Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsPlant Kingdom Chart
Plant Kingdom Chart
Uploaded by
garrysi639Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- New Families Added in NEET 2024 SyllabusDocument8 pagesNew Families Added in NEET 2024 Syllabusvm4327489100% (16)
- Pregnancy Miracle - Holistic and Ancient Chinese System For Getting Pregnant and Having Healthy BabiesDocument99 pagesPregnancy Miracle - Holistic and Ancient Chinese System For Getting Pregnant and Having Healthy BabiesNicole Kaylee20% (10)
- PPT-Science 7 - ReproductionDocument34 pagesPPT-Science 7 - ReproductionArima Kousei50% (4)
- Red Pill BooksDocument2 pagesRed Pill Bookssinchonglo80% (5)
- Atlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaFrom EverandAtlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Sexual EcstasyDocument10 pagesSecrets of Sexual EcstasyGreat HelpNo ratings yet
- Growing Up and Liking ItDocument16 pagesGrowing Up and Liking Iturbster1No ratings yet
- .Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesDocument10 pages.Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWrajatbharti830No ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationketakiNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom PowernotesDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdom Powernotessheikhanzar643No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom M PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom M PDFAbu SubhanNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomInfinite SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 Pteridophyta PsilotopsidaDocument25 pages1 Pteridophyta PsilotopsidaCDB 1st Semester 2077100% (1)
- Kingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratoryDocument6 pagesKingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Table of BryophytesDocument1 pageTable of BryophytesDenielle PayadNo ratings yet
- Fern and Fern Allies 1Document3 pagesFern and Fern Allies 1Paolo TenorioNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomArnavNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument6 pagesCestodesKathryn JeuelNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdominshakhalid2613No ratings yet
- RM 01 Family ChartDocument2 pagesRM 01 Family Chartyogitachandwani19No ratings yet
- Types of PteridophytesDocument1 pageTypes of PteridophytesprathitaprilNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdomrautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Day 2Document15 pagesDay 2saifali986254No ratings yet
- Class 11 Ch3 Pteridophytes L3Document15 pagesClass 11 Ch3 Pteridophytes L3Ayushman RanabirNo ratings yet
- 10-Kingdom PlantaeDocument67 pages10-Kingdom Plantaemilky waysssNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Mind MapDocument4 pagesAnimal Kingdom Mind MapVedanti Naik100% (5)
- Non-Chordates AnimalDocument58 pagesNon-Chordates AnimalToushik Ahamed MollaNo ratings yet
- Zoo 113 Module 3Document35 pagesZoo 113 Module 3Julienne LopezNo ratings yet
- Ribhav Bio Texts: Bryophyta Pteridophyta Gymnosperms AngiospermsDocument2 pagesRibhav Bio Texts: Bryophyta Pteridophyta Gymnosperms AngiospermsMrTeknoholicNo ratings yet
- Zbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Document15 pagesZbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Ashok ParasharNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BotanyDocument9 pagesReviewer BotanyDainielle ShayneNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom AlgaeDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdom AlgaeKhùśh NäùłákhāNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Cycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisDocument9 pagesCycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisTers MedinaNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document6 pagesCH 3Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- BryophytesDocument12 pagesBryophytesAiman KaleemNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fungi (Side Notes)Document4 pagesClassification of Fungi (Side Notes)Reca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- 2 - Bryophyta 17 OkDocument50 pages2 - Bryophyta 17 OkNuruli Fifi aNo ratings yet
- Fungi Kingdom Mycota / Mycetae / Fungi: Monophyletic GroupDocument15 pagesFungi Kingdom Mycota / Mycetae / Fungi: Monophyletic GroupAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Taxanomy - TableDocument1 pageTaxanomy - TableJue Vee LimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 3 Plant KingdomAnushka MishraNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages3 Plant KingdomitzanandNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument5 pagesBiological Classificationakshgoyal71No ratings yet
- Shaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolDocument62 pagesShaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Quick NotesDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdom Quick NotesDevesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomAanchal PandeyNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument7 pagesNotesVermillion ZedNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledsrishtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarDocument14 pagesChapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- Families NewDocument2 pagesFamilies New78x8qcpdq450% (2)
- Kingdom Plantae Animalia ChuchunessDocument61 pagesKingdom Plantae Animalia Chuchuness639289117867 JesusmygodNo ratings yet
- Kingdom ProtozoaDocument3 pagesKingdom ProtozoaIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsAMLAAN 10CNo ratings yet
- Exercise in Bio Lab Report 3Document4 pagesExercise in Bio Lab Report 3Ramnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet
- Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics RepresentatorsDocument1 pageTypes of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics RepresentatorsManja ĆetkovićNo ratings yet
- All FamilyDocument3 pagesAll FamilyRaunak KumarNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAngel MaryNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument72 pagesKingdom PlantaeMr. KNo ratings yet
- BryophytaDocument5 pagesBryophytaAakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Whitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForDocument2 pagesWhitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForLalit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Gametophyte or ProthallusDocument31 pagesGametophyte or Prothallusjha.crexa11No ratings yet
- 7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13Document2 pages7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13WillSmith100% (1)
- Briefly Policy Brief Funding For Effective Teen Pregnancy Prevention InterventionsDocument3 pagesBriefly Policy Brief Funding For Effective Teen Pregnancy Prevention InterventionsrosieNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument9 pagesReproduction in Plantsmr. unknownNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360Document10 pagesClass 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360ANo ratings yet
- Asexuality: An IntroductionDocument31 pagesAsexuality: An IntroductionRose Ann TubuNo ratings yet
- Give Woman A Hand JobDocument3 pagesGive Woman A Hand JobSparky100% (7)
- Vog QDocument62 pagesVog QDeep PatelNo ratings yet
- Son Mania 'Sex Selective Abortion Threat To Women's Position.'Document3 pagesSon Mania 'Sex Selective Abortion Threat To Women's Position.'tatevijayNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesDocument3 pagesReproductive System Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesMark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Ruth Deech and Anna Smajdor - From IVF To Immortality - Controversy in The Era of Reproductive Technology-Oxford University Press (2007)Document248 pagesRuth Deech and Anna Smajdor - From IVF To Immortality - Controversy in The Era of Reproductive Technology-Oxford University Press (2007)Marija PetrovićNo ratings yet
- ReproductivestrategiesDocument21 pagesReproductivestrategiesapi-241062194No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction TestsDocument3 pagesHuman Reproduction TestsKunchaya PitayawongroekNo ratings yet
- Power Point in Biology 2Document25 pagesPower Point in Biology 2ROJANE FLORANo ratings yet
- Inclusive-Language-Tool 1Document2 pagesInclusive-Language-Tool 1api-646865632No ratings yet
- Coitus Reservatus enDocument5 pagesCoitus Reservatus enmesagerdivin17100% (1)
- Penis Clitoris Vagina Cervix, Screwing MassageDocument4 pagesPenis Clitoris Vagina Cervix, Screwing MassageWellington G. Gallardo100% (1)
- Unpacking The Self - Physical and Sexual SelfDocument26 pagesUnpacking The Self - Physical and Sexual SelfDero100% (1)
- Veštačka Oplodnja ZečevaDocument5 pagesVeštačka Oplodnja ZečevamukebosNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography - Eng 112-401Document6 pagesAnnotated Bibliography - Eng 112-401api-490024204No ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument101 pagesInfertilityjojolilimomo100% (1)
- Sex EducationDocument2 pagesSex EducationNur RozieNo ratings yet
- TN XII - STD - Bio-Botany - English - Medium PDFDocument264 pagesTN XII - STD - Bio-Botany - English - Medium PDFSukantaSarkarNo ratings yet
- Sperm Recovery and SurvivalDocument6 pagesSperm Recovery and SurvivalArturo IturraldeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Sexual Orientations PP PresentationDocument42 pagesChapter 10-Sexual Orientations PP PresentationMuhammad Zaky AmaniNo ratings yet
- Best Sex Education and Sex PositionsDocument19 pagesBest Sex Education and Sex PositionsRamraje ShindeNo ratings yet
Plant Kingdom Chart
Plant Kingdom Chart
Uploaded by
garrysi6390 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pagePlant Kingdom Chart
Plant Kingdom Chart
Uploaded by
garrysi639Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
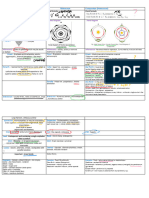
CHARACTER ALGAE BRYOPHYTE PTERIDOPHYTE GYMNOSPERM ANGIOSPERM
Habitat Mostly aquatic Amphibians of Plant K.
Mostly terrestrial Mostly perennial, evergreen, woody, xerophytic trees Mainly terrestrial
Some grow on other plants Mostly terrestrial
Need H2O for fertilization
Some symbiotic Lichen on Need H2O for fertilization
Moist, shady regions
Sloth Bears Moist, shady regions
Aquatic – Azolla, Marsilea
Xerophytic – Equisetum
Epiphytic - Lycopodium
Veg. Structure Thallus, Thalloid – Liverworts
Annual or perennial Roots – Tap Root, Stem, Leaves in variety
Unicellular Foliose – Leaf-like -
True Root (adventitious), stem, o Coralloid – Cycas + BGA
o Motile – Chlamydomonas Mosses leaves o Mycorhizzae – Pinus – Root + endophytic fungus
o Non Motile - Chlorella True roots absent, root- Leaves – Stem – Mostly erect, aerial, solid, cylindrical
Multicellular like rhizoids – Unicellular o Microphylls – (i) Scaly – o Unbranched – Cycas
o Unbranched – Spirogyra (Liverworts)/ Equisetum (ii) Simple Sessile – o Branched – Conifers - Pinus and Cedrus
o Branched – Chara Multicellular (Mosses) – Lycopodium Leaves – Dimorphic (adaptation)
o Macroscopic – Sargassum, Absorb H2O, nutrients and o Macrophyll - Pinnate - Ferns o Foliage – Simple, needle like/ pinnately compound
sea weed fixation Paleozoic era – golden age of o Scale – Small, brown membranous
o Colonial - Volvox pteridophytes
Spl. cell wall Inner Cellulose, Outer Pectin Inner Cellulose, Outer Pectin Inner Cellulose, Outer Pectin Inner Cellulose, Outer Pectin Inner Cellulose, Outer Pectin
Pigments Chl – a – All Chl – a – All Chl – a – All Chl – a – All Chl – a – All
Acessory – Chl – b, c, d; Acessory – Chl – b, c, d; Acessory – Chl – b, c, d; Acessory – Chl – b, c, d; carotenes, xanthophyll Acessory – Chl – b, c, d; carotenes,
carotenes, phycocyanin, carotenes, xanthophyll carotenes, xanthophyll xanthophyll
phycoerythrin, xanthophyll
Reserve food Starch, Laminarin starch, Starch Starch Starch Starch
Mannitol, Floridean starch
Reproduction Fragmentn – filamentous Vegetative prop. – Vegetative – Stolon Vegetative bulbils Vegetative – Tubers, rhizomes, etc. (Refer
Cell division – Unicellular Fragmentation, tuber & Asexual spores produced in Asexual – heterosporous MOFP)
Spores – Motile (zoospores) gemma Sporangia o P.G. in microsporangia Asexual – heterosporous to form
or non-motile (akinete/ Asexual – Spores o Mostly homosporous – E.g. o Megaspores in megasporangia gametophyte
oospores) Sexual - Gametes Lycopodium o They are formed in sporophyll which aggregate to o P.G. in microsporangia
Sexual – Gametes (Motile/ o Heterosporous – Salvinia, form cones/ strobilus/ lax o Megaspores in megasporangia
non-motile) Selaginella Sexual – Gametes – Anemophilous (wind), direct o Ovule in megasporophyll
(Iso – Chlamydomonas o Strobili – Selaginella, pollination (on ovule) – siphonogamous (pollen tube) Sexual – Gametes - Pollination indirect (on
(motile), Spirogyra (non Equisetum stigma) and siphonogamous – may be SP or
motile)/ Aniso – Sexual – Gametes CP – aided by accessory whorls (sepals and
Chlamydomonas some spp./ Apogamy – Haploid sporophyte petal)
Oogamous – Volvox, Fucus) without fertilisn Double Fertilisation
Apospory – Diploid gametophyte o MG + Egg = Zygote
w/o meiosis o MG + Sec. nucleus = PEN
Sporophyte Reduced and diploid Reduced and diploid Dominant, diploid Dominant, diploid Dominant, diploid
Dependent on gametophyte Patially Dependent on Independent Independent Independent
gametophyte Prostate and erect
Gametophyte Dominant and haploid Dominant and haploid Reduced, haploid Recessive, haploid Recessive, haploid
Independent Independent Independent Dependent on sporophyte Dependent on sporophyte
Seeds Absent Absent Absent Phanerogams w/o ovary Present
Flower, Fruit Absent Absent Absent Non-flowering, naked seeds Present
Vascular Absent Absent Primitive Vascular Tracheids and Sieve cells Xylem – Trachea/ Vessels
System Tracheids & Sieve cells Sec. growth due to presence of cambium Sieve tubes & Companion cells
Annular rings are distinct
Other 760 genera, 24000 spp 400 genera, 10500 spp 70 genera, 7255 spp; India -16 genera, 53 spp. Smallest wolffia – 1mm
Imp. Role in succession Living fossil – Gingko biloba Tallest – Eucalyptus – 100 m
on bare rocks/ soil World’s tallest living – Sequia sempervirens -
Californian Giant red wood – 366 feet
Largest girth – Taxodium mucronatum – 125 ft
Smallest – Zamia pygmia – 25 cm
You might also like
- New Families Added in NEET 2024 SyllabusDocument8 pagesNew Families Added in NEET 2024 Syllabusvm4327489100% (16)
- Pregnancy Miracle - Holistic and Ancient Chinese System For Getting Pregnant and Having Healthy BabiesDocument99 pagesPregnancy Miracle - Holistic and Ancient Chinese System For Getting Pregnant and Having Healthy BabiesNicole Kaylee20% (10)
- PPT-Science 7 - ReproductionDocument34 pagesPPT-Science 7 - ReproductionArima Kousei50% (4)
- Red Pill BooksDocument2 pagesRed Pill Bookssinchonglo80% (5)
- Atlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaFrom EverandAtlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Sexual EcstasyDocument10 pagesSecrets of Sexual EcstasyGreat HelpNo ratings yet
- Growing Up and Liking ItDocument16 pagesGrowing Up and Liking Iturbster1No ratings yet
- .Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesDocument10 pages.Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWrajatbharti830No ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationketakiNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom PowernotesDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdom Powernotessheikhanzar643No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom M PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom M PDFAbu SubhanNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomInfinite SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 Pteridophyta PsilotopsidaDocument25 pages1 Pteridophyta PsilotopsidaCDB 1st Semester 2077100% (1)
- Kingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratoryDocument6 pagesKingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Table of BryophytesDocument1 pageTable of BryophytesDenielle PayadNo ratings yet
- Fern and Fern Allies 1Document3 pagesFern and Fern Allies 1Paolo TenorioNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomArnavNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument6 pagesCestodesKathryn JeuelNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdominshakhalid2613No ratings yet
- RM 01 Family ChartDocument2 pagesRM 01 Family Chartyogitachandwani19No ratings yet
- Types of PteridophytesDocument1 pageTypes of PteridophytesprathitaprilNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdomrautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Day 2Document15 pagesDay 2saifali986254No ratings yet
- Class 11 Ch3 Pteridophytes L3Document15 pagesClass 11 Ch3 Pteridophytes L3Ayushman RanabirNo ratings yet
- 10-Kingdom PlantaeDocument67 pages10-Kingdom Plantaemilky waysssNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Mind MapDocument4 pagesAnimal Kingdom Mind MapVedanti Naik100% (5)
- Non-Chordates AnimalDocument58 pagesNon-Chordates AnimalToushik Ahamed MollaNo ratings yet
- Zoo 113 Module 3Document35 pagesZoo 113 Module 3Julienne LopezNo ratings yet
- Ribhav Bio Texts: Bryophyta Pteridophyta Gymnosperms AngiospermsDocument2 pagesRibhav Bio Texts: Bryophyta Pteridophyta Gymnosperms AngiospermsMrTeknoholicNo ratings yet
- Zbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Document15 pagesZbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Ashok ParasharNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BotanyDocument9 pagesReviewer BotanyDainielle ShayneNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom AlgaeDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdom AlgaeKhùśh NäùłákhāNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Cycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisDocument9 pagesCycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisTers MedinaNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document6 pagesCH 3Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- BryophytesDocument12 pagesBryophytesAiman KaleemNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fungi (Side Notes)Document4 pagesClassification of Fungi (Side Notes)Reca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- 2 - Bryophyta 17 OkDocument50 pages2 - Bryophyta 17 OkNuruli Fifi aNo ratings yet
- Fungi Kingdom Mycota / Mycetae / Fungi: Monophyletic GroupDocument15 pagesFungi Kingdom Mycota / Mycetae / Fungi: Monophyletic GroupAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Taxanomy - TableDocument1 pageTaxanomy - TableJue Vee LimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 3 Plant KingdomAnushka MishraNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages3 Plant KingdomitzanandNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument5 pagesBiological Classificationakshgoyal71No ratings yet
- Shaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolDocument62 pagesShaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Quick NotesDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdom Quick NotesDevesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomAanchal PandeyNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument7 pagesNotesVermillion ZedNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledsrishtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarDocument14 pagesChapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- Families NewDocument2 pagesFamilies New78x8qcpdq450% (2)
- Kingdom Plantae Animalia ChuchunessDocument61 pagesKingdom Plantae Animalia Chuchuness639289117867 JesusmygodNo ratings yet
- Kingdom ProtozoaDocument3 pagesKingdom ProtozoaIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsAMLAAN 10CNo ratings yet
- Exercise in Bio Lab Report 3Document4 pagesExercise in Bio Lab Report 3Ramnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet
- Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics RepresentatorsDocument1 pageTypes of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics RepresentatorsManja ĆetkovićNo ratings yet
- All FamilyDocument3 pagesAll FamilyRaunak KumarNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAngel MaryNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument72 pagesKingdom PlantaeMr. KNo ratings yet
- BryophytaDocument5 pagesBryophytaAakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Whitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForDocument2 pagesWhitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForLalit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Gametophyte or ProthallusDocument31 pagesGametophyte or Prothallusjha.crexa11No ratings yet
- 7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13Document2 pages7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13WillSmith100% (1)
- Briefly Policy Brief Funding For Effective Teen Pregnancy Prevention InterventionsDocument3 pagesBriefly Policy Brief Funding For Effective Teen Pregnancy Prevention InterventionsrosieNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument9 pagesReproduction in Plantsmr. unknownNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360Document10 pagesClass 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360ANo ratings yet
- Asexuality: An IntroductionDocument31 pagesAsexuality: An IntroductionRose Ann TubuNo ratings yet
- Give Woman A Hand JobDocument3 pagesGive Woman A Hand JobSparky100% (7)
- Vog QDocument62 pagesVog QDeep PatelNo ratings yet
- Son Mania 'Sex Selective Abortion Threat To Women's Position.'Document3 pagesSon Mania 'Sex Selective Abortion Threat To Women's Position.'tatevijayNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesDocument3 pagesReproductive System Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesMark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Ruth Deech and Anna Smajdor - From IVF To Immortality - Controversy in The Era of Reproductive Technology-Oxford University Press (2007)Document248 pagesRuth Deech and Anna Smajdor - From IVF To Immortality - Controversy in The Era of Reproductive Technology-Oxford University Press (2007)Marija PetrovićNo ratings yet
- ReproductivestrategiesDocument21 pagesReproductivestrategiesapi-241062194No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction TestsDocument3 pagesHuman Reproduction TestsKunchaya PitayawongroekNo ratings yet
- Power Point in Biology 2Document25 pagesPower Point in Biology 2ROJANE FLORANo ratings yet
- Inclusive-Language-Tool 1Document2 pagesInclusive-Language-Tool 1api-646865632No ratings yet
- Coitus Reservatus enDocument5 pagesCoitus Reservatus enmesagerdivin17100% (1)
- Penis Clitoris Vagina Cervix, Screwing MassageDocument4 pagesPenis Clitoris Vagina Cervix, Screwing MassageWellington G. Gallardo100% (1)
- Unpacking The Self - Physical and Sexual SelfDocument26 pagesUnpacking The Self - Physical and Sexual SelfDero100% (1)
- Veštačka Oplodnja ZečevaDocument5 pagesVeštačka Oplodnja ZečevamukebosNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography - Eng 112-401Document6 pagesAnnotated Bibliography - Eng 112-401api-490024204No ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument101 pagesInfertilityjojolilimomo100% (1)
- Sex EducationDocument2 pagesSex EducationNur RozieNo ratings yet
- TN XII - STD - Bio-Botany - English - Medium PDFDocument264 pagesTN XII - STD - Bio-Botany - English - Medium PDFSukantaSarkarNo ratings yet
- Sperm Recovery and SurvivalDocument6 pagesSperm Recovery and SurvivalArturo IturraldeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Sexual Orientations PP PresentationDocument42 pagesChapter 10-Sexual Orientations PP PresentationMuhammad Zaky AmaniNo ratings yet
- Best Sex Education and Sex PositionsDocument19 pagesBest Sex Education and Sex PositionsRamraje ShindeNo ratings yet