Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Troubleshooting Bladder Pressure Tanks
Troubleshooting Bladder Pressure Tanks
Uploaded by
Fawziyyah AgboolaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Troubleshooting Bladder Pressure Tanks
Troubleshooting Bladder Pressure Tanks
Uploaded by
Fawziyyah AgboolaCopyright:
Available Formats
Drinking Water Tech Tips
DOH 331-342
What is a Sept. 2017
Revised
Troubleshooting Bladder Pressure Tanks
bladder pressur
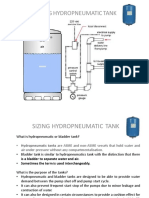
What is a bladder pressure tank?
It is a type of tank containing pressurized air and water separated by a membrane (bladder) and pre-charged
with air at the factory. On average, a bladder pressure tank lasts 5–7 years.
Please refer to Pressure Relief Valves on Pressure Tanks Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4
(331-429), a one-page illustrated tech tip. It explains design
requirements, how pressure relief valves protect pressure tanks, air air air air
and how to ensure pressure relief valves are approved and
installed properly. water
How do bladder pressure tanks work?
As water pressure changes, the volume of air in a bladder 29 psi 30 psi 50 psi Pump Off
pressure tank contracts or expands. Periodically, the amount of Pump on
air in the tank should be measured and the tank recharged if the Typical Pump Cycle
air is too low. Bladder pressure tanks do not provide any actual Step 1. Pump Off: Tank is nearly empty. Air
useful water storage capacity. expands to fill tank volume up to the pre-
charged pounds per square inch (psi).
What functions do bladder pressure tanks serve? Step 2. Pump Starts: Water begins to enter the tank,
compressing the air.
Maintain a desired range of water pressure in the
Step 3. Pump Stops: The system reaches maximum
distribution system. pressure. Air is compressed to the cut-off
Minimize pump cycling. Frequent starts and stops can setting of the pressure switch.
damage facilities. Step 4. Pump Off: When water is demanded, air
Protect against water hammer. pressure forces it into the system, and a new
cycle begins.
Troubleshooting Guide Common pressure ranges are 30 to 50 or 40 to 60 psi.
Check for waterlogged bladder pressure tank problems
When the internal bladder fails and water fills the air Air Charging
space around the bladder inside the tank, the tank is Valve
No Air
waterlogged. You should replace waterlogged tanks.
Gently tipping the tank may identify a waterlogged Precharged
water
Air
tank by weight. Hole in the
The pump motor cycles on/off rapidly. bladder
Pressure
Listen. When you tap on the outside of the tank, it Vessel
sounds different from those with a proper air-water
balance. Bladder
When you depress the central pin of the air-charging
Water
valve, water escapes through the charging valve.
Stale, rusty water appears at the tap due to corrosion
inside the tank.
Bladder Pressure Waterlogged Bladder
Helpful hint! It is often most cost-efficient to replace a Tank Pressure Tank
waterlogged tank.
Check the air charge inside the bladder pressure tank
Air may escape from the bladder tank, just as it does from a bicycle or car tire. Loss of air inside the tank will
result in over-expansion of the bladder, leading to premature bladder failure. Loss of air will lead to excessive
pump cycling, which may shorten the life of the well pump motor. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions if
you have the technical ability to do so safely; otherwise, hire a professional to evaluate your pressure tank.
Helpful hint! Take safety seriously and don’t exceed your experience or knowledge.
Adjust the air pressure in the bladder pressure tank
Read and follow the manufacturer’s safety warnings when working with bladder pressure tanks. Respect
your limits. Contact a professional if you need help or feel uncertain about working conditions. Tank
condition, air compressor and pressure gauge accuracy, the location and condition of pressure relief valves,
and other factors may create a hazardous environment to perform the functions needed to adjust air pressure.
Avoid depressurizing your water system. Depressurizing the water system creates a high risk for backflow
and contamination of the distribution system. Contact your regional office before depressurizing your water
system as part of adjusting air pressure or performing other maintenance on your bladder pressure tank(s).
Typical manufacturer’s instructions include these steps when checking and adjusting the air pressure in a
bladder pressure tank:
1. Turn the power to the pump off or isolate the pressure tank from the rest of the system.
2. Open a faucet to drain the tank completely.
3. Check the air pressure at the air valve on the top of the tank with a pressure gauge.
4. The air pressure should be 2 psi below the start pressure setting of the pump.
5. Use an air compressor to charge the tank to the proper pressure. DO NOT OVER PRESSURIZE!
6. Close the faucet.
7. Turn power back on or open the isolation valve and refill the tank.
8. Check that the pump is turning on/off at the proper pressures using system pressure gauges.
For more information
We offer many publications online at http://doh.wa.gov/odwpubs/.
Contact our nearest regional office from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. Monday through Friday. If you have an after-hours
emergency, call 877-481-4901.
Eastern Region, Spokane Valley 509-329-2100
Adams, Asotin, Benton, Chelan, Columbia, Douglas, Ferry, Franklin, Garfield, Grant, Kittitas, Klickitat,
Lincoln, Okanogan, Pend Oreille, Spokane, Stevens, Walla Walla, Whitman, and Yakima counties.
Northwest Region, Kent 253-395-6750
Island, King, Pierce, San Juan, Skagit, Snohomish, and Whatcom counties.
Southwest Region, Tumwater 360-236-3030
Clallam, Clark, Cowlitz, Grays Harbor, Jefferson, Kitsap, Lewis, Mason, Pacific, Skamania, Thurston, and
Wahkiakum counties.
For people with disabilities, this document is available on request from other formats. To submit a request, please call
1-800-525-0127 (TDD/TTY call 711).
You might also like
- Practical Management Science 4th Edition Winston Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesPractical Management Science 4th Edition Winston Solutions ManualLaurenBatesnqkim100% (14)
- Multi Flow InstructionsDocument9 pagesMulti Flow InstructionsthegoodpatriotNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument69 pagesHydraulicsRamesh SahniNo ratings yet
- Hydro Pneumatic Tank.Document2 pagesHydro Pneumatic Tank.bryesanggalang100% (1)
- Hydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsDocument2 pagesHydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsBlancaNo ratings yet
- Hydropneumatic Schemematics331 380Document2 pagesHydropneumatic Schemematics331 380wnewell1No ratings yet
- CavitationDocument28 pagesCavitationvenkeekuNo ratings yet
- Hydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsDocument3 pagesHydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech Tipsdevrukhkarsani74No ratings yet
- Marine Fresh Water GeneratorDocument6 pagesMarine Fresh Water Generatorazeezur100% (2)
- EL FHT OpInsDocument2 pagesEL FHT OpInsbabjihanumanthuNo ratings yet
- 1998-02 Water HeatersDocument2 pages1998-02 Water HeatersMike PerryNo ratings yet
- Set Up and Tuning of Pressure Switches and Hydropneumatic TanksDocument2 pagesSet Up and Tuning of Pressure Switches and Hydropneumatic TanksReza KhajeNo ratings yet
- FH5 E OpinsDocument2 pagesFH5 E OpinsbabjihanumanthuNo ratings yet
- Flowing Freely, Under No Pressure. To Adjust Pressure, First Loosen The LocknutDocument2 pagesFlowing Freely, Under No Pressure. To Adjust Pressure, First Loosen The LocknutbabjihanumanthuNo ratings yet
- Blowout Simulator BOPDocument3 pagesBlowout Simulator BOPSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Sand Filter Operation Initial Start-Up of FilterDocument2 pagesSand Filter Operation Initial Start-Up of FilterGuglielmoNo ratings yet
- BOILER MOUNTINGS ADocument17 pagesBOILER MOUNTINGS Ahafiz aiman100% (1)
- Pump Troubleshooting: SUBJECT: The Pump Works For A While and Then Loses Suction 10-12Document3 pagesPump Troubleshooting: SUBJECT: The Pump Works For A While and Then Loses Suction 10-12rahulNo ratings yet
- Jet Pump Agdex716c11Document3 pagesJet Pump Agdex716c11YUNASRIL SYARIEFNo ratings yet
- 12.0 RecommendationsDocument9 pages12.0 RecommendationsNurtasha AtikahNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron Pitcher Pump C 01 eDocument1 pageCast Iron Pitcher Pump C 01 eAlex GermainNo ratings yet
- Apco Air Valves For Vertical Turbine Pumps: Bulletin 586 JULY 2011Document8 pagesApco Air Valves For Vertical Turbine Pumps: Bulletin 586 JULY 2011pipinguserNo ratings yet
- Oil Well Blowout Simulator: BackgroundDocument3 pagesOil Well Blowout Simulator: Backgroundhesam abbaszadehNo ratings yet
- Marine Auxiliary MachineryDocument56 pagesMarine Auxiliary MachineryKris100% (3)
- Auxiliary Boiler Operation FinalDocument24 pagesAuxiliary Boiler Operation FinalkimharoldbactatNo ratings yet
- Power Hydrostatic Test Pumps Operator's Manual: Bombas Mecánicas para Pruebas Hidrostáticas Manual Del OperadorDocument12 pagesPower Hydrostatic Test Pumps Operator's Manual: Bombas Mecánicas para Pruebas Hidrostáticas Manual Del Operadorpablo castroNo ratings yet
- Instructions: For Chilled Water Buffer Tank Maintenance MODELS: CVU/CVL 120 - 1000Document2 pagesInstructions: For Chilled Water Buffer Tank Maintenance MODELS: CVU/CVL 120 - 1000Vũ Đình QuangNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument35 pagesCentrifugal PumpArvind Kumar100% (2)
- Birla MEEP Op ManualDocument43 pagesBirla MEEP Op ManualAshok ChettiyarNo ratings yet
- Pumps and Water Distribution 189Document2 pagesPumps and Water Distribution 189Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Operation of A Centrifugal Oil PurifersDocument11 pagesOperation of A Centrifugal Oil PurifersIonescu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Cavitation TheoryDocument6 pagesCavitation TheoryRahimd FoxNo ratings yet
- NPSHaDocument10 pagesNPSHaksqncms9nxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Pumps For Water SupplyDocument29 pagesChapter 10: Pumps For Water SupplyJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Pumps XP IOIDocument8 pagesPumps XP IOIdamiencwalkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Swimming Pool Operation & ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Swimming Pool Operation & ManagementAngelica Rose PonteNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation and ControlDocument99 pagesBoiler Operation and Controlwassli100% (1)
- Hydrophore SystemDocument4 pagesHydrophore SystemSWASTIK MISHRA50% (2)
- Bladder Tank SWG BRS A4 15Document4 pagesBladder Tank SWG BRS A4 15wael72No ratings yet
- PumpsHydrophore BallastDocument10 pagesPumpsHydrophore BallastRS Sporso GuptaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Guide DeaeratorsDocument2 pagesTroubleshooting Guide DeaeratorsMas ZuhadNo ratings yet
- Alberta Pressure TankDocument2 pagesAlberta Pressure Tankrusli bahtiarNo ratings yet
- Pressurised Water OutDocument2 pagesPressurised Water OutabdiNo ratings yet
- Phase II Boiler QuestionsDocument12 pagesPhase II Boiler Questionsabbutalibb5407No ratings yet
- Vacuum Purging and Processing Tips - Skunk Pharm Research LLC PDFDocument46 pagesVacuum Purging and Processing Tips - Skunk Pharm Research LLC PDFAllery100% (1)
- Descaling Plate Heat ExchangersDocument2 pagesDescaling Plate Heat ExchangersrishimaranNo ratings yet
- PUMPDocument38 pagesPUMPMurugavel VenkatNo ratings yet
- Hydro Pneumatic TankDocument15 pagesHydro Pneumatic TankChuck AnsphilNo ratings yet
- Boiler Feed Pump Recirculation ValvesDocument16 pagesBoiler Feed Pump Recirculation ValvesShameer Majeed100% (1)
- Fresh Water Generator Meo Class 2 OralDocument10 pagesFresh Water Generator Meo Class 2 OralSarath KnNo ratings yet
- Bleeding SystemDocument2 pagesBleeding SystemegmbrNo ratings yet
- How Bladder Pressure TankDocument16 pagesHow Bladder Pressure TankVer BautistaNo ratings yet
- PURIFIERSDocument7 pagesPURIFIERSjames dogelioNo ratings yet
- Sizing Pneumatic Tank 1659353147Document15 pagesSizing Pneumatic Tank 1659353147Engineering WavesNo ratings yet
- B&G Hydronics Manual - How System Components Really WorkDocument36 pagesB&G Hydronics Manual - How System Components Really WorkrjcantwellNo ratings yet
- CE PumpsDocument65 pagesCE PumpssarojNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump (Various Air Handling Methods)Document21 pagesCentrifugal Pump (Various Air Handling Methods)karthick_mariner92No ratings yet
- Air Line Equipment: For Quality Compressed AirDocument114 pagesAir Line Equipment: For Quality Compressed AirCastañeda ValeriaNo ratings yet
- Pumping System: Pump Energy Friction Energy + Elevation EnergyDocument36 pagesPumping System: Pump Energy Friction Energy + Elevation EnergyRaisa Aulia HanifahNo ratings yet
- Boom! 50 Fantastic Science Experiments to Try at Home with Your Kids (PB)From EverandBoom! 50 Fantastic Science Experiments to Try at Home with Your Kids (PB)No ratings yet
- JSA Moving Setting UpDocument1 pageJSA Moving Setting UpFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- H112g-Unsteady State Heat Transfer ModuleDocument2 pagesH112g-Unsteady State Heat Transfer ModuleFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Unsteady Heat Conduction Through Short Fin With Applicability of Quasi TheoryDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Unsteady Heat Conduction Through Short Fin With Applicability of Quasi TheoryFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Unsteady State Heat TransferDocument26 pagesExperiment 5 Unsteady State Heat TransferFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- On The Efficacy of A Proposed Unsteady State Heat Loading ProtocolDocument7 pagesOn The Efficacy of A Proposed Unsteady State Heat Loading ProtocolFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- IJREAMV02I082022Document4 pagesIJREAMV02I082022Fawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- CHE 411 Lesson 3 NoteDocument38 pagesCHE 411 Lesson 3 NoteFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Just 5 Theory Practice QuesrionDocument1 pageJust 5 Theory Practice QuesrionFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- NullDocument113 pagesNullFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic MethodsDocument32 pagesChromatographic MethodsFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Main Elements of A ReportDocument13 pagesMain Elements of A ReportFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- ChallengesDocument3 pagesChallengesFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- CHE 411 Lesson 10 NoteDocument39 pagesCHE 411 Lesson 10 NoteFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- CHE 411 Lesson 5 NoteDocument12 pagesCHE 411 Lesson 5 NoteFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- 1645195113green Joanna 407 AssignmentDocument6 pages1645195113green Joanna 407 AssignmentFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Reaction Kinetic ModelDocument18 pagesCatalytic Reaction Kinetic ModelFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Opa Reservoir, Ile-Ife, Southwest Nigeria Using Mormyrus Rume and Tilapia ZilliiDocument10 pagesPreliminary Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Opa Reservoir, Ile-Ife, Southwest Nigeria Using Mormyrus Rume and Tilapia ZilliiFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment in NigerDocument10 pagesDeterminants of Foreign Direct Investment in NigerFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- CHE 411 Lesson 2 NoteDocument13 pagesCHE 411 Lesson 2 NoteFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Legal and Institutional Frameworks For Settlement of Foreign Investment Disputes in NigeriaDocument18 pagesLegal and Institutional Frameworks For Settlement of Foreign Investment Disputes in NigeriaFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- CHM 201 Assignment 2#Document6 pagesCHM 201 Assignment 2#Fawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- CHE 202 Tutorial QuestionDocument6 pagesCHE 202 Tutorial QuestionFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- A Brief On How The Chiller Works: Compressor, Separator, Here TheDocument2 pagesA Brief On How The Chiller Works: Compressor, Separator, Here TheFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Medical School Personal Statement Example PDFDocument5 pagesMedical School Personal Statement Example PDFHassan Luka JumaNo ratings yet
- All Universities of PakistanDocument131 pagesAll Universities of PakistanziaNo ratings yet
- TRIO Manual enDocument4 pagesTRIO Manual enmihailmiNo ratings yet
- Tadano Faun HK 60Document13 pagesTadano Faun HK 60Abdallah GomaaNo ratings yet
- Haas VMC ManualDocument268 pagesHaas VMC Manualgaurav_mob33% (3)
- CH 6 SOC210 Powerpoint FA2020Document17 pagesCH 6 SOC210 Powerpoint FA2020janNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Relational ModelDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Relational ModelHimanshiNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis All Subjects-2013Document26 pagesItem Analysis All Subjects-2013acerblancaNo ratings yet
- ABB - Motor Protection and Control Catalogue - 20221216 - DIGITALDocument1,036 pagesABB - Motor Protection and Control Catalogue - 20221216 - DIGITALTomas VelasquezNo ratings yet
- 16 Front+suspension PDFDocument28 pages16 Front+suspension PDFtomNo ratings yet
- LNG 26-62Document37 pagesLNG 26-62mohkal1260No ratings yet
- Corporate - Communication - Final ExamDocument15 pagesCorporate - Communication - Final ExamtawfikNo ratings yet
- Vmware Data Protection With Hitachi Data Protection Suite: Please Insert Your Hitachi Truenorth Partner Logo HereDocument21 pagesVmware Data Protection With Hitachi Data Protection Suite: Please Insert Your Hitachi Truenorth Partner Logo HereWildan AbdatNo ratings yet
- Gazette SSC A2023 UpdatedDocument1,705 pagesGazette SSC A2023 UpdatedRoman SadiqNo ratings yet
- Colleg Fee StructureDocument1 pageColleg Fee StructureSriram SaiNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Metal CastingDocument100 pagesModule-3 Metal CastingAbdul KhadarNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Good PresentationDocument11 pagesHow To Make A Good PresentationIndira PradnyaswariNo ratings yet
- Taxonomia y Variacion Geográfica de Especies Del Genero Alouatta en BrasilDocument81 pagesTaxonomia y Variacion Geográfica de Especies Del Genero Alouatta en BrasilGerardo RiveroNo ratings yet
- Relational ScmTop DooTop DooCommon DooConstraintsDocument1 pageRelational ScmTop DooTop DooCommon DooConstraintsKhalil De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Equipment List IrisDocument14 pagesEquipment List IrisTubagus DikaNo ratings yet
- C.V. - Amr - Konswa - Jan. - 2012Document2 pagesC.V. - Amr - Konswa - Jan. - 2012Amr KonswaNo ratings yet
- Filler in ConcreteDocument8 pagesFiller in ConcretecuibaprauNo ratings yet
- 29-Horizontal Subsea Xmas Tree en PDFDocument2 pages29-Horizontal Subsea Xmas Tree en PDFarietilangNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Private Vs Public Banks :HR PolicyDocument16 pagesPresentation - Private Vs Public Banks :HR Policyminal670% (1)
- Case Study Summary:: A Strategy-Focused OrganizationDocument11 pagesCase Study Summary:: A Strategy-Focused OrganizationEngMohamedReyadHelesyNo ratings yet
- Mass Upload and Mass Update GuideDocument23 pagesMass Upload and Mass Update GuideGeb SopNo ratings yet
- RJ3 Controller RestoreDocument8 pagesRJ3 Controller RestoreSam KarnsNo ratings yet
- Entregable 2 Ingles TecnicoDocument7 pagesEntregable 2 Ingles TecnicoLuis CrisólogoNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Partial Replacement of Cement Using Eucalyptus Die Leaves AshDocument5 pagesExperimental Study of Partial Replacement of Cement Using Eucalyptus Die Leaves AshIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet