Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Absar Baig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesOriginal Title
CHAPTER 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesChapter 2
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Absar BaigCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
CHAPTER: 02
GLOBALIZATION OF MARKETS AND THE
INTERNATIONALIZATION OF THE FIRM
Q: How international business contribute to improving business method
International business improves methods by promoting cross-cultural collaboration, fostering
innovation through diverse perspectives, and encouraging companies to adapt and optimize
strategies to meet global market demands. The competition on a global scale also drives
continuous improvement, pushing businesses to adopt best practices and invest in advanced
technologies to stay competitive.
Q: Provide example on socialization and actualization
Socialization:
Socialization is the process through which individuals learn and internalize the values, norms,
and behaviors of their society.
Consider an employee joining a new company and adapting to its organizational culture through
interactions with colleague and training programs.
Actualization
Occurs when individuals or groups from one culture come into contact with another culture and
adopt some of its elements.
Example of acculturation is when someone moves to a new country and begins to celebrate local
holidays or adopts certain customs from the new culture while retaining aspects of their own.
Q: Difference between Relativism and Normativism
Relativism:
• Values are subjective and vary across cultures.
• Emphasizes cultural diversity.
• Ethical standards are context-dependent.
• Encourages tolerance for diverse moral perspectives.
• Opposes absolute moral judgments.
Normativism:
• Advocates for universal values.
• Emphasizes certain norms apply universally.
• Asserts the existence of objective ethical standards.
• Posits universal principles guiding behavior.
• Supports absolute moral judgments.
Q: Globalization of markets
Refers to the process where businesses operate on a worldwide scale, selling and buying goods
and services internationally. It involves breaking down traditional barriers, allowing companies
to reach customers in different countries, leading to a more interconnected and interdependent
global economy.
Q: value chain
A value chain is like a step-by-step journey that a product takes from raw materials to the hands
of the customer. It includes all the activities involved in making, selling, and delivering a
product. Each step adds value to the product, making it better or more useful, until it reaches the
customer. It helps companies understand where they can improve and be more efficient in
creating and delivering their products or services.
Q: Phases of Globalization
First Phase (Pre-1800s):
Limited international trade, mainly local or regional.
Second Phase (1800s - Mid-20th Century):
Industrial Revolution boosts global trade; rise of multinational corporations.
Third Phase (Mid-20th Century - Present):
Post-WWII technological advancements; liberalization of trade; global interconnectedness.
Q: The Drivers of Market Globalization
Q: Technological Advances & Globalization in context of:
1. Information Technology:
• Advances: Rapid growth of computers, internet, and data processing.
• Example: Global access to information through the internet and instant communication.
2. Digitalization:
• Advances: Transformation of analog data into digital formats.
• Example: Digital payment systems replacing traditional cash transactions globally.
3. Manufacturing:
• Advances: Automation, robotics, and 3D printing revolutionizing production.
• Example: Global supply chains using automation for efficient and cost-effective
manufacturing.
4. Communication:
• Advances: Instant global communication through smartphones and social media.
• Example: Real-time collaboration among people worldwide using messaging apps and
video calls.
5. Transportation:
• Advances: Faster and more efficient modes of global transportation.
• Example: Air cargo enabling swift movement of goods between continents, reducing
shipping times.
Q: Dimensions of Market Globalization
1. Integration and Interdependence of National Economies:
• Description: Increased connections between economies, fostering interdependence.
• Example: Global supply chains where components are sourced from different countries.
2. Rise of Regional Economic Integration Blocs:
• Description: Formation of groups of countries cooperating economically.
• Example: European Union (EU) facilitates trade and economic cooperation among
member nations.
3. Growth of Global Investment and Financial Flows:
• Description: Increase in cross-border investments and financial transactions.
• Example: Foreign direct investment (FDI) from one country into businesses in another.
4. Convergence of Consumer Lifestyles and Preferences:
• Description: Similarities in consumer behaviors and preferences worldwide.
• Example: Global popularity of smartphones and international fast-food chains.
5. Globalization of Production:
• Description: Manufacturing processes spread across different countries.
• Example: Car components manufactured in various countries, then assembled globally.
6. Globalization of Services:
• Description: Internationalization of service-based industries.
• Example: Outsourcing customer support to a call center in another country.
Q: Societal Consequences of Globalization
1. Contagion: Rapid Spread of Monetary and Financial Crises:
• Description: Financial issues in one country quickly impacting others.
• Example: The 2008 financial crisis originating in the U.S. affecting global markets.
2. Loss of National Sovereignty:
• Description: Reduced control and influence of individual nations.
• Example: Adherence to global trade agreements limiting policy autonomy.
3. Offshoring:
• Description: Shifting business operations to other countries.
• Example: A company in the U.S. moving its customer service to a call center in India.
4. Reshoring:
• Description: Bringing previously offshored activities back to the home country.
• Example: A company relocating manufacturing back to the U.S. for quality control.
5. Effect on the Poor:
• Description: Impact on income inequality and job opportunities.
• Example: Job loss in local industries due to global competition affecting lower-income
workers.
6. Effect on Sustainability and the Natural Environment:
• Description: Environmental impact of global production and consumption.
• Example: Increased carbon emissions from long-distance transportation of goods.
7. Effect on National Culture:
• Description: Influence of global trends on local traditions and values.
• Example: Adoption of Western lifestyles impacting traditional cultural practices.
You might also like
- Bergerac Systems: The Challenge of Backward IntegrationDocument3 pagesBergerac Systems: The Challenge of Backward IntegrationPulkit Aggarwal100% (1)
- Restoring Economic Health To The North SeaDocument28 pagesRestoring Economic Health To The North SeajombibiNo ratings yet
- A Handbook On Supply Chain ManagementDocument89 pagesA Handbook On Supply Chain ManagementSimejNo ratings yet
- School of Business and Management CHRIST (Deemed To Be University) BBH361B Healthcare Services Management CIA-1Document9 pagesSchool of Business and Management CHRIST (Deemed To Be University) BBH361B Healthcare Services Management CIA-1sara shendeNo ratings yet
- Quality Enhancement in Voluntary Carbon Markets: Opening up for MainstreamFrom EverandQuality Enhancement in Voluntary Carbon Markets: Opening up for MainstreamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BowersoxDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Bowersoxssregens82100% (1)
- Inb 372 Chapter 1Document24 pagesInb 372 Chapter 1Jawadul IslamNo ratings yet
- Globalisation PPT (Mahima)Document18 pagesGlobalisation PPT (Mahima)Rahul BhardwajNo ratings yet
- International Business ManagementDocument44 pagesInternational Business ManagementAniket KolheNo ratings yet
- IBEDocument15 pagesIBEchaudharimohit693No ratings yet
- Unit2: Globalization, Addressing A VUCA Environment With A Bottoms - Up Approach (Volatile, Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous Time)Document39 pagesUnit2: Globalization, Addressing A VUCA Environment With A Bottoms - Up Approach (Volatile, Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous Time)Rajeshree Jadhav100% (1)
- PrinciplesofManagement 16 GlobalizationAndBusinessDocument40 pagesPrinciplesofManagement 16 GlobalizationAndBusinesssabyasachibbaNo ratings yet
- IB Chapter 2Document39 pagesIB Chapter 2qianqianNo ratings yet
- Session 3 TheoryDocument57 pagesSession 3 TheoryNachiket BanNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 2) Globalization of Markets & The Internationalization of The FirmDocument57 pages(Chapter 2) Globalization of Markets & The Internationalization of The FirmPatrice MarandaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Globalization On Organizational Behaviour: John Rhoniel B. Mateo, RN, LPTDocument10 pagesImpact of Globalization On Organizational Behaviour: John Rhoniel B. Mateo, RN, LPTjohn_mateoNo ratings yet
- IB - CHAPTER ONE - SM MajorDocument32 pagesIB - CHAPTER ONE - SM Majorriham abdelsalamNo ratings yet
- Mid 1 IBDocument10 pagesMid 1 IBSafat ArafatNo ratings yet
- The Structures OF Globalization: - Global EconomyDocument46 pagesThe Structures OF Globalization: - Global EconomyPrincess BersaminaNo ratings yet
- Global Issues: BS Economics 7Document15 pagesGlobal Issues: BS Economics 7Broken AngelNo ratings yet
- 405 - U1Global Strategic ManagementDocument30 pages405 - U1Global Strategic ManagementPRASHANT KUMBHARNo ratings yet
- Belab Unit 2Document37 pagesBelab Unit 2vartikajaiswal753No ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument13 pagesInternational BusinessdalveerchoudharyNo ratings yet
- Globalization PowerpointDocument15 pagesGlobalization Powerpoint21426.2023No ratings yet
- 2 - Drivers of International BusinessDocument11 pages2 - Drivers of International BusinessSudhamathiNo ratings yet
- 405 U1Global Strategic ManagementDocument30 pages405 U1Global Strategic ManagementAkanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- International Business: Chapter No. 1Document42 pagesInternational Business: Chapter No. 1saqib ghiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Pbs3233Document22 pagesChapter 1 Pbs3233Atikah Izzati100% (1)
- 1 Answer Introduction: Globalization Is Defined As An Interdependence of World Economies. ItDocument7 pages1 Answer Introduction: Globalization Is Defined As An Interdependence of World Economies. ItAkshatNo ratings yet
- International Financial ManagementDocument45 pagesInternational Financial Managementboburovich122No ratings yet
- Economic GlobalizationDocument9 pagesEconomic GlobalizationlatigayjohnreyNo ratings yet
- 405: Global Strategic ManagementDocument19 pages405: Global Strategic ManagementSiddharth AhireNo ratings yet
- Combinepdf 1-4Document86 pagesCombinepdf 1-4ahmadnurhanifs2No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - GlobalizationDocument26 pagesTopic 1 - Globalizationahmadnurhanifs2No ratings yet
- AGB 204 - Trade &globalization - Lecture 6 May 2024Document20 pagesAGB 204 - Trade &globalization - Lecture 6 May 2024Rene Aubert MbonimpaNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationofservicesDocument18 pagesGlobalizationofservicesDurgesh AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument11 pagesGlobalizationtacangbadetteNo ratings yet
- GlobalisationDocument14 pagesGlobalisationPragya Rathor Shah100% (1)
- INB 372 Lec-1 GLOBALIZATION & INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Fall 2018Document31 pagesINB 372 Lec-1 GLOBALIZATION & INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Fall 2018Aryan Bin Reza 1931031630100% (1)
- D Efin Itio N - Differences B/W Domestic and IB - Evolution - Nature - Reasons/Benefits - Stages Of: - Approachesofib - DriversofglobalisationDocument36 pagesD Efin Itio N - Differences B/W Domestic and IB - Evolution - Nature - Reasons/Benefits - Stages Of: - Approachesofib - DriversofglobalisationSarita PrasadNo ratings yet
- Global Business Environment: Presented By-Ashmi Neupane Roll No - 2 Sec - BDocument45 pagesGlobal Business Environment: Presented By-Ashmi Neupane Roll No - 2 Sec - Bneupane ashmiNo ratings yet
- Exam Q - ADocument3 pagesExam Q - AbinhadisuperstoreNo ratings yet
- Business & The International EconomyDocument16 pagesBusiness & The International Economypalakmankani02No ratings yet
- International Business and Trade - Ba MGT104 - General ReviewerDocument30 pagesInternational Business and Trade - Ba MGT104 - General ReviewerFelix Dichoso UngcoNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and International Advertising Imp QuestionsDocument5 pagesGlobalisation and International Advertising Imp QuestionsK P CreationNo ratings yet
- A Look at Globalization and International BusinessDocument19 pagesA Look at Globalization and International BusinessRony TolingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GlobalizationDocument12 pagesChapter 1 GlobalizationAqib Ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Group 5 IB CAT 1 PresentationDocument16 pagesGroup 5 IB CAT 1 PresentationMoann JhaNo ratings yet
- International Marketing 10th Edition Czinkota Solutions Manual 1Document17 pagesInternational Marketing 10th Edition Czinkota Solutions Manual 1donna100% (55)
- International Marketing 10Th Edition Czinkota Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesInternational Marketing 10Th Edition Czinkota Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFchristine.carpenter904100% (19)
- International Marketing 10th Edition Czinkota Solutions Manual 1Document34 pagesInternational Marketing 10th Edition Czinkota Solutions Manual 1alexstanleyqzjncmtrwe100% (33)
- Enhancement 1 TCW Review MaterialDocument15 pagesEnhancement 1 TCW Review Materialdarcyy2003No ratings yet
- Comparitive Managment SystemDocument15 pagesComparitive Managment SystemAhsan Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Drivers of Services To Global MarketDocument11 pagesDrivers of Services To Global MarketkrishcatNo ratings yet
- 405 AssignmentDocument14 pages405 AssignmentadhikaNo ratings yet
- Andi Tahmid Aswan. N - 22080574100 - MN 2022 I - InterBizDocument3 pagesAndi Tahmid Aswan. N - 22080574100 - MN 2022 I - InterBizandi.22100No ratings yet
- Vi. Key Strategic Management TopicsDocument31 pagesVi. Key Strategic Management Topicsploey326No ratings yet
- Eco ProjectDocument26 pagesEco ProjectCutepieNo ratings yet
- Drivers & Dimensions of Market Globalization by Martinson T. YeboahDocument37 pagesDrivers & Dimensions of Market Globalization by Martinson T. YeboahMartinson Tenkorang Yeboah100% (4)
- International and Global StrategiesDocument43 pagesInternational and Global StrategiesDayu IsmieyNo ratings yet
- Need and Importance of HRDDocument9 pagesNeed and Importance of HRDShreekant ShahNo ratings yet
- Global Corporate StrategyDocument24 pagesGlobal Corporate StrategyAik Luen LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document19 pagesChapter 2Vickie RushNo ratings yet
- International Business Unit 03Document37 pagesInternational Business Unit 03suprithchinnu1525No ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument6 pagesGlobalizationMorio MosoroNo ratings yet
- Askari Bank LTD Askari Bank LTD Askari Bank LTD Askari Bank LTDDocument1 pageAskari Bank LTD Askari Bank LTD Askari Bank LTD Askari Bank LTDAhmad Din ThaheemNo ratings yet
- KB Vision: Outsource Accounting & IT Services (Private) LimitedDocument5 pagesKB Vision: Outsource Accounting & IT Services (Private) LimitedAbsar BaigNo ratings yet
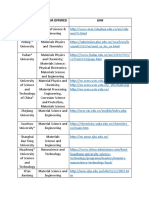
- CSC University ListDocument2 pagesCSC University ListAbsar BaigNo ratings yet
- PH211 Physics of MaterialsDocument3 pagesPH211 Physics of MaterialsAbsar BaigNo ratings yet
- Surface Modification (1) - BOOKDocument6 pagesSurface Modification (1) - BOOKAbsar BaigNo ratings yet
- Rule in Boolean AlgebraDocument2 pagesRule in Boolean AlgebraAbsar BaigNo ratings yet
- We Have Made The HA. Next Step: - Making of Glass - Making of GIC by Reaction With Acids - ISO StandardsDocument8 pagesWe Have Made The HA. Next Step: - Making of Glass - Making of GIC by Reaction With Acids - ISO StandardsAbsar BaigNo ratings yet
- Plant Design AssignmentDocument4 pagesPlant Design AssignmentAbsar BaigNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Department of Materials Engineering School of Chemical and Materials Engineering 1 of 5Document5 pagesLesson Plan: Department of Materials Engineering School of Chemical and Materials Engineering 1 of 5Absar BaigNo ratings yet
- 2e. Supply Chain Analytics - PresentationDocument39 pages2e. Supply Chain Analytics - PresentationLeo Angelo C. RabagoNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel Is - PalfingerAG Case Study enDocument4 pagesTata Steel Is - PalfingerAG Case Study enGopi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- T2 Om&scm - 2023 24 EmbaaDocument14 pagesT2 Om&scm - 2023 24 EmbaaArka BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Supplier Quality General RequirementsDocument19 pagesSupplier Quality General RequirementsJaydip ParmarNo ratings yet
- GMA 2010 Logistics Benchmark ReportDocument24 pagesGMA 2010 Logistics Benchmark ReportPeter PoonNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Operations Management Processes and Supply Chains 11 e Lee J Krajewski Manoj K Malhotra Larry P RitzmanDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Operations Management Processes and Supply Chains 11 e Lee J Krajewski Manoj K Malhotra Larry P Ritzmanstudioustapa4839100% (37)
- E-Commerce Client Server ArchitectureDocument29 pagesE-Commerce Client Server ArchitectureVipul MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement Toolkit: SIPOC AnalysisDocument42 pagesContinuous Improvement Toolkit: SIPOC AnalysisRichard Canas100% (1)
- IFS PACsecure enDocument150 pagesIFS PACsecure enlenuxxxNo ratings yet
- Asian Paints: Submitted byDocument10 pagesAsian Paints: Submitted byDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Operations Best 5 PracticesDocument4 pagesWarehouse Operations Best 5 PracticesJochie Teruel100% (1)
- Vda 232-101 Gadsl Global Automotive Declarabe Substance ListDocument44 pagesVda 232-101 Gadsl Global Automotive Declarabe Substance ListAugusto Kuribara100% (1)
- TTM 03Document3 pagesTTM 03rehman11424No ratings yet
- Lean Enterprise ModelDocument40 pagesLean Enterprise ModelAnne FrancineNo ratings yet
- 574 - Assignment 1 FrontsheetDocument15 pages574 - Assignment 1 FrontsheetMặt Nạ Cho DaNo ratings yet
- TM Forum Poster Business Process Framework Frameworx 13Document1 pageTM Forum Poster Business Process Framework Frameworx 13Joanna OchoaNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation Motivations and Pathways FoDocument7 pagesDigital Transformation Motivations and Pathways Fofaizal ardiNo ratings yet
- C2. StrategyDocument38 pagesC2. StrategyNancy TrầnNo ratings yet
- Smart Sustainable Modern Agriculture Through Rural Technopreneurship ProgrammeDocument4 pagesSmart Sustainable Modern Agriculture Through Rural Technopreneurship ProgrammemfomfoNo ratings yet
- Identifying Entrepreneurial Opportunities - PPTDocument10 pagesIdentifying Entrepreneurial Opportunities - PPTShabtab QuaiserNo ratings yet
- SM Module 6Document81 pagesSM Module 6Suhil KhanNo ratings yet
- Mis 2023Document62 pagesMis 2023Ana Mae MunsayacNo ratings yet
- Job Description-Maintenance EngineerDocument2 pagesJob Description-Maintenance Engineerblack_3289No ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cable Blowing MachinesDocument7 pagesFiber Optic Cable Blowing MachinesDiar FatahNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain WalmaktDocument53 pagesSupply Chain WalmaktNirmal PatelNo ratings yet