Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tuto 10 - 220414 - 115251
Tuto 10 - 220414 - 115251
Uploaded by
2023269176Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tuto 10 - 220414 - 115251
Tuto 10 - 220414 - 115251
Uploaded by
2023269176Copyright:
Available Formats
PHY 098
SERWAY VUILLE, COLLEGE PHYSICS, 11TH EDITION
2021/2022
Tutorial 10
Chapter 24.9, 22.1-22.2, 23.1-23.2
Multiple Choice Questions
1. _________ states that the intensity of plane-polarized light that passes through an analyser
varies as the square of the cosine of the angle between the plane of the polarizer and the
transmission axes of the analyser.
A. Brewster’s law
B. Reflection law
C. Malus law
D. Snell’s law
2. A linearly polarized wave is always __________
A. in x-y plane
B. a transverse wave
C. in y-z plane
D. a longitudinal wave
3. A virtual, upright and smaller in size of image can be produced by ___________.
A. plane mirror
B. concave mirror
C. blurry mirror
D. convex mirror
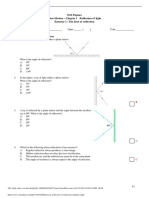
4. Choose the correct answer for the types of mirrors and their description.
A. Concave mirror converging the light rays
B. Plane mirror diverging the light rays
C. Plane mirror always produce inverted image
D. Convex mirror always produce real image
PHY098 Sem II 2021/2022
1 Prepared by Mas Fiza Mustafa, Nor Faridah Hanim Mat Junit, Noor Arda Adrina Daud, Norjuliyati Hamzah
PHY 098
SERWAY VUILLE, COLLEGE PHYSICS, 11TH EDITION
2021/2022
Structured Questions
Chapter 24.9
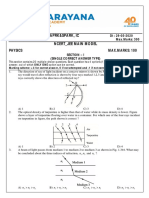
1. Three polarizing plates whose planes are parallel are centered on a common axis. The directions
of the transmission axes relative to the common vertical direction are shown in Figure P24.51.A
linearly polarized beam of light with plane of polarization parallel to the vertical reference
direction is incident from the left onto the first disk with intensity Ii=10.0 units(arbitrary).Calculate
the transmitted intensity If when 𝜃1 = 20.0𝑜 ,𝜃2 = 40.0𝑜 ,𝜃3 = 60.0𝑜.
Answer: 6.89 units
2. Figure 2 shows an unpolarized light passes through two Polaroid sheets. The transmission axis
of the analyzer makes an angle of 35.0o with the axis of the polarizer.
Analyzer
Polarizer
Unpolarized
light Figure 2
Calculate
(a) the transmitted intensity of the original unpolarised light after passing through the analyser.
Answer: 0.336 Io
(b) the intensity absorbed by the analyzer? (Leave your answer in terms of Io)
Answer: 0.164 Io
PHY098 Sem II 2021/2022
2 Prepared by Mas Fiza Mustafa, Nor Faridah Hanim Mat Junit, Noor Arda Adrina Daud, Norjuliyati Hamzah
PHY 098
SERWAY VUILLE, COLLEGE PHYSICS, 11TH EDITION
2021/2022
Chapter 22.1-22.2
3. Two plane mirrors are at an angle of 𝜃1 = 50𝑜 with each other as in the side view shown in
Figure P22.14.If a horizontal ray is incident on mirror 1,at what angle 𝜃2 does the outgoing
reflected ray make with the surface of mirror 2.
Answer: 80.0o
Chapter 23.1-23.2
4. A dentist uses a mirror to examine a tooth that is 1.00 cm in front of the mirror. The image of
the tooth is formed 10.0 cm behind the mirror. Determine (a) the mirror’s radius of curvature
and (b) the magnification of the image.
Answer: a) +2.22 cm, b) +10.0
5. At an intersection of hospital hallways, a convex spherical mirror is mounted high on a wall to
help people avoid collision. The magnitude of the mirror’s radius of curvature is 0.550 m.(a)
Locate the image of a patient located 10.0 m from the mirror.(b) Indicate whether the image is
upright or inverted.(c) Determine the magnification of the image.
Answer: a) -26.8cm (behind the mirror), b) upright, c) +0.0268
Additional Question
A concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 24.0 cm.(a) Determine the object position for
which the resulting image is upright and larger than the object by a factor of 3.00.(b) Draw a ray
diagram to determine the position of the image.(c) Is the image real or vir tual.
Answer: a) +8.00cm, c) virtual
PHY098 Sem II 2021/2022
3 Prepared by Mas Fiza Mustafa, Nor Faridah Hanim Mat Junit, Noor Arda Adrina Daud, Norjuliyati Hamzah
You might also like
- (Solution Manual) Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 4ed - Sadiku-Pages-774-800Document35 pages(Solution Manual) Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 4ed - Sadiku-Pages-774-800Leo Aude100% (1)
- AC17-602P-REGUNAYAN-End of Chapter 1 ExercisesDocument15 pagesAC17-602P-REGUNAYAN-End of Chapter 1 ExercisesMarco RegunayanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 - QDocument3 pagesTutorial 10 - Qsitibahyah41No ratings yet
- Test 2 Semester 1Document2 pagesTest 2 Semester 1Tiro RamatlakadibeNo ratings yet
- Term-II Question Paper Class - XIIDocument3 pagesTerm-II Question Paper Class - XIIJASWINDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- W44 5.3 Total Internal ReflectionDocument6 pagesW44 5.3 Total Internal ReflectionBid HassanNo ratings yet
- Part 0ne: Multiple Choice Questions (20 Points) Circle The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesPart 0ne: Multiple Choice Questions (20 Points) Circle The Correct Answersaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2023-24Document8 pagesPractice Questions 2023-24Vaishnavi GNo ratings yet
- PS_CB_X_Sci_Light - Reflection and Refraction (2)Document7 pagesPS_CB_X_Sci_Light - Reflection and Refraction (2)atharvathange0No ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2021 VInsp 3 QN ADocument21 pagesTrialstpm 2021 VInsp 3 QN AASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 The Laws of Reflection Solutions 1 PDFDocument5 pagesExercise 2 The Laws of Reflection Solutions 1 PDFhexu wangNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics TestDocument4 pagesRay Optics TestPaarth GulatiNo ratings yet
- Physics Optics: XY. The Lines Ef and GH Represent Wavefronts of The Light Wave in Medium-2 After RefractionDocument1 pagePhysics Optics: XY. The Lines Ef and GH Represent Wavefronts of The Light Wave in Medium-2 After RefractionPornachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- PS PFE 14 Electromagnetic Waves-Light and Geometric OpticsDocument1 pagePS PFE 14 Electromagnetic Waves-Light and Geometric OpticsOnel TyNo ratings yet
- University Physics Exam Example p214SampleMT1Document12 pagesUniversity Physics Exam Example p214SampleMT1carlos519520% (1)
- 9569941-Class 10 - Science - Physics - Light - Reflection and Refraction-Part 2 - WS With Ans. - VipinaDocument10 pages9569941-Class 10 - Science - Physics - Light - Reflection and Refraction-Part 2 - WS With Ans. - VipinaMd Shadab AlamNo ratings yet
- Science PhysicsDocument6 pagesScience Physics?ジェーNo ratings yet
- Light - Worksheet 2 SCDocument7 pagesLight - Worksheet 2 SC。无名。。No ratings yet
- Light Revision Class 10Document34 pagesLight Revision Class 10karun.senthil.kumar.25No ratings yet
- G10 - Refraction - Q BankDocument21 pagesG10 - Refraction - Q BankUrmila GNo ratings yet
- CP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionDocument4 pagesCP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionRashed AlawaishehNo ratings yet
- 01 Ray Optics MMDocument71 pages01 Ray Optics MMmonikeshNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH-10,11,12,13Document12 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH-10,11,12,13sumitsagar2405No ratings yet
- 10th Light Numerical Question Test Paper-3Document1 page10th Light Numerical Question Test Paper-3Priya TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Refraction, Lenses TestDocument5 pagesRefraction, Lenses TestAndrew Nicholas100% (1)
- g10 ScienceDocument21 pagesg10 ScienceMOHAMMADMUNAWARSAIFNo ratings yet
- SR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Document8 pagesSR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment - Reflection and RefractionDocument5 pagesRevision Assignment - Reflection and RefractionanaythesuperheroNo ratings yet
- 3.2 LightDocument8 pages3.2 LightAyana AkjolovaNo ratings yet
- Phy WsDocument3 pagesPhy WsmotivationdailyguyNo ratings yet
- Soal Daily Test Static Optics - 1Document3 pagesSoal Daily Test Static Optics - 1Gregorius Bryan H RNo ratings yet
- Light WorksheetDocument11 pagesLight Worksheetkobayashirei602No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1Document6 pagesGrade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1NONO0% (1)
- GZBXHHWPHYSICSWSJUNE2425pdf 202405310831 9Document3 pagesGZBXHHWPHYSICSWSJUNE2425pdf 202405310831 9vatsdakshataNo ratings yet
- Xii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsDocument3 pagesXii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsMaster GamingNo ratings yet
- Rau Optics WsDocument3 pagesRau Optics Wssagarikaarun06No ratings yet
- 2.wave OpticsexerciseDocument32 pages2.wave OpticsexerciseGomes RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2nd QDocument5 pagesReviewer 2nd QJohndel CorderoNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Physics Preboard Term 2 FinalDocument4 pagesCLASS XII Physics Preboard Term 2 FinalParth SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10 THDocument3 pages10 THRohitNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 M5 2023-24Document3 pagesPhysics Class 12 M5 2023-24Sonu6 SiddNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Paper CBSEDocument4 pagesXII Physics Paper CBSESanjna ParikhNo ratings yet
- 2224 - Physics (IIT 4)Document4 pages2224 - Physics (IIT 4)1harshikaNo ratings yet
- Ch9-10 CBSE 2023Document4 pagesCh9-10 CBSE 2023tebor93898No ratings yet
- Ray Optics Rudra SeriesDocument154 pagesRay Optics Rudra SeriesAniket kumarNo ratings yet
- Go (Jee Main Online)Document19 pagesGo (Jee Main Online)balvantgk.hemant123No ratings yet
- Insp Lectures Geometrical Optics - Reflection (Mirrors)Document159 pagesInsp Lectures Geometrical Optics - Reflection (Mirrors)arorayash603No ratings yet
- CH 14.2 QuizDocument4 pagesCH 14.2 QuizAlex ChenNo ratings yet
- Pre-Term-Ii: (For CBSE Board) Class-Xii PhysicsDocument3 pagesPre-Term-Ii: (For CBSE Board) Class-Xii PhysicsBadAss GamingNo ratings yet
- XII Q Group 3Document3 pagesXII Q Group 3Sanskriti VermaNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Quiz - Secondary 2Document6 pagesLIGHT Quiz - Secondary 2priyaNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics ExercisesDocument12 pagesS4 Physics ExercisesMUKIZA ISAACNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document2 pagesLecture 2Rupam SenNo ratings yet
- 13a-Waves and Optics MC Practice Problems - Section C Geometric OpticsDocument19 pages13a-Waves and Optics MC Practice Problems - Section C Geometric OpticsIan StantonNo ratings yet
- BVOPT-103 Geometrical Optics-IDocument13 pagesBVOPT-103 Geometrical Optics-IManisha khanNo ratings yet
- Assignement Optics Phadtx2Document5 pagesAssignement Optics Phadtx2lehlohonolotsotetsi27No ratings yet
- X - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Document2 pagesX - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Shweta DuhanNo ratings yet
- HW14-Light - 1 (学生版) - 021527Document14 pagesHW14-Light - 1 (学生版) - 021527Jun WuNo ratings yet
- PART I - Multiple Choice. Encircle The Letter That Corresponds To The Correct Answer in EachDocument6 pagesPART I - Multiple Choice. Encircle The Letter That Corresponds To The Correct Answer in EachJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test ch9 PhiysicsDocument1 pageMonthly Test ch9 PhiysicsMalik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Thomas ParallelsNewTestamentDocument3 pagesThomas ParallelsNewTestamentRebekka KingNo ratings yet
- Motivational Case Study ExerciseDocument3 pagesMotivational Case Study ExerciseMelnicof DanyNo ratings yet
- Architectural Fasteners & Fittings - Stainless Steel - AnzorDocument18 pagesArchitectural Fasteners & Fittings - Stainless Steel - AnzorBhaiJan59No ratings yet
- Learning Styles and Learning PreferencesDocument32 pagesLearning Styles and Learning Preferencespatterson nji mbakwaNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Declaración de Qingdao (2015) PDFDocument50 pagesUnesco - Declaración de Qingdao (2015) PDFAlberto Pariona LlanosNo ratings yet
- Models of Management in Socio-Political Environment..: Presented By.. The A' Factors. Roll No. 1-9Document13 pagesModels of Management in Socio-Political Environment..: Presented By.. The A' Factors. Roll No. 1-9amritaagarwal23No ratings yet
- Fashion and ConsumerismDocument28 pagesFashion and ConsumerismAhmedNagyNo ratings yet
- Who Invented The Periodic TableDocument1 pageWho Invented The Periodic TableJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Sir Samuel CunardDocument1 pageSir Samuel CunardMarknel LasernaNo ratings yet
- Report Long FormDocument5 pagesReport Long FormEmotion JarNo ratings yet
- PTR 38Document23 pagesPTR 38CyNo ratings yet
- 10W Single Output Industrial DIN Rail Power Supply: SeriesDocument2 pages10W Single Output Industrial DIN Rail Power Supply: SeriesCiprian BalcanNo ratings yet
- Rock MechanicsDocument33 pagesRock MechanicsErnesto Oporto VergaraNo ratings yet
- Anskey Sqp1 Cs Xii t2 2022 YkDocument7 pagesAnskey Sqp1 Cs Xii t2 2022 YkSUDHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Administrative Theory of ManagementDocument7 pagesAdministrative Theory of ManagementAxe PanditNo ratings yet
- Joy Hermalyn CV 2020Document5 pagesJoy Hermalyn CV 2020api-518378178No ratings yet
- Public Revenue Management 6Document43 pagesPublic Revenue Management 6mohamedNo ratings yet
- NYXBrand BookDocument34 pagesNYXBrand BookCristian Fernandez100% (1)
- Department of Manufacturing Engineering Laporan Makmal / Laboratory Report BDX 10703 Material Engineering Technology Lab Front Cover Full ReportDocument8 pagesDepartment of Manufacturing Engineering Laporan Makmal / Laboratory Report BDX 10703 Material Engineering Technology Lab Front Cover Full ReportDas SagaNo ratings yet
- Achieving Parity - The Role of AutomaticreinforcementDocument2 pagesAchieving Parity - The Role of AutomaticreinforcementevanschneidermanNo ratings yet
- Instructional Module and Its Components (Guide) : Course Ccs 3 Developer and Their BackgroundDocument7 pagesInstructional Module and Its Components (Guide) : Course Ccs 3 Developer and Their BackgroundAhljairo TerradoNo ratings yet
- MachinesDocument2 pagesMachinesShreyas YewaleNo ratings yet
- Ions & Ionic Bonds (Multiple Choice) QPDocument7 pagesIons & Ionic Bonds (Multiple Choice) QPBăng Băng LêNo ratings yet
- Bidder Manual - Tender SubmissionDocument54 pagesBidder Manual - Tender SubmissionSDOT AshtaNo ratings yet
- Kisi-Kisi Soal Pas Kelas XDocument14 pagesKisi-Kisi Soal Pas Kelas XRionaNo ratings yet
- Triceratops Hat Pattern by IraRottDocument21 pagesTriceratops Hat Pattern by IraRottRomi Guadarrama100% (1)
- Noncavernous Arteriovenous Shunts Mimicking Carotid Cavernous FistulaeDocument5 pagesNoncavernous Arteriovenous Shunts Mimicking Carotid Cavernous FistulaeClarithq LengguNo ratings yet
- Tsheet 1 KskaakkaDocument2 pagesTsheet 1 Kskaakkaimtiyaz ahmad0% (1)