Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polyesters and Polyamides
Polyesters and Polyamides
Uploaded by
becky.brownu7460 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Polyesters+and+polyamides
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesPolyesters and Polyamides
Polyesters and Polyamides
Uploaded by
becky.brownu746Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Polyesters and polyamides
Types of polymer
• Addition polymers – formed from alkene monomers. The C=C bond breaks,
allowing the carbon to attach to another alkene.
• Condensation polymers – formed when two functional groups react. A bond is
formed through the removal of water (a condensation reaction.)
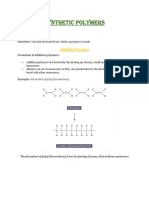
Addition polymerisation
• Addition polymers are formed by joining lots of alkene monomers in a chain.
• The double carbon bond breaks, allowing another alkene to connect to the carbon.
• They are represented by drawing a single subunit (the monomer) inside square
brackets, with a little ‘n’ in the right-hand corner. Remember to draw bonds sticking
outside the square brackets to make it clear that the chain continues.
• Polymers are named according to the monomer it’s made from and ‘poly’ as a prefix.
E.g., poly(ethene) is a polymer made of ethene monomers.
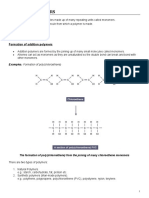
Condensation polymerisation
• Condensation polymers form when monomer functional groups reach, forming a
connecting bond and a water molecule.
• Monomers join in a condensation reaction.
• Polyesters are a type of condensation polymer — they are used for making plastics
and clothing.
• An ester is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol.
• A polyester forms when a molecule with two carboxylic acids groups (a
dicarboxylic acid) reacts with a molecule with two alcohol groups (a diol).
• The carboxylic acid group on one molecule and the alcohol group on another
molecule react to form an ester bond (-COO).
• This reaction happens several times until a long chain is formed, made up of
monomers connected by ester bonds.
• Polyamides are another type of condensation polymer, formed when an amine
reacts with a carboxylic acid.
• A molecule of water is removed, leaving behind the amide (-CONH) linkage between
the monomers.
• The formation of both ester bonds and amide bonds are examples of condensation
reactions.
Hydrolysis of polyesters and polyamides
The addition of a water molecule in a hydrolysis reaction breaks apart the ester/amide
linkage to form the original monomers.
Hydrolysis is usually done with the addition of an acid (for polyamide hydrolysis) or a base
(for polyester hydrolysis) to speed up the reaction.
You might also like
- O'Level Organic Chemistry Brief NotesDocument5 pagesO'Level Organic Chemistry Brief NotesHassan Daud Khalid100% (3)
- PolymersDocument36 pagesPolymersSherry-Ann Wint-TurnerNo ratings yet
- Classification of PolymersDocument14 pagesClassification of PolymersFA Ay67% (6)
- Organic Chem - PolymersDocument16 pagesOrganic Chem - PolymersThamiso GolwelwangNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument24 pagesPolymersPaul AckermannNo ratings yet
- Production Of: Mate RialsDocument40 pagesProduction Of: Mate RialsWulan SariNo ratings yet
- Monomers and PolymersDocument8 pagesMonomers and PolymersmnathanaelandrewNo ratings yet
- F324 Condensation PolymersDocument7 pagesF324 Condensation PolymersDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- 3.12 PolymersDocument13 pages3.12 PolymersRida Nadeem SheikhNo ratings yet
- Polymerisarion PMTDocument8 pagesPolymerisarion PMTChristine MoyoNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Properties of PolymersDocument48 pagesThe Structure and Properties of PolymersShoaib JadoonNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument3 pagesPolymerfarzinahammedNo ratings yet
- 31.6: Step-Growth Polymers-Condensation PolymersDocument5 pages31.6: Step-Growth Polymers-Condensation PolymersLakshmi PatreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document20 pagesLecture 5يوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Pom ChemDocument15 pagesPom ChemalbiNo ratings yet
- 8.31 PolymersDocument3 pages8.31 PolymerslovejoyNo ratings yet
- POLYMERISATIONDocument24 pagesPOLYMERISATIONPaul sichaliNo ratings yet
- Polymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)Document10 pagesPolymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)John Nelson LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Synthetic PolymersDocument7 pagesSynthetic PolymersHalal BoiNo ratings yet
- Unit 20 - Petrochemicals & Polymers: 20A 1. Common Fossil FuelsDocument9 pagesUnit 20 - Petrochemicals & Polymers: 20A 1. Common Fossil FuelsanayNo ratings yet
- POLYMERISATIONqDocument6 pagesPOLYMERISATIONqjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- BME 1103 Lecture 2Document31 pagesBME 1103 Lecture 2Mulongo LinoNo ratings yet
- Dental PolymerDocument36 pagesDental PolymerAmniAzmi100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry-Polymers-OL-NotesDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry-Polymers-OL-Notesroshanehkhalid243No ratings yet
- Polymersclass12 160109135318Document33 pagesPolymersclass12 160109135318Dev Printing SolutionNo ratings yet
- Condensation PolymersDocument3 pagesCondensation PolymersBryar XalilNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument48 pagesPolymerKhalnayak YtNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For IGCSE ChemistryDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry For IGCSE Chemistrydanielmahsa100% (1)
- 06 SynthesisDocument6 pages06 SynthesisRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- POLYMERS 1st Sem 2021 2022Document67 pagesPOLYMERS 1st Sem 2021 2022EGAS JAYSON RABENo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Molecules - 281123Document37 pagesUnit 2 Molecules - 281123DAN DNANo ratings yet
- "A Polymer Is Defined As A Macromolecule Formed by The RepeatedDocument45 pages"A Polymer Is Defined As A Macromolecule Formed by The Repeated21MEB358 Kunal AryaNo ratings yet
- 6.2. Nitrogen Compounds, Polymers and SynthesisDocument17 pages6.2. Nitrogen Compounds, Polymers and Synthesistomtinoy2019No ratings yet
- 1.mechanism of PolymerizationDocument6 pages1.mechanism of PolymerizationShalynee SuthaharNo ratings yet
- PolimerDocument12 pagesPolimerMuhammad IkramullahNo ratings yet
- Presentation 39Document18 pagesPresentation 39Farhad MalikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument34 pagesLecture 1 PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Condensation PolymerizationDocument6 pagesCondensation PolymerizationSiya ChiniahNo ratings yet
- 2019-2020 Condensation PolymersDocument8 pages2019-2020 Condensation PolymersAgustina DenaNo ratings yet
- Enginering Chemistry (CHEM-136) Dr. Subhadra RajpootDocument35 pagesEnginering Chemistry (CHEM-136) Dr. Subhadra RajpootChandrachur DeoNo ratings yet
- Polymer Science: Varsha AwasarkarDocument38 pagesPolymer Science: Varsha AwasarkarAnugraha GarmentsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Polymer Chemistry: What Is A Polymer?Document7 pagesIntroduction To Polymer Chemistry: What Is A Polymer?kkaya19No ratings yet
- Synthetic PolymersDocument6 pagesSynthetic PolymersMangetsu HozukiNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument67 pagesPolymersANABEL EGOCNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 025 (Polymers)Document3 pagesChemsheets A2 025 (Polymers)lianchen251110No ratings yet
- Alkenes P3 ADocument22 pagesAlkenes P3 ANazil HaziqNo ratings yet
- Polymer FinalDocument35 pagesPolymer FinalAnkur singh JethuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter2:Molecular Biology: Pages (63-130)Document114 pagesChapter2:Molecular Biology: Pages (63-130)Hamzeh ZNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument17 pagesPolymersleaf5No ratings yet
- PolymersDocument3 pagesPolymerss_s_i_hassaanNo ratings yet
- Polymer Chemistry MKBDocument54 pagesPolymer Chemistry MKBJHidgiwiwNo ratings yet
- Written Report (Polymer Chemistry)Document20 pagesWritten Report (Polymer Chemistry)Daphnie Anne DeduqueNo ratings yet
- 2008 Chemistry NotesDocument20 pages2008 Chemistry NotesJohndoeNo ratings yet
- Condensation PolymersDocument13 pagesCondensation PolymersJavariaAjmalNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Properties of Polymers - Dr. Mirzi BetasoloDocument22 pagesThe Structure and Properties of Polymers - Dr. Mirzi BetasoloIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- Important Selected Questions and Answers in Polymer ChemistryDocument18 pagesImportant Selected Questions and Answers in Polymer ChemistryYaseen RashidNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument83 pagesPolymersDaily Learners KalraNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and CycloalkenesDocument27 pagesAlkenes and CycloalkenesNicole ElnasNo ratings yet
- Self-Assembly: From Surfactants to NanoparticlesFrom EverandSelf-Assembly: From Surfactants to NanoparticlesRamanathan NagarajanNo ratings yet