Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectros
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectros
Uploaded by
Laís PittaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 9 E.T.H.E.RDocument53 pages9 E.T.H.E.Rjamjam_95678853100% (18)
- Unit VI Molecular Spectroscopy: Physical ChemistryDocument17 pagesUnit VI Molecular Spectroscopy: Physical ChemistryDewal Deshmukh100% (1)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy - Instrumentation - Microbe NotesDocument2 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy - Instrumentation - Microbe Notesjimgitonga100% (2)
- NMR Spectroscopy)Document3 pagesNMR Spectroscopy)smart ptmNo ratings yet
- Xray, NMR, 2dpageDocument4 pagesXray, NMR, 2dpageUnnimaya GNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1Document26 pagesAtomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1Hammed LawalNo ratings yet
- DRAFT Physical Methods in Biology and Medicine Biophysics Finals RequirementsDocument16 pagesDRAFT Physical Methods in Biology and Medicine Biophysics Finals RequirementsALNo ratings yet
- 1 - Elemental Analysis - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument2 pages1 - Elemental Analysis - Chemistry LibreTextspearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Spectroscopy - FullDocument105 pagesUnit 5 - Spectroscopy - FullJeetender MishraNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy TechniquesDocument3 pagesSpectroscopy TechniquesSantosh prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Spectroscopy - EC I B.techDocument31 pagesUnit - II Spectroscopy - EC I B.techTelugu BadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectroscopy: LiteratureDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Spectroscopy: LiteratureYahya RajputNo ratings yet
- MRS BasicDocument13 pagesMRS BasicAmajida RizkyNo ratings yet
- SPECTROSCOPY - Docx Senthil - Docx 1......Document17 pagesSPECTROSCOPY - Docx Senthil - Docx 1......Zaidh. fd100% (1)
- Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy - WikipediaLuan D SouzaNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument7 pagesSpectrosSuraj RarathNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MRSDocument9 pagesJurnal MRSAirinTrisniNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetic AssignmentDocument16 pagesBioenergetic Assignmentshanza FaheemNo ratings yet
- Atkin 12001 Molekular Spectroscopy 001Document5 pagesAtkin 12001 Molekular Spectroscopy 001Nikke ArdilahNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Klasifikasi RadiasiDocument39 pages1.1 Klasifikasi RadiasiulalaNo ratings yet
- AsdfsdfDocument19 pagesAsdfsdfanmolkapoorfbtestNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic TechniqueDocument24 pagesSpectroscopic TechniqueJubair Al-rashidNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument10 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosLaura CelisNo ratings yet
- SpectroDocument3 pagesSpectroAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of SpectrosDocument10 pagesBasic Principles of SpectrosAlexiss Chavez-De la MoraNo ratings yet
- Chem 3052 CHAPTER 1 (Introduction To Spectroscopy)Document22 pagesChem 3052 CHAPTER 1 (Introduction To Spectroscopy)ashenafiNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy Is The Study of TheDocument51 pagesSpectroscopy: Spectroscopy Is The Study of ThePalwan SaryNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Revised 10oct22 PDFDocument43 pagesSpectroscopy Revised 10oct22 PDFGundanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Raman Spectroscopy in Cancer DiagnosisDocument27 pagesApplications of Raman Spectroscopy in Cancer DiagnosiscarlosbokorNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument46 pagesSpectroscopy - WikipediaAnubhav VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Written Report NMR SpectrometryDocument6 pagesWritten Report NMR SpectrometryRye M. BirungNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument50 pagesFinalarfa2009No ratings yet
- The Expanding Role of Mass Spectrometry in BiotechnologyDocument14 pagesThe Expanding Role of Mass Spectrometry in BiotechnologyplasmaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Imaging in Animal ResearchDocument20 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Imaging in Animal ResearchZerlyndaBunga'alloNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument21 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDawoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 NMRDocument20 pagesChapter - 9 NMRMadhur ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- NMR Imaging in MedicineDocument14 pagesNMR Imaging in MedicineGary Trump100% (1)
- Lec.1 Introduction PDFDocument17 pagesLec.1 Introduction PDFAsim Alaa Al SalehiNo ratings yet
- NMR SpectrometryDocument7 pagesNMR SpectrometryferngetapeNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Attenuation Map in Emission Tomography: Special ContributionsDocument26 pagesDetermination of The Attenuation Map in Emission Tomography: Special ContributionsartspiceNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Rodney F. Boyer (Z-Lib - Org) - 221-253Document33 pagesBiochemistry Rodney F. Boyer (Z-Lib - Org) - 221-253amhiraNo ratings yet
- Optical Manipulation of Nanoparticles: A Review: Maria Dienerowitz, Michael Mazilu, and Kishan DholakiaDocument32 pagesOptical Manipulation of Nanoparticles: A Review: Maria Dienerowitz, Michael Mazilu, and Kishan DholakiaZakir AhmedNo ratings yet
- ZwnjatnKcB AnalChem2.1 Chapter 10 Spectroscopic MethodsDocument120 pagesZwnjatnKcB AnalChem2.1 Chapter 10 Spectroscopic MethodsNguyễn Hoàng QuânNo ratings yet
- Uv VisablespectroscopyatheerDocument18 pagesUv Visablespectroscopyatheerareej juttNo ratings yet
- Star NMRDocument20 pagesStar NMRstarskyhutch0000No ratings yet
- WHAT ROLES For TRACK-STRUCTURE and MICRODOSIMETRYDocument4 pagesWHAT ROLES For TRACK-STRUCTURE and MICRODOSIMETRYnuova0No ratings yet
- Chm580 NMRDocument8 pagesChm580 NMRNorHidayu Azmi50% (2)
- Dynamic Properties of Photonic Crystals and Their Effective Refractive IndexDocument9 pagesDynamic Properties of Photonic Crystals and Their Effective Refractive IndexAnonymous 6w0gAQNo ratings yet
- Detectors - Electron Spin ResonanceDocument7 pagesDetectors - Electron Spin ResonancegdgdfgNo ratings yet
- MG Zno Photodetector Grown by Chemical Spraying Pyrolysis TechniqueDocument6 pagesMG Zno Photodetector Grown by Chemical Spraying Pyrolysis TechniqueerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Fullerton 1982Document15 pagesFullerton 1982سيف فلاح حسنNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research ADocument7 pagesNuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Acordella_francescoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Christopher J. RhodesDocument52 pagesMagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Christopher J. RhodesSonia Ayu AndiniNo ratings yet
- Magnetism of Materials: Theory and Practice in Magnetic Resonance ImagingDocument18 pagesMagnetism of Materials: Theory and Practice in Magnetic Resonance ImagingThuyet Nguyen PhuocNo ratings yet
- Structural Elucidation of Small Organic Molecules by 1d 2d and Multi Dimensional Solution NMR Spectroscopy 2155 9872.S11 001Document8 pagesStructural Elucidation of Small Organic Molecules by 1d 2d and Multi Dimensional Solution NMR Spectroscopy 2155 9872.S11 001PriyosetyokoNo ratings yet
- Pha052 TG 9Document14 pagesPha052 TG 9Alcea InguilloNo ratings yet
- 2005 Zhang 3Document12 pages2005 Zhang 3ben0706No ratings yet
- Ka Iii Teknik Spektroskopik 2021Document10 pagesKa Iii Teknik Spektroskopik 2021peter sihotangNo ratings yet
- Resonancia Magnetica en Animales de CompañíaDocument11 pagesResonancia Magnetica en Animales de CompañíaEnrique A. Vega NuñezNo ratings yet
- Shining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.From EverandShining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.No ratings yet
- Laser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsFrom EverandLaser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Desalination: Shaheen Fatima Anis, Boor Singh Lalia, Raed HashaikehDocument8 pagesDesalination: Shaheen Fatima Anis, Boor Singh Lalia, Raed HashaikehSK SahooNo ratings yet
- Differential Protection: Document byDocument26 pagesDifferential Protection: Document byS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Lab ManualDocument22 pagesMachine Design Lab Manualsarathsaravanan100% (4)
- Influence of Soil-Structure Interaction On The Fundatmental Period of BuildingsDocument23 pagesInfluence of Soil-Structure Interaction On The Fundatmental Period of BuildingsMILL3482No ratings yet
- Chapter 3-3 Signal Processing Elemnt Part ThreeDocument43 pagesChapter 3-3 Signal Processing Elemnt Part Threedan gNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene Glycol-Salt PDFDocument14 pagesPolyethylene Glycol-Salt PDFlauraNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDocument5 pagesOpen Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt Generatorramniwas123No ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Activity1 Horizontally Launched Projectiles 1Document3 pagesActivity1 Horizontally Launched Projectiles 1EeyyaaNo ratings yet
- Aakash Sample Engineering Paper Class 11Document21 pagesAakash Sample Engineering Paper Class 11anishkumarraushan2007No ratings yet
- Transition Metal Joints For Steam GeneratorsDocument15 pagesTransition Metal Joints For Steam GeneratorsMahsaNo ratings yet
- Newton 2nd and 3rd Laws Chapter 4-3Document20 pagesNewton 2nd and 3rd Laws Chapter 4-3Jams FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of 3D2D Perovskite Heterostructures Via Inhibition of Ion Diffusion by Cross-Linked Polymers For Solar Cells With Improved PerformanceDocument12 pagesStabilization of 3D2D Perovskite Heterostructures Via Inhibition of Ion Diffusion by Cross-Linked Polymers For Solar Cells With Improved PerformanceJogi PaulNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Pattern: Time: 3 Hours 15 Minutes Max. Marks: 100 InstructionsDocument36 pagesQuestion Paper Pattern: Time: 3 Hours 15 Minutes Max. Marks: 100 InstructionsVardhaman BilagiNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab:Coefficient of Linear ExpansionDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab:Coefficient of Linear ExpansionNatalie Sherwood100% (1)
- 4x10 1Cx70 MergedDocument10 pages4x10 1Cx70 MergedJalal AlbadriNo ratings yet
- Purpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryDocument12 pagesPurpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryGauri ThakurNo ratings yet
- Deney 3Document22 pagesDeney 3baratniloy1No ratings yet
- Features: WWW - Domin.co - Uk +44 (0) 1761 252650 Info@domin - Co.ukDocument4 pagesFeatures: WWW - Domin.co - Uk +44 (0) 1761 252650 Info@domin - Co.uk只要香菜No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Principle: Arrow) Are Present: The Hook Holds TheDocument7 pagesEquilibrium Principle: Arrow) Are Present: The Hook Holds TheYady S. Londoño L.No ratings yet
- Achievement Test Science 5 Regular ClassDocument13 pagesAchievement Test Science 5 Regular ClassArman Berina CortezNo ratings yet
- Mitsu C004e-I Solid End MillsDocument358 pagesMitsu C004e-I Solid End MillskatomegumioncrackNo ratings yet
- OSE 40-0196-067 - 25 - Data Sheet - 2018Document6 pagesOSE 40-0196-067 - 25 - Data Sheet - 2018Centrifugal SeparatorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Fast Drying of High-Alumina MgO-bonded Refractory CastablesDocument12 pages2020 - Fast Drying of High-Alumina MgO-bonded Refractory CastablesKhaled BOUALINo ratings yet
- C) Isolated System:: Unit-6Document16 pagesC) Isolated System:: Unit-6MUHAMMAD YASEENNo ratings yet
- Experiment Two: 2. Angular MeasurementDocument4 pagesExperiment Two: 2. Angular Measurementahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- IB Test Review Trig With Calculator MSDocument15 pagesIB Test Review Trig With Calculator MSGa-Eun YooNo ratings yet
- Appliedstat 2017 Chapter 10 11Document23 pagesAppliedstat 2017 Chapter 10 11Vivian HuNo ratings yet
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectros
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectros
Uploaded by
Laís PittaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectros
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectros
Uploaded by
Laís PittaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: Insights into Molecules & Diagnostics
Group 7, Lais P.C Alexandra P
Description of the application of interest
Introduction
Absorption and Emission of Electromagnetic Radiation:
Study Objectives:
Basic principles of the general technique (chromatographic or
The objective of this study was to use nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to
By applying a specific frequency of electromagnetic radiation (radio waves) to the sample, the nuclei can absorb
spectroscopic) identify and analyze metabolic alterations associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD)
energy and transition to a higher-energy state. This absorption occurs at a frequency that matches the energy
What is spectroscopic: spectroscopy, is the study of the absorption and emission of light and other progression. The study aimed to provide a better understanding of the metabolic changes
difference between the two spin states, determined by the external magnetic field strength.
radiation by matter, as related to the dependence of these processes on the wavelength of the occurring in patients with CKD and potentially identify target pathways that could be modified
radiation. More recently, The definition has been expanded to include the study of the interactions to slow down the disease's progression.
Resonance Condition:
between particles such as electrons, protons, and ions, as well as their interaction with other
The frequency at which the nuclei absorb electromagnetic radiation is known as the resonance frequency. It depends
particles as a function of their collision energy. Application of the Method:
on the strength of the magnetic field and the type of nucleus being observed. The resonance frequency can be
Basic principles of the selected method (GC, HPLC, SEC, IEC, TLC, UV-VIS, IR, The researchers employed 1H NMR spectroscopy combined with multivariate analysis to
calculated using the Larmor equation: ω = γB₀, where ω is the resonance frequency, γ is the gyromagnetic ratio of the
AA, MS) analyze serum metabolites in patients with various stages of CKD. They compared the
nucleus, and B₀ is the magnetic field strength.
metabolite profiles of CKD patients with those of healthy controls using NMR spectroscopy and
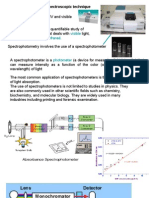
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to study
explored the differences in metabolite concentrations and pathways.
the molecular structure and dynamics of organic and inorganic compounds. It provides information Integration:
about the arrangement of atoms in a molecule, their connectivity, and the environment they are in. The area under an NMR signal is proportional to the number of equivalent nuclei giving rise to that signal. This
Significant Findings/Results:
integration can provide information about the relative number of different types of nuclei in a molecule.
The 1H NMR spectroscopy analysis combined with multivariate analysis revealed significant
NMR is based on the interaction between the nuclei of certain atoms and an external magnetic field.
differences in the metabolite profiles between CKD patients and healthy controls. The study
Nuclei with an odd number of protons or neutrons (i.e., having a nuclear spin) possess a magnetic 2D NMR Techniques: identified 15 endogenous metabolites that differed between the two groups. Metabolic
moment and can absorb and emit radiofrequency (RF) energy when placed in a strong magnetic Two-dimensional NMR techniques, such as COSY (correlation spectroscopy), NOESY (nuclear Overhauser effect
Pathway Analysis (MetPA) further demonstrated significant intergroup differences in five
field and subjected to RF radiation. Here are the basic principles of NMR spectroscopy: spectroscopy), and HSQC (heteronuclear single quantum coherence), allow for the identification of connectivities
potential target pathways and 14 metabolites. The discriminant models based on these
between different nuclei in a molecule, enabling the determination of complex molecular structures.
NMR Spectrometer: findings indicated that CKD patients and healthy controls could be differentiated based on
An NMR spectrometer is the instrument used to measure the absorption and emission of their metabolic fingerprints. The results suggested that CKD and its progression have an
Nuclear Spin Relaxation: impact on selected metabolic pathways.
electromagnetic radiation by the nuclei. It consists of a strong magnet to create a uniform magnetic After absorbing energy, the nuclei return to their lower-energy state, releasing the absorbed energy as electromagnetic
field, A radiofrequency (RF) source to generate the excitation pulses, and a detector to measure the radiation. This relaxation process occurs through two mechanisms: spin-lattice relaxation (T₁) and spin-spin relaxation
emitted signals.
Conclusion:
(T₂). T₁ represents the time taken for the nuclear spin to recover parallel to the magnetic field, while T₂ represents the The study demonstrated the application of 1H NMR spectroscopy in identifying metabolic
time for the loss of phase coherence between spins. disorders associated with CKD. The findings provided valuable insights into the metabolic
Instrumentation:
NMR spectrometers consist of a strong magnet, a sample holder, and RF equipment. The most alterations occurring in CKD patients and highlighted specific target pathways that may be
Applications: modified to slow down the disease's progression. The use of NMR spectroscopy for rapid
common nuclei used in NMR are hydrogen (^1H) and carbon-13 (^13C), due to their high natural
NMR spectroscopy is widely used in organic chemistry, biochemistry, drug discovery, and material science to determine detection of endogenous metabolites offers the potential for monitoring and understanding
abundance and sensitivity.
molecular structures, study reaction mechanisms, analyze molecular dynamics, and investigate intermolecular CKD-related metabolic changes, potentially leading to improved prevention and
interactions. management strategies.
Nuclear Spin:
Atomic nuclei with an odd number of protons or neutrons possess an intrinsic property called spin.
Overall, NMR spectroscopy provides detailed information about the structure, dynamics, and interactions of molecules, Summary of method and
This spin creates a magnetic moment that interacts with an external magnetic field.
making it an indispensable tool in various scientific disciplines.
application of interest
Chemical Shift: The study utilized 1H NMR spectroscopy to
The chemical shift is a crucial parameter in NMR spectroscopy. It is the difference in resonance frequency of a nucleus in a analyze serum samples from CKD patients and
compound compared to a reference compound (often tetramethylsilane, TMS). Chemical shifts are measured in parts per million
(ppm) and provide information about the local electronic environment of the nuclei.
healthy controls. The technique allowed for the
detection and quantification of endogenous
Spin-Spin Coupling (J-Coupling): metabolites in the samples. The obtained NMR
Adjacent nuclei with different spins can influence each other's resonance frequencies through a spectra were subjected to multivariate analysis
process called spin-spin coupling. This interaction results in the splitting of NMR signals into to identify significant differences in the
multiplets, providing insights into the connectivity of neighboring atoms. metabolite profiles between the two groups. This
approach provided insights into the metabolic
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: alterations associated with CKD and identified
When a sample containing nuclei with spin is placed in a strong magnetic field, the nuclear target pathways that could be potentially
magnetic moments align either with or against the external field. This alignment creates a slight modified to slow down the progression of the
excess of nuclear spins in the lower-energy state disease.
FollowShiqi WangMSCA Early Stage Researcher at Imperial College London. (2014, October 28). Nuclear magnetic
resonance spectroscopy (NMR spectroscopy) - ITN snal - marie curie initial trainin
g network. ITN SNAL - Marie Curie Initial Training Network - Smart Nano-objects for Alteration of Lipid bilayers
. https://itn-snal.net/2014/10/nuclear-magnetic-resonance-spectroscopy/
References:
Chu, S. , Graybeal, . Jack D. , Stoner, . John Oliver and Hurst, . George Samuel (Invalid Date).
spectroscopy. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/spectroscopy
Holger Försterling, F. (2010). Spin dynamics: Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Second
Edition. Medical Physics, 37(1), 406–407. American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3273534
Mika, A., Wojtowicz, W., Ząbek, A., Młynarz, P., Chmielewski, M., Sledzinski, T., & Stepnowski, P.
(2018). Application of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for the detection of metabolic
disorders in patients with moderate kidney insufficiency. Journal of Pharmaceutical and
Pourmodheji, H., Ghafar-Zadeh, E., & Magierowski, S. (2016). A Multidisciplinary Approach to High Throughput Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Mika, A., Wojtowicz, W., Ząbek, A., Młynarz, P., Chmielewski, M., Sledzinski, T., & Stepnowski, P. (2018). Application of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for the detection of metabolic Biomedical Analysis, 149, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.10.037
Spectroscopy. Sensors, 16(6), 850. MDPI AG. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/s16060850rrafo disorders in patients with moderate kidney insufficiency. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 149, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.10.037
You might also like
- 9 E.T.H.E.RDocument53 pages9 E.T.H.E.Rjamjam_95678853100% (18)
- Unit VI Molecular Spectroscopy: Physical ChemistryDocument17 pagesUnit VI Molecular Spectroscopy: Physical ChemistryDewal Deshmukh100% (1)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy - Instrumentation - Microbe NotesDocument2 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy - Instrumentation - Microbe Notesjimgitonga100% (2)
- NMR Spectroscopy)Document3 pagesNMR Spectroscopy)smart ptmNo ratings yet
- Xray, NMR, 2dpageDocument4 pagesXray, NMR, 2dpageUnnimaya GNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1Document26 pagesAtomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1Hammed LawalNo ratings yet
- DRAFT Physical Methods in Biology and Medicine Biophysics Finals RequirementsDocument16 pagesDRAFT Physical Methods in Biology and Medicine Biophysics Finals RequirementsALNo ratings yet
- 1 - Elemental Analysis - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument2 pages1 - Elemental Analysis - Chemistry LibreTextspearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Spectroscopy - FullDocument105 pagesUnit 5 - Spectroscopy - FullJeetender MishraNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy TechniquesDocument3 pagesSpectroscopy TechniquesSantosh prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Spectroscopy - EC I B.techDocument31 pagesUnit - II Spectroscopy - EC I B.techTelugu BadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectroscopy: LiteratureDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Spectroscopy: LiteratureYahya RajputNo ratings yet
- MRS BasicDocument13 pagesMRS BasicAmajida RizkyNo ratings yet
- SPECTROSCOPY - Docx Senthil - Docx 1......Document17 pagesSPECTROSCOPY - Docx Senthil - Docx 1......Zaidh. fd100% (1)
- Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy - WikipediaLuan D SouzaNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument7 pagesSpectrosSuraj RarathNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MRSDocument9 pagesJurnal MRSAirinTrisniNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetic AssignmentDocument16 pagesBioenergetic Assignmentshanza FaheemNo ratings yet
- Atkin 12001 Molekular Spectroscopy 001Document5 pagesAtkin 12001 Molekular Spectroscopy 001Nikke ArdilahNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Klasifikasi RadiasiDocument39 pages1.1 Klasifikasi RadiasiulalaNo ratings yet
- AsdfsdfDocument19 pagesAsdfsdfanmolkapoorfbtestNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic TechniqueDocument24 pagesSpectroscopic TechniqueJubair Al-rashidNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument10 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosLaura CelisNo ratings yet
- SpectroDocument3 pagesSpectroAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of SpectrosDocument10 pagesBasic Principles of SpectrosAlexiss Chavez-De la MoraNo ratings yet
- Chem 3052 CHAPTER 1 (Introduction To Spectroscopy)Document22 pagesChem 3052 CHAPTER 1 (Introduction To Spectroscopy)ashenafiNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy Is The Study of TheDocument51 pagesSpectroscopy: Spectroscopy Is The Study of ThePalwan SaryNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Revised 10oct22 PDFDocument43 pagesSpectroscopy Revised 10oct22 PDFGundanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Raman Spectroscopy in Cancer DiagnosisDocument27 pagesApplications of Raman Spectroscopy in Cancer DiagnosiscarlosbokorNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument46 pagesSpectroscopy - WikipediaAnubhav VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Written Report NMR SpectrometryDocument6 pagesWritten Report NMR SpectrometryRye M. BirungNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument50 pagesFinalarfa2009No ratings yet
- The Expanding Role of Mass Spectrometry in BiotechnologyDocument14 pagesThe Expanding Role of Mass Spectrometry in BiotechnologyplasmaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Imaging in Animal ResearchDocument20 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Imaging in Animal ResearchZerlyndaBunga'alloNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument21 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDawoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 NMRDocument20 pagesChapter - 9 NMRMadhur ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- NMR Imaging in MedicineDocument14 pagesNMR Imaging in MedicineGary Trump100% (1)
- Lec.1 Introduction PDFDocument17 pagesLec.1 Introduction PDFAsim Alaa Al SalehiNo ratings yet
- NMR SpectrometryDocument7 pagesNMR SpectrometryferngetapeNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Attenuation Map in Emission Tomography: Special ContributionsDocument26 pagesDetermination of The Attenuation Map in Emission Tomography: Special ContributionsartspiceNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Rodney F. Boyer (Z-Lib - Org) - 221-253Document33 pagesBiochemistry Rodney F. Boyer (Z-Lib - Org) - 221-253amhiraNo ratings yet
- Optical Manipulation of Nanoparticles: A Review: Maria Dienerowitz, Michael Mazilu, and Kishan DholakiaDocument32 pagesOptical Manipulation of Nanoparticles: A Review: Maria Dienerowitz, Michael Mazilu, and Kishan DholakiaZakir AhmedNo ratings yet
- ZwnjatnKcB AnalChem2.1 Chapter 10 Spectroscopic MethodsDocument120 pagesZwnjatnKcB AnalChem2.1 Chapter 10 Spectroscopic MethodsNguyễn Hoàng QuânNo ratings yet
- Uv VisablespectroscopyatheerDocument18 pagesUv Visablespectroscopyatheerareej juttNo ratings yet
- Star NMRDocument20 pagesStar NMRstarskyhutch0000No ratings yet
- WHAT ROLES For TRACK-STRUCTURE and MICRODOSIMETRYDocument4 pagesWHAT ROLES For TRACK-STRUCTURE and MICRODOSIMETRYnuova0No ratings yet
- Chm580 NMRDocument8 pagesChm580 NMRNorHidayu Azmi50% (2)
- Dynamic Properties of Photonic Crystals and Their Effective Refractive IndexDocument9 pagesDynamic Properties of Photonic Crystals and Their Effective Refractive IndexAnonymous 6w0gAQNo ratings yet
- Detectors - Electron Spin ResonanceDocument7 pagesDetectors - Electron Spin ResonancegdgdfgNo ratings yet
- MG Zno Photodetector Grown by Chemical Spraying Pyrolysis TechniqueDocument6 pagesMG Zno Photodetector Grown by Chemical Spraying Pyrolysis TechniqueerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Fullerton 1982Document15 pagesFullerton 1982سيف فلاح حسنNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research ADocument7 pagesNuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Acordella_francescoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Christopher J. RhodesDocument52 pagesMagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Christopher J. RhodesSonia Ayu AndiniNo ratings yet
- Magnetism of Materials: Theory and Practice in Magnetic Resonance ImagingDocument18 pagesMagnetism of Materials: Theory and Practice in Magnetic Resonance ImagingThuyet Nguyen PhuocNo ratings yet
- Structural Elucidation of Small Organic Molecules by 1d 2d and Multi Dimensional Solution NMR Spectroscopy 2155 9872.S11 001Document8 pagesStructural Elucidation of Small Organic Molecules by 1d 2d and Multi Dimensional Solution NMR Spectroscopy 2155 9872.S11 001PriyosetyokoNo ratings yet
- Pha052 TG 9Document14 pagesPha052 TG 9Alcea InguilloNo ratings yet
- 2005 Zhang 3Document12 pages2005 Zhang 3ben0706No ratings yet
- Ka Iii Teknik Spektroskopik 2021Document10 pagesKa Iii Teknik Spektroskopik 2021peter sihotangNo ratings yet
- Resonancia Magnetica en Animales de CompañíaDocument11 pagesResonancia Magnetica en Animales de CompañíaEnrique A. Vega NuñezNo ratings yet
- Shining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.From EverandShining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.No ratings yet
- Laser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsFrom EverandLaser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Desalination: Shaheen Fatima Anis, Boor Singh Lalia, Raed HashaikehDocument8 pagesDesalination: Shaheen Fatima Anis, Boor Singh Lalia, Raed HashaikehSK SahooNo ratings yet
- Differential Protection: Document byDocument26 pagesDifferential Protection: Document byS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Lab ManualDocument22 pagesMachine Design Lab Manualsarathsaravanan100% (4)
- Influence of Soil-Structure Interaction On The Fundatmental Period of BuildingsDocument23 pagesInfluence of Soil-Structure Interaction On The Fundatmental Period of BuildingsMILL3482No ratings yet
- Chapter 3-3 Signal Processing Elemnt Part ThreeDocument43 pagesChapter 3-3 Signal Processing Elemnt Part Threedan gNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene Glycol-Salt PDFDocument14 pagesPolyethylene Glycol-Salt PDFlauraNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDocument5 pagesOpen Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt Generatorramniwas123No ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Activity1 Horizontally Launched Projectiles 1Document3 pagesActivity1 Horizontally Launched Projectiles 1EeyyaaNo ratings yet
- Aakash Sample Engineering Paper Class 11Document21 pagesAakash Sample Engineering Paper Class 11anishkumarraushan2007No ratings yet
- Transition Metal Joints For Steam GeneratorsDocument15 pagesTransition Metal Joints For Steam GeneratorsMahsaNo ratings yet
- Newton 2nd and 3rd Laws Chapter 4-3Document20 pagesNewton 2nd and 3rd Laws Chapter 4-3Jams FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of 3D2D Perovskite Heterostructures Via Inhibition of Ion Diffusion by Cross-Linked Polymers For Solar Cells With Improved PerformanceDocument12 pagesStabilization of 3D2D Perovskite Heterostructures Via Inhibition of Ion Diffusion by Cross-Linked Polymers For Solar Cells With Improved PerformanceJogi PaulNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Pattern: Time: 3 Hours 15 Minutes Max. Marks: 100 InstructionsDocument36 pagesQuestion Paper Pattern: Time: 3 Hours 15 Minutes Max. Marks: 100 InstructionsVardhaman BilagiNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab:Coefficient of Linear ExpansionDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab:Coefficient of Linear ExpansionNatalie Sherwood100% (1)
- 4x10 1Cx70 MergedDocument10 pages4x10 1Cx70 MergedJalal AlbadriNo ratings yet
- Purpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryDocument12 pagesPurpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryGauri ThakurNo ratings yet
- Deney 3Document22 pagesDeney 3baratniloy1No ratings yet
- Features: WWW - Domin.co - Uk +44 (0) 1761 252650 Info@domin - Co.ukDocument4 pagesFeatures: WWW - Domin.co - Uk +44 (0) 1761 252650 Info@domin - Co.uk只要香菜No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Principle: Arrow) Are Present: The Hook Holds TheDocument7 pagesEquilibrium Principle: Arrow) Are Present: The Hook Holds TheYady S. Londoño L.No ratings yet
- Achievement Test Science 5 Regular ClassDocument13 pagesAchievement Test Science 5 Regular ClassArman Berina CortezNo ratings yet
- Mitsu C004e-I Solid End MillsDocument358 pagesMitsu C004e-I Solid End MillskatomegumioncrackNo ratings yet
- OSE 40-0196-067 - 25 - Data Sheet - 2018Document6 pagesOSE 40-0196-067 - 25 - Data Sheet - 2018Centrifugal SeparatorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Fast Drying of High-Alumina MgO-bonded Refractory CastablesDocument12 pages2020 - Fast Drying of High-Alumina MgO-bonded Refractory CastablesKhaled BOUALINo ratings yet
- C) Isolated System:: Unit-6Document16 pagesC) Isolated System:: Unit-6MUHAMMAD YASEENNo ratings yet
- Experiment Two: 2. Angular MeasurementDocument4 pagesExperiment Two: 2. Angular Measurementahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- IB Test Review Trig With Calculator MSDocument15 pagesIB Test Review Trig With Calculator MSGa-Eun YooNo ratings yet
- Appliedstat 2017 Chapter 10 11Document23 pagesAppliedstat 2017 Chapter 10 11Vivian HuNo ratings yet