Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circuits Can Be Classified Into Various Types Based On Their Configuration
Circuits Can Be Classified Into Various Types Based On Their Configuration
Uploaded by
Ankit GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuits Can Be Classified Into Various Types Based On Their Configuration
Circuits Can Be Classified Into Various Types Based On Their Configuration
Uploaded by
Ankit GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
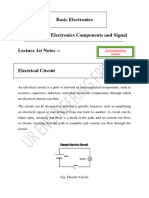
Circuits can be classified into various types based on their configuration, components, and
function. Here are some common types of circuits:
1. Series Circuit: In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, forming a single
pathway for current to flow. The same current flows through each component, and the total
resistance is the sum of individual resistances.
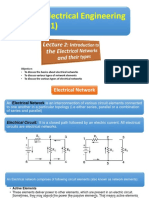
2. Parallel Circuit: In a parallel circuit, components are connected across common points,
providing multiple pathways for current to flow. The voltage across each component is the
same, while the total current is the sum of currents through individual branches.
3. Series-Parallel Circuit: This type of circuit combines elements of both series and parallel
configurations. Components are arranged in both series and parallel connections, offering a
balance between voltage and current division.
4. Resistive Circuit: A resistive circuit consists of resistors connected in various
configurations, such as series, parallel, or a combination of both. These circuits are used to
control current flow, voltage division, and power dissipation.
5. Capacitive Circuit: A capacitive circuit includes capacitors that store and release electrical
energy in the form of electric fields. These circuits are used in filtering, timing, and energy
storage applications.
6. Inductive Circuit: An inductive circuit contains inductors that store and release electrical
energy in the form of magnetic fields. These circuits are used in applications such as
electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression and energy storage.
7. RL Circuit: An RL circuit consists of resistors and inductors connected in series or parallel
configurations. These circuits exhibit transient behavior due to the presence of inductance,
affecting the rate of change of current.
8. RC Circuit: An RC circuit contains resistors and capacitors connected in series or parallel
configurations. These circuits exhibit transient behavior due to the presence of capacitance,
affecting the rate of change of voltage.
9. RLC Circuit: An RLC circuit combines resistors, inductors, and capacitors in various
configurations. These circuits exhibit a wide range of behaviors, including resonance,
filtering, and impedance matching.
10. Digital Circuit: Digital circuits use logic gates and digital components to process binary
signals (0s and 1s). They are the basis of modern computing systems, including
microprocessors, memory modules, and digital signal processors.
These are just a few examples of the different types of circuits commonly encountered in
electrical and electronic systems, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
You might also like
- Types of CricuitsDocument10 pagesTypes of Cricuitsgosaiankkosh07No ratings yet
- Types of Electrical NetworkDocument2 pagesTypes of Electrical NetworkFRANCISCO JERHYL KEITH G.No ratings yet
- PDU Lab 89Document10 pagesPDU Lab 89Yassir ButtNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceDocument17 pagesDifferent Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceVIPIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics M1Document13 pagesBasic Electronics M1roshansingh906585730No ratings yet
- Series CircuitsDocument3 pagesSeries CircuitsEnglish TeacherNo ratings yet
- Relay Protection - Discussioin-KEADocument43 pagesRelay Protection - Discussioin-KEAShirajul IslamNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Relays and Their Working PrinciplesDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Relays and Their Working PrinciplesArslan AliNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Charging and DischargingDocument2 pagesCapacitor Charging and Dischargingpranjalnegi6699No ratings yet
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocument12 pagesEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleNo ratings yet
- Study of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical EngineeringDocument7 pagesStudy of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical Engineeringnational printersNo ratings yet
- BCM Practical 1 2Document9 pagesBCM Practical 1 2Adi KhardeNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument7 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering Friendapjvlogs0No ratings yet
- Ayu Novita - Answer of Final TermDocument3 pagesAyu Novita - Answer of Final TermAyu Novita AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- EECT Lab ManualDocument4 pagesEECT Lab ManualBlaze fireNo ratings yet
- Guide To RelaysDocument5 pagesGuide To RelaysAbhinandan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Types of RelaysDocument24 pagesTypes of RelayselmerNo ratings yet
- Abuchi Seminar Topic On RelayDocument18 pagesAbuchi Seminar Topic On Relayfrancis abuchiNo ratings yet
- Relay: HistoryDocument11 pagesRelay: HistoryEngr WekiNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument6 pagesElectronic ComponentsEmey SantosNo ratings yet
- Module in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument39 pagesModule in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringEbacuado, Regine Mae F.No ratings yet
- Numerical RelayDocument19 pagesNumerical RelayRajesh Naik Dharavath100% (1)
- Basic Electronics L1Document19 pagesBasic Electronics L1msellereneNo ratings yet
- ConnectorsDocument9 pagesConnectorsROHININo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesDocument18 pages1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesEphraem RobinNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 1 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument6 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 1 by Ur Engineering Friendapjvlogs0No ratings yet
- Basic Circuit ComponentsDocument3 pagesBasic Circuit ComponentsJhoker SudzNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control SystemDocument20 pagesTraffic Control SystemRam SaiNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument1 pageElectronic ComponentJedediah D. MagannonNo ratings yet
- BLE - Module 4Document139 pagesBLE - Module 4David ManiNo ratings yet
- Simple CircuitsDocument3 pagesSimple CircuitsOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Use of Capacitor and InductorDocument5 pagesUse of Capacitor and InductorRohit Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Resistor: V Iri VRDocument2 pagesResistor: V Iri VRDany AlfiyandiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Document6 pagesPower Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Asha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Principles Form The Foundation of Modern Electrical Engineering and Are Crucial For Understanding The Behavior of Electrical SystemsDocument1 pageElectrical Circuit Principles Form The Foundation of Modern Electrical Engineering and Are Crucial For Understanding The Behavior of Electrical Systemssuliman bobNo ratings yet
- CAPACITORSDocument12 pagesCAPACITORSAnitha PragasamNo ratings yet
- Common Electronic ComponentsDocument41 pagesCommon Electronic ComponentsangelynNo ratings yet
- Batch 3 Report 18.06.22Document68 pagesBatch 3 Report 18.06.22Sujesh ChittarikkalNo ratings yet
- What Is RelayDocument8 pagesWhat Is RelayLorenz BanadaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document1 pageExperiment 1hiren_powerNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 - 3 - 4Document17 pagesMod 2 - 3 - 4Georji kairuNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 - 3 - 4 - 5Document26 pagesMod 2 - 3 - 4 - 5Georji kairuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Networks, Network ElementsDocument11 pagesElectrical Networks, Network ElementsMansi NegiNo ratings yet
- October 2023 - CrisDocument4 pagesOctober 2023 - CrisChristopher FredrickNo ratings yet
- 4-Protection SystemsDocument3 pages4-Protection SystemsAbdulhakim TREKINo ratings yet
- Experiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesExperiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsAdesh Bhortakke100% (2)
- Relay: Relay Is Basically A Magnetism Based Switch. It Consists of A Coil Through Which Current Passes and OnDocument9 pagesRelay: Relay Is Basically A Magnetism Based Switch. It Consists of A Coil Through Which Current Passes and OnAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terminologies.Document20 pagesElectrical Terminologies.brazilacademicNo ratings yet
- Topic One Introduction To ElectronicsDocument22 pagesTopic One Introduction To ElectronicsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- RelayDocument89 pagesRelayHarsh GajeraNo ratings yet
- BME213L (1695) LongQuiz PonteroDocument3 pagesBME213L (1695) LongQuiz Ponteroklyn ponteroNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument9 pagesBasic Electronic ComponentsMackRoss PerezNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document12 pagesLab 1hussainNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 - 3Document11 pagesMod 2 - 3Georji kairuNo ratings yet
- Module 1.Ppt NetworkDocument55 pagesModule 1.Ppt NetworkbijukumargNo ratings yet
- Service 3Document22 pagesService 3Hriday PaulNo ratings yet
- Active & PassiveDocument3 pagesActive & Passivevirendra.aryaNo ratings yet
- Corona EffectDocument2 pagesCorona EffectJefferson Nolty GenoviaNo ratings yet
- Familiarization of Electrical DevicesDocument14 pagesFamiliarization of Electrical DevicesJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- Clock Distribution Using VHDLDocument66 pagesClock Distribution Using VHDLBridget GrahamNo ratings yet
- FA - Inverter BN44-00124DDocument9 pagesFA - Inverter BN44-00124DEsmir MarinNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument12 pagesTransistorssNo ratings yet
- ECE131 UNIT5 Part3Document88 pagesECE131 UNIT5 Part3abhi shek100% (1)
- FET AC Analysis PDFDocument20 pagesFET AC Analysis PDFnupur kesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Agilent Optocoupler Selection GuideDocument2 pagesAgilent Optocoupler Selection GuideJesus OlivaresNo ratings yet
- HBE Basic iLABDocument10 pagesHBE Basic iLABThichanon RomsaiyudNo ratings yet
- CH 17 - Methods of Analysis of Ac CircuitsDocument29 pagesCH 17 - Methods of Analysis of Ac Circuitsعبدالله المعتقNo ratings yet
- Design Differentiator AmplifierDocument10 pagesDesign Differentiator Amplifierhareesh.makesu0% (1)
- Gate Ec: Q. 1-30 Carry One Mark EachDocument44 pagesGate Ec: Q. 1-30 Carry One Mark EachSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Ece 4103 01Document9 pagesEce 4103 01TI NafisNo ratings yet
- 80 Watts Subwoofer Mono Audio Amplifier Board DIY TIP3055 & TIP2955 Transistor (Hindi) PDFDocument4 pages80 Watts Subwoofer Mono Audio Amplifier Board DIY TIP3055 & TIP2955 Transistor (Hindi) PDFKulwinder100% (2)
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument4 pagesDC Regulated Power Supplyusama zeeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 6 - VCODocument2 pagesLaboratory 6 - VCOAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lab MANUALDocument70 pagesAnalog Electronics Lab MANUALSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- 74HC595 Shift RegisterDocument5 pages74HC595 Shift RegisterIqra ArainNo ratings yet
- Ece3002 Vlsi-system-Design Eth 1.2 49 Ece3002 41Document2 pagesEce3002 Vlsi-system-Design Eth 1.2 49 Ece3002 41SMNo ratings yet
- P1 - Logic GateDocument25 pagesP1 - Logic GateaasmabakaNo ratings yet
- Oscillators and MultivibratorsDocument2 pagesOscillators and MultivibratorsRed David BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Tonepad Distortion1Document1 pageTonepad Distortion1BAMFNo ratings yet
- List of 7400 Series Integrated Circuits - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesList of 7400 Series Integrated Circuits - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHermes Heli Retiz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Logic Families Unit 2Document27 pagesLecture 3-Logic Families Unit 2q898awaNo ratings yet
- Chp-7-First Order CircuitsDocument25 pagesChp-7-First Order CircuitsHuman BeingNo ratings yet
- Complete LICA Lab ManualDocument54 pagesComplete LICA Lab Manualnuthan9150% (2)
- Realisation of Basic Gates Using Universal Gates: ObjectDocument6 pagesRealisation of Basic Gates Using Universal Gates: ObjectMouboni 04No ratings yet
- Lab 10Document16 pagesLab 10Souban JavedNo ratings yet
- Transceivers For Millimeter WavesDocument35 pagesTransceivers For Millimeter WavesmpoornishwarNo ratings yet
- 5 Channel DC/DC Converter + V Slice + Power Good: Datasheet ONDocument2 pages5 Channel DC/DC Converter + V Slice + Power Good: Datasheet ONRepararelcd Lcd100% (1)
- MC14094B 8-Stage Shift/Store Register With Three-State OutputsDocument9 pagesMC14094B 8-Stage Shift/Store Register With Three-State Outputsdeilyn rivasNo ratings yet
- ECE3110Fa10 HW1solDocument7 pagesECE3110Fa10 HW1solSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet