Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrictyyyyy
Electrictyyyyy
Uploaded by
Quamrul Islam MilonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrictyyyyy
Electrictyyyyy
Uploaded by
Quamrul Islam MilonCopyright:
Available Formats
Electron & proton both
have same charge
──
Electron (Negative
charge), ߚ
+
Proton (Positive
Charge) , ߙ
Neutron (have no
charge), ߛ
Positive ion : hLb GKwU an atom lose electron & Negative Ion : when an atom gains Electron. Avi
GB Electrostatic gvcvi †QvU GKK n‡jv Kzj¤^|
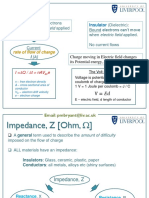
Current, Risestance, Voltage
Current : The rate of flow of charge. Gi GKK n‡jv Ampere. Z‡e GK Ampere GK Coulomb G mgvb|
‡Kvb gva¨‡g 2 wgwb‡U 3 A¨vw¤úqvi cÖevwnZ n‡j, PvR© Q = I ൈ t or, 3 ൈ 120s = 360 Coulomb
ௐ
Voltage : Potential diference between two points. V = , W = energy & Q = charge
ொ
Resistance : Collisions between charge carriers and atoms pf materials. this unit is Ohm (Ωሻ
R=
ூ
Ohm’s Law (V = I ൈ R)
Current +
Battery Resistor (Load) Potential
(Source) difference,V
-
Current
Q : 0.1A & 220 Ω what’s voltag drop?
V = I ൈ R or, 0.1 ൈ 220 = 22v
Q : 18Ω, 12v battery, What’s current flow?
ଵଶ
I= or, = 2.4A
ோ ଵ଼
Power & Energy :
Power is the rate at which energy is converted form one form to another form. It measure in
watts.
ௐ
Power , P = watts, W = energy; t for time .GmKj wnmve memgq †m‡K‡Û KvD›U Kiv nq| Z‡e wnmve
௧
myweav‡_© N›Uvq Kiv nq|
Energy, w = (P ൈ t) jule
You might also like
- Soal Soal HallidayDocument65 pagesSoal Soal HallidayFiza RyanNo ratings yet
- Voltage ControlDocument25 pagesVoltage Controlbenson215100% (2)
- EEE 209 LN1 Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument130 pagesEEE 209 LN1 Basic Principles of ElectricityMine KayaNo ratings yet
- NMAT - Electricity and MagnetismDocument56 pagesNMAT - Electricity and MagnetismPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- L2-3 - M3 Electrotech - Physics - EN PDFDocument12 pagesL2-3 - M3 Electrotech - Physics - EN PDFAnnemarija KalninaNo ratings yet
- Physics at Work - Unit 02 - DC ElectricityDocument11 pagesPhysics at Work - Unit 02 - DC ElectricitySam PereraNo ratings yet
- EEE 209 Presentation 2 (Electrical Circuits)Document130 pagesEEE 209 Presentation 2 (Electrical Circuits)Mert YılmazNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Electrical Potential For Advanced Level StudentsDocument45 pagesLecture On Electrical Potential For Advanced Level StudentsTauseef AminNo ratings yet
- Review of Electrical Circuits Review of Electrical Circuits Theory TheoryDocument74 pagesReview of Electrical Circuits Review of Electrical Circuits Theory Theoryalan_tamNo ratings yet
- Module3 MCQDocument2 pagesModule3 MCQLukkuman ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Electric Charges and ForcesDocument25 pagesChapter 22 - Electric Charges and ForcesUltimateDeathGodNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermBryan PongaoNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Final Exams Revision: Electrical ChargeDocument19 pagesElectrostatics - Final Exams Revision: Electrical ChargeThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Electric Filed and PotentialDocument16 pagesElectric Filed and Potentialsanjay sNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic ElectrostaticsDocument21 pages1 Basic ElectrostaticsAyera Fareenah JamelNo ratings yet
- EMT Lecture 1Document21 pagesEMT Lecture 1Arslah ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential & Capacitance - 1-12Document12 pagesElectric Potential & Capacitance - 1-12Akash SureshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - 10th. Edition - (2022-1) ADocument20 pagesChapter 21 - 10th. Edition - (2022-1) Anouf AldosareNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument1 pageElectricity and MagnetismJulia KarakiNo ratings yet
- PB - Device Physics 2021 Lecture 3Document33 pagesPB - Device Physics 2021 Lecture 3keke renNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge, EtcDocument38 pagesElectric Charge, EtcJohn Dave LarrozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Electrostatics Genius Series Formula SheetDocument52 pagesChapter 11 Electrostatics Genius Series Formula SheetHaseebShahNo ratings yet
- Basic Electromagnetism 1Document89 pagesBasic Electromagnetism 1Waruni NisansalaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential-IDocument33 pagesElectric Potential-ISumaya Akter Ruhi 2022610642No ratings yet
- Physics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Summer 23)Document18 pagesPhysics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Summer 23)fardinmojumdar123No ratings yet
- BEEE MCTR Unit-1Document43 pagesBEEE MCTR Unit-1thaffin4132No ratings yet
- H3 ImpedanceDocument29 pagesH3 ImpedanceShageeshan AlagesanNo ratings yet
- Potential and Capacitance-1 (OCR) (OCR)Document90 pagesPotential and Capacitance-1 (OCR) (OCR)19giditanujNo ratings yet
- Phy126 - Electric ChargeDocument68 pagesPhy126 - Electric ChargeDavid EbikaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Chapter 16 Electric Potential, Energy, and CapacitanceDocument63 pagesAP Physics Chapter 16 Electric Potential, Energy, and Capacitancejerin123No ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument19 pagesElectrostaticsmthembuandile279No ratings yet
- Physics Formula ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesPhysics Formula Electrostaticskehangilani007No ratings yet
- Chap 22 Electric Fields: PHYS 102 Dr. Bassem HmoudaDocument32 pagesChap 22 Electric Fields: PHYS 102 Dr. Bassem HmoudajoyceNo ratings yet
- XbhV0ZrZoi6rHwunv4Ou 1Document32 pagesXbhV0ZrZoi6rHwunv4Ou 1patlibhindi420No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Lec 1,2,3,4,5 SummaryDocument5 pagesElectrical Circuits Lec 1,2,3,4,5 SummaryRaghad Al-ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CirTheo-CH1 - IntroaDocument33 pagesCirTheo-CH1 - Introasjbong0904No ratings yet
- S.No Questions Answers: Perpendicular To Each Other and The Direction of Wave Propagation. IfDocument20 pagesS.No Questions Answers: Perpendicular To Each Other and The Direction of Wave Propagation. IfchennipadmaNo ratings yet
- Study Material 12 PhysicsDocument117 pagesStudy Material 12 PhysicsVaishu Uparkar100% (1)
- Basic ElectricityDocument61 pagesBasic ElectricityManny Anacleto100% (6)
- Physics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Fall 2023-24)Document18 pagesPhysics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Fall 2023-24)famidrabbifrNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 12 Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance PDFDocument42 pagesNCERT Class 12 Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance PDFAlice AntilNo ratings yet
- BEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesDocument20 pagesBEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesMondaya, Jake Armond D.No ratings yet
- Electricity L6Document24 pagesElectricity L6sowmeya veeraraghavanNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-+2 Physics FOCUS AREA Notes by NSSDocument29 pagesHsslive-+2 Physics FOCUS AREA Notes by NSSaryan.chithra2020No ratings yet
- November 02Document14 pagesNovember 02Yash KalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Circuit VariablesDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Circuit VariablesHackerzillaNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Electric Potential Final EditionDocument112 pagesElectric Fields and Electric Potential Final Editionraie saadNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument22 pagesPhysicsFurqan Ali CheemaNo ratings yet
- Active Power, Reactive Power, Apparent Power, and The Role of Power Factor - Technical ArticlesDocument7 pagesActive Power, Reactive Power, Apparent Power, and The Role of Power Factor - Technical ArticlesSoy ChandaraNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldsDocument48 pagesMagnetic Fieldsdayana hanis hassanNo ratings yet
- PhyschemDocument7 pagesPhyschemStephany Mae ChiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Energy PotentialDocument12 pagesLesson 8 - Energy PotentialElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Week 001 Electric Forces and Fields, Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawDocument19 pagesWeek 001 Electric Forces and Fields, Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawYukiko HachiNo ratings yet
- Electrometallurgy PDFDocument34 pagesElectrometallurgy PDFJeremy PutraNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-Introduction To DC Analysis - SlidesDocument43 pagesUnit-1-Introduction To DC Analysis - SlidesGanesha Dattatraya Gaonkar CFALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21. Electric Charge and Electric Field: © Physics 72 ArciagaDocument4 pagesChapter 21. Electric Charge and Electric Field: © Physics 72 ArciagaNathan VeracruzNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Full GuideDocument135 pages12 Physics Full GuideangelinerosedeborahNo ratings yet
- OCR A Physics A Level: Topic 6.2: Electric FieldsDocument8 pagesOCR A Physics A Level: Topic 6.2: Electric FieldsjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Calculation Transient Electromagnetic Field Around A Transmission Line Subjected To Lightning StrokesDocument4 pagesCalculation Transient Electromagnetic Field Around A Transmission Line Subjected To Lightning StrokesTlili MahmoudiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS) Class: Vii: Subject: PhysicsDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQS) Class: Vii: Subject: PhysicsnaylinaungNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q2 2nd Summative TestDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q2 2nd Summative TestpabsNo ratings yet
- Electricity Magnetism: I I I F I F + + Q Q F F F FDocument46 pagesElectricity Magnetism: I I I F I F + + Q Q F F F FMARIAMA SILLAHNo ratings yet
- Photoelasticity Diffused Light Polariscope - 2019 - SOMDocument7 pagesPhotoelasticity Diffused Light Polariscope - 2019 - SOMKamini GoyalNo ratings yet
- Celda Catalogo GmaDocument56 pagesCelda Catalogo GmaRoberto RobalinoNo ratings yet
- Model Met-C1 Cde (D148/D149/D150) Parts CatalogDocument266 pagesModel Met-C1 Cde (D148/D149/D150) Parts CatalogRoberto BernardiNo ratings yet
- Utilities Compiled ProblemsDocument4 pagesUtilities Compiled ProblemsNexy LoberianoNo ratings yet
- TE 271 Part 1Document58 pagesTE 271 Part 1Emmanuel EduafulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9-2015Document24 pagesLecture 9-2015Ahmedash1No ratings yet
- Pemakaian Listrik Alat KesehatanDocument6 pagesPemakaian Listrik Alat KesehatanipsrsNo ratings yet
- 4PH1 - 1PR - Rms - 20230824 6Document18 pages4PH1 - 1PR - Rms - 20230824 6bperiscasanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Flowmeter Upser Manual External PoweredDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic Flowmeter Upser Manual External Poweredevct1989No ratings yet
- THIRD PERIODICAL TEST IN SCIENCE Grade 5Document2 pagesTHIRD PERIODICAL TEST IN SCIENCE Grade 5Edelyn Unay92% (13)
- Physics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1Document11 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1JatinNo ratings yet
- LV PH 2020 - Electrical Lighting 05182020Document8 pagesLV PH 2020 - Electrical Lighting 05182020art cafeNo ratings yet
- Car Starting & Charging System Trainer (Generator Circuit) : FeatureDocument1 pageCar Starting & Charging System Trainer (Generator Circuit) : FeatureIman SetyoajiNo ratings yet
- PRO-76T: Multifunctional Drilling & Tapping MachineDocument4 pagesPRO-76T: Multifunctional Drilling & Tapping MachineBouraoui Ben AyedNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Testing (A) Suggest Suitable Method and Justify Why You Choose The MethodDocument6 pagesPenetrant Testing (A) Suggest Suitable Method and Justify Why You Choose The MethodImelda TiongNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering: BY R. Sivaprasad, Lecturer in Eee, Govt. Polytechnic, SatyaveduDocument69 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering: BY R. Sivaprasad, Lecturer in Eee, Govt. Polytechnic, Satyavedurathina4careerNo ratings yet
- Excitation Signal: Fig: Dispersive Propogation of The WaveDocument7 pagesExcitation Signal: Fig: Dispersive Propogation of The WaveHarsh KhotNo ratings yet
- 22.01 Problem Set 4 Homework Solutions: Q M) Q E M)Document5 pages22.01 Problem Set 4 Homework Solutions: Q M) Q E M)Aurélie MaillardNo ratings yet
- AP Chapter 6 Powerpoint For WebsiteDocument70 pagesAP Chapter 6 Powerpoint For WebsiteMalik ForbesNo ratings yet
- SGVT ErrataDocument5 pagesSGVT ErrataJuan Emanuel VenturelliNo ratings yet
- PQIM PaperDocument2 pagesPQIM PaperDarshan VoraNo ratings yet
- Physics-XII Chapter - 12 (Electric Flux and Electric Potential) Practice Sheet-02Document5 pagesPhysics-XII Chapter - 12 (Electric Flux and Electric Potential) Practice Sheet-02Ghulam NabiNo ratings yet
- Richard Wolf 2271Document39 pagesRichard Wolf 2271Akram AlwahibiNo ratings yet
- Subject: SCIENCE Level: 10 Quarter: 2 Week: 5 Melc: Competency CodeDocument6 pagesSubject: SCIENCE Level: 10 Quarter: 2 Week: 5 Melc: Competency CodeTrexia SingsonNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law and Kirchhoffs Law Lab ReportDocument8 pagesOhms Law and Kirchhoffs Law Lab Reportlove to readNo ratings yet
- Physics Mdcat: D) 4 L A) Sine WaveDocument6 pagesPhysics Mdcat: D) 4 L A) Sine WaveahmedNo ratings yet