Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Att d5tZkrj9klfg4uLoxZcDtw4F5Qe336ivwxKOyi2HtKs
Att d5tZkrj9klfg4uLoxZcDtw4F5Qe336ivwxKOyi2HtKs
Uploaded by
Jennelle LacastesantosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Att d5tZkrj9klfg4uLoxZcDtw4F5Qe336ivwxKOyi2HtKs
Att d5tZkrj9klfg4uLoxZcDtw4F5Qe336ivwxKOyi2HtKs
Uploaded by
Jennelle LacastesantosCopyright:
Available Formats
Immunology is the study of the immune system & the immune
response.
Immunogen is any substance that is capable of
inducing an immune response, whether humoral or cellular, or both.
Antigen is a substance that is recognized
Properties of Immunogen:
1. Foreignness are genetically foreign to the host,
2. Chemical Composition most organic substances can be antigenic, except for pure lipids &
nucleic aids..
3. Molecular size molecules w/ molecular weights below 10,000 daltons
4. Chemical complexity
5. Genetic constitution of the host animal the ability to respond to a particular immunogen is
predetermined by the genetic constitution
6. Antigen dose & Method of administration the dose of the antigen introduced
Lines of Defense:
1. First line of Defense to prevent the entry
Mucous membranes
Keratin layer of the skin acts as a mechanical barrier that prevents the entry of
microorganisms.
Fatty acids in the skin
Normal flora of the diff. parts of the body
Enzymes found in tears & other secretions
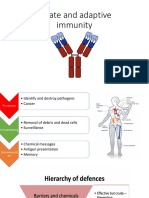
2. Second line of Defense destroying the organisms or by limiting their growth.
Innate Arm of the Immune System the main factor involved here is the inflammatory
response.
3. Third line of Defense unsuccessful in destroying the invading microorganism.
Adaptive Arm of the Immune System this immune response involves the action of the B cells
& T cells
Immune System to defend the host against infection.
T Lymphocytes (T cells)
make up 60-80% of the circulating lymphocytes in the blood.
a. T helper cells (CD4+ T cells) promote inflammation & Ab production.
b. Cytotoxic T cells (Cytolytic T cells or CD8+ T cells)
recognize & kill virus-infected cells, tumor cells & foreign cells (e.g. tissue grafts).
Innate Immunity is also known as natural immunity.
You might also like
- MIcro - Immunology - Lec.1Document13 pagesMIcro - Immunology - Lec.1زين العابدين محمد عويش مشريNo ratings yet
- Aminoden Immunology Activity 1 2021Document3 pagesAminoden Immunology Activity 1 2021hanzala macabandoNo ratings yet
- Immuno Logy: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirDocument22 pagesImmuno Logy: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirRakib's exploration worldNo ratings yet
- Immunology NotesDocument18 pagesImmunology NotesSharath SNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewDocument87 pagesBasic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewnovelraaaNo ratings yet
- Module 12Document12 pagesModule 12mirai desuNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris Isi (English) 2003Document26 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris Isi (English) 2003Reza ShinodaNo ratings yet
- Chronic InfectionsDocument7 pagesChronic InfectionsAsad ullahNo ratings yet
- Management For Immune Defense: Taghreed Hamza HawswiDocument39 pagesManagement For Immune Defense: Taghreed Hamza HawswiRani AlfiyyahNo ratings yet
- THE Immune ResponseDocument14 pagesTHE Immune ResponseMarc Company MartínezNo ratings yet
- Immunology 1Document57 pagesImmunology 1navid akibNo ratings yet
- Immunology Teaching Objectives:: I. Overview of The Immune SystemDocument12 pagesImmunology Teaching Objectives:: I. Overview of The Immune SystemOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Immunology & Serology ReviewerDocument71 pagesImmunology & Serology ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- 1 Imm A What Is ImmunityDocument12 pages1 Imm A What Is ImmunityroshnayimNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument19 pagesIMMUNITYMuslimNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document24 pagesLec 1Ab AbNo ratings yet
- 4 Immune DisordersDocument11 pages4 Immune DisorderscedonuliNo ratings yet
- Organization of Immune SystemDocument44 pagesOrganization of Immune SystemSaubie AslamiahNo ratings yet
- MCP 08.14 Immune System IDocument23 pagesMCP 08.14 Immune System IHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Adaptive and Innate ImmunityDocument63 pagesAdaptive and Innate ImmunitySarvesh Patil100% (1)
- Innate and Acquired ImmunityDocument5 pagesInnate and Acquired Immunitydebarajroy1998No ratings yet
- Defence Mechanism of The BodyDocument72 pagesDefence Mechanism of The BodyRawal Rafiq LeghariNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural ImmunityDocument20 pagesDiseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural Immunitymano343No ratings yet
- Defence SystemDocument33 pagesDefence Systemboneheaded9No ratings yet
- L07: The Immune System and The Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument10 pagesL07: The Immune System and The Diseases of The Immune Systemhstest842No ratings yet
- Dermatology 2Document82 pagesDermatology 2Rajibni Aziza YussyamNo ratings yet
- Review Flash Card by Dr. Mitch Roy MaristelaDocument205 pagesReview Flash Card by Dr. Mitch Roy MaristelaMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument8 pagesImmunologyabiyotNo ratings yet
- Immunology & Serology Lecture 2Document31 pagesImmunology & Serology Lecture 2Jo Änna CampayneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemArun Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Nonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNDocument51 pagesNonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNjonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09. Host Response To InfectionDocument51 pagesChapter 09. Host Response To InfectionZin LimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 ImmunologyDocument24 pagesLesson 6 ImmunologyVictor Z. DyNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument57 pagesImmunologynavid akibNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Combined Class (Mental Health Psichatry, Clinical Anastasia, & Clinical Sciences) Year 2 30/03/2022Document30 pagesImmunology: Combined Class (Mental Health Psichatry, Clinical Anastasia, & Clinical Sciences) Year 2 30/03/2022Derick NKANDU KALUBANo ratings yet
- BCM 127 Immunology Lecture Series 2020 01Document77 pagesBCM 127 Immunology Lecture Series 2020 01Barnabas KipngetichNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument4 pagesIMMUNITYSoni VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - 2023Document50 pagesChap 3 - 2023ngoclan4304No ratings yet
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7. CH - 16 - Lecture - Presentation Innate Immunity 2019 (NJ)Document68 pagesLecture 7. CH - 16 - Lecture - Presentation Innate Immunity 2019 (NJ)Moshe Cohen'sNo ratings yet
- Clinical Immunology Lecture 2Document53 pagesClinical Immunology Lecture 2jibril channelNo ratings yet
- ImmunesystemDocument69 pagesImmunesystemayamgosonggosongNo ratings yet
- L 1 Introduction and Types of ImmunityDocument13 pagesL 1 Introduction and Types of ImmunityaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BTDocument27 pagesUnit-3 BTDhananjay KhadeNo ratings yet
- 1.notes PowerpointDocument27 pages1.notes Powerpointt4ths999No ratings yet
- Types of ImmunityDocument13 pagesTypes of ImmunityKailash Nagar100% (3)
- Project CertificateDocument10 pagesProject CertificateZubair ahmadNo ratings yet
- مناعة 1Document28 pagesمناعة 1hussein.al-bohaija.nurs1765No ratings yet
- Non-Specific Host Defenses Against Microbial PathogensDocument5 pagesNon-Specific Host Defenses Against Microbial PathogensSakil MunnaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDocument16 pagesDrugs Acting On The Immune SystemRellie Castro0% (2)
- CL-1.Chaplin (2006) Immune ResponseDocument6 pagesCL-1.Chaplin (2006) Immune ResponseemidinNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview of Immune SystemDocument14 pagesIntroduction and Overview of Immune SystemEssington BeloNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument178 pagesImmunologyarbazsabir88No ratings yet
- Assignment BiotechnologyDocument14 pagesAssignment BiotechnologyArshad AlamNo ratings yet
- Sas Hes032 9Document6 pagesSas Hes032 9Jose Melmar Autida AutenticoNo ratings yet
- Immunity - Ag-Ab ReactionDocument120 pagesImmunity - Ag-Ab Reactionnuaa11140No ratings yet
- Kuliah ImunologiDocument59 pagesKuliah ImunologiUmmi Rinandari100% (1)
- Preclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet