Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internal Control
Internal Control
Uploaded by
buse3erginCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Auditing Exam Revision Notes PDFDocument3 pagesAuditing Exam Revision Notes PDFJonalyn GabrilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Internal ControlDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Internal ControlCazia Mei JoverNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsMaeNo ratings yet
- BT Kiem ToanDocument5 pagesBT Kiem Toantrangnguyen.31221021691No ratings yet
- Overview of AuditingDocument5 pagesOverview of AuditingMylene Sunga AbergasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AudcisDocument6 pagesChapter 1 AudcisJaylin DizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Nicale JeenNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 2 ExercisesDocument8 pagesMODULE 1 2 ExercisesAMNo ratings yet
- Aa 3201Document4 pagesAa 3201Lance UrichNo ratings yet
- PSA NotesDocument15 pagesPSA NotesHanis MaisarahNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER2 - Introduction To Audit of Historical Financial InformationDocument8 pagesREVIEWER2 - Introduction To Audit of Historical Financial InformationErine ContranoNo ratings yet
- Macaila Aud SummaryDocument24 pagesMacaila Aud Summarypopla poplaNo ratings yet
- AUDITING IN CIS ENVIRONMENT Reviewer Chap 1 3Document11 pagesAUDITING IN CIS ENVIRONMENT Reviewer Chap 1 3Michaela De guzmanNo ratings yet
- Auditing - Introduction To Auditing NotesDocument2 pagesAuditing - Introduction To Auditing NotesCharlize Natalie ReodicaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Internal AuditDocument10 pagesCorporate Governance and Internal AuditItdarareNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Accounting System and Related Internal ControlsDocument24 pagesLesson 7 - Accounting System and Related Internal Controlskipngetich392No ratings yet
- AUD 1 & 2 NotesDocument5 pagesAUD 1 & 2 NotesAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Internal ControlsDocument5 pagesLesson 6 - Internal ControlsAllaina Uy BerbanoNo ratings yet
- Objective of The Auditor:: Study and Evaluation of Internal ControlDocument4 pagesObjective of The Auditor:: Study and Evaluation of Internal ControlTatyanna KaliahNo ratings yet
- Larrys Cheat Sheet Auditing TechniquesDocument2 pagesLarrys Cheat Sheet Auditing TechniquesMay Chen100% (1)
- Auditing in Cis Environment - Chapter 1Document4 pagesAuditing in Cis Environment - Chapter 1Giyah UsiNo ratings yet
- (MA 4221) - Notes Extern Audit RequirementsDocument3 pages(MA 4221) - Notes Extern Audit RequirementsMichael Tom BucalonNo ratings yet
- LS 2.80C - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementDocument4 pagesLS 2.80C - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- Internal Control AND Business ProcessesDocument21 pagesInternal Control AND Business ProcessesInnah MayNo ratings yet
- Small Business: Sarbanes-OxleyDocument4 pagesSmall Business: Sarbanes-Oxleymohamed sobhyNo ratings yet
- AAI 2 Part 6A PSA 315 & PSA 265 N Internal Control - Rev PDFDocument101 pagesAAI 2 Part 6A PSA 315 & PSA 265 N Internal Control - Rev PDFAbigailNo ratings yet
- Tolerable Misstatement Specified For The AssertionDocument5 pagesTolerable Misstatement Specified For The AssertionmoreNo ratings yet
- Notes For Audit by ChaptersDocument7 pagesNotes For Audit by ChaptersFarah KhattabNo ratings yet
- Auditing Concepts and Standards: Understanding AuditsDocument3 pagesAuditing Concepts and Standards: Understanding AuditsShamsah MaqboolNo ratings yet
- GTAG3 Audit KontinyuDocument37 pagesGTAG3 Audit KontinyujonisupriadiNo ratings yet
- Operations Auditing ConceptDocument12 pagesOperations Auditing ConceptLindsay RegalaNo ratings yet
- 74949bos60526 cp16Document37 pages74949bos60526 cp16Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Acctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlDocument12 pagesAcctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlTrayle HeartNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance PrincipleDocument2 pagesAudit and Assurance PrincipleIsabell CastroNo ratings yet
- Internal Controls ComparisonDocument3 pagesInternal Controls ComparisonJen AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance PrinciplesDocument10 pagesAuditing and Assurance PrinciplesJoannah maeNo ratings yet
- 1) Lec 1 - The Auditing Assurance EnvironmentDocument15 pages1) Lec 1 - The Auditing Assurance Environmentcats singhNo ratings yet
- What Is An Audit Committee? Discuss Its Value in An OrganizationDocument6 pagesWhat Is An Audit Committee? Discuss Its Value in An Organizationjoyce KimNo ratings yet
- ConceptsDocument6 pagesConceptsLala LenkaNo ratings yet
- ACCA F2 Audit, Financial Control, Fraud & Money LaunderingDocument27 pagesACCA F2 Audit, Financial Control, Fraud & Money LaunderingAhmud SaaniaNo ratings yet
- EXTAUDDocument19 pagesEXTAUDwalsonsanaani3rdNo ratings yet
- Extaud Reviewer 1Document38 pagesExtaud Reviewer 1nizaberi406No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Lecture NotesAnthony Ariel Ramos DepanteNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceDocument7 pages01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceBts Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- AU 9 Consideration of ICDocument11 pagesAU 9 Consideration of ICJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- MGT 209 - Overview of Internal ControlDocument8 pagesMGT 209 - Overview of Internal ControlCrystelNo ratings yet
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument4 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlFritzie Ann ZartigaNo ratings yet
- Systems and Controls Kaplan Chapter 8: Acca Paper F8 Int Audit and AssuranceDocument24 pagesSystems and Controls Kaplan Chapter 8: Acca Paper F8 Int Audit and AssuranceAbdullah HaddadNo ratings yet
- Internal Control: Consideration ofDocument35 pagesInternal Control: Consideration ofMa. KristineNo ratings yet
- Auditing-Internal ControlDocument6 pagesAuditing-Internal ControlRhn Habib RehmanNo ratings yet
- E Audit NoteDocument31 pagesE Audit NoteNur ZawaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2ADocument10 pagesChapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2AjejelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsKatherine MagpantayNo ratings yet
- INS3116 - CHAPTER 2 - Internal Control Framework - COSODocument25 pagesINS3116 - CHAPTER 2 - Internal Control Framework - COSOThuỳ Linh Bùi100% (1)
- "Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerDocument4 pages"Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Audi 21 (Reviewer)Document9 pagesAudi 21 (Reviewer)ninja ni ashley de sagunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Auditing and Internal ControlsDocument51 pagesChapter 1: Auditing and Internal ControlsRizabelle Valencia BandojoNo ratings yet
- Advance Auditing and Assurance PDFDocument182 pagesAdvance Auditing and Assurance PDFSaddy Butt100% (1)
- Chapter 6-8Document10 pagesChapter 6-8DeyNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CFAP 06 Ebook Part 1Document130 pagesCFAP 06 Ebook Part 1Muneeb AfzalNo ratings yet
- USAID Financial Audit Guide For Foreign Organizations A Mandatory Reference For ADS Chapter 591 591maa - 101023Document52 pagesUSAID Financial Audit Guide For Foreign Organizations A Mandatory Reference For ADS Chapter 591 591maa - 101023Alonso RamosNo ratings yet
- 17the Auditor's ReportDocument8 pages17the Auditor's ReportIrish SanchezNo ratings yet
- ITC 2024 Audit and Assurance Examinable PronouncementsDocument3 pagesITC 2024 Audit and Assurance Examinable PronouncementsbernicealaliNo ratings yet
- IIA Standard Two Way Mapping 2017 Vs 2024 1707708882Document166 pagesIIA Standard Two Way Mapping 2017 Vs 2024 1707708882Yashika KapdiNo ratings yet
- CA Final Audit List of Important Topivs May 2024 by CA Rishabh JainDocument18 pagesCA Final Audit List of Important Topivs May 2024 by CA Rishabh Jainrathiharsh.indiaNo ratings yet
- BM1909 Syllabus and Course Outline (BSA)Document6 pagesBM1909 Syllabus and Course Outline (BSA)Laiza JavierNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FS Audit and Pre-Engagement ActivitiesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To FS Audit and Pre-Engagement ActivitiesEarl EzekielNo ratings yet
- Issai 1700 PNDocument6 pagesIssai 1700 PNbkomen638No ratings yet
- SA List For CA InterDocument3 pagesSA List For CA InterJeetendraNo ratings yet
- 2023 Resolution No. LT-04 Establishment of External Audit CommitteeDocument3 pages2023 Resolution No. LT-04 Establishment of External Audit CommitteeRAMIL AMILNo ratings yet
- Audit by Sir Asif Vol 2Document102 pagesAudit by Sir Asif Vol 2ls786580302No ratings yet
- Activity 1 Week 1 Audit TheoryDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Week 1 Audit TheoryGONZALES, MICA ANGEL A.No ratings yet
- Auditing Theory Material For DLSU Dasma - Batch 24 - Students (0524)Document26 pagesAuditing Theory Material For DLSU Dasma - Batch 24 - Students (0524)Abbey Emmanuelle ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- CA Ravi Agarwal's CA Final Audit CompilerDocument820 pagesCA Ravi Agarwal's CA Final Audit Compiler6dzk78g2vyNo ratings yet
- Leykun Proposal (Recovered)Document22 pagesLeykun Proposal (Recovered)samuel kenetoNo ratings yet
- PRTC Aud 1st PB 05 Audit Problem and Solution - CompressDocument14 pagesPRTC Aud 1st PB 05 Audit Problem and Solution - CompressNovemae CollamatNo ratings yet
- Pertamina Geothermal Energy 31 Des 2023 ReleasedDocument132 pagesPertamina Geothermal Energy 31 Des 2023 ReleasedTaufiq Wahyu HidayatNo ratings yet
- Audit Checklist & ReportDocument12 pagesAudit Checklist & ReportRaajha MunibathiranNo ratings yet
- 74949bos60526 cp16Document37 pages74949bos60526 cp16Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Manual Example 2024Document24 pagesInternal Audit Manual Example 2024DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- LK Audited 2023Document234 pagesLK Audited 2023muhammad3gibran03No ratings yet
- Audit ReportDocument33 pagesAudit ReportShinosuke ExtendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Quiz EnglishDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - Quiz EnglishFitri-ssiNo ratings yet
- Auditing Assurance in HK (6th Ed) - Ch.16 ADocument29 pagesAuditing Assurance in HK (6th Ed) - Ch.16 A1234778No ratings yet
- Assessment 1Document14 pagesAssessment 1Cường MidomotojiNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Auditing: A Practical Approach With Data Analytics by Raymond N. Johnson All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Auditing: A Practical Approach With Data Analytics by Raymond N. Johnson All Chaptermufilaake100% (7)
- ISA 520 Analytical ProceduresDocument8 pagesISA 520 Analytical ProcedurestapiwanashejakaNo ratings yet
- Caf 8 Mi Vol 1Document345 pagesCaf 8 Mi Vol 1Taha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Auditing PDFDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Auditing PDFzeiqxsbnd100% (1)
Internal Control
Internal Control
Uploaded by
buse3erginOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internal Control
Internal Control
Uploaded by
buse3erginCopyright:
Available Formats
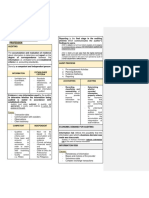
Internal control: --int aud.
/ operational audit: control whether the results of activities of
-done by int. auditors Internal auditors: buss org. reach the goals and objectives and resources are used
-indispensable element Commonly perform compliance audit. They report to committee of board effectively
-elaborates what shouldn’t be done of directors to remain independent. int control vs int audit:
-main duty is detect errors frauds int control is a process operated under the responsibility of employees at
-COSO(committee of sponsoring org) is ordering, management, Requirements for becoming cpa: all levels. It exist whether the business type, bakkal vs her şeyde
coordination of the works, mechanism that regulates or directs the -education -uniform CPA examination provides reasonable assurance
operation of system. -experience But int audit isn’t essential for business. Iş büyüdükçe int aud
-according to coso, there is a need for predetermined obj. (purpose) gereksinimi artar. Institutionalization için en önemli tool.
Activity created in bus. to improve and add value. can be from outside
functions of management: Audit concept:
-assertions Int control vs independent audit:
-planning, organization, execution, coordination, control -collecting audit evidence --are disclosed to collect public evidence in an impartial and systematic
-correspondence with standards approach in order to compliance of the fin info presented in fin st. with
definition of inter. control by coso: int cont is generally effected by the -whether assertions are correct or not the gaap/ifrs and evaluate results, present their opinions ab. the accuracy
entity’s board of directors. It is a process designed to provide reasonable -audit reports of in info in the form of report.
assurance ab. the achievement of objectives regarding effectiveness of
oper., reliability of fin. reporting, compliance with laws. --an independent auditor must obtain information about the operating
In first statement, aud. Investigates whether the fin st are prepared in conditions of the entity and its relations with its environment to apply
accordance with rules, and in second statements investigates whether the additional indep. audit tekniks to identify the risk of mat. missta.
purpose of int control: is protect the assets of the bank, to ensure
acc system meets the criteria of efficiency and reliability --collects info ab risk assessm. Methods including its int control system
effectiveness, in accordance with laws, ensure reliability. Carried out by
the administration. Definition is a mix of COSO and AICPA and analyze info, reveal material errors and other info presented my mng.
Auditor Types: -- takes into acc possibilities of risk and tries to reach prof. judgement
Auditing is the accumulation and evaluation of evidence about info to -independent/external auditors --within scope of risk asses. determine the degree of materiality, evaluate
determine and report the degree of correspondence bet ween info and -internal auditors they’re in accordance with obj of business or not
established criteria. -govt auditors --tries to determine the internal control risk by conducting continuous
internal control tests and in this context.
Auditing should be done by a competent and independent person --independent: cpa’s, smmm(kgk/pcaob certificate) -- IAASB within IFAC determines the criteria and regulate the
To do an audit, there must be a info verifieb by FASB and IASB responsibilities of indep audi. It adopted the int cont approach COSO.
Evidence: transaction data, commun with outsiders, observations, client --govt auditors: --indep auditors are responsible for notifying the mngment regarding the
testimony -state supervisory board: works by order of the president, conduct inadequacy of int cont.
Final stage is reporting examinations, researches -- int control deficiency görürse, önemli mi değil mi, önemliyse mng
-turkish chart of acc audit (TCA): responsible for the effective, bilgilendir
Auditing vs accounting: acc is recording, classifying and summarizing economic, efficient and lawful functioning of public administrations
events to provide fin info for dec. making. Auditing focuses on recorded -inspection boards affiliates to ministries (devlet denetleme kurumu) with Control example: first stage: fireproof properties? Nerede falan. Second
info is correct or not. approval of the minister stage: Çalışanlar nerede oldugunu, nasıl kullanıldıgını biliyor mu. Third
Info risk: possibility that info used to decision making was inaccurate. -turkish ombudsman institution: with the law, stage: bunlara ragmen mng will take out insurance policy
Auditing reduces info risk. All acts of administration are in working area
With a private budget with understanding of justice based on human Int control under corp. govt. principles
--Causes of info risk: -- rights OECD (org. for development)
remoteness of info(dec makers don’t have firsthand knowledge) -regulatory and supervisory boards: bddk, spk,kgk to regulate, supervise, The main task of this organization is to support policies for: contributing
Biases and motives of the provider monitor the org to econ. growth at sustainable level, increasing the standard of living,
Voluminous data developm. of world econ. promote well-being, equality, opportunity and
Complex exchange transactions --internal auditors-- is the person who reports to a management unit that well being for all.
will evaluate the results of the audit actions carried out within the Good governance (corporate governance) helps create the climate of trust
--reducing info risk— business organization in the most effective way within the organization. --It has been accepted as one of the 12 important standards. These
User verifies info: go to business and verify Int audit deals with both fin and non-fin transactions. principles also form the basis for a comprehensive program of
User shares info risk with mngement --int aud./ Fin st. audit: investigates the accuracy and reliability of the cooperation between OECD member countries and non-OECD countries,
Audited fin st are provided: external auditors acc info that forms the basis of fin st. detection and prevention of errors and reinforce the corporate governance element of the World Bank/IMF
and frauds. Reports on the Observance of Standards and Codes (ROSC).
--primary types of audits performed by CPA’s— --int aud./ compliance audit: measure the compliance of business --ensure liability of reporting and contr. Systems and board of directors
-operational audit: evaluate efficiency and effectiveness activities with the policies, procedures, laws determined by mng. sets clear lines of responsibility. (boards of dire.: it should ensure
-compliance audit: following procedures, regulations or not controls can be carried out approp. by top mng. Its achieved by internal
-fin st audit: whether in accordance with us gaap or ifrs audit, reporting directly to board (audit committee)
While providing reasonable assurance, internal controls are not error- Control Environment: Establishes standards, processes, and structures for
Int. contr. models and approaches wordwide proof. internal control.
Historical Definitions and Evolution: Risk Assessment: Identifies and manages risks associated with business
AICPA's 1949 definition focused on asset protection, data accuracy, Misconceptions: objectives.
activity execution, and policy adherence. -int control always starts with written policies and procedures Control Activities: Implements policies and procedures to mitigate risks
AICPA revised it into administrative and accounting control components. -int cont. is a job that should be done by int auditors (every employee) effectively.
SAS 55 (1988) defined internal control with three components. -int control is just a fin issue Information and Communication: Ensures effective exchange of
COSO's SAS 78 emphasized financial statement reliability. -int control tells you what not to do (ensures job done accurate) information within the organization.
-waste of time (part of job, process) Monitoring: Observes processes and implements necessary changes for
Global Adoption: -must be built on buss activities (places inside processes not over them) adaptability.
COSO's definition adopted worldwide by various organizations and - if int contr are strong, no possib. of committing fraud, Interrelationships:
countries. Aims: achievement of its profitability goal, ensure effective operation,
Including England (Cadbury, Greenbury, Hampel, Turnbull Reports), reduce risk of asset losses, ensure reliability All components and principles interact and are interdependent for
France (Vienot Report), Netherlands (Peters Report), and others. effective internal control.
Adopted by IFAC, GAO, INTOSAI, BIS (BCBS), CICA, ISACF Fraud triangle: The control environment is influenced by various internal and external
(COBIT), SEC, British Treasury, and J-SOX Regulation in Japan. -pressure: debt, revenge, bad habits, passion for luxury, econ troubles factors.
-opportunity: weak int contr, uneffec. aud, lack of corp governance It provides discipline and order, supporting risk assessment, control
Role and Importance: -rationalization: everyone is doing the same, I wasn’t promoted, actions, information exchange, and monitoring.
Turnbull Report (England) highlights internal control's role in managing
risks for business objectives. Constraints that affect the probability of success of int cont:
Strong internal control protects assets, enhances operational -mng and staff omissions and violations
effectiveness, ensures reporting reliability, and aids in compliance. -top mng’s ineffectiveness of int cont.
Internal control, as defined by IFAC and INTOSAI, ensures financial -acting jointly
reliability, operational effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. -cost
The Basel Committee emphasizes continuous control processes involving 1) the judgements of bus. mngers during dec making may be wrong or all
all levels of management. emp may make simple mistakes
COBIT and SAC Report align with COSO, defining internal control as 2) two or more emp.’s can override contr. by colluding with each other
policies and procedures for goal achievement and risk prevention. 3) mng’s ability to override internal cont. is always present
Regulatory standards from the British Treasury focus on efficiency,
compliance, and risk management. Goals of int control:
The Institute of Internal Auditors stresses the importance of effective -operational objectives: effectiveness, efficiency, performance, protection
internal control for confident business advancement and resource against losses
preservation. -reporting objectives: fin and nonfin reporting, reliability, timeliness,
Overall, COSO's control model, widely adopted by U.S. and international transparency
regulatory agencies, sets the global standard for internal control practices. -compliance objectives: org’s adherence to laws and regulations
Misconceptions and facts on int control: Relationship bween objectives and components:
Facts: most imp element, reasonable assurn.
Emp. at all levels, human element so always possibility that controls will Internal Control Components and Principles:
be ineffective Seventeen principles stem directly from components for effective internal
Not a panacea(her derde deva) control.
Internal controls act as early warnings for management decisions amidst An effective system reduces the risk of failing to achieve objectives to an
external factors. acceptable level.
They enhance accuracy in commercial and economic decisions. All components and associated principles must be available and
Internal controls aid in fraud detection and prevention. operational for effectiveness.
They provide crucial evidence for audits but don't ensure perfect Constraints and Requirements:
financial reporting. Internal controls act as early warnings but cannot guarantee success.
Fraudulent financial reporting often involves senior executives bypassing Despite limitations, controls offer reasonable assurance regarding
controls. operations, financial reliability, and legal compliance.
Periodic controls ensure legal compliance but can't guarantee adherence. Management must address constraints like human judgment errors and
Employees may still violate internal controls, limiting their effectiveness. external events.
Despite limitations, internal controls offer stakeholders reasonable COSO Components and Principles:
assurance.
You might also like
- Auditing Exam Revision Notes PDFDocument3 pagesAuditing Exam Revision Notes PDFJonalyn GabrilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Internal ControlDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Internal ControlCazia Mei JoverNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsMaeNo ratings yet
- BT Kiem ToanDocument5 pagesBT Kiem Toantrangnguyen.31221021691No ratings yet
- Overview of AuditingDocument5 pagesOverview of AuditingMylene Sunga AbergasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AudcisDocument6 pagesChapter 1 AudcisJaylin DizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Nicale JeenNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 2 ExercisesDocument8 pagesMODULE 1 2 ExercisesAMNo ratings yet
- Aa 3201Document4 pagesAa 3201Lance UrichNo ratings yet
- PSA NotesDocument15 pagesPSA NotesHanis MaisarahNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER2 - Introduction To Audit of Historical Financial InformationDocument8 pagesREVIEWER2 - Introduction To Audit of Historical Financial InformationErine ContranoNo ratings yet
- Macaila Aud SummaryDocument24 pagesMacaila Aud Summarypopla poplaNo ratings yet
- AUDITING IN CIS ENVIRONMENT Reviewer Chap 1 3Document11 pagesAUDITING IN CIS ENVIRONMENT Reviewer Chap 1 3Michaela De guzmanNo ratings yet
- Auditing - Introduction To Auditing NotesDocument2 pagesAuditing - Introduction To Auditing NotesCharlize Natalie ReodicaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Internal AuditDocument10 pagesCorporate Governance and Internal AuditItdarareNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Accounting System and Related Internal ControlsDocument24 pagesLesson 7 - Accounting System and Related Internal Controlskipngetich392No ratings yet
- AUD 1 & 2 NotesDocument5 pagesAUD 1 & 2 NotesAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Internal ControlsDocument5 pagesLesson 6 - Internal ControlsAllaina Uy BerbanoNo ratings yet
- Objective of The Auditor:: Study and Evaluation of Internal ControlDocument4 pagesObjective of The Auditor:: Study and Evaluation of Internal ControlTatyanna KaliahNo ratings yet
- Larrys Cheat Sheet Auditing TechniquesDocument2 pagesLarrys Cheat Sheet Auditing TechniquesMay Chen100% (1)
- Auditing in Cis Environment - Chapter 1Document4 pagesAuditing in Cis Environment - Chapter 1Giyah UsiNo ratings yet
- (MA 4221) - Notes Extern Audit RequirementsDocument3 pages(MA 4221) - Notes Extern Audit RequirementsMichael Tom BucalonNo ratings yet
- LS 2.80C - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementDocument4 pagesLS 2.80C - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- Internal Control AND Business ProcessesDocument21 pagesInternal Control AND Business ProcessesInnah MayNo ratings yet
- Small Business: Sarbanes-OxleyDocument4 pagesSmall Business: Sarbanes-Oxleymohamed sobhyNo ratings yet
- AAI 2 Part 6A PSA 315 & PSA 265 N Internal Control - Rev PDFDocument101 pagesAAI 2 Part 6A PSA 315 & PSA 265 N Internal Control - Rev PDFAbigailNo ratings yet
- Tolerable Misstatement Specified For The AssertionDocument5 pagesTolerable Misstatement Specified For The AssertionmoreNo ratings yet
- Notes For Audit by ChaptersDocument7 pagesNotes For Audit by ChaptersFarah KhattabNo ratings yet
- Auditing Concepts and Standards: Understanding AuditsDocument3 pagesAuditing Concepts and Standards: Understanding AuditsShamsah MaqboolNo ratings yet
- GTAG3 Audit KontinyuDocument37 pagesGTAG3 Audit KontinyujonisupriadiNo ratings yet
- Operations Auditing ConceptDocument12 pagesOperations Auditing ConceptLindsay RegalaNo ratings yet
- 74949bos60526 cp16Document37 pages74949bos60526 cp16Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Acctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlDocument12 pagesAcctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlTrayle HeartNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance PrincipleDocument2 pagesAudit and Assurance PrincipleIsabell CastroNo ratings yet
- Internal Controls ComparisonDocument3 pagesInternal Controls ComparisonJen AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance PrinciplesDocument10 pagesAuditing and Assurance PrinciplesJoannah maeNo ratings yet
- 1) Lec 1 - The Auditing Assurance EnvironmentDocument15 pages1) Lec 1 - The Auditing Assurance Environmentcats singhNo ratings yet
- What Is An Audit Committee? Discuss Its Value in An OrganizationDocument6 pagesWhat Is An Audit Committee? Discuss Its Value in An Organizationjoyce KimNo ratings yet
- ConceptsDocument6 pagesConceptsLala LenkaNo ratings yet
- ACCA F2 Audit, Financial Control, Fraud & Money LaunderingDocument27 pagesACCA F2 Audit, Financial Control, Fraud & Money LaunderingAhmud SaaniaNo ratings yet
- EXTAUDDocument19 pagesEXTAUDwalsonsanaani3rdNo ratings yet
- Extaud Reviewer 1Document38 pagesExtaud Reviewer 1nizaberi406No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Lecture NotesAnthony Ariel Ramos DepanteNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceDocument7 pages01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceBts Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- AU 9 Consideration of ICDocument11 pagesAU 9 Consideration of ICJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- MGT 209 - Overview of Internal ControlDocument8 pagesMGT 209 - Overview of Internal ControlCrystelNo ratings yet
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument4 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlFritzie Ann ZartigaNo ratings yet
- Systems and Controls Kaplan Chapter 8: Acca Paper F8 Int Audit and AssuranceDocument24 pagesSystems and Controls Kaplan Chapter 8: Acca Paper F8 Int Audit and AssuranceAbdullah HaddadNo ratings yet
- Internal Control: Consideration ofDocument35 pagesInternal Control: Consideration ofMa. KristineNo ratings yet
- Auditing-Internal ControlDocument6 pagesAuditing-Internal ControlRhn Habib RehmanNo ratings yet
- E Audit NoteDocument31 pagesE Audit NoteNur ZawaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2ADocument10 pagesChapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2AjejelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsKatherine MagpantayNo ratings yet
- INS3116 - CHAPTER 2 - Internal Control Framework - COSODocument25 pagesINS3116 - CHAPTER 2 - Internal Control Framework - COSOThuỳ Linh Bùi100% (1)
- "Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerDocument4 pages"Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Audi 21 (Reviewer)Document9 pagesAudi 21 (Reviewer)ninja ni ashley de sagunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Auditing and Internal ControlsDocument51 pagesChapter 1: Auditing and Internal ControlsRizabelle Valencia BandojoNo ratings yet
- Advance Auditing and Assurance PDFDocument182 pagesAdvance Auditing and Assurance PDFSaddy Butt100% (1)
- Chapter 6-8Document10 pagesChapter 6-8DeyNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CFAP 06 Ebook Part 1Document130 pagesCFAP 06 Ebook Part 1Muneeb AfzalNo ratings yet
- USAID Financial Audit Guide For Foreign Organizations A Mandatory Reference For ADS Chapter 591 591maa - 101023Document52 pagesUSAID Financial Audit Guide For Foreign Organizations A Mandatory Reference For ADS Chapter 591 591maa - 101023Alonso RamosNo ratings yet
- 17the Auditor's ReportDocument8 pages17the Auditor's ReportIrish SanchezNo ratings yet
- ITC 2024 Audit and Assurance Examinable PronouncementsDocument3 pagesITC 2024 Audit and Assurance Examinable PronouncementsbernicealaliNo ratings yet
- IIA Standard Two Way Mapping 2017 Vs 2024 1707708882Document166 pagesIIA Standard Two Way Mapping 2017 Vs 2024 1707708882Yashika KapdiNo ratings yet
- CA Final Audit List of Important Topivs May 2024 by CA Rishabh JainDocument18 pagesCA Final Audit List of Important Topivs May 2024 by CA Rishabh Jainrathiharsh.indiaNo ratings yet
- BM1909 Syllabus and Course Outline (BSA)Document6 pagesBM1909 Syllabus and Course Outline (BSA)Laiza JavierNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FS Audit and Pre-Engagement ActivitiesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To FS Audit and Pre-Engagement ActivitiesEarl EzekielNo ratings yet
- Issai 1700 PNDocument6 pagesIssai 1700 PNbkomen638No ratings yet
- SA List For CA InterDocument3 pagesSA List For CA InterJeetendraNo ratings yet
- 2023 Resolution No. LT-04 Establishment of External Audit CommitteeDocument3 pages2023 Resolution No. LT-04 Establishment of External Audit CommitteeRAMIL AMILNo ratings yet
- Audit by Sir Asif Vol 2Document102 pagesAudit by Sir Asif Vol 2ls786580302No ratings yet
- Activity 1 Week 1 Audit TheoryDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Week 1 Audit TheoryGONZALES, MICA ANGEL A.No ratings yet
- Auditing Theory Material For DLSU Dasma - Batch 24 - Students (0524)Document26 pagesAuditing Theory Material For DLSU Dasma - Batch 24 - Students (0524)Abbey Emmanuelle ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- CA Ravi Agarwal's CA Final Audit CompilerDocument820 pagesCA Ravi Agarwal's CA Final Audit Compiler6dzk78g2vyNo ratings yet
- Leykun Proposal (Recovered)Document22 pagesLeykun Proposal (Recovered)samuel kenetoNo ratings yet
- PRTC Aud 1st PB 05 Audit Problem and Solution - CompressDocument14 pagesPRTC Aud 1st PB 05 Audit Problem and Solution - CompressNovemae CollamatNo ratings yet
- Pertamina Geothermal Energy 31 Des 2023 ReleasedDocument132 pagesPertamina Geothermal Energy 31 Des 2023 ReleasedTaufiq Wahyu HidayatNo ratings yet
- Audit Checklist & ReportDocument12 pagesAudit Checklist & ReportRaajha MunibathiranNo ratings yet
- 74949bos60526 cp16Document37 pages74949bos60526 cp16Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Manual Example 2024Document24 pagesInternal Audit Manual Example 2024DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- LK Audited 2023Document234 pagesLK Audited 2023muhammad3gibran03No ratings yet
- Audit ReportDocument33 pagesAudit ReportShinosuke ExtendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Quiz EnglishDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - Quiz EnglishFitri-ssiNo ratings yet
- Auditing Assurance in HK (6th Ed) - Ch.16 ADocument29 pagesAuditing Assurance in HK (6th Ed) - Ch.16 A1234778No ratings yet
- Assessment 1Document14 pagesAssessment 1Cường MidomotojiNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Auditing: A Practical Approach With Data Analytics by Raymond N. Johnson All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Auditing: A Practical Approach With Data Analytics by Raymond N. Johnson All Chaptermufilaake100% (7)
- ISA 520 Analytical ProceduresDocument8 pagesISA 520 Analytical ProcedurestapiwanashejakaNo ratings yet
- Caf 8 Mi Vol 1Document345 pagesCaf 8 Mi Vol 1Taha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Auditing PDFDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Auditing PDFzeiqxsbnd100% (1)