radius Diameter
6. 12 cm
7. 488 cm
8. 112 dm
9. 36 m
10. 27 km
V. ASSIGNMENT
Cut out at least five (5) pictures of things around us that best represent a circle. Glue it on a
short bond paper.
Prepared by:
AZEL D. GANTALA
Grade 7 Mathematics Teacher
Checked by:
DR. GRACE T. AUPE
Asst. Principal
Downloaded by Cher Cris (chercris1224@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Grade 5 Final History SS Lesson Plans Term 3Document10 pagesGrade 5 Final History SS Lesson Plans Term 3Tankiso Teekay MorotoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3rd Quarter MathDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 3rd Quarter MathAira Joyce Nepomuceno Cuaterno79% (19)
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 - contextualized-COTDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7 - contextualized-COTAzh Zel100% (12)
- Final Demo Feb 19 Circles Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFinal Demo Feb 19 Circles Lesson PlanClaudineGlenogo80% (5)
- Circle Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument4 pagesCircle Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsMark Paul Luna100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan - Distance and Midpoint Formula Grade 10Document4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan - Distance and Midpoint Formula Grade 10Rhadca Joy Santos80% (5)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Ed TechDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Ed TechJera Obsina100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotLeizel Samson100% (1)
- Department of Education: Division of General Santos CityDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Division of General Santos CityEdstreamx 08No ratings yet
- Classroom Observation 3rd Quarter Math 7 LPDocument3 pagesClassroom Observation 3rd Quarter Math 7 LPOdilio PilarcaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan MathDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan MathArlene SonNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanAira Joyce Nepomuceno CuaternoNo ratings yet
- Q3 W4 Mathematics 5Document90 pagesQ3 W4 Mathematics 5Michelle Ann DomagtoyNo ratings yet
- Circles Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCircles Lesson PlanReichelle FuaNo ratings yet
- 4as Lesson PlanDocument5 pages4as Lesson PlanEllajean Ojil100% (1)
- My Lesson plan for demo teachingDocument5 pagesMy Lesson plan for demo teachingconcharc1998No ratings yet
- CLASSROOM OBSERVATION LESSON PLAN - Mathematics VDocument3 pagesCLASSROOM OBSERVATION LESSON PLAN - Mathematics VMay Ann Somer-Maglahus Antiquisa67% (3)
- Circumference of A Circle Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesCircumference of A Circle Lesson PlanRhoda Mae CocjinNo ratings yet
- LUCERO - BEED2 1 - 5E Model Lesson Plan in Mathematics Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument2 pagesLUCERO - BEED2 1 - 5E Model Lesson Plan in Mathematics Technology For Teaching and LearningracelisjeahliemaeNo ratings yet
- Davao Oriental State UniversityDocument5 pagesDavao Oriental State UniversityMateo, Elijah Jonathan C.No ratings yet
- Math 10 LP4Document8 pagesMath 10 LP4Jara ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Mini - Task (AS) : Subject MatterDocument5 pagesMini - Task (AS) : Subject MatterTiffany Joy Lencioco GambalanNo ratings yet
- Final Demo BlueprintDocument2 pagesFinal Demo Blueprintjennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- Activity Tpack Output FormDocument8 pagesActivity Tpack Output FormJoni Czarina AmoraNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade School GeometryDocument53 pages8th Grade School Geometryعصام الشطناويNo ratings yet
- Aljun Pinaca 7 Doscst Mathematics Bsed-Mathematics 3rd AsynchronousDocument7 pagesAljun Pinaca 7 Doscst Mathematics Bsed-Mathematics 3rd Asynchronousgina bayateNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleKRISTINE JANE VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 - Q3 - Mod5 - Proving Theorems On The Different Kinds of Parallelogram - V3Document17 pagesMathematics 9 - Q3 - Mod5 - Proving Theorems On The Different Kinds of Parallelogram - V3alexablisss50% (2)
- Right TriangleDocument7 pagesRight TriangleMaine LegaspiNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN in MATH IV Parts ofDocument3 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN in MATH IV Parts ofaimeeNo ratings yet
- Math 105 Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMath 105 Lesson Planapi-250245193No ratings yet
- Area and Circumference of A CircleDocument2 pagesArea and Circumference of A CircleJovie Mae SabanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PlanningDocument2 pagesMathematics PlanningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Circumferenceofcircle 140708163044 Phpapp02Document5 pagesCircumferenceofcircle 140708163044 Phpapp02Donna Mae SuplagioNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry SimplifiedDocument60 pagesCircle Geometry Simplifiedcrass5469No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in SecantsDocument4 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Secantsmarygrace idananNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7 Quarter 3 Module 1Document25 pagesMathematics 7 Quarter 3 Module 1jun bonifacioNo ratings yet
- EdmathDocument3 pagesEdmaththanpinado21No ratings yet
- REVISION PAPER - IntermediateDocument7 pagesREVISION PAPER - Intermediatevongtranduykhoi020409v.tNo ratings yet
- Circle LPDocument8 pagesCircle LProse FrondaNo ratings yet
- Math5 Q3 Module9Document16 pagesMath5 Q3 Module9CyanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesDocument20 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesJennyNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q2 - Week 9Document16 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Week 9Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Equation of A CircleDocument7 pagesEquation of A CircleMellard JapsonNo ratings yet
- Math10 q2 Mod8of8 Graph of Circle and Other Geometric Figures v2Document15 pagesMath10 q2 Mod8of8 Graph of Circle and Other Geometric Figures v2Ledesma, Elijah O.No ratings yet
- Demo Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDemo Lesson Planjennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- CCA School, Gurugram (Session 2021-22) Holiday Homework (May - June) Class - IX A) EnglishDocument7 pagesCCA School, Gurugram (Session 2021-22) Holiday Homework (May - June) Class - IX A) EnglishJiya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Circle GeometryDocument4 pagesCircle GeometryJulius Fernan VegaNo ratings yet
- Stem Demo SampleDocument4 pagesStem Demo SampleEstacio B. Iraida JunaNo ratings yet
- 2nd COT The Equation of A CircleDocument5 pages2nd COT The Equation of A CircleDivina Dacalos-ClaroNo ratings yet
- TPC 5Document21 pagesTPC 5mukona199No ratings yet
- Techdrawg7 q2 w6 Las1Document1 pageTechdrawg7 q2 w6 Las1Van TotNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Section: - ScoreDocument8 pagesName: - Date: - Section: - ScoreDelaCruz Alburo DennisMark100% (1)
- Common Assessment 4 v4 FixDocument9 pagesCommon Assessment 4 v4 Fixdavidkw88No ratings yet
- LP CircleDocument7 pagesLP CircleJoan Grimpola SisonNo ratings yet
- Sim Math 8Document15 pagesSim Math 8May JavellanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Math7Document4 pagesLesson Plan Math7Annie Glen LovesParamore CanilaoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2 LPDocument6 pagesMathematics 2 LPRichell RueloNo ratings yet
- Cot Math 5 Q3Document9 pagesCot Math 5 Q3Roberto QuijanoNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson PlanJee Han100% (1)
- SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionFrom EverandSAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- W6las 4Document1 pageW6las 4Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- W7las 3Document1 pageW7las 3Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- W6las 2Document1 pageW6las 2Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ReadingDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in ReadingCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- M7-Q4-W5 - Las 4Document1 pageM7-Q4-W5 - Las 4Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- M7-Q4-W5 - Las-2Document1 pageM7-Q4-W5 - Las-2Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Catch-Up Fridays Teaching GuideDocument3 pagesCatch-Up Fridays Teaching GuideCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Teaching - Guide - Peace EducationDocument2 pagesTeaching - Guide - Peace EducationCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- 7cr CrackDocument12 pages7cr CracksniperiNo ratings yet
- Rencana Strategis Dinas Pekerjaan Umum Kabupaten Bengkulu Utara Tahun 2016-2021Document5 pagesRencana Strategis Dinas Pekerjaan Umum Kabupaten Bengkulu Utara Tahun 2016-2021Tendo SanNo ratings yet
- IMWA2016 Coetzee 66Document6 pagesIMWA2016 Coetzee 66Glenn NyirendaNo ratings yet
- Deped Naga City - Schools Division: Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Quarter 1, HEALTH 8Document4 pagesDeped Naga City - Schools Division: Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Quarter 1, HEALTH 8Jo DVera Gonzales IINo ratings yet
- MSI Algebra MemosDocument7 pagesMSI Algebra Memosmphodau92No ratings yet
- ACELEC 321 Module 2Document17 pagesACELEC 321 Module 2CAMILA RAFAELNo ratings yet
- Test - WASH PM Assistant - TemplateDocument6 pagesTest - WASH PM Assistant - Templatealgodami100% (6)
- CH 2 Summary The Disciplined Trader by Mark DouglasDocument2 pagesCH 2 Summary The Disciplined Trader by Mark Douglasdilipp_2No ratings yet
- Evaluation Form 1Document2 pagesEvaluation Form 1Cherissa Abay OmegaNo ratings yet
- Loch Ness Monster Research PaperDocument5 pagesLoch Ness Monster Research Paperegabnlrhf100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Biogas Production PDFDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Biogas Production PDFRosieNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 ArkhangelskiiDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 ArkhangelskiiEvgeniiNo ratings yet
- Zlib - Pub - Swarm Intelligence Methods For Statistical RegressionDocument137 pagesZlib - Pub - Swarm Intelligence Methods For Statistical RegressionASDSADNo ratings yet
- Patentable and Non Patentable InventionsDocument11 pagesPatentable and Non Patentable InventionsAniket SantraNo ratings yet
- Elgi LubricantsDocument1 pageElgi LubricantsANILNo ratings yet
- Review Chapter 2-PS-Fall2012Document4 pagesReview Chapter 2-PS-Fall2012Nguyễn DuyNo ratings yet
- Sara's Leadership StyleDocument5 pagesSara's Leadership StyleSara IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Kitcharao Central Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Kitcharao Central Elementary SchoolMalou EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Social Worker CV by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesSocial Worker CV by SlidesgoHadiNo ratings yet
- Reading Plus Houses and Homes Unit 7: Cambridge English Empower B1+Document2 pagesReading Plus Houses and Homes Unit 7: Cambridge English Empower B1+Sara AljoozNo ratings yet
- If You Steal From One Author - Quote InvestigatorDocument7 pagesIf You Steal From One Author - Quote InvestigatorhompfNo ratings yet
- ST202 NotesDocument52 pagesST202 NotesCharlieNo ratings yet
- Base Isolation - Seismic and WindsDocument2 pagesBase Isolation - Seismic and WindskamakshiNo ratings yet
- SUJ2 DatasheetDocument2 pagesSUJ2 DatasheetGyurmoooNo ratings yet
- USP 1228 DepyrogenationDocument5 pagesUSP 1228 Depyrogenationmustafa huseiny100% (1)
- Msme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: BatchDocument7 pagesMsme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: Batcharyan banchhorNo ratings yet
- Jobs To Be Done - JOB STATEMENT CANVAS - JOKULL - Helge Tenno - WlinkDocument1 pageJobs To Be Done - JOB STATEMENT CANVAS - JOKULL - Helge Tenno - WlinkbrisNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Drift AnalysisDocument2 pagesPreliminary Drift AnalysisNeil BeeraspatNo ratings yet
- Half Bridge Converter PaperDocument6 pagesHalf Bridge Converter PaperAryaNo ratings yet