Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Pathology Notes 1
Oral Pathology Notes 1
Uploaded by
MohamadWehbiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- INBDE High-Yield Conditions To KnowDocument17 pagesINBDE High-Yield Conditions To KnowРами Кальмат100% (1)
- Class I, II & VI Amalgam RestorationDocument2 pagesClass I, II & VI Amalgam RestorationSahil SraNo ratings yet
- Patho Lec 4THDocument3 pagesPatho Lec 4THJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Anomalies - LectureDocument10 pagesAnatomic Anomalies - LectureKhalid BhatNo ratings yet
- Classification of Anomaly2Document213 pagesClassification of Anomaly2samar yousif mohamed100% (1)
- Cawsons Chapter 2Document4 pagesCawsons Chapter 2Katie WithersNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Teeth Eruption, Structure, Form, Number, and SizeDocument48 pagesAbnormalities of Teeth Eruption, Structure, Form, Number, and SizeNoor AlsanouriNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Teeth1.2020Document5 pagesAbnormalities of Teeth1.2020Farhaana ShaboodienNo ratings yet
- Dr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyDocument62 pagesDr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyoladunniNo ratings yet
- Dev Dis ToothDocument92 pagesDev Dis ToothVaishnavi ThatiparthiNo ratings yet
- Developmental DefectsDocument29 pagesDevelopmental DefectsPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Oral Path PDFDocument367 pagesOral Path PDFAashka Desai100% (2)
- Developmental Anomalies of TeethDocument78 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of TeethPauline Joy Cayago CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dental Anomalies ملخصDocument8 pagesDental Anomalies ملخصهند عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Sequelae of TraumaDocument27 pagesSequelae of TraumaDr.O.R.GANESAMURTHINo ratings yet
- Dental Anomalies Lecture IIDocument23 pagesDental Anomalies Lecture IIqpnbzsbkqgNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Teeth: Environmental and Developmental AlterationsDocument114 pagesAbnormalities of Teeth: Environmental and Developmental AlterationsoiljimmyNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of The Teeth PDFDocument75 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of The Teeth PDFIbrahim HashimiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic IIDocument11 pagesTherapeutic IIkimiaNo ratings yet
- Pathological AnalysisDocument58 pagesPathological AnalysisAhella AlaaNo ratings yet
- Aetiology of MalocclusionDocument5 pagesAetiology of MalocclusionSRO oONo ratings yet
- Os MidtermDocument2 pagesOs MidtermGuen ColisNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery 5Document18 pagesOral Surgery 5youssefkamal838No ratings yet
- Patología ORAL MVRDocument18 pagesPatología ORAL MVRMonserrath VidalesNo ratings yet
- Developmental TeethDocument53 pagesDevelopmental Teethlyli Star AngeloNo ratings yet
- APznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17ZdDocument24 pagesAPznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17Zdclassybrands0No ratings yet
- Odontogenic TumorsDocument32 pagesOdontogenic Tumorssatya_mds100% (2)
- Oral PathologyDocument184 pagesOral Pathologyyalahopa100% (1)
- Oral Pathology ModuleDocument31 pagesOral Pathology ModuleDenee Vem MatorresNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Pathology: Glo Arby Arguelles, DMDDocument27 pagesPediatric Pathology: Glo Arby Arguelles, DMDRayne GelleNo ratings yet
- ORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensDocument24 pagesORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensPravin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologyDocument38 pagesDevelopmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologydrchakshuaggarwalNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of Tooth PDFDocument97 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of Tooth PDFEmad AlriashyNo ratings yet
- Dental AbnormalitiesDocument19 pagesDental AbnormalitiesKha KinNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumors IIDocument24 pagesOdontogenic Tumors IIIbn HabibNo ratings yet
- Pedo2013 14Document189 pagesPedo2013 14Vladimir Argirovic100% (4)
- OriginalDocument10 pagesOriginalAmir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Q1. Difference Between:: GeminationDocument3 pagesQ1. Difference Between:: GeminationRadaina NiazNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DentistryDocument96 pagesPediatric DentistryChinielee R ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Document41 pagesCysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Seca mandiNo ratings yet
- Dental TerminologiesDocument2 pagesDental TerminologiesPauline BulaunNo ratings yet
- Ortho - Application-As-A-GdpDocument8 pagesOrtho - Application-As-A-Gdprajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Toolbox: Oral Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesToolbox: Oral Health and Diseasena rinNo ratings yet
- Toolbox: Oral Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesToolbox: Oral Health and DiseasePrimaNo ratings yet
- ECTOPICERUPTION HandoutDocument4 pagesECTOPICERUPTION HandoutDr-Basel RehawiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders of TeethDocument64 pagesDevelopmental Disorders of TeethPatterson MachariaNo ratings yet
- Enamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationDocument41 pagesEnamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationMohammad ANo ratings yet
- Teeth DefectsDocument32 pagesTeeth DefectsManoj NaiduNo ratings yet
- Variation in Tooth Morphology Anatomy PDFDocument9 pagesVariation in Tooth Morphology Anatomy PDFadriiianaiiioanaNo ratings yet
- $pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerDocument96 pages$pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerGhadeerHassaanNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2008 35 636-641Document5 pagesDent Update 2008 35 636-641bkprosthoNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2008 35 636-641 PDFDocument5 pagesDent Update 2008 35 636-641 PDFbkprosthoNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiology: A Guide To Radiographic InterpretationDocument16 pagesDental Radiology: A Guide To Radiographic InterpretationCeline BerjotNo ratings yet
- XXXXX 22222Document5 pagesXXXXX 22222Hans GuilasNo ratings yet
- Structure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Document36 pagesStructure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Khushi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Sakeena Assad PresentationDocument93 pagesSakeena Assad Presentationjenny girlNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Macroscopic Anatomy and Pulp Space MorphologyDocument24 pagesMacroscopic Anatomy and Pulp Space MorphologyKhaled Elshabrawy100% (1)
- Kti Vida HusniaDocument49 pagesKti Vida HusniaElsa AghniaNo ratings yet
- L5 Dental Indices SSDocument77 pagesL5 Dental Indices SSShmoukhNo ratings yet
- Facemask MC NamaraDocument11 pagesFacemask MC NamaraMenakaNo ratings yet
- 2007 - Orthodontics and MicroimplantsDocument356 pages2007 - Orthodontics and MicroimplantsInês FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Management of Impacted Maxillary Canines Using The Kilroy Spring: A Case SeriesDocument7 pagesManagement of Impacted Maxillary Canines Using The Kilroy Spring: A Case SeriesThang Nguyen TienNo ratings yet
- Tooth PreparationDocument105 pagesTooth Preparationbarsha0% (1)
- Majalah Ikorti Des 2016 PDFDocument54 pagesMajalah Ikorti Des 2016 PDFvalitAuliaNo ratings yet
- EndoTriad May2015Document7 pagesEndoTriad May2015puspasimanungkalit270586No ratings yet
- Management of Ankylosed Primary Molars With Premolar Successors A Systematic ReviewDocument11 pagesManagement of Ankylosed Primary Molars With Premolar Successors A Systematic ReviewIbraheem SNo ratings yet
- The Bone Shielding Versus Dual-Zone Concept in TreatingDocument13 pagesThe Bone Shielding Versus Dual-Zone Concept in Treatingahmadalturaiki1No ratings yet
- Prezzano 1951Document10 pagesPrezzano 1951Rockey ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Modern Anterior Endodontic Access and Directed Dentin Conservation David Clark & John Khademi PDFDocument5 pagesModern Anterior Endodontic Access and Directed Dentin Conservation David Clark & John Khademi PDFizeldien5870No ratings yet
- The Bionator: British Journal of OrthodonticsDocument5 pagesThe Bionator: British Journal of OrthodonticsRaphael DutraNo ratings yet
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument69 pagesClassification of MalocclusionBatman 02053No ratings yet
- FogfelismerésDocument11 pagesFogfelismerésdb nklttNo ratings yet
- Incisors - Type TraitsDocument4 pagesIncisors - Type TraitsVanissa KarisNo ratings yet
- Deep-Bite Fontaine-Sylvestre - CatherineDocument126 pagesDeep-Bite Fontaine-Sylvestre - CatherineEttore AccivileNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Occlusion On 11 May 2022Document25 pagesSeminar On Occlusion On 11 May 2022Dr Saurav kumar DuttaNo ratings yet
- PD 4.histopathology of Dental CariesDocument40 pagesPD 4.histopathology of Dental CariesUmaima Khan100% (1)
- Stainless Steel CrownDocument6 pagesStainless Steel CrownWen Shu GohNo ratings yet
- BleachingDocument62 pagesBleachingوردة صبرNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy QuizDocument5 pagesDental Anatomy QuizSereen Abd El-rahman0% (1)
- Radiology Paralleling TechniqueDocument67 pagesRadiology Paralleling TechniqueFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument51 pagesClassification of MalocclusionYuvashreeNo ratings yet
- Prepared Cavities On The StrenDocument4 pagesPrepared Cavities On The StrenPriyank RaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PulpDocument10 pagesLecture 5 Pulpمؤمل رياض سعد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Botos Alexandra - Oral SemiologyDocument46 pagesBotos Alexandra - Oral SemiologyMaria OlteanNo ratings yet
- Abutments in Fixed Partial DenturesDocument19 pagesAbutments in Fixed Partial DenturesKashish08No ratings yet
Oral Pathology Notes 1
Oral Pathology Notes 1
Uploaded by
MohamadWehbiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oral Pathology Notes 1
Oral Pathology Notes 1
Uploaded by
MohamadWehbiCopyright:
Available Formats
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
Oral Pathology Keywords
Study online at quizlet.com/_8i4lm8
1. Anadotia All teeth are missing, rarely occurs, usually ass. with Hereditry Ectodermal Dysplasia
2. Partial anodotia Congenital absence of one or more, most common
Upper lateral incisor, Lower second premolar
Uncommon in primary, if happens usually upper B
3. Oligodontia absence of 6 or more
4. Hypodontia absence of less than 6 teeth
5. Supernumerary teeth More common in Maxilla than mandible, like Mesiodens, distomolar & paramolar, +1
6. Mesiodens Most common supernumerary teeth, smaller with cone shaped crown & short roots.
Removal just prior to eruption of permanent teeth
7. Natal & Neonatal Teeth present when baby born or in the first 30 days, usually it's just prematurely erupted deciduous
teeth 90%
Removal only if mobile with risk of aspiration
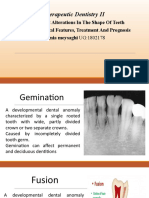
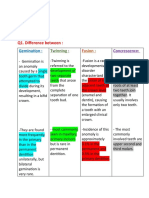
8. Gemenation 2 crown, 1 root with same number of teeth, usually bifid crown and in incisor primary teeth
9. Fusion Fusion of 2 separate tooth buds, number -1, usually in Mandible primary incisors
10. Twinning Complete division of single bud into 2 teeth, number +1
11. Concrescence Union of roots of 2 teeth or more by confluence of their Cementum, related to truma, Commonly
upper 7&8.
12. Dens-in-Dent Invagination "A tooth within a tooth"; a developmental anomaly that results when the enamel organ invaginates
into the crown of a tooth before mineralization.
Maxillary lateral incisor are the most common tooth
Thin layer of Enamel make it vulnerable & easy to develop pulpitis & pulp necrosis
13. Dens evaginatus Evagination of the inner enamel Epi., more common in Premolars mandibular teeth.
Accessory cusp which contain enamel & dentin, with pulp in only 50%.
Posterior --- Cusp of carebelli
Anterior --- Talon cusp or Shovel-shaped incisors
14. Ankylosis Replacement Cementum directly with bone, many factors like trauma or thermal irritation.
resorption Most Common Primary lower D&E then Upper D&E. Permanent Upper & lower first molar then
Upper Canine.
Infra occlusion with metallic solid sound with percussion.
15. Hypersementosis Cemental Secondry cementum usually confined to apical half or the root, VITAL mandibular molars &
Hyperplasia premolars.
Unbroken periodontal membrane space & normal lamina dura
Assio. with Pager's disease
16. Dilaceration Abnormal curve of the root, result of trauma.
Assio. with congenital ichthyosis
Require surgical removal
17. Taurodontism Bull-like tooth Large & long pulp chamber with bifurcation close to the root apex.
Due to Late invagination of Hertwig's rooth sheath
Usually in pt. with Hypodontia, cleft lip & palate
18. Ectopic enamel Enamel Cells of Hertwig's Epi. root sheath do not migrate away from the dentin & differentiate into
pearls Enameloma ameloblast giving enamel
Maxillary molar are the most common site in bi & tri furcation area
X-Ray--- Well defined RO nodules along the rooth surface
19. Abrasion Non-masticatory, due to mechanical forces usually horizontal tooth brushing, common in contra
lateral side of the Pt. dominant hand.
V-shaped wide notch in cervical area, affecting more than 1 teeth, usually canine & premolars.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
20. Attrition Up normal mastication like bruxism leaves bolished Facets on incisal & occlusal surfaces.
Assio. with Class III & edge to edge, considered normal in old age.
21. Erosion Non mechanical it's chemical in nature, in Pt. with bulimic condition, usually affect the palatal of
upper incisors.
May affect the buccal aspect, if it's due to using Aspirin tablets or citrus foods.
22. Abfraction Masticatory in nature, fracture off due to flexure of the tooth.
Deep narrow v-shaped, may affect single tooth
23. Amelogenesis Imperfecta Inherited ectodermal disorder, 3 types:
1-Hypoplastic:
Most common form, defect in the amount of enamel present it's well mineralized & does not
chip.
Teeth are smaler than normal with open interproximal contact, normal to opaque white color,
X-ray Enamel is more RO than dentin
2-Hypomaturation:
Normal thickness but matrix is immature (containing residual enamel protein), enamel chips
easily.
Creamy opaque to yellow/brown color, With soft & rough surface.
Dental sensitivity, X-ray E=D in RO
3-Hypocalcified:
Enamel is normal in thickness & poorly calcified (Lack of enamel protien), chips easily same
like Hypomaturation but X-ray E less RO than dentin.
24. Enamel hypoplasia Localized form affecting few teeth, due to environmental factors rather than genetic, small pits
or affect the entire surface, both sets of teeth are affected.
Open contact, rapid break down of occlusal surface with yellowish- brown color.
Assio. Vit. A,C & D diffidence
25. Turner's hypoplasia Local infection or truma to the primary teeth, usually affect permanent premolars, defect may
be just spot or affect the whole surface.
26. Dental fluorosis Excess amount of Fluoride, appears white & chalky area to mottled brown, severity is dose
dependent.
Water fluoridation usually between 0.7-1.2 PPM.
Affect the crowns of Maxillary central incisors
27. Dentinogenesis Imperfecta - autosomal dominant disorders, Enamel is normal but chips due to week dentin beneath, with
Hereditary opalescent dentin translucent or opalescent appearance with yellow-brown to grey color.
Excessive constrication at CEL leads to Bell or Tulip shape, 3 types:
1- Type 1:
Assio. with Osteogenesis imperfecta with history of bone fracture & blue sclera.
Obliterated pulp chambers, bulbous crown, short roots & amber color.
Primary more affected than permanent teeth
2-Type 2:
Same as 1 but without Osteogenesis imperfecta, Primary & permanent are equally affected.
3-Type 3: Brandywine type Multiple pulp exposure & periapical RL, as the dentin is thin with
large pulp champers. Shell like appearance
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
28. Dentin Dysplasia autosomal dominant disorder not related to dentinogenesis imperfecta or osteogenesis
1- Type 1 Radicular dysplasia:
Most common type, primary & permanent are affected with NORMAL appearance & color, with
increased mobility.
Extremely short roots, obliterated pulp chambers & Periapical RL
CHEVRONS
2- Type 2 Coronal dysplasia
Primary are opalescent while permanent are normal in color.
Enlarged pulp chambers with Thistle tube appearance with pulp stones. No periapical RL.
29. Regional odontodysplasia Localized non hereditary abnormalities affect ALL E,D& pulp.
More common in upper permanent anterior teeth, which appear as ghost teeth with short roots,
open apices & enlarged pulp chambers.
30. Melanoplakia Generalized, symmetrical & presistant pigmentation.
Darker skin people in attached gingiva.
Increase melanin production in basal keratinocytes
No increase in melanocytes with No TTT
31. Smoker's melanoma Increase in melanin production in basal layer due to chemicals from tobaco.
It's benign condition with no increase in melanocytes
Lower anterior labial mucosa, stop smokingg result in improvement in months or years.
Biopsy incase of sudden increase or irregulates
32. Malanotic macule - Focal Most common melanotic lesion
melanosis Focal increase in melanin production which is solitary, well demarcated, dark to brown
asymptomatic 7MM or less.
Vermilion border of lower lip, which is independent of sun exposure.
No malignant transformation
33. Nevus - Moles congenital (Higher chance of malignant transformation) or acquired (More common)
Due to increase in numbers of melanocytes.
Raised dark growth 1 Cm in diameter, which is more in skin than oral cavity.
Oral --- Hard palate, gingiva or lip
Intramucosal --- Most common intraorally
Intradermal --- Most common lesion of skin
Junctional --- Most common acquired malignant transformation
No TTT, biopsy only if ulceration or increase in size
34. Peutz-Jeghers syndrom - autosomal dominant disorder, ChCh. with
Hereditary interstinal polyposis Multiple macules
Gastrointestinal polyps
Gastrointestinal polyps in small intestine Jejunum & Ileum hich is painful with rectal bleeding and
diarrhea and malignant trasformation --- Colorectal adenocarcinoma
Intraoral & preoral macule which is first to appear in lower lip, buccal mucosa, gingiva & hard
palate
35. Muccune-Albright syndrom genetic disorder with Tried
- Polystotic fibrous dysplasia
- Cafe-au-lait pigmentation well defined or irregular usually unilateral tan macule on trunk &
thighs
- Endocrine dysfunction with precocious puberty breast Dev. & premature vaginal bleeding and
pubic hear growth
Pigmentation usually at Truck, thigh & oral sometimes
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
36. Addison's disease destruction of adrenal cortex leads to insufficient production of corticosteriods.
Leads to increase production of ACTH which is created from same precursors as MSH, which
stimulates malanocytes to do more melanin.
Bronzing of the skin, with diffuse batchy macule pigmentation
Leads to weakness, irritability, depression and fatigue wt/ loss, HT, N&V.
Gingiva, tongue, hard palate & buccal mucosa
37. Amalgam tatto - Focal argyosis Most common oral pigmentation
Due to amalgam restoration in oral cavity
black-blue to gray macule, well defined or irregular or diffuse
Gingiva, buccal mucosa & Alveolar ridge
X-ray --- RO particles siver fragment in C.T
No TTT
Excisional biopsy may be done to confirm
38. Heavy metal ingestion Bluish line of the marginal gingiva or spots on papollae
due to ingestion of arcenic, bismuth, lead or silver
used to treat diseases
39. Drug induced pigmentation Minocycline cause pigmentation of the alveolar bone
Choroquine --- Blue or gray on palate as it stimulate melanocytes.
Discontinue using of medication leads to fading of the pigmentation
40. B-L mole syndrome - Dysplastic Large pigmentation usually atypical nevi with high risk of malignant transformation
nevus syndrome
41. Acute atrophic candidiasis Candidiasis happens due to long term use of broad spectrum AB.
(Antibiotic sore mouth) Painful attophic patches intraorally
Cytological smear --- Hyphae present
TTT --- Stop AB and use antifungal drugs
42. Chronic atrophic candidiasis Asymptomatic red lesion on the palate of denture wearers.
(Denture stomatitis) ill fitting denture with poor oral hygiene who wear the denture over night.
Xerostmia and candida organism are contributing factors.
start as area if hyperemia to diffuse erythema then papillary hyperplasia in advanced stages.
TTT --- Anti fungal drugs and fix the denture to remove the cause.
surgical excision is needed in severe cases to remove the tissue before doing a new denture
43. Median Rhomboid Glossitis ( Central Asymptomatic Smooth & erythematous rhomboid patch on the mid dorsal of the tongue,
papillary atrophy) lack the filiform papillae.
Just anterior to cirumvallate papillae
Caused by Candida Albicans infection
Pt is usually diabetic or immunosuppressed
may be found in the junction between soft & hard palate --- Kissing lession
44. Angular cheilitis Multifactor disorder with inflammation, erythema, fissuring, erosion of the angle of the mouth.
Candida, Staphylococci, streptococci, iron def. anemia, Vit. B def. Reduced vertical dimension
burning sensation with time of remission& exacerbation
TTT --- remove the cause
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
45. Burning mouth syndrome BMS Pt. feels the lining of his mouth is being scaled (burned) --- Metalic test despite the
(stomatopyrosis, glossopyrosis) normal saliva & the lining of the mouth appears NORMAL.
Post menopausal women.
Anterior 2/3 of the tongue
Diagnosis of exclusion --- Based on detailed history, clinical examination &
LABORATORY STUDIES
SECONDRY BMS
ass. with underling local (Xerostomia, chronic mouth breathing, oral candidiasis)
or systemic (Vit B def. anxiety, stress & depression)
TTT
1- Correcting underlying condition
2- Pharmacologic therapies
3- Cognitive behavioral therapy
46. Erythroplakia Pre-malignant red patch, which is well demarcated & fairy red with smooth velvety
surface.
Old pt 50-70 Male=Females
less common but much greater potential for malignancy
Location --- Floor of the mouth, tongue & soft palate.
Asymptomatic usually and may be ass. with leukoplakia
Ass. with Tobacco & alcohol
Histology ---
Lack of keratin or even atrophic
90% show severe dysplasia, carcinoma in situ or invasion squamous
TTT --- Excision with long term follow up & removal of the cause
47. Osler-Rendu-Webner syndrome numerous spider like telangiectasia & anteriovenous fistula --- Liver & lung which is
(Hereditary hemoragic telangiectasia) fragile and rapture easily causing GIT bleeding & iron def. anemia.
may also be found on face, neck, chest, lips & Gingiva
It's small dilated arteries near the surface of the skin or mucosa 1-3 MM
Frequent nosebleeds.
48. Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis macular Hemangioma that follows the distribution of the trigeminal nerve --- Port wine
(Sturage-Webner syndrome) stain
Uncommon congenital disorder
Neurological problems include seizures & intellectual disabilities
Glaucoma is also present
Intraoral --- hype vascular changes in the ipsilateral of the gingiva which may leads to
gingival hyperplasia
TTT --- Anticonvulsant therapy is used to control both
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
49. Hemangiomas & Most common tumor of the childhood, more in females
Vascular malformation Benign tumors arise during the first 8 weeks of life
Location --- Dorsum of the tongue, gingiva & buccal mucosa
At age of 5 --- 50% resolved
At age of 9 --- 90% resolved
After age of 9 --- 10% presistant
Vascular malformation
structural abnormalities of BV with normal endothelial turnover
Present at birth and persist all life
Range in color from red to blue
2 types:
Capillary -- small vessels
Cavernous -- large thin walled vascular spaces
Congenital hemangioma Strawberry Nevus
form of hemangioma fully formed at birth
Diascopy to differentiate between
Hemangioma -- blanch
Hematomas -- No blanch
50. Varix (Varicosity) acquired vascular malformation with focal dilation of a single vein
Rare in children and common in old pt.
Location --- Sublingual, lip & buccal mucosa
Blanch with compression & usually Asymptomatic with no TTT
51. Pyogenic Granuloma Mass of vascular granulation tissue due to minor trauma or chronic irritation
( Lobular capillary No infection No pus
hemangioma) Present as Pedunculated or sessile exophytic mass with deep red color
Bleeds easily as it's highly vascular and have a raspberry-like appearance.
Pregnant pt. which usually resoles after pregnancy
TTT -- excision & debridement down to periosteum
Recurrence 3-15%
52. Peripheral giant cell well-defined firm growth occurs on the gingiva or edentulous ridge with sessile base and smooth or
granuloma slightly granular surface and color from pink to dark red bluish purple.
Found on the mandible between first molar and the incisors
It's a REACTIVE LESION
Can't be distinguished from Pyogenic granuloma CLINICALLY
BUT
It's aggressive in nature, may leads to bone resorption leading to Cup shaped RL in x-ray.
Histologically --- Fibroblast & Multinucleated giant cells in a stroma containing collagen
TTT--- conservative excision & curettage of the underlying bone
10-18% recurrence
53. Epulis Granulomatosa Benign tumor on the gingiva or alveolar mucosa represent hyperplastic granulation tissue arises from post
EXO socket.
Caused by retained foreign material in the socket
Soft & bleeds easily.
TTT --- Curettage
54. parulis (Gum boil) raddish, raised sessile nodule on the gingiva on the site of a draining sinus tract
Pain is typical, but as pus escape pain is relieved
Gutta percha is used to tract the source of the pus to the tooth with X-Ray.
TTT --- Exo or RCT to the tooth
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
55. Traumatic Ulcer Solitary, erythema, yellow base, red halo. History of trauma.
Acute -- Pain Labial/Buccal mucosa, palate and tongue
Chronic -- No pain with elevated margins Especially in tongue Clinical appearance
mimics carcinoma and infectious ulcers
TTT Correct the cause first, wait for healing, otherwise take biopsy. Topical anesthetic.
Heal in 7-10 D after removal of the cause, if not Biobsy
56. Recurrent Aphtous (Canker sore) Multiple painful recurrent ulcers, white/gray or yellow surrounded by a bright red halo.
Related to T.cell mediated immunologic reaction. More common in Females, between 10
to 30 YO. Occasional prodromal symptoms of tingling or burning.
Ulcers NOT preceded by Vesicles
Minor
Most common, 1-5 per event less than 1 Cm with few recurrence in buccal & labial
mucosa, last 7-10 days heal with out a scar
Major
1-10 per event, larger & deeper 1-3 Cm, common in HIV pt, labial mucosa & soft palate,
last up to 6 weeks heal with a scar
Herpatiform
The greatest number & recurrence
100 per event, minic Hepres but in UNKERATINIZED mucosa like
Vestibular & buccal mucosa, last 7-10 days heal with out a scar.
- Systemic disorders that increase the prevalence of aphtous-like ulcers:
Crohn's disease, Behcet's syndrome, Celiac sprue, AIDS, Cyclic neutropenia, Nutritional
deficiencies
TTT --- Palliative for discomfort (Topical anesthetics), topical corticosteroids.
57. Behcet's Syndrome Immune syndrome triggered by infectious or environmental agent in a genetically
predisposed individual. Males, 30-40 YO.
1- Small vessel vasculitis
2- Recurrent oral (mostly minor aphtous in Soft palate and oropharynx)
3- eye: conjunctivitis, uveitis and genital aphtous-type ulcers.
TTT --- Steroids and immunosuppressants
58. Wegener Granulomatosis Vasculitis + Necrosis + Granulomas. Rare chronic immune disorder, unknown cause.
(Granulomatosis with polyangiitis)
Lesions of respiratory tract, necrotizing glomerulonephritis, vasculitis of small vessels.
Oral: Strawberry gingivitis, ulceration on any mucosal surface.
Clinical presentation + microscopic findinsg of necrotizing and granulomatous vasculitis
will lead the diagnose
Lab markers: cANCAs and pANCAs
TTT--- Corticosteroids and Cyclophosphamide (chemo drug)
59. Midline Granuloma - Malignant Thought to be a peripheral representation of T-cell lymphomas
granuloma - Lethal midline granuloma Unifocal, destructive and aggressive process.
Midline of the oronasal region, perforation of nasal septum and hard palate may be seen.
Necrotic ulcers, progressive and nonhealing.
TTT --- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
60. Deep Fungal Oral lesions appear as indurated, painful, nonhealing ulcers.
Infections
Primary involvement of lungs.
Oral: tongue, palate, buccal mucosa
Causative organism --- Histoplasmosis and Coccidiodomycosis
61. Opportunistic 2nd most common fungal infection in Pts on chemo after candidiasis
Fungal Infections
Causative organism --- genera Mucor and Rhizopus
Mucormycosis (Zygomycosis):
insulin-dependent diabetics, with uncontrolled diabetes and ketoacidotic. Immunocompromised Pts ( AIDS,
bone marrow transplant recipients, corticosteroid therapy)
Destructive ulcerations in palate, paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity.
TTT --- Amphotericin B
Aspergillosis:
Noninvasive affects normal host Invasive: Immunocompromised
Necrotic ulcerations, dark gray pseudomembranous on gingiva and hard palate
TTT --- Systemic Amphotericin B
62. Actinomycosis Chronic granulomatous infectious caused by actinomyces israelli BACTERIA(normal oral flora).
Enter deep tissue through source of trauma. Direct extension through soft tissue.
"Woody hard" lesions which form a central, softer area of abscess, many draining sinuses that discharge large
yellowish specks: colonies of bacteria called Sulfur Granules
55% cases Dx in Cervicofacial region. Soft tissues of submandibular, submental and cheek areas. Most
common in angle of the mandible "Lumpy jaw"
TTT --- Abscess drainage + excision of sinus tract + Long term high dose antibiotic therapy (Penicillin)
Early: after 5-6 weeks of antibiotic therapy. Deep: Up to 12 months
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
63. Syphilis STD disease caused by Treponema Pallidum. Transmitted also mother to fetus. 3 stages + congenital syphilis
1-Primary syphilis:
CHANCRE: solitary painless ulceration with no exudate. Clinically evident 9 to 30 days after initial exposure. If
untreated, will heal and progress to 2nd stage.
Regional bilateral lymphadenopathy
Oral: Lip, buccal mucosa, tongue, palate, gingiva and tonsils
2-Secondary (disseminated) syphyilis:
4 to 10 weeks after initial infection. Painless lymphadenopathy, sore throat, malaise, headache, weight loss, fever,
muculoskeletal pain. If untreated, will heal and go latent.
Oral lesions:
Snail's track ulcers-->mucous patches (reddish brown maculopapular and mucosal ulcers) Verrucal plaques:
Condylomata Lata in skin and mucosal surfaces
3-Latent stage:
between 2ry and 3rd syphilis. Free of lesions & Symptoms, 1 to 30 years.
4-Tertiary syphilis:
Vascular and CNS significantly affected (Neurosyphilis)
GUMMA: scattered foci of granulomatous infection, indurated, nodular or ulcerated lesion, can cause extensive tissue
destruction.
5-Congenital syphilis:
Hutchinson triad:
Interstitial keratitis (Cornea), Eight-nerve deafness, Dental abnormalities. Hutchinson incisors, Mulberry molars
Infected infants can display signs within 2 to 3 weeks of birth.
Histopathology
Biopsy or Dark-field examination of a smear of an active lesion. Treponema Palllidum: Gram negative, anaerobic,
spirochete.
TTT --- Penicillin; dose and administration varies according to stage, neurologic involvement and immune status
64. Tuberculosis Chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Transmitted through airborne droplets from a Pt
(TB) with active disease
Sx: Cough with blood-tinged sputum, fever, cervial lymphadenopathy, night sweats, weight loss.
Oral: Indurated, chronic, nonhealing, painful ulcer in tongue, palate.
Histopathology
Aerobic, non-spore-forming bacillus. Thick, waxy coat that retain red dyes-->Ziehl-Neelsen. Known as acid- fast bacilli.
Granulomatous inflammation showing central casseous necrosis
TTT--- Multiagent Therapy: PIER for 2 months, then Isoniazid and Rifampin for 4 months.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
65. Herpes Simplex Virus Spread through infected saliva or active perioral lesions.
1 (HSV1) 1-Primary: Initial exposure, individual without antibodies to the virus, typically at a young age.
Acute herpetic gingivoestomatitis (primary herpes):
Children from 6 months to 5YO and Young Adults.
90% cases subclinical (No symptoms) or Prodromal general Flu-like signs & symptoms.
Numerous pinhead Vesicles-->Red Lesions (Erythematous)--> Ulceration covered in yellow fibrin (Painful) Self
Inoculation of the fingers "Herpetic Whitlow".
Both Keratinized and Non-keratinized mucosa
Mild: 5 to 7 days. Severe: 2 weeks
Latent stage: The virus is taken up by sensory nerves to the assoc sensory or autonomic ganglia and here it
remains latent. HSV-1: Trigeminal Ganglion.
Recurrent (Secondary): Reactivation of the virus due to many environmental factors.
Location: Pharynx, Intraoral mucosa, Lips, Eyes, Skin ABOVE the waist.
Recurrent Herpes Simplex Infections (secondary herpes):
Prodromal Signs &Symptoms 6 to 24 hrs (Virus active replication) Multiple small, erythematous papules--
>Vesicles-->Ulcers
Herpes Labialis: Vermilion border and adjacent skin of lips ("Cold sore" or "Fever Blister") Recurrent Herpetic
Stomatitis: Keratinized Mucosa
7-10 days, no scar
Histopathology:
HSV infected epithelial cells: (Cytologic Smear)
Tzanck Cells: Acantholysis Ballooning degeneration: Nuclear clearing and enlargement.
Lipschultz bodies: Dark spots within cells with protein content (Sites of viral replication)
TTT--- Supportive:
Fluid intake, analgesics, topical anaesthetics.
Systemic: Antivirals ONLY first 3 symptomatic days. Acyclovir, Valacyclovir
66. Herpes Simplex Virus Transmitted predominantly through sexual contact
2 (HSV2) Genital zone, Skin BELOW the waist
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
67. Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV)- VZV may spread through air droplets or direct contact with active lesions.
Human Herpes Virus-3 (HHV-3) It becomes dormant in nerve ganglion after its primary infection (Dorsal root ganglia).
Immunosuppression, IS drugs, HIV, Radiation, Malignancy, old age, stress, alcohol abuse, etc
predispose for reactivation.
Unlike HSV, VZV only has ONE RECURRENCE
1. Varicella (Chickenpox):
Primary Infection, Painless. Most cases are symptomatic (fever, chills, malaise, pharyngitis,
headache)-->Pruritic Vesicular rash-->Pustules-->Scab over.
Complications:
Children: Secondary skin infections, encephalitis and neumonia. Adults: Pneumonitis +
encephalitis
Face and trunk, eventually the extremities Intraoral: Palate and Buccal Mucosa
TTT--- Supportive: analgesics, and antipruritics
Mild: 1 to 3 days Severe: 5 to 10 days
2. Herpes Zoster (Shingles):
3 phases:
1.Prodromal (1 to 4 days before lesion development Virus replication-->severe neuralgia)
2.Acute (Vesicles 1-4mm, ulcerate within 3-4days).
3.Chronic (Postherpetic Neuralgia): Risk Factors: Female, Older age, Pain in Prodromal and Acute
phase. Complications: Ramsay Hunt Syndrome (Ipsilateral, Facial nerve affected)
Painful vesicles along distribution of sensory nerve, unilateral pattern Oral Lesions: Trigeminal
nerve DO NOT cross the midline
Acute Phase: Skin and mucosa
TTT--- Supportive: antipruritics and Non-aspirin antipyretics Systemic: Antivirals reduce healing
time and likelihood to develop Post Herpetic Neuralgia
Acute Phase: 2-3 weeks in healthy Patients. Chronic Phase: Pain 1-3 months after resolution of
rash. Resolved within 1 year
Histopathology
Cytologic smear + Clinical will help Diagnose. Tzanck Cells present in VZV
68. Coxsackie Virus Most cases, Herpangina and HFM are self limiting
1. Herpangina:
Coxsackie A, transmitted by contaminated saliva and feces. Affects Infant and young children,
flu-like symptoms Red macules-->Vesicles-->Ulcers
Soft Palate Tonsillar pillars
Systemic: few days Ulcers: 7 to days No scar
2. Hand-Foot-And-Motuh Disease:
Acute and contagious, flulike symptoms. Small vesicles--> Shallow ulcer with a red halo
Palm of hands, soles of feet, Mucosa of the anterior part of the mouth (tongue, buccal and labial
mucosa)
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
69. Pemphigus Vulgaris Autoimmune mucocutaneos , Intraepithelial blister formation. Antibodies will destroy
desmosomes, which hold epithelial cells together. 50 YO.
Rupture blisters within epithelium--> Painful debilitation--> Fluid loss--> Electrolyte imbalance.
Oral Lesions first sign of disease *First to show, Last to go
4 types of pemphigus: 1.P. Vulgaris (Most Common). 2.P. Vegentans. 3.P. Foliaceus. 4.P.
Erythematosus
Palate, labial and buccal Mucosa, ventral tongue, gingiva are often involved
Histopathology
Intraepithelial clefting. Vesicles and Bullae: Entirely intra-epithelial (Suprabasilar vesicles)
Basal cells: "Row of tombstones".
Cells of Spinous Layer: acantholysis, Tzanck Cells.
Take 2 Biopsies: Regular microscopic and DIF (to confirm "chickenwire" pattern)
Positive Nikolsky sign
TTT--- Systemic Corticosteroids + Immunosuppressive drugs
70. Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Mostly Females between 50-60 YO.
(MMP) - Cicatricial Pemphigoid Antibodies attack hemidesmosomes which attach epidermal cells to the basement membrane.
Vesicle or Bullae--> Large superficial ulcers (painful). Bulla is Thicker than PV.
Affects mainly oral and ocular membranes. Also nasal, esophageal, laryngeal, vaginal
mucosas.
Gingiva->"Desquamative Gingivitis".
Ocular--> Blindness (most significant complication)
Ulcerated lesion can last weeks to months if untreated
Histopathology
Subepithelial clefting.
No evidence of acantholysis, No Tzanck Cells.
Take 2Biopsies:
Regular microscopic and DIF (to confirm "chickenwire" pattern)
MAY BE +Nikolsky sign
71. Erythema Multiforme (EM) Type 3 hypersensitivity, perivascular inflammation and necrosis. Mainly young adults.
3 forms: Positive Nikolsky sign
1.EM Minor: HSV associated, Prodromal signs. Small vesicles-->Erosion with pseudo membrane
(painful).
Skin (75%)--> Target Lesions (bull's eye). Hemorrhagic crusting of the vermilion zone of the lips
2.Chronic EM Minor: Mildest, small and short duration lesions.
Target Lesions less common
3. EM Major (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome): Severe, triggered by sulphonamides (Drug) extensive
vesicles-->Ulcers with pseudo membrane (painful).
Oral mainly non-keratinized mucosa, always present.
Skin: Target Lesions.
Triad: Eye (Conjunctivitis), genital (balanitis, vulvovaginitis) and oral lesions (Stomatitis).
TTT---
Mild: antihistamines, analgesics and antipyretics + oral rinses of antihistamine. *Use of
corticosteoids is controversial
If triggered by HSV: Oral antiviral.
If a causative drug is identified: remove immediately
Self-limiting: 2 to 6 weeks
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
72. Leukemia Cause unknown, Malignancy from Hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow --> Peripheral blood (> Cancer cells,
< normal cells: erythrocytes, platelets and leukocytes).
Contribute factors:
Family tendency, Congenital disorders, Virus, Ionizing radiation.
Malignant Cells can cause splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy
Acute Leukemia: Rapidly progressive, functionless WBCs in the marrow and blood. Bone marrow, liver and spleen
are the main organs involved. Death in months if not treated.
Chronic Leukemia: Slower onset, weakness, weight loss, less agressive. Main organ BM, followed by liver, spleen
and lymph nodes.
1- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML):
Malignancy Myeloid immature WBCs. Adults, rises rapidly after 50 YO. Sudden onset.
Leukemic cell Infiltration causing diffuse, non tender swelling, may or may not be ulcerated --> Diffuse Gingival
Enlargement
>20% Myeloblasts found in bone marrow or peripheral blood. Cytoplasm contains Auer rods (acidophilic bodies)
Death in 1 to 3 months if not treated
2-Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL):
Leukemic lymphoblasts cells found in bone marrow and periph. Blood. Common type in children.
Neoplastic cells can expand in lymph nodes, liver, spleen, CNS.
Most cases Null Cells
Most responsive to Ttt, remission rates: 90% Cure: 70%
3-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL):
Malignancy in mature B Lymphocytes. More common in Adults. Slow lymph infiltration in bone marrow.
Least Malignant type.
4-Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML):
Aggressive neoplasm of mature Myeloid WBCs. Philadelphia chromosome (90% cases).
Overall Poor prognosis
73. Agranulocytosis Mostly idiopathic, Chemo drugs can trigger autoimmune reaction which will destroy granulocytes or decrease cell
maturation, mainly neutrophils (Antithyroid drugs).
Erythrocytes and Platelets are normal.
Symptoms occurs fast (Flu-like, bacterial infections, bone pain) May result in death
Deep necrotizing punched out ulcers in Buccal mucosa, Tongue, Palate and Gingiva.
Little or No inflammatory cells around bacterial infected regions
TTT---
*Stop offending drug,
*Pts with Chemo: Excellent oral hygiene (mouth rinse with Chlorhexidine).
*Filgrastin (G-CSF) for Pts that didn't recover.
10 to 14 days after drug discontinuation
74. Cyclic Rare Idiopathic disorder, every 21 days reduction in neutrophil counts, last for 3-6 days and starts again.
Neutropenia Symptoms with recurrent events begin in
childhood: fever, anorexia, cervical lymphadenopathy, malaise, pharyngitis and oral ulcerations
Oral mucosal ulcerations, most severe in gingiva. Severe periodontal bone loss, gingival recession, tooth mobility.
Antibiotic therapy for significant infections, Optimal oral higyene, and Granulocyte-CSF
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
75. Polycythemia Idiopathic. Too many functioning RBCs circulating. Blood becomes so thick, it can not pass through small
vessels (thrombus formation). Affects older adults
1-Primary (Polycythemia Vera):
due to tumors abnormalities, increase in platelets and leukocytes.
2-Secondary:
Increase in numbe of erythrocytes due to chronic tissue hypoxia or high altitude.
Initial: Headache, weakness, sweating, weight loss, visual disturbances. Hypertension, splenomegaly due to
increased vascular congestion.
Oral: petechia,purpura, ecchymoses and gingival hemorrhage
TTT --- Flebotomy, removal of 500mL of blood every other day until Hematocrit: < 45%
76. Thrombocytopenia Decrease in circulating platelets due to
Reduced production, Increased destruction or Sequestration in the spleen. <100.000/mm3
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP):
Increased consumption of platelets assoc with abnormal blood clot formation that can damage kidney, heart
and brain.
Minor trauma in oral mucosa will cause damage to blood vessels. Spontaneous gingival bleeding, prolonged
bleeding after dental procedure.
Severe cases: Internal organs bleeding (brain, GIT, Lungs) could be fatal.
TTT--- Life-threatening hemorrhage: platelet transfusions and corticosteroid therapy.
77. Anemia Deficiency in Erythrocytes to transport oxygen due to decreased # of RBCs, size or hemoglobin content.
MCV: average RBC size (80-100fL). <80fL:microcytic. >100fL: macrocytic.
MCHC: Hb concentration (300-370 g/L). Hypochromic: <MCHC; RBCs paler than usual Hyperchromic:
>MCHC; increased Hb in RBCs.
Normal Hb: 2alfa chains & 2beta chains
78. Iron Deficiency Most common Hypochromic, Microcytic RBCs. low iron levels to produce enough erythrocytes may be due to:
Anemia Excessive blood loss, Increase demands for RBCs, Decrease intake of Iron or Decreased absorption of iron
Systemic: (Anemia Sx) Fatigue, palpitations, light headedness, lack of energy.
Oral: Angular Cheilitis and Glossitis
TTT--- Dietary Iron Supplementation oral ferrous sulfate
RBCs# return to normal within 1 to 2 months
79. Plummer-Vinson combines iron deficiency anemia Hypochromic, Microcytic RBCs, glossitis, dysphagia and koilonychias.
Syndrome Premalignant (5-50% increase in oral and esophageal SCC).
Systemic: Anemia Sx.
Oral: Burning sensation in tongue and oral mucosa, Angular cheilitis.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
80. Pernicious Anemia Poor intestinal absorption of Vitamin B12, due to a lack of intrinsic factor secreted by parietal cells of the
stomach.
Causes: Autoimmune destruction of parietal cells, GI bypass SX, Strict Vegetarians.
Systemic: Anemia Sx, paresthesia, tingling or numbness of the extremities.
Oral: atrophic glossitis (Hunter glossitis), burning sensation of tongue, lips, buccal mucosa.
Macrocytic anemia, reduced Vit B12 levels.
Schilling test 24hr Urine Test (Vit B12 secretion/absorption)
Monthly IO or IM Vit B12 injections
81. Aplastic Anemia Failure of the hematopoietic precursor cells in the bone marrow: Pancytopenia.
Causes: Immune, Environmental toxins, Drug Tx, Virus Infection.
Fatigue, tachycardia, light headedness & weakness.
Tendency for bruising & hemorrhage of internal organs
Pale oral mucosa, oral ulceration, gingival hemorrhage, oral Petechiae & ecchymosis
Bone marrow biopsy: acellular marrow with extensive fatty infiltration
Supportive: ABX for infections. RBCs transfusions: anemia
Platelets admin: bleeding problems.
Definitive: Replace defective marrow
Patients < 50 YO with HLA-matched donor have the best prognosis
82. Sickle Cell Anemia Co-dominant severe genetic disorder. Mutation in beta-globin chain so abnormal Hb is formed (Hb S)
resulting in Sickle Shape RBCs.
"Sickle cell trait" Only one parent have the defective gene (50% normal RBCs).
Prone to infections (spleen destruction)
Common in African Americans (8%) Abnormal cells, fragile than normal (hemolytic anemia), reduced life
span (from 120 to 20 days). Sickle shape RBCs can clot in vessels causing "Sickle Cell Crisis" (Ischemia,
infarction and tissue death).
X-ray: enlarged bone marrow spaces, less trabecular (Incr. Hematopoiesis).
Lateral X-ray: "Hair on end" appearance
Supportive to control crisis: Fluids, analgesics, rest.
83. Thalassemia (Cooley's Inherited abnormal formation of one of Hb chains (either alfa or beta).
anemia, Mediterranean Hemolytic anemia, 2 forms (Major and minor).
anemia): Pts with thalassemia are resistant to Malaria. To maintain adequate oxygenation--> RBCs increased--
>massive bm hyperplasia
Painless enlargement of mandible and maxilla.
"Chipmunk" facies, small size of paranasal sinuses, frontal bossing , flaring of maxillary anterior teeth.
Lateral X-ray: "Hair on end" appearance, more common in Sickle cell anemia Generalized maturational and
developmental delay.
Hypochromic, Microcytic anemia.
Blood transfusions every 2 to 3 weeks
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
84. Erythroblastosis Fetalis Mother's immune system creates antibodies and attacks the fetus RBC due to incompatibility blood
types.
Ab cross the placenta (IgG) destroying fetus RBCs --> Hemolytic Anemia of newborns
Systemic signs in newborn:
jaundice, cyanosis, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, edema.
Oral:
Intrinsic staining of primary teeth (hyperbilirrubinemia), enamel hypoplasia
Blood transfusions to correct anemia
85. Leukoplakia. White patch - Homogeneous Granular, Speckled, Verrucous.
(85% Precancerous lesion, Biopsy mandatory)
- Tobacco, Alcohol, chronic local friction, radiation and microorganism (Candida, HPV, Treponema
Palladium)
- Older 40y70% lip vermillion, buccal mucosa and gingiva.In Tongue /floor mouth 90% developed
in Ca
-
86. PVL - Proliferative Verrucous Mainly slowly spreading white plaques w/ rough surface projections.(Hight risk to transform in
Leukoplakia Dysplasia and then Squamous cell Ca)
87. Hairy Leukoplakia Caused by EBV - Epstein Barr Virus
- White, asymptomatic mucosal plaques, bilateralDOES NOT RUB OFF
NOT PRECANCEROUS
- Lateral surface of tongue, with vertical orientation
- May use antivirals, but usually not requird
88. Lichen Planus UNKNOW but considered Immunologically mediated process) T-cell mediated)
show lymphatic cell infiltration
- Reticular= asymptomatic, bilateral white papules (Wickham Striae)
Erosive = Desquamative Gingivitis Symptomatic, burning, discomfort
Plaque (no common orally)
Bulbous (no common orally)
- Most common in women older than 30y
Reticular:
tongue, buccal mucosa
Erosive:
Gingiva
- Reticular = not required
Erosive= Topical Corticoids
89. GVHD -Graft Versus-Host Sequela when immunologically active donor T- cells attacks the host
disease Acute: first 100 days
Chronic 3- 12 months
- Mimic oral lichen planus, burning sensation.
- TongueLabia mucosa Bucal mucosa
- Topical corticosteroids
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
90. Nicotine Stomatitis - Smokers Palate Pipe/ Cigar smoking
Diffusely gray or white numerous, slightly elevated papules
Hard palatal
Eliminating predisposing factors.
91. Snuff Pouch - Smokeless Tobacco Tobacco
Keratosis
White patches, dental abrasion, periodontal disease
Muco-buccal fold of mandible (incisor or molar area)
Eliminating predisposing factors. If lesion persist after 6 weeks do biopsy
92. Oral Submucous Fibrosis Chewing of a betel quid, paan gutka, tobacco, slacked lime.
Bcz inhibit collagenase
Mucosa pallor, fibrous, blotchy.
Hight risk of squamous cell carcinoma
Buccal mucosa Retromolar area Soft palate
Mild: Corticoids
Moderate: surgical splitting
or excision.
93. Cinnamon Contact Stomatitis Inflammatory reaction by artificial cinnamon (gum, toothpaste, candies)
Erosive lesion, painful and burning
Buccal mucosa Lateral borders of the tongue Gingiva
Eliminating predisposing factors.
94. Chemical Burn Red connective tissue covers by yellowish fibrinopurulent membrane.Superficial areas of
necrosis
Buccal Mucosa
Eliminating predisposing factors.
Topical anesthetics.
95. Uremic Stomatitis Renal Failure/mucosa damaged by ammonia
Unpleasant taste and burning White plaques distributed in more than one area
Buccal mucosa TongueFloor of the mouth
Mildly acid mouth rinse Topical anesthetics for the pain.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
96. Candidiasis Caused by Candida albicans
Pseudomembranous soft white & elevated (Thrush) most common, diffused white mucosal plaques
CAN BE RUB OFF reveal erthymatis base
Chronic Hyperplastic C. white patch. DOES NOT RUB OFF
Pseudomembranous: Cheeks, palate, buccal mucosa,
dorsal tongue.
Chronic Hyperplastic
Candidiasis: Anterior buccal mucosa
Exfoliative Cytology --- Hyphae
Antifungal therapy (Nystatin/Azoles) If it does not work do Biopsy
97. Geographic Tongue - Unknown, but has a strong association with fissured tongue
Erythema Migrants -
Benign Migratory Glossitis Asymptomatic, Erythematous Depapillated lesions surrounded by white borders.
Tongue- dorsal
98. Hairy Tongue Poor hygiene, Systemic Corticoids, Smoking, Radiation, long term Antibiotic
Accumulation of Keratin on the filiform papillae. Appearance like hair. Color varies from white,
brown and black.
Tongue- dorsal
Eliminating etiological factors. Keratolytic agents (Podophyllin) and brushing the tongue
99. Saburral Tongue History of Flu, Yellowish-white superficial layer of the tongue (dorsal) Malodorous plaque, bad
breath. DOES NOT RUB OFF
Tongue- dorsal
Brush the tongue, improve oral hygiene
100. Fordyce's Granules Ectopic sebaceous glands, Multiple yellow-white asymptomatic papules.
Buccal mucosa Vermillion upper lip, No TTT
101. Leukoedema Unknown. More in black people then whites
Disappears when mucosa is stretched Asymptomatic, diffuse wrinkled greyish - white bilateral
opalescence DOES NOT RUB OFF
Buccal mucosa
No TTT
102. White Sponge Nevus Genetically inherited (mutation of genes coding Keratin 4-13) No Malignant
Appears in birth or childhood, asymptomatic, bilateral, white, corrugated, spongy, diffuse plaques
Buccal mucosaVentral tongue, labial mucosa, soft palate, alveolar mucosa and floor of the mouth
No TTT
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
103. Lupus Erythematosus Autoimmune multisystem disease
1- Discoid (DLE)
Skin lesions are disc shape, atrophic red with center white.
IO: Erythematous or ulcerative lesions w/white Keratotic striae.
Site: Oral mucosa, face, ears, scalp.
TTT: Avoid sun light, Topical corticosteroids or NSAIDs combined w/ antimalarial drugs
(hydroxychloroquine)
2- Systemic (SLE)
Butterfly shaped erythematous rash (malar rash).
IO: same as DLE
Site: Kidneys, hearth, lungs, joints, skin, mucous membranes, blood vessels. Nose/malar (Butterfly shaped
erythematous)
TTT: Systemic corticoids,
immunosuppressive drugs
104. Frictional Keratosis Chronic rubbing or friction
Hyperkeratotic white lesion analogous to a callus of skin
Site: Edentulous ridge (alveolar ridge keratosis) retromolar pad, buccal mucosa, tongue and lips
TTT:Eliminating etiological factors.If does not work, do biopsy
105. Linea Alba -White line Pressure, frictional irritation or sucking trauma
Bilateral asymptomatic white lines
Buccal mucosa at the same level as the occlusal plane
No treatment(Is considered a normal anatomical variation
106. Squamous Papilloma Caused by HPV(type 6-11)
Soft asymptomatic, pink to white exophytic nodule or CAULIFLOWER, solitary or multiple lesions
Histologically: Cells called "KOILOCYTES"
Bening
Site: Palate, Tongue, lips
TTT: Surgical excision included base of the lesion
107. Verruga Vulgaris - Caused by HPV.(Type 2) Easy to contagious and spread
Common Wart
Asymptomatic, papule or nodule with pebbly surface
Site: Skin Infrequent in oral mucosa
TTT: Surgical excision including the base of the lesion
108. Lipoma - Benign tumor 40 years old, no children
of fat
Buccal mucosa & vestibule,tongue & floor of the mouth.
Asympotomatic yellowish submucosal masses with intact overlying Epi.
Well cirumscribed lobulated mass of mature fat cells.
Local excision
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
109. Neurilemmoma - Benign neoplasm of schwanncells of neurilema
Schwannoma - young adult
- Tounge
*Slowly growing encapsulated asymptomatic submucosal mass push the nerve aside.
*Bony lesion in posterior mandible appears well defined radiolucency with corticated periphery and may
cause pain
*Encapsulated tumor showing
Antoni A: Spindle shaped cells surrounding an acellular Eosinophilic zone in a palisaded apperance
called Verocy bodies
Antoni B: spindle cells haphazardly distributed in delicate fibrillar matrix.
Surgical excision
110. Traumatic Neuroma Reactive lesion not a true neoplasm
Trauma to prepherial Nerve
Mental foramen area, tounge and lower lip
Smooth surface non ulcerated nodule Painful to pressure
Surgical excision includes small portion of proximal nerve bundle
111. Systemic Sclerosis - Autoimmune disease of unknown cause --- increase dense collagen 1&3 Deposited in body tissue
Scleroderma Deposition of collagen 1&3 in various body tissue
1- Limited (Morphea)
In skin & underlying tissue No internal organs. Rarely life threatening
2- Diffuse
In skin & underlying tissue Internal organs Kidney, GIT, Joints, Blood vessels
Lung--- Pulmonary fibrosis & hypertension
Heart --- Heart failure
Skin manifestation*
Diffuse hard texture *Skin looks smooth (Mask-like face)
*Atrophy of skin over digits (Claw like fingers)
*Mouse face --- Alae atrophy & pinched apperance of nose
Oral manifestations
*Microstomia
* Purse string appearance of mouth
* Dysphagia
* Xerostomia
* Firm hypomobile tongue
* Diffuse widening of PDL space
Raynaud's symptoms --- Emotional stress or cold leads to V.C of vessels leads tofingers & toes white -
blue to red color which give Throbbing pain
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
112. Nodular Fascitis - Pseudosarcomatous Unknown, proliferation of fibroplast as it's bengin
fascitis /reactive proliferation of super facial fasia.
Young adult and adult
Rapid growing firm mass which is tender
Buccal mucosa
Local excision 2% recurrence
113. Fibromatosis Fibrous proliferation --- infiltrative distructive. Recurrance growth.
Children and young adult
Firm asymptomatic slowly growing
*Paramandibular soft tissue regoin
*Head & neck
*Extra abdominal desmoid Fibromatosis
Wide surgical excision with normal tissue margin
* No metastasis
*30% recurrence
114. Multiple endocrine neoplasia sydrom rare inherited hyperplastic or tumor of neuroendocrine tissue
MEN syndrom
MENS I
pituitary gland
Parathyroid gland
*Pancreas
*Adrenal cortex
MENS II
*Parathyroid hyperplasia &adenoma
*Medullary carcinoma of thyroid.
*Pheochromocytoma of adrenal medulla.
MENS III
*Medullary carcinoma of thyroid.
*Pheochromocytoma of adrenal medulla.
ORAL:
*Asymptomatic soft nodule Lip, anterior tongue, buccal mucosa, palate & gingiva.
Mucocutanous numerous oral mucosal neuroma is the first sign to appear --- important to
early diagnosis.
If present --- endocrine examination is indicated
Metastasis to lymph nodes & distant organs.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
115. Lymphangioma (Lymphatic deformaty) Bengin hamartoma of lymph vessel early in life
Skin & mucous membrane head and neck
Oral --- Anterior 2/3 of the tongue
* Tongue macro glossia
* Asymptomatic
* Soft fluctuant noduleor vesicles
* Range in size & color
1- Macro cystic (Cystic hygroma) Site --- Neck may be life threatening
Cl/F -- 2 Cm or more cyst like space.
*Prognosis -- life threatening might involve vital structure in neck
*Respiratory distress, interleional hemorrage and disfgurment.
*Macroscopic cyst like structure
Med size -- Surgical excisionand sclerotherapy.
Large size --- Sclerotherpy first then Surgery.
High recurrance rate, as it's highly infiltrating with no capsule
2.Microcystic
site -- Oral cavity
Cl/F --- less than 2 Cm
*Mild dilation in lymphatic vessels Spontaneous regression in 3% of cases.
Small size --- Observation
Mixed Combination between Micro and macro cystic
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
116. Neurofibroma Most common bengin neoplasm of preipheral nerve
Schwann cells + perineural fibroblast
1.Solitary
Small to large painless nodule which is slowly growing
Tongue & buccal mucosa
Surgical excision.
Unilocular
2.Multiple (neurofibromatosis type I) (Van Recklinhouse Syndrom)
Most Common due to Mutation in gene NF1, Autosomal dominant inherited
Oral:*Multiple neurofibroma.
*Enlargement of Fungiform papollae resulting in tongue enlargement.
Skin:
*Café-au-lauit Pigmentation.
*Iris frecking (Lisch nodules).
*Auxillary freckling (Crowe sign).
Systemic:
*Hypertension.
*Pheochromocytoma.
*CNS tumors.
*Mental deficiency.
*Seizures.
Mainly in Tongue
Prevention & management of symptoms
Unilocular or Multilocular Enlargement of mandibular foramen and canal.
Increase in bone density Increase in size of coronoid notch
117. Cleft Lip Lack of fusion of lateral portion of Max. process & medialnasal process
6-7 WIU - 1:1000 birth
Unilateral 20%(leftside)
males
118. Cleft palate Faliure of fusion of palatal shelves of Max.process.
8-10 WIU, by 12 WIU completion of fusion of primary palate progressing posteriorly
females
1:2000 birth
119. Cleft lip&palate Most common craniofacial Mal. Formation.
Maternal alchohol .Maternal smoking.Anti-convalsant drugs.Folic acid def.
lead to
Malocclusion.Crown defect.Missing teeth.Supernumerary teeth.*Difficult speech & swallowing.
120. Paramedian lip pit rare congenital invagination of lower lip
Bilateral symmetric fistulas on eitherside of midline of lower lip.
121. Commissural lip pit Invagination of mucosa of corner of the mouth due toFailure of fusion of Max. & Man. Process
Commissueal lip pit Lateral facial cleft 0.3% of cleft cases
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
122. Condylar Facial Asymmetry PrognathismCrossbite Open bite*Hyperplasia in one side leading to deviation to the
Hyperplasia other Unaffected side
123. Condylar Hypoplasia Congenital -- Treacher coliin syndromAcquired -- Truma, infection, Radiation therapy
Unilateral or bilateral hypoplasiaSmall mandible with class II with open mouth.*Unilateral hypoplasia leads
to depression of face in the affected side & midline shift to affected side.
124. Hemi-hyperplasia Alone or part of mal-formation Neurofibroma*Mccune-Albright syndrom
Hemi-facial hyperplasia of soft tissue& boneUnilateral Macroglossia.Premature Dev. & eruption of tooth
of affected side.Increase in crown & root of teeth.
125. Cerberal palsy *Abnormal damage to brain during Dev. In pregnancy or delivery or first year of life
*Spastic paralysis.
*Impairment of control & coordination of muscle.
Seizures Visual disorders Enamel hypoplasiaDelayed eruption Mouth breathing Open biteGingival
hyperplasia increase incidence of Class II
126. Ectodermal Inherited disease.Most common type is Hypo
Dysplasia hydrotic x-linked recessive inheritance
Female carrier Male affected
Aplasia or hypoplasia in ectodermal
Skin--- smooth & dry
Hair --- hypotrichosis thin blond hair &eye brow
Nails --- dystrophic & brittle
Glands --- no sweet gland leads to heat intolerance
Xerostomia ---- hypoplastic salivary gland
Bone --- depressed nasal bridge & midfacail hypoplasia
Teeth --- Anodontia or Oligodontia tapered, pointed, conical shape.
127. Cleidocranial Inherited autosomal dominant disorder
Dysostosis *Mutation in RUNX2 gene which is responsible for bone differentiation & maturation.
(Dysplasia)
Hypoplasia/ aplasia
*Clavicle --- hyper-mobility of shoulders
*Skull --- Large, shortened, prominent frontal eminence ,Defective ossification
Oral findings
*Over retention of primary teeth.
*Failure of eruption of permenant teeth.
*Numerous supernumerary teeth.
*Dentigrous cyst.
128. Piere Robin Syndrom Inherited Dev. Disorder
Cl/F
*Cleft palate
*Micrognathia-- Class II
*Glossoptosis --Posterior displacement of tongue
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
129. Apert Syndrom - Acro-cephalo- Autosomal Dominant
syndactyly Malformation of skull & digits
*Craniosynostosis--Premature fusion of fibrous sutures by bone.
*Acrobrachycephaly-- tower skull, mid facial hypoplasia, relative mandibular prognathism
*Occular proptosis, hypertelorism, increase intracranial pressure.
*Bifid uvula, cleft palate, severe crowding, open bite, anterior & posterior cross bite,
shovel shaped incisors, delayed eruption.
* Syndactyly-- fusion of 2 or more digits
130. Crouzon Syndrom - Craniofacial Autosomal dominant craniofacial disorder
dysostosis
Skull:
*Craniosynostosis--Premature fusion of fibrous sutures by bone.
*Brachycephaly (Short head)
*Occular proptosis, hypertelorism, increase intra cranial pressure.
Intraoral:
*Midface hypoplasia, underdeveloped maxilla leads to Class III, bilateral posterior cross
bite, over crowding of teeth.
* X-Ray of the skull show increased digital markings called Beaten-Metal
131. Treacher Collins Syndrom - Autosomal dominant disorder leads to anomalies structures from 1&2 branchial arch.
Mandibulofacial Dysostosis
Craniofacial:
Hypo plastic zygoma Narrow face *Depressed check
*Ear defects
*Downward-slanting of eye
*Hypoplasia of nasopharynx & oropharynx.
Oral:
*Mandibular hypoplasia.
Mid-face hypoplasia. Retorted chin. *Cleft palate
*Malocclusion
*Flattened aplastic condyle & cronoid process.
132. Rieger's syndrom - Craniofacial Rare genetic disorder
dysostosis
Craniofacial:
Hypertolerism Flat face*Hypoplastic maxilla
Protrude lower lip Broad flat nasal ridge
Intraoral:
*Anodontia or hypodontia
Microdontia with conical crownEnamel hypoplasia *Malposition of teeth
Eye:
*Glucoma.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
133. Down syndrom - Trisomy 21 Craniofacial:
*Face short,broad and flat,hypoplastic mid face
Ocular Hypertolerism Hypoplastic maxilla
Downward-slanting of eye Upward-slanting palpebral fissures.*Flat nasal bridge.
Oral:
Macroglossia-- large fissured protruding tongueMouth breathing & open bite with class III*Increase
periodontal disease.
*Dental caries not greater than normal person.
Delayed eruption of teeth & malocclusion.Hypodontia & high arched palate.*Relative mandibular
prognathism.
Systmic:
Mental & physical delayed Dev.Congenital heart diseases.
134. Ankyloglossia - Tongue tie *May cause speech & swallowingproblems, localized lingual gingival recession of lower teeth.
No TTT if mild, Frenectomy orFrenuloplasty if severe speech and periodontal problems.
135. Fissured Tongue - Scrotal *Deep fissures or grooves6MM in depth.
tongue *common with Geographic tongue & Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrom.
136. Macroglossia *Multinodular appearance of thetongue.
*Crenated lateral border of the tongue, open bite & Mandibular prognathism.
*Airway obstruction.
137. Osteomalacia Metabolic condition ch.ch by decrease Vit. D after puberty
Cause Decrease intake of Vit.DImproper Met. Of Vit.D(chronic pancreatitis)*Defective mineralization
Cl/F
Bone softeningHour glass thoraxBowing of long boneIncrease bone fractureBiconcave vertebral
bodies
Lab. Inves.
Decrease Ca+2 & Phosphorus Increase Alkaline Phosphatase
138. Rickets Metabolic condition ch.ch by decrease Vit. D before puberty
Cl/F
Systemic:
Irritability Bone fracture Growth impairmentSkeletal deformatiyProminance of Costochonddral
juncationsBow legs
Oral:
Delayed eruption malocclusion Increase caries index Teeth hyper-mobility
Lab. Inves.
Decrease Ca & PhosphoursIncrease Alkaline Phosphatase
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
139. Osteoporosis Most common metabolic disorder
Metabolic condition ch.ch by decrease Ca, Phosphor.
Primary: Senile, post menopause
Secondry: Cancer, hormonal disturb.
Drugs (Prolonged Steriods)
Skeletal:
Thin cortical boneDecrease bone denistyLarge medullary cavityDecrease cancellous trabeculation
TTT
Bisphosphatase, estrogenVit,D & Ca supplement
140. Osteopetrosis - Inherited metabolic condition ch.ch by increase bone density Reduced osteoclast activity lead to increase
Marble bone disease bone density
Skeletal:
Increase density of cortical and cancellous bone but fragileBone pain Anemia & granulocytopenia
Growth impairment Blindness Deafness*Facial paralysis (Cranial nerve comprasion)
*Osteomyelitis is common
Dental:
Delayed eruption Cong. Missing teeth Uneruped & malformed teethEnamel hypoplasia*Mandibular
prognathism
X-Ray:
*Difficult to visualize the root coz increase density of bone
141. Pituitary Dwarfism Decrease secretion of G.H from pituitary or decrease response of the tissue
Body:
Short statureNormal body proportions
Oral:
Delayed eruption & sheddingSmall crown & roots*Mal-occlusion due to small jaws
142. Achondroplasia Most common form of Dwarfism Autosomal dominant
20% Sporadic mutation 80
Body:
*Normal torso & short extremities
Craniofacial:
Macrocephaly (Large head)Frontal bossingSaddle like noseMax. hypoplasia*Man. Prognathism
Oral:Normal size teethOver crowding*Mal-occlusion
143. Gigantism Most common metabolic disorder
Increase G.H secretion due to:Pituitary AdenomaHyperpituitarism before closure of Epiphysesis before
adolescence
Body:
Increase body heightEnlargement of hand & feetEnlargement of facial tissueGrowth not related to growth
spurt
Oral:
Man. prognathismMacrodontia*Hypercementosis
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
144. Acromegly - Increase G.H after closure of Epiphysesis, after adolescence due:Pituitary AdenomaHyperpituitarism
Marble bone
disease Systemic:
Hypertension D.M Heart Dis.Arthritis *Peripheral neuropathy
Body:
Renewed growth of hand, feet, jaw and skull Soft tissue like soft palate also
Oral:
Mand. PrognathismOpen biteTeeth spacingMacroglossia*Hypercementosis
145. Hypothyroidism Most common thyroid abnormally
Cause
Congenital defect Idiopathic Iodine Def. GoitreAutoimmune (Hashimotothyroditis)--most common Disease
of pituitary & hypothalamusOver treatment of hyperthyroidism--Second most
Primary: Due to thyroid gland itself
Secondary: Decrease TCH from pituitary-gland like post radiation therapy
Myxedema: For adult,Glycosaminoglycans deposition in skin, collect water causing swelling & puffiness.
Cretism: For children, mental retardation, delayed growth of vault, reduced facial height, delayed tooth
eruption, swollen face & lips, short stature
146. Hyperthyroidism - Increase production of T3&T4 triiodothyronine, Thyroxine
Thyrotoxicosis
*Graves (Diffuse toxic goiter):Autoantibody to receptors of TSH leads to increase production of TSH
*Plummer's(Toxic nodular goiter): Autonomously Func.Nodules in thyroid gland Elder individuals over 50
Systemic:
Warm smooth skin TremorsHeat intolerance GoiterNervousness & Wt. lossHeart palpitation & tachycardia
Increase BMRExophthalmos is rare
NOTE: Uncontrolled thyroid pt. avoid EPI. As it may leads to thyroid-crisis
147. Hypoparathyroidism Cause
Congenital, idiopathic or autoimmuneDecrease PTH production or decrease tissue response to PTH Cl/F
Systemic:
Tetany, metabolic alkalosis Ca level < 2.5-3 mg/dl
Oral:
Delayed eruption of teeth Enamel hypoplasia & pitted *Blunt root apices
Diagnosis
*Chivostik sign: twitching of lower lip when tapping facial Nv.
*Trousseau sign: applying pressure with blood pressure cuff above 20 mm Hg for 3-5 Min. leads to Occ. Of
branchial arteryIrritability of nerve, flexion of wrist & metacarpal phalangealExtension of the interphalangeal
joints & carpal spam
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
148. Hyperparathyroidism Primary: Adenoma, hyperplasia of thyroid Gland
- Secondry: Kidney dialysis, choric renal failure, intestinal malabsorption leads to decrease Ca+2 level then
Von Rockling PTH
housen of bone -
brown tumor Systemic:
Bone: Pain, fracture, subperiostal bone resorption of phalanges of index & middle fingerKidney stone,
pain & increase in urination ConstipationFatigue, weakness, memory loss & confusion *Peptic ulcer
Oral:
Loss of PDl Thining of cortical plate of boneLoss of tabulation pattern & density (Ground glass
appearance)Unilocular or multilocular radiolucancy called Brown tumor*Central degeneration & fibrous
replacement of brown tumor leads to osteitis fibrous cystica
*Similar to central giant cell granuloma fibroblast & multinuclatedin fibrocellular stroma
*Lab. --
Increase Ca & PTH levelsBrown tumor due to Acc. Of hemosidren & extravasated red cells
TTT:
Primary need surgery, Secondry Bisphosphanate
149. Hypo-phosphatasia Inherited metabolic disorder disease
Deficiency in Alkaline phosphatase enzyme
*Neonatal:Very severe, survive only for few hours dut to respiraroty faliure
*Infantile:Immature loss of primary teeth, skeletal deformation(like Rickets)
*Childhood:Premature loss of primary teeth, large pulp chamber, alveolar bone loss, frontal bossing & short
stature
*Adult:Edentulous with premature loss teeth, bone fracture with mild Trauma
*Odontohypophosphatasia: premature loss of incisors teeth
Oral:
Premature loss of primary teeth with hypoplasia or aplasia of cementom over rootAlveolar bone loss
Enlarged pulp chamberDefective root development *Hypoplastic enamel
150. Osteogensis Inherited metabolic disorder ch.ch. By osteopenia (low bone density) Mutation in type I collagen gene leads
imperfecta to less collagen formation or poor Quality
Skeletal:
Blue sclera Deafness Bone fragilityJoint hyper-extensibility Curved spineTriangular face Frontal
bossingFlattened vertex & skull base
Oral:
Dentinogensis imperfectaBulblous crown Short rootsPulpal obliteration *Class III with open bite & cross
bite
Classification:
*Class I: Most common, mildest form
*Class II: Most severe (Multiple fracture from birth process)
*Class III: Most severe form beyond the perinatal period
*class VI: Mild to moderate bone fragility
No TTT, physiotherapy & Rehabilitation Bisphosphatase May need surgery
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
151. Paget's disease - osetitis Abnormal resorption & deposition of bone ch.ch. By skeletal distortion & weakening.
deformation Unknown may be genetic or environmental May affect more or more bone likeSkull, sternum,
vertebrae, pelvis, tibia humerus
Systemic:
Bone is painful, thick, enlarged with increase risk of fractureIncrease skin Temp. over the bone, due
to increase vascularity *Headache, auditory & vision problems
Facial paralysis & vertigolarge head *Increase size of Max.>Man
Oral:
Bilateral symmetrical jaw enlargementSpacing & loosening of teeth (Acquired diastemes) Denture
doesn't fitHypercementosis Oblitration of PDLRoot resorbation
X-Ray:
Skull-- slow cotton wool appearancePatchy sclerotic Histology:*Mosaic pattern with multinucleate
Lab.
Normal Ca & phosphrus Increase Alkaline phosphatates Increase Hydroxy
152. Cheurbism Rare Autosomal dominant
Craniofacial:
*Max. tuberosity & palate vault
*Man. Condyle, ascending ramous & coronoid prosess
*Bilateral painless bony expansion of posterior mandible (Chubby cheeks)
Mastication & speech problemsupper airway obstruction*Vision & hearing loss
The floor of the orbit:
Upward tilt of the eye ballretracted lower eye led (Turned upward to heaven)
Teeth displacement & mobilityDelayed eruption*Mal-occlusiion & ectopic eruption
X-Ray:
Well defined multilocular apperance on Occ.radiograch (Soap bubble)
Histology:
Like central giant cell granuloma
TTT
Self limiting & regressiveIn severe cases may need surgery
153. Nasolabial Cyst - Upper lip swelling, unilateral. Elevation of the ala of the nose
Nasoalveolar Cyst the fusion of MAX,Medial and Lateral nasal process
TTT Surgical Excision
154. Nasopalatine Duct Cyst - 1st MOST frequent TYPE OF NONODONTOGENIC CYST
Incisive Canal Cyst Rest of cells of the Nasopalatine duct.
Median Anterior Maxillary
Cyst Swelling of anterior palatal, some times pain and drainage
Vital teeth
Heart or inverted pear shape in X- ray
Divergent roots of upper anterior teeth
TTT Enucleation
155. Median Palatal Cyst - Remain of epithelium at the line of fusion between lateral palatal shelves
Palatine cyst Asymptomatic
Fluctuant swelling posterior of the palatine papilla
Well circumscribed RL in the mid line of palate
TTT excision
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
156. Globulomaxillary Cyst Fissural cyst. Between Globular and Max process.
Lateral and canine RL pear shaped
TTT Excision
157. Palatal Cyst of the Newborn Epstein Pearls
Fissural/development cyst
1-3mm
Palatal raphe
Bohn's Nodules
Residual epithelial of the minor salivary gland
Hard Palatal
TTT self limiting
158. Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Most Common Developmental Cyst
Residual epithelial in Thyroglossal duct.
Asymptomatic, fluctuant, movable swelling.
Symptomatic if is as a secondary infection
Neck mid line
TTT excision (Sistrunk Procedure)
159. Branchial Cleft Cyst Remenats from 2nd branchial arch
Cervical Lymphoepithelial cyst Asymptomatic Unilateral, Soft, fluctuant swelling,
1-10 cm
Symptomatic if is as a secondary infection
Upper lateral side of the neck
TTT excision
160. Oral lymphoepithelial Cyst Intraoral counterpart of the branchial cyst
Painless white yellowish small
(<1cm) firm or soft mucosal swelling, non ulcerated
Floor of the mouth.
Ventral tongue
Post-lat tongue
Palatine Tonsil
Soft Palatal
TTT excision
161. Dermoid Cyst Developmental Cyst From embryological, epithelial remnants
w/ dermal structures.
W/O Dermal structures is called EPIDERMOID CYST
Considered as a Simple form of Teratoma
Painless, slow growing, swelling, soft, doughy to palpation.
Middle line of the floor of the mouth.
Above Geniohyoid muscle (Tongue displaced)
Below Geniohyoid muscle (doble chin)
TTT excision
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
162. Dentigerous Cyst - follicular cyst 2nd most common Odontogenic Cyst
Most common developmental
By separation of the follicle from around the crown
Un erupted / Impacted Tooth Asymptomatic.
Symptomatic when is Displacement of the bone of the involved tooth
Lower third molar
RL peri coronal, unilocular around the crown of un erupted tooth
Dentigerous cyst >5mm
Hyperplastic Dental Follicle <5mm
TTT
Enucleation with removal of the un erupted tooth.
If untreated:
Could developed Ameloblastoma and rarely Squamous cell
Carcinoma
163. Eruption Cyst - Eruption Hematoma Soft tissue variant of the dentigerous cyst
Most common in Primary dentition <10yo
Smooth, reddish, pink or bluish,
fluctuant localized swelling at Alveolar ridge over crown of unerupted tooth
TTT
Simple Excision to help the tooth eruption
164. Lateral Periodontal Cyst From rest of the dental lamina.
Is counterpart of Gingival Cyst in Adulthood
Painless Vital teeth
Lateral surface of the roots of MANDIBULAR Canine/Premolar
RL well circumscribed
Unilocular Teardrop shaped area
Rarely Multilocular (Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst)
High recurrence, as it's difficult to excise completely
165. Gingival Cyst of the newborn From remnants of the dental lamina
Multiple smooth white nodules along alveolar
ridge (1-3mm) , filled w/ keratin
maxillary alveolar ridge
No TTT
166. Primordial Cyst "CYST INSTEAD OF THE TOOTH"
Cystic degeneration of the stellate reticulum.
Before the formation of enamel and dentin.
Mandibular third molar --- which is missing
RL circumscribed area w/No calcified structures
TTT
Enucleation & curettage
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
167. Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC) Rest of dental lamina
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor Small:
Asymptomatic
Large:
Symptomatic (pain, swelling and drainage)
With Impacted tooth --- lower third molar
grow Antro-posteriorly with Palasiding & wavy pattern
Root absorption is common, Uni or multilocular RL
TTT
Enucleation and curettage.
Or
Peripheral Ostectomy W/ Carnoy's solution
after Cyst removal to prevent recurrence.
Hight Recurrence
(30%)
168. Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome Autosomal dominant disease
Gorlin Goltz Syndrome
Multiple Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)
Palmar/plantar pits
Rib anomalies
Spina bifida
Mild ocular
hypertelorism
Epidermal cyst of the skin
169. Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst - Calcifying Cystic Remnants of the odontogenic epithelium
Odontogenic - Tumor-Gorlin Cyst Associated w/Impacted tooth, usually canine.
"GHOST CELLS"
Uni or Multilocular RL w/well demarcated margins
Root resorption and/or divergence of adjacent teeth
170. Radicular Cyst - Periapical Cyst 1st MOST COMMON ODONTOGENIC CYST.
From a preexisting periapical granuloma.
(Rest of Malassez) Inflammatory process
Asymptomatic, mobility NON-VITAL Tooth
Histological:
Rushton Bodies and Cholesterol Clefts
RL lesion at the tip of the root. Root resorption.
TTT
RCT w/apicoectomy (>2cm)
Or
Extraction and curettage
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
171. Residual Cyst Tooth with Radicular Cyst
associated was extracted and
Cyst not removed or curetted out of the the socket
TOOTH EXTRATED
RL, rounded or oval at the site a previous tooth extraction
172. Symple bone Cyst - Traumatic Bone Thin loose connective tissue membrane
Cyst. NOT-EPITHELIUM
Solitary Bone Cyst Intraosseous EMPTY CAVITY, or fluid content (blood, debris)
Asymptomatic, Young patients
VITAL TEETH
Most common Mandible between Canine / Ramus posterior
Inter-radicular Scalloping
TTT Curettage
173. Stafne Bone Cyst - Static Bone Cyst Invagination of the lingual surface
of the jaw Intraosseous EMPTY CAVITY, or salivary gland tissue, muscle, blood vessels)
Posterior mandibular
BELOW the mandibular canal With sclerotic border
RL. Uni or Multilocular
No Treatment required
174. Aneurismal Bone Cyst. - ABC Osteolytic lesion of bone with proliferation of vascular tissue.
Rapid enlarging swelling is common.
Patients <30 yo Affects long bones and vertebrates
Only 2% Posterior region of MAN/MAX
RL. Uni or multilocular
Teeth may be displaced w/ or w/o External root resorption.
Enucleation Or Curettage
Hight recurrence
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
175. Ameloblastoma Most common epithelial odontogenic tumor
Benign but Aggressive
From the cells that form enamel lining.
More aggressive and has Hight recurrence
TYPES:
· Conventional, Solid or Multi-cystic, 86%: Painful or not, Swelling, expansion of the jaw.
· RL Multilocular "SOAP BUBBLE"
(large lesion)
"HONEYCOMBET"
(Small lesion)
Marginal Resection
· Unicystic, 13%:
Symptomatic or
Asymptomatic, depend of the amount of the bone involve
Most common Mand 3rd Molar
RL surrounding the crown of unerupted tooth. Or Sharply defined RL
· Enucleation And /or curettage
· Peripheral or Extraosseous 1%:
Painless, nonulcerated, sessile or pedunculated mucosa
Gingival or Alveolar mucosa
"CUP SHAPE" RL
Beneath the elevated nodule
Surgical Excision w/small margin
Acanthomatous, granular cell, desmoplastic and basal cells.
Follicular (most common) and
Plexiform patterns.
176. Ameloblastic Fibroma Contain Epithelial and mesenchymal (connective) tissue
Younger patients
70% Mandibular molar-ramus and associated w/impacted teeth.
RL unilocular.
Rare multilocular
Curettage or surgical excision.
177. Ameloblastic Fibroma-Odontoma Contains Odontoma Dentin -Enamel
Children
RL unilocular w/ RO area (odontoma)
Conservative Curettage
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
178. Calcified Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor From the epithelial cells
(CEOT) - Pindborg Tumor
Associated w/impacted molar.
Slow painless, swelling.
Btwn 30-50 yo
Molar ramus of mandible (3rd molars)
RL, Uni/Multilocular w/ Scalloped margins.
May have Calcified opaque structures of dif. Sizes.
Epithelial cells w/ amyloid that have Liesegang Rings
Concentric calcified deposite
Recurrence is common
Resection of the area
179. Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor From the epithelial cells
(AOT)
Commonly in females 10-19 yo. Asymptomatic and rarely >3cm.
· Follicular Form:
75%, Unerupted tooth Canine
RL. surrounds the crown of unerupted tooth.
EXTENDS THE CEMENTO-ENAMEL JUNCTION
· Extrafollicular:
Btwn roots of erupted teeth
RL Btwn roots of erupted teeth w/ SNOWFLAKE SHAPE (calcifications)
Adenomatoid surrounded by fibrous capsule. --- Duct-like
Enucleation
180. Squamous Odontogenic Tumor From the epithelial cells. Associated with roots of the teeth
No symptoms
Anterior Maxilla And Posterior Mandible
RL. SEMILUNAR lesion
Conservative Excision
181. Clear Cell Odontogenic Tumor From the epithelial cells
Locally aggressive, metastasis to lung and regional lymph.
Any area of the Max/Mand bone.
Poorly circumscribed RL lesion
Resection of the affected area
182. Odontogenic Mixoma From the dental pulp or Follicular Connective tissue
Btwn 25-30 yo
Painless, slowly enlarging swelling.
Teeth displacement and root resorption in Mandible
Uni or Multilocular RL areas w/ margins Scalloped.
"SOAP BUBBLE" or "TENNIS RACKET" pattern (trabeculae)
Stellate, Spindle -Shaped w/ loose myxoid stroma (gelatinous)
Surgical Excision
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
183. Cementoblastoma - True Cementoma Proliferation of Cementoblasts
Pain, Swelling Posterior Mandible.
Most common 1st Molar.
VITAL TOOTH
RO mass fused to the root.
Root resorption
Extraction of the tooth.
184. Central Odontogenic Fibroma Counterpart of Peripheral O. Fibroma
1/3 of cases of the unerupted teeth
Small lesions Asymptomatic.
Large lesions Associated w/ bone expansion and loosening of teeth.
MAXILLARY: Anterior to the 1st Molar.
MANDIBULAR: Posterior to the 1st Molar
Uni or Multilocular RL.
Root Resorption.
Enucleation and Curettage
185. Odontoma MOST COMMON ODONTOGENIC TUMOR
Hamartomatous lesion (Enamel, Dentin and pulp)
Children /Young Adults
· Complex Odontoma
Posterior Jaw · Amorphous RO mass
· Compound Odontoma
Anterior Jaw. · RO Multiple small tooth
Local Excision.
186. Tori Asymptomatic, non-neoplastic, cover by normal mucosa
· Torus Mandibularis:
Bilateral, Mandible
Premolars (4-5)
· Torus Palatinus: Most common
Middle line of hard palate
Dense RO shadow.
No need it.
Unless denture need a necessary surgical removal of tori.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
187. Fibrous Dysplasia Fibrous connective tissue become bone fragile
Replacement of medullary bone by fibrous C.T
Slowly growth, asymptomatic, can cause expansion of the bone.
· Monostotic:
Single bone Most common 70%
Maxilla more than mandible
Tibia, femur & ribs also common location
· Polyostotic:
Multiple bones
ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE elevated (30%) pts)
Maxillary sinus, Zygoma, Floor (orbit) Sphenoid bone.
1% develops into osteosarcoma
RO lesions. W /appearance of:
GROUND-GLASS Or ORANGE PEEL Or FINGER- PRINT
Bucco-lingual bone expansion
Obturation of Lamina dura, L.D blend with the bone
Osteoid and osseous material
Bone in appearance of CHINESE CHARACTERES
Small resection Or Major Surgery
188. McCune Albright Syndrome Genetic Disorder
Endocrine abnormalities --
Tried
- Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia.
- Premature puberty in females.
- Unilateral "Café-au-lait" spots
Hyperthyroidism, pituitary adenoma
189. Ossifying Fibroma Osteofibroma Fibro-osteoma, Cementifying fibroma
it's bengin
Undifferentiated cells from PDL Slow growing /expansile lesion
Usually Asymptomatic
Females 3rd-4rd decade
Mandible more than Maxilla
RL w/ RO (calcified structures) well defined borders
Connective tissue w/immature bone
Enucleation
Resection for larger lesions
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
190. Periapical Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia Reactive lesion to local factors rather than neoplasm.
Periapical Cementoma
Asymptomatic.
Preference for middle age women African decent.
VITAL TEETH
Lower anterior periapical area
3 stages:
· Osteolyctic: RL
· Cementoblastic: RL/RO
· Mature: RO /RL around.
191. Osteoblastoma Rare benign tumor
Arising from Osteoblast
Dull pain, tenderness and swelling
Males under 30yo
Posterior Mandible
Oval RL w/ areas of mineralization
192. Gardner's Syndrome Autosomal dominant disorder. Inherited
Dental abnormalities.
MULTIPLE IMPACTED / SUPERNUMERARY TEETH
MULTIPLE JAW OSTEOMAS: "COTTON WOOL"
MULTIPLE ODONTOMAS
Multiple osteomas
Fibromas of the skin
Abnormalities of the retina.
Colorectal polyps (become adenocarcinoma by 5th decade of life)
193. Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG) Bengin tumor
TYPES:
· Non-Aggressive:
Most common, slow expansile Asymptomatic
NO ROOT RESOPRTION
· Aggressive:
rapid grow, cortical perforation, ROOT RESOPRTION Hight recurrence
Jaws of Young adults
Anterior to the Molars, Frequently CROSS THE MIDDLE LINE
Unilocular, like Periapical Granuloma or Multilocular like ameloblastoma
Spindled fibroblast and multinucleated giant cells in a stroma of collagen
Curettage
Other TTT:
Calcitonin injections, interferon injections, steroids and bisphosphonates
Recurrence rate 20%
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
194. Langerhans Cell Disease Idiopathic Histiocytosis - Nonlipid Reticule- endotheliosis
Clonal proliferation of Langerhans cells
Tenderness, pain, swelling of bone.
Premature tooth exfoliation.
Variations:
· Eosinophilic: Chronic localized. Most common. Bone lesion only
· Hand Schuller-Christian Syndrome:
Chronic Disseminating. bad prognosis
TRIAD:
Lytic bone,
Exophthalmos,
Diabetes Insipidus.
(bone, skin, visceral organs)
· Letterer-Siwe Disease:
Acute Disseminating Bones, organs skin. Usually affect Infants FATAL
Multiple RL lesions w/ "scoop out" pattern. "floating in the air"appearance.
Large pale cells, Multinucleated giant cells.
Langerhans Cell w/ rod shapes called "Birbeck Granules"
195. Squamous Cell Carcinoma MOST COMMON ORAL CANCER 90% ORAL CAVITY 2ND Skin Cancer
(SCC)
Malignant neoplasm of stratified squamous epithelium. Rests of Malassez and enamel epithelium,
Tobacco (smoking, smokeless), HPV, EBV
Clinical Features:
Leukoplakia,Erythroplakia, Erythroleukoplakia, Occasional loosening of teeth, Exophytic: Fungating,
papillary and verruciform.
Endophytic: (invasive, indurated, ulcerated), Possible paresthesia of teeth and lower lip
· Lip: Vermillion of lower lip Most common site of oral cancer.
· Tongue. Most common IO Post, Lat Border of the tongue. Ease to produce metastasis in lymph nodes
of the neck. Death.
· Floor of the mouth: 2nd most common IO
Anterior or either side of middle line. Poor prognosis.
· Maxillary Sinus: Chronic Sinusitis, paresthesia in cheek, loosening of teeth.
· Nasopharynx: Less common
RL large area. Atrophy of cortical lamina, Excisional surgery.
Mohs surgery.
Radiation/ Chemotherapy, Topical medications
196. Verrucous Carcinoma Squamous cell neoplasm of soft tissue, Tobacco, HPV (16-18)
Invasive, Broad base CAULIFLOWER
Mandibular, Muco-buccal fold, Alveolar mucosa and Palate
197. Basal Cell Carcinoma - MOST COMMON SKIN CANCER
Rodent Ulcer UV-radiation exposure. Female more than male
Non- healing indurated chronic ulcer, locally destructive
Nose & mid - face
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
198. Malignant Melanoma MOST FATAL, 3rd most common skin cancer
UV-radiation exposure, Sunburns
Superficial: Most common, Flat irregular shape.
Lentigo: Hutchinson Freckle, bcz sun damage, skin on the face.
Acral: less common
Nodular: start as a raised areas Poorest prognosis with vertical
growth
Palate, Maxillary Gingival, Alveolar Ridge
Two Grow Phases:
· Radial: Horizontal plane, less metastasis, ABCDE's of Melanoma
(Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving) (Superficial, Lentigo y Acral Melanomas) cure
rate 100%
Vertical: Vertical growing, Metastasis. (Nodular Melanoma) cure rate 70%
199. Multiple Myeloma - Plasma Cell Abnormal plasma cells build up in bone marrow
Myeloma Pain in lumbar or thoracic region, and renal failure.
Swelling, loosening of teeth, and paresthesia, Molar ramus
Multiple, small RL "Punched-out" Lat. Skull is the best Xray to diagnosis.
Abnormality of Plasma Cells, "M Spike" abnormal IgG, IgA
Bence Jones Proteinuria, urinary monoclonal light chain proteins.
200. Plasmacytoma Neoplastic collection of monoclonal plasma cells
ONE LESION, localized, neoplastic. Swelling, bone pain
Spine
201. LYMPHOMA Malignancy of the lymphoid organs and tissues.
In Head-Neck starts in MALT Lymphomas (mucosal-associated lymphoid tissues)
IO Cavity WALDEYER'S RING:Ring of Lymphatic tissue ( 2 palatine tonsils, pharyngeal tonsil
and lingual tonsil)
202. HODQKIN LYMPHOMA (HL) Malignancy of B-Lymphocyte, EBV
Painless mass, firmly, non tender, enlarged lymph nodes.
Cervical/Supraclavicular, Nodes w/ rubbery consistency
If untreated -- spleen, extra lymphatic
Ann Arbor System Staging Curability 75%
Red- Stenberg Cells
203. NON-HODQKIN LYMPHOMA Malignancy of B- T Lymphocyte, Sjogren Syndrome, AIDS
(NHL)
Painless lymph node(s) slow growing (months).
B symptoms: persistent fever of unknown cause, night sweat,weight loss
Common involve WALDEYER'S RING:Ring of Lymphatic tissue (2 palatine tonsils, pharyngeal
tonsil and lingual tonsil.
Abdominal & chest pain
Mandible (numb Chin syndrome) Pain, paresthesia
Teeth: divergent, or root resorption
Buccal vestibule, post hard palate & gingiva Curability 25%
Irregular poorly marinated RL
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
204. BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA Malignancy of B-Lymphocyte, Associated w/ EBV, Very Aggressive and grows rapidly.
· Classic Endemic (African) Maxilla
· Sporadic (American) · Abdominal mass
· Immunodeficiency-associated Burkitt Lymphoma: Facial swelling, proptosis, Tooth mobility, alveolar
bone destruction, pre mature exfoliation of deciduous teeth
"STARRY-SKY" cells appearance
205. OSTEOSARCOMA - MOST COMMON PRIMARY BONES TUMORS AND PEDIATRIC PATIENTS.
Osteogenic Sarcoma Pagett's Disease, Alkylating agents, Radiation exposure
Swelling, localized pain, paresthesia of IA Nerve or Infra Orbital Nerve
loosening teeth and/or displacement.
Common metastasis to lungs and brain
Mandible: 60% on the body of mandible has better prognosis
Symmetrical widening of the PDL space. Periosteal Reaction "SUNBURNST" appearance RO mixed w/
RL Or Entirely RL
206. Chondrosarcoma Cartilage produce by tumor cells
Ill-fitting dentures Painless, swelling and expansion of the bone
Loosening teeth.
"MOTH-EATEN" RL solitary or multilocular to diffuse RO lesions
207. ERWING SARCOMA HIGHLY LETAL Unknown, Round cell sarcoma of bone
Loosening teeth, alveolar bone destruction and paresthesia.
Children/young adults Pain, swelling of the bone.
Metastasis to lungs, other bones and lymph nodes
Ramus of the mandible.
"MOTH-EATEN" Destructive RL of medulla
Periosteal "ONION-SKIN" appearance
Ewing Sarcoma Cells contain glycogen
208. Kaposi Sarcoma Unique form of ANGIOSARCOMA
Malignancy of endothelial cells Associated to AIDS HHV8 (etiologic role)
Small red papules which enlarge and fuse to Purple-brown spongy nodules
Most common in Hard palate. Gingival, and buccal mucosa
209. Metastatic Jaw Lesions Evidence of dissemination of a known tumor:
Adenocarcinoma or carcinoma
Bone pain, loosening teeth, lip paresthesia, swelling, gingival mass, possible pathologic fracture
Angle/body of mandible
Poor RL irregular "MOTH-EATEN"
Diagnosis by
IMMUNOPEROXIDASE STAIN CYTOKERATIN which is present in all Carcinomas cells
TT : surgical, Radiotherapy
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
210. MUCOCELE · Mucus Extravasation Cyst:
Traumatic break of minor salivary duct, · Painless, smooth surface, ma be bluish, dome-shape
fluctuant. MOST COMMON Lower lip
· Mucus Retention Cyst:
True cyst, Obstruction of the salivary gland duct, · Asymptomatic, swelling (no previous injury)
Buccal mucosa. In patients older than 50yo.
Surgical Excision with removal of associated gland.
211. RANULA Mucoceles in the floor of the mouth. SUBLINGUAL GLAND.
(Submandibular gland or minor salivary glands)
Blue fluctuant dome shape swelling, usually larger than mucoceles.
Sometimes elevation of the tongue.
Floor of the mouth. Lateral to the middle line. to distinguish it from mid line dermoid cyst
· Plunging or Cervical Ranula: Spilling mucin dissects to the mylohyoid muscle and produce
swelling of the neck
· Increases before or during the meal and decrease btwn meals.
Surgical Excision with removal of the feeding Sublingual Gland.
Marsupialization.
212. MAXILLARY SINUS RETENTION Blockage of sinus seromucous glands Asymptomatic, usually found in Panoramic x-ray.
CYST - ANTRAL Maxillary Sinus
PSEUDOCYST
Well defined NONCORTICATED smooth dome shape RO mass within the maxillary sinus
No treatment
213. SIALOLITH - Sialolithiasis Stone within a salivary gland or duct.
Pain during salivary stimulation, is intensify at mealtimes.
Submandibular Gland is the MOST COMMON
due to long, upward path of the canal & thick secretion
Parotid gland Sublingual gland
OCCLUSAL XRAY RO well define area close to the duct gland
Surgical Excision with removal of associated gland.
214. NECROTIZING Ischemia of the minor salivary gland. Locally destructive inflammatory condition.
SIALOMETAPLASIA Asymptomatic, necrotic, ulcerated area.
Necrosis of the glandular parenchyma w/ associated squamous metaplasia and hyperplasia of
the duct.
Palatal, hard palate
Biopsy to confirm the diagnosis thenNo treatment.
Heals by its own over 5-6 weeks.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
215. INFECTIOUS SIALADENITIS Inflammation of the salivary gland due to bacterial or viral infection
Mumps (most common) CMV.
· ACUTE:
usually after major surgery. (abdominal Surgery) · Swollen, painful erythematous skin. Purulent
exudate of the orifice of the duct. Associated Fever and trismus.
Parotid Gland
· CHRONIC:
Staphylococcus Aureus, Streptococcus
· due to current or persistent ductal obstruction
Swelling and pain when gland is stimulated.
Sialography often shows Sialectasia (ductal dilatation)
216. MUMPS - EPIDERMIC Acute viral illness caused by PARAMYXOVIRUS
PAROTITIS
Sudden salivary gland swelling, mild fever, malaise and anorexia.
90% before 14 yo Parotid Gland.
Palliative
Non aspirin analgesics, and antipyretics.
217. MIKULICZ'S DISEASE BENING LYMPHOEPITHELIAL LESION IgG4 RELATED DISEASE
Unknow, but may be autoimmune.
Enlargement of salivary or lacrimal gland.
Asymptomatic, starts unilateral but can become bilateral.
Commonly in females around 50 yo
Salivary or Lacrimal glands.
218. SJOGREN SYNDROME - Chronic systemic Autoimmune disorder
SICCA SYNDROME
· Primary: alone
Secondary: associated w SLE, Rheumatoid arthritis
Dry mouth- XEROSTOMY, cause caries.
Dry eyes- KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS SICCA
Difficult in swollen, alternate taste, oral mucosa red and tender, tongue fissured and atrophic.
XRAY: Sialography shows
Sialectasia w/ "Fruit-laden" or "branchless tree" pattern.
HISTO:
Lymphocytic infiltration causing destruction in acinar cells
219. SARCOIDIOSIS Multisystem disorder called GRANULOMAS in certain organs of the body
Submucosal mass and area of granularity or ulceration.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
220. PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA - MOST COMMON SALIVARY GLAND TUMOR
Mixed of ductal epithelium and myoepithelial into mesenchyme area.
Slow growing painless and firm mass. Smooth or lobulated.
Parotid Gland: swelling overlaying mandible ramus
Intraoral: Posterior Palate (minor salivary glands)
Well circumscribed, encapsulated tumor.
221. MONOMORPHIC ADENOMA BASAL CELL ADENOMA
Benning tumor of Parotid Gland
Slow growing, movable mass, less than 3cm, older females
Parotid Gland with Cells looks like basal cells.
CANALICULAR ADENOMA
Minor salivary glands
Slow growing, movable mass, less than 2cm, older females
Upper Lip with Single layer of cuboidal or columnar epithelium
Recurrent is common
222. WATHIN'S TUMOR - PAPILLARY CYSTADENOMA Benign Neoplasm in the Parotid Gland Nontender, slowly enlarging, firm to
LYMPHOMATOSUM fluctuant nodule. Uni or bilateral.
Olders (60-70 yo) More in Males
Mandible: angle or ramus.
Glandular/cystic tumor. Ductal epithelium, lymphoid stroma.
Multiple Papillary producing Cystic Spaces
223. ADENOCARCINOMA aggressive tumor Pain, facial weakness, firm mass w/ irregular borders and
infiltration into surrounding tissue
Solid tumor Parotid Gland
224. ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA Pain, and tendency to Show perineural invasion
Minor Salivary gland of the palatal (50-70%)
Major Glands: Parotid and Submandibular
Cilibriform "SWISS CHEESE", tubular and solid cells pattern.
225. MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA MOST COMMON MALIGNANT TUMOR IN MINOR/MAJOR GLANDS
Asymptomatic swelling
Parotid (45-70%) Palate.
Central or intraosseous Mucoepidermoid adenocarcinoma in posterior of the
Mandible.
Mucus cells And Epidermoid cells
226. ACINIC CELL CARCINOMA 2nd most common parotid malignancy Parotid
Abnormal (malignant) growth of salivary gland cells
Slow growing mass, associated with pain or tenderness in 50% of the cases
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
227. Malignant Mixed 1. Carcinoma ex-mixed tumor From the epithelium
Tumors
2. Carcinoma True malignant tumor Stroma and epithelial
3. Metastasizing mixed tumor From Pleomorphic adenoma that Develops metastatic deposits
Slow growing mass, associated with pain or tenderness
228. POLYMORPHOUS 2nd most common malignancy in MINOR SALIVARY GLANDS
LOW-GRADE
ADENOCARCINOMA Abnormal (malignant) growth of salivary gland cells
Slow growing mass, associated with pain or tenderness
Palate Lip Buccal Mucosa
229. Impetigo Bacterial, superficial skin infection caused by Staph aureus alone or with Strep pyogenes. Increased
prevalence in HIV, type 2 diabetes or dyalisis.
Nonbullous impetigo: more common in school-aged children, also adults. Red macule or papules-->fragile
vesicles-->rupture and covered with thick crust. Legs, trunk, scalp and face.
Bullous impetigo: Infants and newborns, superficial vesicles-->larger flaccid bullae-->rupture with thin brown
crust
TTT Small lesions: Topical fusidic acid. Extensive lesions: 1 week systemic oral antibiotics (Cephalexin)
230. Crohn's Disease - Inflammatory, immunologically mediated condition of unknown cause. Affects the distal portion of the small
Erosional Enteritis bowel and proximal colon but may be seen anywhere in the GI tract.
S&S: abdominal cramping and pain, nausea, diarrhea, fever, weight loss.
Diffuse nodular swelling of the oral and perioral tissues. Non caseating granulomatous LINEAR Ulcers in
buccal vestibule. Edema and hyperplasia --> cobblestone mucosa appearance. Patchy erythematous
macules and plaques in attached and unattached gingiva: mucogingivitis
To control symptoms: dietary adjustment, costicosteroids, antibiotics, sulfasalazine, immunosuppressants.
231. Infectious Exposure to Epstein-Barr Virus (HHV-4). Spreads through intimate contact: "kissing disease" and remains in
Mononucleosis - host 4ever.
Glandular Fever
Sx: Fever, lymphadenopathy, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, petechiae on the palate.
B-Lymphocytes and Monocytes cells increased--> Leukocytosis.
2 Tests to detect Ab against EBV: Monospot and All panel test.
Supportive: fluid intake, nutrition and NSAIDs Self limiting within 4-6 weeks
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
232. Human Belongs to retrovirus family, transmission via blood, semen, vaginal fluid or breast milk.
Immunodeficiency HIV infects CD4+ T helper cells, macrophages and certain nerve cells. HIV has clinical stages where the viral
Virus (HIV) load increases while the CD4 count decreases.
CD4 average count: 500-1200 cells/mm3 AIDS: CD4 count is below 200 cells/mm3
S&S: HIV flu-like, In progression to AIDS: Rapid weight loss; profuse night sweats; extreme tiredness; prolonged
swelling of lymph nodes in armpits, groin or neck; diarrhea that lasts > than a week, sores of mouth, genitals,
anus; pneumonia; memory loss, depression.
Strongly associated with HIV:
Candidiasis (both types) is the most common infection
Hairy Leukoplakia
Kaposi's sarcoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Periodontal disease: LINEAR gingival erythema, NUG and NUP.
HIV confirmation through Ab testing Combination antiretroviral therapy (cART)/ Highly active antiretroviral
treatment (HAART)
Early initiation reduces risk for AIDS, death and disease transmission.
233. Linear Gingival Uncommon gingival lesion associated with HIV-->unusual pattern of candidiasis.
Erythema Red band along the margin of the gingiva (2-3mm apically to attached gingiva), remaining attached gingiva
shows diffuse erythema.Rare gingival bleeding.
Debridement, chlorhexidine mouth rinse, and/or antifungals
234. Measles - Morbilli, Highly contagious caused by measles virus (paramyxoviridae family). Transmission through respiratory
Rubeola, droplets.
Red Measles Fever (40ºC)+3 C's: Cough, Coryza (head cold, sneeezing), Conjunctivitis.
Measles rash: Red generalized, maculopapular rash. Starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body.
Koplik's spots: cluster of white lesions on the buccal mucosa (opposite to 1 and 2nd molars)and is prodromal to
the measles rash.
Prevention with MMR vaccine.
1st dose: 12-15 months 2nd dose: 4-6 YO Supportive: fluids, NSAIDs, symptomatic relief.
235. Rubella - German Contagious disease caused by a virus of the togavirus family. It can spread through respiratory droplets.
Measles Mild and short duration symptoms (rash, fever, respiratory issues) Cause congenital defect in a developing
fetus (1st trimester pregnancy)-->
Congenital rubella syndrome: deafness, heart disease and cataracts. NO Koplik's spots
Prevention with MMR vaccine. 1st dose: 12-15 months 2nd dose: 4-6 YO Supportive: fluids, NSAIDs,
symptomatic relief.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
236. Viral Hepatitis Hepatitis A: RNA Enterovirus. Incubation 3-6 weeks, transmission fecal-oral route. No carrier state.
Sx: fever, malaise, abdominal pain, anorexia and jaundice. Self limiting
Hepatitis B: Double stranded DNA virus. Incubation 6-8 weeks. Transmitted through parenteral and sexual contact.
Pt is a carrier.
Sx: fever, malaise, abdominal pain, anorexia and jaundice.
Prevention with Hep B vaccine. Zero, One and Six months.
Anti-HBs levels above 10mIU/mL: Complete protection against HBV
Hepatitis C: Blood to blood transmission, Most common after blood transfusion
Initial symptoms are subtle but it causes a higher incidence of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular
carcinoma
Hepatitis D: Found in Pts with Hep B, makes the infection more severe.
Increased serum levels of liver enzymes (transaminase)
237. Cystic Fibrosis Autosomal recessive disorder. Gene mutation with exocrine glands producing abnormally viscous secretions (low
(CF) H2O, high Na and Cl), blocking the ducts in the pancreas, sweat glands and lungs--> bacterial proliferation.
Sx: foul smelling, poor weight and growth, intestinal blockage, persistent cough with thick mucus, wheezing,
breathlessness, exercise intolerance, repeated lung infections.
Reduces caries rate (normal flora affected due to elevated intake of antibiotics). Tetracycline staining of teeth
Delayed Dental development and eruption. Enamel hypoplasia
Sweat Test: Elevated levels of sodium and chloride
TTT Antibiotic, mucous thinning drugs, bronchodilators
238. Rheumatoid Chronic autoimmune disorder with non-suppurative inflammation of joints, skin and organs.
Arthritis Cross-reaction between Ab and streptococci or other
M.O. Affects women more than men. Periods of activity and remission. Small joints of the hands and feet High
rheumatoid factor in 80% of patients related with open bite
No cure Supportive: NSAIDs and corticosteroids
239. Scarlet Fever Caused by group A, beta-hemolytic Streptococci, Children from 3 to 12 YO, infection spread through droplets.
Disease begins as tonsillitis with pharyngitis, fever and swollen lymph nodes. Exanthematous rash on the trunk
and extremities.
Complications: Glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever Strawberry tongue, only fungiform papillae can be seen.
Enanthem of oral mucosa, tonsils, pharynx and soft palate. Antibiotic therapy: oral penicillin, if allergic-->
macrolides
240. Creutzfeldt- Rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease, appears in later life, always fatal (within 1 year). Caused by Prions.
Jakob Disease CJD Prions are abnormally folded proteins, which are insoluble and collect in the CNS disrupting neural signaling.
(CJD) In sporadic CJD (85%), most common. The disease appears with unknown risk factors for the disease.
S&S: varies on the type, include dementia, behavioral/psychiatric problems In hereditary CJD (15%), the person
may have a family history of the disease and test positive for a genetic mutation associated with CJD
241. Vitamin A Maintenance of vision, growth and tissue differentiation.
(retinol)
Dif
Night blindness, dryness of the skin and conjunctiva. Ulceration of the cornea leading to blindness. Increase in
keratinization.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
242. Vitamin B1 (thiamin) Coenzyme for several metabolic reaction and maintains proper functioning of neurons.
Dif
Beriberi syndrome (Cardiovascular and neurologic problems). Wernicke-Korsakoff's syndrome
(progressive mental deterioration)
243. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) Important for cellular oxidation reduction reactions.
Dif
Disturbance in metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids; Anemia; Angular cheilitis; Glossitis
(magenta); Dermatitis
244. Vitamin B3 (niacin) Coenzyme for oxidation reduction reaction
Dif
Triad of Sx: Diarrhea, Dermatitis and Dementia. Mucosal Sx: Glossitis, Atrophic stomatitis and Cheilitis.
Rough skin (Pellagra)
245. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) Participate in Amino acid synthesis.
Dif
Weakness, dizziness, seizure disorders. Oral: Cheilitis and Glossitis
246. Vitamin B9 (folate) Lower the risk of birth defects of the brain and spinal cord.
Dif
Megaloblastic anemia, neural tube defects and other birth defects.
247. Vitamin E (alfa- Fat-soluble vitamin functions as an antioxidant
tocopherol)
Dif
Severe malabsorption of all-fat soluble vitamins, abnormalities in the CNS and PNS
248. Vitamin K Fat-soluble vitamin necessary for synthesis clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X. 1972
Dif
Coagulopathy manifested intraorally by gingival bleeding
249. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Occurs in people who lack a diet of fresh fruit and vegetables. Vit C is essential for collagen synthesis.
Scurvy
Dif
Weakened vascular walls causing haemorrhagia, Wound healing is delayed.
Oral: generalized gingival swelling with spontaneous hemorrhaging, ulceration, tooth mobility, and an
increased periodontal infection.
250. BELL'S PALSY HERPES VIRUS, Otitis media, ischemia of the facial nerve near the stylomastoid foramen.
One side of the Face droop, affected Taste and tear production.
Unilateral face
Heals in 2-3 weeks (85%)
Systemic Corticoids
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
251. TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA Compression of the nerve by varies anatomical structures.
TIC DUOLOUREUX
TRIGUER POINT like (brushing teeth)
Extreme PAIN-ELECTRIC SHOCK- LIKE Paroxysmal or lancinating
Trigeminal nerve area
Carbamazepine (anticonvulsive)
252. GLOSSOPHARINGEAL Neuralgia of IX cranial nerve or trigger factors (cold drinks, sneezing, coughing, talking)
NEURALGIA
Sharp, stabbing pulses of pain
Back of the throat, tongue, tonsils, and middle ear.
Anticonvulsants
253. POSTHEPETIC NEURALGIA Nerve damage by Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
Pain severe, stabbing/ burning.
May persist by months, years or life
Same dermatotic area of the outbreak occurred
Tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin) and opioids
254. FREY'S SYNDROME When auriculotemporal nerve after Parotid gland removed, heals innervating accidentally sweat
AURICULOTEMPORAL glands of the face instead.
SYNDROME
Gustatory sweating Patient refers
Flushing and sweating on his/her face during eating.
Face
No Treatment required
255. MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Autoimmune neuromuscular disease.
Destruction of receptors for Acetylcholine at the muscular junction which prevents muscle
contraction.
Muscle's weakness, mouth drop, dysphagia, flaccid and furrowed tongue.
Gingival hyperplasia from cyclosporine use.
Xerostomia, and may be Rampant caries.
Flat smile, double vision, difficult to eat, droopy eyes w/ slow papillary light response
Face Muscles.
Anticholines and Immunosuppressors
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
256. MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Chronic autoimmune disease which attacks the CNS.
Usually in females Btwn 20-40 yo.
Facial and jaw weakness.
Tingling, numbness to paralysis and blindness may appear.
Bell palsy and Trigeminal neuralgia found in MS.
Face Muscles
257. MUSCULAY DYSTROPHY Progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscles
Weakness in the muscles of mastication, decreased in maxillary biting force, mouth
breathing and open bite
Face Muscles
258. CHEILITIS GLANDULARIS Tobacco, poor hygiene and hereditary
Swelling of the LOWER LIP due to Hypertrophy and inflammation of the glands.
Mucopurulent secretions can be produced. And sometimes erosions and ulcers.
Lower lip
Vermilionectomy
259. CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA Chronic disorder w/ non-caseating (non-necrotizing) granulomatous inflammation
Painless and persistent swelling of one or both lips.
Small vesicle, ulcers and erosions may occur.
Lips
Steroids, surgery removal of suspect allergen
260. MELKERSSON-ROSENTHAL TRIAD:
SYNDROME · Cheilitis Granulomatosa
· Facial paralysis (unilateral)
· Fissured tongue
261. EXFOLIATIVE CHEILITIS Excessive production and desquamation of superficial keratin in lips
Chronic inflammation of lips causing scaling, crusting and erythema of vermilion border.
Vermillion of lips Topical Steroids or
topical ointment or Tacrolimus
262. CONTACT CHEILITIS - CONTACT Contact w/ various allergens
STOMATITIS (Mouthwashes, gum/rubber dam, restorative metals, dental materials, etc.)
Chronic dryness, scaling, fissuring or cracking of the vermillion border.
Remove the offending agent, and Topical corticosteroids
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
Done By: Mohamed Moussa
263. ACTINIC CHEILITIS ACTINIC CHEILOSIS SOLAR CHEILITIS
Long term to exposure to sunlight
Premalignant condition affects middle age to elderly.
Tobacco and immunosuppression increase malignancy to Squamous cell Carcinoma
Erythema, edema and dryness with blurring of the margin btwn vermillion and the adjacent skin.
Chronic ulceration may be.
Lower Lip Sun protection Vermilionectomy
264. LIP-LICKING DERMATITIS Chronic licking by children
Erythematous and scaly w/ burning sensation.
Lip Avoid lip licking
265. MEDIAN LIP FISSURE Persistent deep vertical lesion at the lip
Can be infected by bacteria or candida.
spontaneous bleeding, discomfort and pain
Middle of the lip
Topical steroids and antimicrobials.
Surgery in severe cases.
https://quizlet.com/ShetoTheDentist Done By: Mohamed Moussa www.fb.com/sheto
You might also like
- INBDE High-Yield Conditions To KnowDocument17 pagesINBDE High-Yield Conditions To KnowРами Кальмат100% (1)
- Class I, II & VI Amalgam RestorationDocument2 pagesClass I, II & VI Amalgam RestorationSahil SraNo ratings yet
- Patho Lec 4THDocument3 pagesPatho Lec 4THJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Anomalies - LectureDocument10 pagesAnatomic Anomalies - LectureKhalid BhatNo ratings yet
- Classification of Anomaly2Document213 pagesClassification of Anomaly2samar yousif mohamed100% (1)
- Cawsons Chapter 2Document4 pagesCawsons Chapter 2Katie WithersNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Teeth Eruption, Structure, Form, Number, and SizeDocument48 pagesAbnormalities of Teeth Eruption, Structure, Form, Number, and SizeNoor AlsanouriNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Teeth1.2020Document5 pagesAbnormalities of Teeth1.2020Farhaana ShaboodienNo ratings yet
- Dr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyDocument62 pagesDr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyoladunniNo ratings yet
- Dev Dis ToothDocument92 pagesDev Dis ToothVaishnavi ThatiparthiNo ratings yet
- Developmental DefectsDocument29 pagesDevelopmental DefectsPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Oral Path PDFDocument367 pagesOral Path PDFAashka Desai100% (2)
- Developmental Anomalies of TeethDocument78 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of TeethPauline Joy Cayago CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dental Anomalies ملخصDocument8 pagesDental Anomalies ملخصهند عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Sequelae of TraumaDocument27 pagesSequelae of TraumaDr.O.R.GANESAMURTHINo ratings yet
- Dental Anomalies Lecture IIDocument23 pagesDental Anomalies Lecture IIqpnbzsbkqgNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Teeth: Environmental and Developmental AlterationsDocument114 pagesAbnormalities of Teeth: Environmental and Developmental AlterationsoiljimmyNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of The Teeth PDFDocument75 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of The Teeth PDFIbrahim HashimiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic IIDocument11 pagesTherapeutic IIkimiaNo ratings yet
- Pathological AnalysisDocument58 pagesPathological AnalysisAhella AlaaNo ratings yet
- Aetiology of MalocclusionDocument5 pagesAetiology of MalocclusionSRO oONo ratings yet
- Os MidtermDocument2 pagesOs MidtermGuen ColisNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery 5Document18 pagesOral Surgery 5youssefkamal838No ratings yet
- Patología ORAL MVRDocument18 pagesPatología ORAL MVRMonserrath VidalesNo ratings yet
- Developmental TeethDocument53 pagesDevelopmental Teethlyli Star AngeloNo ratings yet
- APznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17ZdDocument24 pagesAPznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17Zdclassybrands0No ratings yet
- Odontogenic TumorsDocument32 pagesOdontogenic Tumorssatya_mds100% (2)
- Oral PathologyDocument184 pagesOral Pathologyyalahopa100% (1)
- Oral Pathology ModuleDocument31 pagesOral Pathology ModuleDenee Vem MatorresNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Pathology: Glo Arby Arguelles, DMDDocument27 pagesPediatric Pathology: Glo Arby Arguelles, DMDRayne GelleNo ratings yet
- ORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensDocument24 pagesORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensPravin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologyDocument38 pagesDevelopmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologydrchakshuaggarwalNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of Tooth PDFDocument97 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of Tooth PDFEmad AlriashyNo ratings yet
- Dental AbnormalitiesDocument19 pagesDental AbnormalitiesKha KinNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumors IIDocument24 pagesOdontogenic Tumors IIIbn HabibNo ratings yet
- Pedo2013 14Document189 pagesPedo2013 14Vladimir Argirovic100% (4)
- OriginalDocument10 pagesOriginalAmir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Q1. Difference Between:: GeminationDocument3 pagesQ1. Difference Between:: GeminationRadaina NiazNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DentistryDocument96 pagesPediatric DentistryChinielee R ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Document41 pagesCysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Seca mandiNo ratings yet
- Dental TerminologiesDocument2 pagesDental TerminologiesPauline BulaunNo ratings yet
- Ortho - Application-As-A-GdpDocument8 pagesOrtho - Application-As-A-Gdprajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Toolbox: Oral Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesToolbox: Oral Health and Diseasena rinNo ratings yet
- Toolbox: Oral Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesToolbox: Oral Health and DiseasePrimaNo ratings yet
- ECTOPICERUPTION HandoutDocument4 pagesECTOPICERUPTION HandoutDr-Basel RehawiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders of TeethDocument64 pagesDevelopmental Disorders of TeethPatterson MachariaNo ratings yet
- Enamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationDocument41 pagesEnamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationMohammad ANo ratings yet
- Teeth DefectsDocument32 pagesTeeth DefectsManoj NaiduNo ratings yet
- Variation in Tooth Morphology Anatomy PDFDocument9 pagesVariation in Tooth Morphology Anatomy PDFadriiianaiiioanaNo ratings yet
- $pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerDocument96 pages$pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerGhadeerHassaanNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2008 35 636-641Document5 pagesDent Update 2008 35 636-641bkprosthoNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2008 35 636-641 PDFDocument5 pagesDent Update 2008 35 636-641 PDFbkprosthoNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiology: A Guide To Radiographic InterpretationDocument16 pagesDental Radiology: A Guide To Radiographic InterpretationCeline BerjotNo ratings yet
- XXXXX 22222Document5 pagesXXXXX 22222Hans GuilasNo ratings yet
- Structure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Document36 pagesStructure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Khushi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Sakeena Assad PresentationDocument93 pagesSakeena Assad Presentationjenny girlNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Macroscopic Anatomy and Pulp Space MorphologyDocument24 pagesMacroscopic Anatomy and Pulp Space MorphologyKhaled Elshabrawy100% (1)
- Kti Vida HusniaDocument49 pagesKti Vida HusniaElsa AghniaNo ratings yet
- L5 Dental Indices SSDocument77 pagesL5 Dental Indices SSShmoukhNo ratings yet
- Facemask MC NamaraDocument11 pagesFacemask MC NamaraMenakaNo ratings yet
- 2007 - Orthodontics and MicroimplantsDocument356 pages2007 - Orthodontics and MicroimplantsInês FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Management of Impacted Maxillary Canines Using The Kilroy Spring: A Case SeriesDocument7 pagesManagement of Impacted Maxillary Canines Using The Kilroy Spring: A Case SeriesThang Nguyen TienNo ratings yet
- Tooth PreparationDocument105 pagesTooth Preparationbarsha0% (1)
- Majalah Ikorti Des 2016 PDFDocument54 pagesMajalah Ikorti Des 2016 PDFvalitAuliaNo ratings yet
- EndoTriad May2015Document7 pagesEndoTriad May2015puspasimanungkalit270586No ratings yet
- Management of Ankylosed Primary Molars With Premolar Successors A Systematic ReviewDocument11 pagesManagement of Ankylosed Primary Molars With Premolar Successors A Systematic ReviewIbraheem SNo ratings yet
- The Bone Shielding Versus Dual-Zone Concept in TreatingDocument13 pagesThe Bone Shielding Versus Dual-Zone Concept in Treatingahmadalturaiki1No ratings yet
- Prezzano 1951Document10 pagesPrezzano 1951Rockey ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Modern Anterior Endodontic Access and Directed Dentin Conservation David Clark & John Khademi PDFDocument5 pagesModern Anterior Endodontic Access and Directed Dentin Conservation David Clark & John Khademi PDFizeldien5870No ratings yet
- The Bionator: British Journal of OrthodonticsDocument5 pagesThe Bionator: British Journal of OrthodonticsRaphael DutraNo ratings yet
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument69 pagesClassification of MalocclusionBatman 02053No ratings yet
- FogfelismerésDocument11 pagesFogfelismerésdb nklttNo ratings yet
- Incisors - Type TraitsDocument4 pagesIncisors - Type TraitsVanissa KarisNo ratings yet
- Deep-Bite Fontaine-Sylvestre - CatherineDocument126 pagesDeep-Bite Fontaine-Sylvestre - CatherineEttore AccivileNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Occlusion On 11 May 2022Document25 pagesSeminar On Occlusion On 11 May 2022Dr Saurav kumar DuttaNo ratings yet
- PD 4.histopathology of Dental CariesDocument40 pagesPD 4.histopathology of Dental CariesUmaima Khan100% (1)
- Stainless Steel CrownDocument6 pagesStainless Steel CrownWen Shu GohNo ratings yet
- BleachingDocument62 pagesBleachingوردة صبرNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy QuizDocument5 pagesDental Anatomy QuizSereen Abd El-rahman0% (1)
- Radiology Paralleling TechniqueDocument67 pagesRadiology Paralleling TechniqueFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument51 pagesClassification of MalocclusionYuvashreeNo ratings yet
- Prepared Cavities On The StrenDocument4 pagesPrepared Cavities On The StrenPriyank RaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PulpDocument10 pagesLecture 5 Pulpمؤمل رياض سعد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Botos Alexandra - Oral SemiologyDocument46 pagesBotos Alexandra - Oral SemiologyMaria OlteanNo ratings yet
- Abutments in Fixed Partial DenturesDocument19 pagesAbutments in Fixed Partial DenturesKashish08No ratings yet