Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flowchart AOM
Flowchart AOM
Uploaded by
clinicuc02Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- New Vet Jumpstart Guide: Twenty common general practice cases simplifiedFrom EverandNew Vet Jumpstart Guide: Twenty common general practice cases simplifiedNo ratings yet
- One Day On The RoadDocument3 pagesOne Day On The RoadRichard Adam Sison74% (77)
- GR10-12 Delphi Cram Notes - Revision1Document20 pagesGR10-12 Delphi Cram Notes - Revision1Adams Adams Sheldon100% (1)
- Infections in Primary CareDocument5 pagesInfections in Primary CareAtta Muhammad Memon100% (1)
- ReligionsDocument4 pagesReligionsPia Flores67% (3)
- Respiratory Tract Infections - Med DidacticsDocument59 pagesRespiratory Tract Infections - Med Didacticsapi-649060644No ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media (Aom) (Children) : Symptoms and DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAcute Otitis Media (Aom) (Children) : Symptoms and DiagnosisRoxana SurliuNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsDocument1 pageAcute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsSreya SanilNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM)Document1 pageAcute Otitis Media (AOM)f.sistersonNo ratings yet
- Parasitic WormsDocument4 pagesParasitic WormsEricNo ratings yet
- Suspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsDocument6 pagesSuspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsMuhamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Condition Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Ears Acute Otitis Media Exam: Bulging, Opaque, and Watchful Waiting (F/u Over Phone ConditionDocument12 pagesCondition Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Ears Acute Otitis Media Exam: Bulging, Opaque, and Watchful Waiting (F/u Over Phone ConditionAlexaNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1Document1 pageCOVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1shivani shindeNo ratings yet
- New May2020 PDFDocument7 pagesNew May2020 PDFDoctorMoodyNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysDocument3 pagesDiarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysKassem HijazyNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument1 pageAcute Otitis MediaAhmad Syahmi YZNo ratings yet
- NHS Antibiotice PDFDocument2 pagesNHS Antibiotice PDFHoratiu OanaNo ratings yet
- Aseptic Technique: Wound Assessment On A Patient (Open or Closed)Document4 pagesAseptic Technique: Wound Assessment On A Patient (Open or Closed)AbigailNo ratings yet
- Stepwise Approach in Longterm Management of Asthma in ChildrenDocument41 pagesStepwise Approach in Longterm Management of Asthma in ChildrenAris BayuNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome Relapse Clinical PathwayDocument8 pagesNephrotic Syndrome Relapse Clinical Pathwaydr.salimuzzamanNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Syndromic ApproachDocument1 pageAIIMS Syndromic ApproachRagul VNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- Abnoba ViscumDocument44 pagesAbnoba ViscumAlexandre Funcia100% (1)
- Acute Otitis Media in ChildrenDocument7 pagesAcute Otitis Media in ChildrenssssceNo ratings yet
- Famotidine Drug Card PDFDocument2 pagesFamotidine Drug Card PDFKish AmoreNo ratings yet
- Lupus: Therapy T.Document10 pagesLupus: Therapy T.Sharifah ManuelNo ratings yet
- CPAMSDocument7 pagesCPAMSDominic chuaNo ratings yet
- COVID - Management 14 April 2021Document20 pagesCOVID - Management 14 April 2021Zain ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Acute Rheumatic Fever: 2020 Updated Australian Criteria For ARF DiagnosisDocument3 pagesDiagnosis of Acute Rheumatic Fever: 2020 Updated Australian Criteria For ARF DiagnosisRichard SsenyondoNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument5 pagesDiphtheriahertezjogie669No ratings yet
- IMCI TECHNICAL UPDATES: The KEY To Your Success!! Pls..... Read.. Read.. Read.Document10 pagesIMCI TECHNICAL UPDATES: The KEY To Your Success!! Pls..... Read.. Read.. Read.Kim RamosNo ratings yet
- (Clinical Clerkship - Dermatology) Theracon - Antifungals - 09222021Document90 pages(Clinical Clerkship - Dermatology) Theracon - Antifungals - 09222021Jolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Asthma ZENDocument57 pagesAsthma ZENKonjit MitikuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study TramadolLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae: Click HereDocument3 pagesStreptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae: Click HereSiti Hidayatul FitriNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Guidelines Nephrotic Syndrome 2018Document8 pagesPaediatric Guidelines Nephrotic Syndrome 2018lilydariniNo ratings yet
- Fever Measles Ear ProblemsDocument10 pagesFever Measles Ear ProblemsEBNo ratings yet
- National Malaria Drug PolicyDocument22 pagesNational Malaria Drug Policydocsaurabh777No ratings yet
- Safe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingDocument16 pagesSafe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingJo ckerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLDocument12 pages2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLSutirtha RoyNo ratings yet
- PHARMA LE1 Asthma & Cough Cram SheetDocument1 pagePHARMA LE1 Asthma & Cough Cram SheetMarjorie MonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Darunday Rotation 6Document11 pagesDrug Study Darunday Rotation 6Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Materi 1. Update On Diagnosis and Management of Acute Asthma in Children - Dr. EryDocument25 pagesMateri 1. Update On Diagnosis and Management of Acute Asthma in Children - Dr. EryadfirdaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument26 pagesCommunicable Diseasested deangNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument27 pagesAcute Otitis MediassssceNo ratings yet
- PertussisDocument11 pagesPertussissribaccayNo ratings yet
- Treatment Protocol Covid-19Document4 pagesTreatment Protocol Covid-19Shiv singhNo ratings yet
- HSB Pneumonia Antibiotic AlgorithmDocument4 pagesHSB Pneumonia Antibiotic AlgorithmDr.Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Tetanus and Antibiotic Prophylaxis, Wound and Minor Soft Tissue TumorsDocument81 pagesTetanus and Antibiotic Prophylaxis, Wound and Minor Soft Tissue TumorsNárēsh Yadav GäddēNo ratings yet
- BISMILLAH LOLOS UKAI 2022 NewDocument5 pagesBISMILLAH LOLOS UKAI 2022 NewMaya SeptianaNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pharmacoogy Guide PDFDocument18 pagesUltimate Pharmacoogy Guide PDFElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- DiseaseDocument2 pagesDiseaseFermin K. CuasitoNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAppendicitisYosuaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease DrugsDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease DrugsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- REVISED-Med TaperingDocument3 pagesREVISED-Med TaperingDwi HerawatiNo ratings yet
- CPG'_for_DFCM_JBLMRHDocument22 pagesCPG'_for_DFCM_JBLMRHPunsalan ChecaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LoperamideDocument3 pagesDrug Study - LoperamideCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- GHC Lower Respiratory Tract Antimicrobial Guideline V 3 FinalDocument19 pagesGHC Lower Respiratory Tract Antimicrobial Guideline V 3 FinalNicthe Ruiz RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Infections BNHFT 2010 PDFDocument3 pagesBone and Joint Infections BNHFT 2010 PDFDanissa Fidia PuteriNo ratings yet
- Medicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver1Document4 pagesMedicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver1TrisNo ratings yet
- Complete Using ConditionalsDocument2 pagesComplete Using ConditionalsicecrisNo ratings yet
- CT6302B Datasheet V1.2: I. Product OverviewDocument17 pagesCT6302B Datasheet V1.2: I. Product Overviewrummy squaresNo ratings yet
- Img 0004Document7 pagesImg 0004velavan100% (1)
- Taylor's Scientific ManagementDocument7 pagesTaylor's Scientific Managementsipanjegiven0% (1)
- Volume Kerja English Year 4Document6 pagesVolume Kerja English Year 4kamiliamawaddahNo ratings yet
- NIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 EmotionsDocument4 pagesNIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 Emotionsmanahil dollNo ratings yet
- Class XII Applied Mathematics 2023-24 (K R Mangalam School)Document7 pagesClass XII Applied Mathematics 2023-24 (K R Mangalam School)GouriJayanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Flexfields 58987177.doc Effective Mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 24 Rev 1Document24 pagesOverview of Flexfields 58987177.doc Effective Mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 24 Rev 1sudharshan79No ratings yet
- COT1-3rd HirarkiyaDocument49 pagesCOT1-3rd HirarkiyaRommel LasugasNo ratings yet
- Research GR 2 Pinaka Final 1Document36 pagesResearch GR 2 Pinaka Final 1Richeille JoshNo ratings yet
- Psalm 127 - Overview"Document1 pagePsalm 127 - Overview"Malcolm CoxNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education Project Final VersionDocument16 pagesNutrition Education Project Final Versionapi-535168013No ratings yet
- Variables, Validity & ReliabilityDocument42 pagesVariables, Validity & ReliabilityNsem Rao100% (1)
- Epe 2013111515302022Document5 pagesEpe 2013111515302022qais652002No ratings yet
- D D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationDocument13 pagesD D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationWelleyNo ratings yet
- Teaching For Reading MiDocument17 pagesTeaching For Reading MiRevi WijanarkoNo ratings yet
- Liebherr Brochure Boom Pumps enDocument20 pagesLiebherr Brochure Boom Pumps enVikash PanditNo ratings yet
- Chemf 2007 3Document124 pagesChemf 2007 3Anupam AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Deped Order No.31 S. 2020 Interim Guidelines For Assessment and Grading in Light of The Basic Education Learning Continuity PlanDocument24 pagesDeped Order No.31 S. 2020 Interim Guidelines For Assessment and Grading in Light of The Basic Education Learning Continuity PlanAlyssa AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Submarine Cable Installation ContractorsDocument19 pagesSubmarine Cable Installation Contractorswiji_thukulNo ratings yet
- Aegis - Designer and AnalyzerDocument26 pagesAegis - Designer and Analyzeropenid_S1hHcZODNo ratings yet
- Short Questions For Ayub Khan DownfallDocument9 pagesShort Questions For Ayub Khan Downfallabdullah sheikhNo ratings yet
- Solución: R T β T R (T) = 1000 Ω ΩDocument6 pagesSolución: R T β T R (T) = 1000 Ω ΩDuvan BayonaNo ratings yet
- TOS JRMSU 2nd SemDocument24 pagesTOS JRMSU 2nd SemCris Ann PausanosNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics PDFDocument2 pagesComputer Graphics PDFAakash KhannaNo ratings yet
- Timeline Bendahara DesemberDocument2 pagesTimeline Bendahara DesemberSuci Ayu ChairunaNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement Engineering - CS708 Power Point Slides Lecture-09Document25 pagesSoftware Requirement Engineering - CS708 Power Point Slides Lecture-09ALTAIRI SALEHNo ratings yet
Flowchart AOM
Flowchart AOM
Uploaded by
clinicuc02Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flowchart AOM
Flowchart AOM
Uploaded by
clinicuc02Copyright:
Available Formats
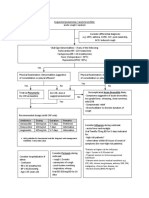
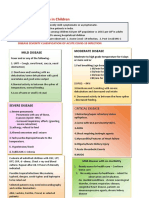
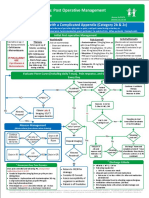
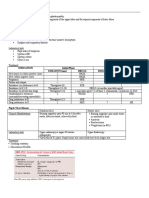
Antibiotic Decision Making
for Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Terms:
AOM = Acute Otitis Media
AOE = Acute Otitis Externa
OME = Otitis Media With Effusion
Severe signs = Fever >39 °C or moderate-severe otalgia¹ Age 6 months to 12 years
or otalgia1 ≥48 hours with signs/symptoms of an
ear infection:
Watchful waiting = Initial observation
po = by mouth fever, otalgia1, fussiness,
sleep disturbance
Note: YES
Know seasonal epidemiology and when rapid diagnostic
testing is warranted (RSV, influenza).
Optimize management of a child with asthma. Additional symptoms suggestive of AOM: Not AOM: Do not treat
with antibiotics
Moderate-severe TM bulging
or mild bulging and recent otalgia¹ onset NO
or mild bulging and intense erythema If middle ear effusion only:
or new onset otorrhea not due to AOE Do not treat OME with
antibiotics
YES (AOM confirmed)
Severe Nonsevere
Age: 6–23 months Age: ≥24 months
Severe signs Bilateral AOM without Unilateral AOM without Unilateral or bilateral AOM
severe signs severe signs Without severe signs
Fever ≥39°C or moderate-
severe otalgia¹ or Fever <39°C and mild otalgia Fever <39°C and mild otalgia Fever <39°C and mild otalgia
or otalgia <48 hours or otalgia <48 hours or otalgia <48 hours
otalgia1 ≥48 hours Watchful waiting preferred Watchful waiting preferred
Assess for initial
High-Dose Amoxicillin2 High-Dose Amoxicillin2 observation (watchful Watchful High-Dose Amoxicillin2
waiting) waiting 80–90 mg/kg/day po divided BID
80–90 mg/kg/day po 80-90 mg/kg/day po not
divided BID (max dose 2 g) divided BID (max dose 2 g) Discuss with parents / (max dose 2 g)
chosen
for 10 days for 10 days caregivers. Mechanism for Duration:
follow-up required. 10 days if severe signs
10 days if <2 years
Footnotes 5–7 days if nonsevere and ≥6 years
1. Otalgia: May present as holding, tugging, rubbing of the ear in a nonverbal Watchful waiting chosen 7 days if nonsevere and 2–5 years
child. Pain relief is indicated for otalgia.
2. Alternate therapy is indicated if patient has history of:
• Amoxicillin treatment in last 30 days, concurrent purulent
conjunctivitis, or history of recurrent AOM unresponsive to amoxicillin: Symptoms persist or worsen over
Amoxicillin-clavulanate 90 mg/kg/day of amoxicillin with 6.4 mg/kg/day next 48–72 hours:
clavulanate po divided in 2 doses (max 2 g/dose) for 10 days.
Symptoms improve over Treat with High-Dose Amoxicillin2
• Severe or nonsevere penicillin allergy: Cefdinir 14 mg/kg/day po divided next 48–72 hours:
1 or 2 doses (max dose 600 mg/day), or cefpodoxime 10 mg/kg/day po 80–90 mg/kg/day po divided BID
divided BID (max 400 mg/dose) or cefuroxime 30 mg/kg/day po in 2 Do not treat with (max dose 2 g)
divided doses (max 500 mg/dose) for the duration recommended for antibiotics
amoxicillin per algorithm above, or ceftriaxone 50 mg/kg IM/IV per day Duration:
(max 2 g/dose) for 1–3 days.
10 days if severe signs
Macrolides: Not recommended unless severe allergy to penicillin and
cephalosporins exist. Resistance is well known and treatment failures related 10 days if <2 years
to macrolide resistance have occurred. 5-7 days if nonsevere and ≥6 years
7 days if nonsevere and 2–5 years
Reference
Lieberthal AS, Carroll AE, Chonmaitree T, et al. AAP Clinical Practice
Guideline: the diagnosis and management of acute otitis
media Pediatrics 2013;131(3):e964-e999
Copyright © 2021 American Academy of Pediatrics
You might also like
- New Vet Jumpstart Guide: Twenty common general practice cases simplifiedFrom EverandNew Vet Jumpstart Guide: Twenty common general practice cases simplifiedNo ratings yet
- One Day On The RoadDocument3 pagesOne Day On The RoadRichard Adam Sison74% (77)
- GR10-12 Delphi Cram Notes - Revision1Document20 pagesGR10-12 Delphi Cram Notes - Revision1Adams Adams Sheldon100% (1)
- Infections in Primary CareDocument5 pagesInfections in Primary CareAtta Muhammad Memon100% (1)
- ReligionsDocument4 pagesReligionsPia Flores67% (3)
- Respiratory Tract Infections - Med DidacticsDocument59 pagesRespiratory Tract Infections - Med Didacticsapi-649060644No ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media (Aom) (Children) : Symptoms and DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAcute Otitis Media (Aom) (Children) : Symptoms and DiagnosisRoxana SurliuNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsDocument1 pageAcute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsSreya SanilNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM)Document1 pageAcute Otitis Media (AOM)f.sistersonNo ratings yet
- Parasitic WormsDocument4 pagesParasitic WormsEricNo ratings yet
- Suspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsDocument6 pagesSuspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsMuhamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Condition Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Ears Acute Otitis Media Exam: Bulging, Opaque, and Watchful Waiting (F/u Over Phone ConditionDocument12 pagesCondition Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Ears Acute Otitis Media Exam: Bulging, Opaque, and Watchful Waiting (F/u Over Phone ConditionAlexaNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1Document1 pageCOVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1shivani shindeNo ratings yet
- New May2020 PDFDocument7 pagesNew May2020 PDFDoctorMoodyNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysDocument3 pagesDiarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysKassem HijazyNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument1 pageAcute Otitis MediaAhmad Syahmi YZNo ratings yet
- NHS Antibiotice PDFDocument2 pagesNHS Antibiotice PDFHoratiu OanaNo ratings yet
- Aseptic Technique: Wound Assessment On A Patient (Open or Closed)Document4 pagesAseptic Technique: Wound Assessment On A Patient (Open or Closed)AbigailNo ratings yet
- Stepwise Approach in Longterm Management of Asthma in ChildrenDocument41 pagesStepwise Approach in Longterm Management of Asthma in ChildrenAris BayuNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome Relapse Clinical PathwayDocument8 pagesNephrotic Syndrome Relapse Clinical Pathwaydr.salimuzzamanNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Syndromic ApproachDocument1 pageAIIMS Syndromic ApproachRagul VNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- Abnoba ViscumDocument44 pagesAbnoba ViscumAlexandre Funcia100% (1)
- Acute Otitis Media in ChildrenDocument7 pagesAcute Otitis Media in ChildrenssssceNo ratings yet
- Famotidine Drug Card PDFDocument2 pagesFamotidine Drug Card PDFKish AmoreNo ratings yet
- Lupus: Therapy T.Document10 pagesLupus: Therapy T.Sharifah ManuelNo ratings yet
- CPAMSDocument7 pagesCPAMSDominic chuaNo ratings yet
- COVID - Management 14 April 2021Document20 pagesCOVID - Management 14 April 2021Zain ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Acute Rheumatic Fever: 2020 Updated Australian Criteria For ARF DiagnosisDocument3 pagesDiagnosis of Acute Rheumatic Fever: 2020 Updated Australian Criteria For ARF DiagnosisRichard SsenyondoNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument5 pagesDiphtheriahertezjogie669No ratings yet
- IMCI TECHNICAL UPDATES: The KEY To Your Success!! Pls..... Read.. Read.. Read.Document10 pagesIMCI TECHNICAL UPDATES: The KEY To Your Success!! Pls..... Read.. Read.. Read.Kim RamosNo ratings yet
- (Clinical Clerkship - Dermatology) Theracon - Antifungals - 09222021Document90 pages(Clinical Clerkship - Dermatology) Theracon - Antifungals - 09222021Jolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Asthma ZENDocument57 pagesAsthma ZENKonjit MitikuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study TramadolLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae: Click HereDocument3 pagesStreptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae: Click HereSiti Hidayatul FitriNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Guidelines Nephrotic Syndrome 2018Document8 pagesPaediatric Guidelines Nephrotic Syndrome 2018lilydariniNo ratings yet
- Fever Measles Ear ProblemsDocument10 pagesFever Measles Ear ProblemsEBNo ratings yet
- National Malaria Drug PolicyDocument22 pagesNational Malaria Drug Policydocsaurabh777No ratings yet
- Safe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingDocument16 pagesSafe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingJo ckerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLDocument12 pages2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLSutirtha RoyNo ratings yet
- PHARMA LE1 Asthma & Cough Cram SheetDocument1 pagePHARMA LE1 Asthma & Cough Cram SheetMarjorie MonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Darunday Rotation 6Document11 pagesDrug Study Darunday Rotation 6Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Materi 1. Update On Diagnosis and Management of Acute Asthma in Children - Dr. EryDocument25 pagesMateri 1. Update On Diagnosis and Management of Acute Asthma in Children - Dr. EryadfirdaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument26 pagesCommunicable Diseasested deangNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument27 pagesAcute Otitis MediassssceNo ratings yet
- PertussisDocument11 pagesPertussissribaccayNo ratings yet
- Treatment Protocol Covid-19Document4 pagesTreatment Protocol Covid-19Shiv singhNo ratings yet
- HSB Pneumonia Antibiotic AlgorithmDocument4 pagesHSB Pneumonia Antibiotic AlgorithmDr.Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Tetanus and Antibiotic Prophylaxis, Wound and Minor Soft Tissue TumorsDocument81 pagesTetanus and Antibiotic Prophylaxis, Wound and Minor Soft Tissue TumorsNárēsh Yadav GäddēNo ratings yet
- BISMILLAH LOLOS UKAI 2022 NewDocument5 pagesBISMILLAH LOLOS UKAI 2022 NewMaya SeptianaNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pharmacoogy Guide PDFDocument18 pagesUltimate Pharmacoogy Guide PDFElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- DiseaseDocument2 pagesDiseaseFermin K. CuasitoNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAppendicitisYosuaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease DrugsDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease DrugsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- REVISED-Med TaperingDocument3 pagesREVISED-Med TaperingDwi HerawatiNo ratings yet
- CPG'_for_DFCM_JBLMRHDocument22 pagesCPG'_for_DFCM_JBLMRHPunsalan ChecaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LoperamideDocument3 pagesDrug Study - LoperamideCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- GHC Lower Respiratory Tract Antimicrobial Guideline V 3 FinalDocument19 pagesGHC Lower Respiratory Tract Antimicrobial Guideline V 3 FinalNicthe Ruiz RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Infections BNHFT 2010 PDFDocument3 pagesBone and Joint Infections BNHFT 2010 PDFDanissa Fidia PuteriNo ratings yet
- Medicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver1Document4 pagesMedicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver1TrisNo ratings yet
- Complete Using ConditionalsDocument2 pagesComplete Using ConditionalsicecrisNo ratings yet
- CT6302B Datasheet V1.2: I. Product OverviewDocument17 pagesCT6302B Datasheet V1.2: I. Product Overviewrummy squaresNo ratings yet
- Img 0004Document7 pagesImg 0004velavan100% (1)
- Taylor's Scientific ManagementDocument7 pagesTaylor's Scientific Managementsipanjegiven0% (1)
- Volume Kerja English Year 4Document6 pagesVolume Kerja English Year 4kamiliamawaddahNo ratings yet
- NIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 EmotionsDocument4 pagesNIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 Emotionsmanahil dollNo ratings yet
- Class XII Applied Mathematics 2023-24 (K R Mangalam School)Document7 pagesClass XII Applied Mathematics 2023-24 (K R Mangalam School)GouriJayanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Flexfields 58987177.doc Effective Mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 24 Rev 1Document24 pagesOverview of Flexfields 58987177.doc Effective Mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 24 Rev 1sudharshan79No ratings yet
- COT1-3rd HirarkiyaDocument49 pagesCOT1-3rd HirarkiyaRommel LasugasNo ratings yet
- Research GR 2 Pinaka Final 1Document36 pagesResearch GR 2 Pinaka Final 1Richeille JoshNo ratings yet
- Psalm 127 - Overview"Document1 pagePsalm 127 - Overview"Malcolm CoxNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education Project Final VersionDocument16 pagesNutrition Education Project Final Versionapi-535168013No ratings yet
- Variables, Validity & ReliabilityDocument42 pagesVariables, Validity & ReliabilityNsem Rao100% (1)
- Epe 2013111515302022Document5 pagesEpe 2013111515302022qais652002No ratings yet
- D D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationDocument13 pagesD D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationWelleyNo ratings yet
- Teaching For Reading MiDocument17 pagesTeaching For Reading MiRevi WijanarkoNo ratings yet
- Liebherr Brochure Boom Pumps enDocument20 pagesLiebherr Brochure Boom Pumps enVikash PanditNo ratings yet
- Chemf 2007 3Document124 pagesChemf 2007 3Anupam AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Deped Order No.31 S. 2020 Interim Guidelines For Assessment and Grading in Light of The Basic Education Learning Continuity PlanDocument24 pagesDeped Order No.31 S. 2020 Interim Guidelines For Assessment and Grading in Light of The Basic Education Learning Continuity PlanAlyssa AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Submarine Cable Installation ContractorsDocument19 pagesSubmarine Cable Installation Contractorswiji_thukulNo ratings yet
- Aegis - Designer and AnalyzerDocument26 pagesAegis - Designer and Analyzeropenid_S1hHcZODNo ratings yet
- Short Questions For Ayub Khan DownfallDocument9 pagesShort Questions For Ayub Khan Downfallabdullah sheikhNo ratings yet
- Solución: R T β T R (T) = 1000 Ω ΩDocument6 pagesSolución: R T β T R (T) = 1000 Ω ΩDuvan BayonaNo ratings yet
- TOS JRMSU 2nd SemDocument24 pagesTOS JRMSU 2nd SemCris Ann PausanosNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics PDFDocument2 pagesComputer Graphics PDFAakash KhannaNo ratings yet
- Timeline Bendahara DesemberDocument2 pagesTimeline Bendahara DesemberSuci Ayu ChairunaNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement Engineering - CS708 Power Point Slides Lecture-09Document25 pagesSoftware Requirement Engineering - CS708 Power Point Slides Lecture-09ALTAIRI SALEHNo ratings yet