Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Environmental Systems and Societes - Unit 1 Summary
Environmental Systems and Societes - Unit 1 Summary
Uploaded by
Emma FernandezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Environmental Systems and Societes - Unit 1 Summary
Environmental Systems and Societes - Unit 1 Summary
Uploaded by
Emma FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
22/03/24
Review for exam
● Foundations of environmental systems and societies
➔ Environmental value system: Is not talking about the environment, is talking
about the society.
★ Ecologist: Their value is to protect nature at all cost. Earth centered.
➢ Deep ecologist:They r the extreme, they don't believe that they
are the better species. They only use the environment when
they need it.
➢ Soft ecologist: They are taken into account but they are not as
extreme as the deep ones.
★ Anthropocentric: Human Centered, it's the thought that humans are the
dominant species
★ Tecnocentrics: The problems caused by humans can be saved by
technology.
➢ Cornucopians: See the world as having infinite resources to
benefit humanity, We can solve everything with technology.
➢ Environmental managers: Similar to anthropocentric views,
thay have more consciousness about the environment while the
cornucopians don't.
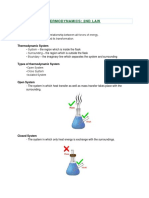
➔ Systems and models.
★ Systems can be on any scale, small or large. A system is the
representation of a model of a real thing.
➢ Open system: Exchange energy and matter
➢ Close system: Exchange Energy but not matter
➢ Isolated system: Does not exchange energy or matter. Do not
exist in real life as it's impossible to not exchange energy or
matter. Example the universe, we can say that it is isolated as
we don't know what's more than the universe.
In an open system we can know:
Transfers: Passage from one thing to another place, example: Water moving from a river to
the sea
Transformation: Change the state of the matter of something, example: Liquid to gas, light
to chemical energy.
Input: Something that gets inside our system.
Output: Something that gets outside our system.
★ Energy and equilibria.
★ Energy:
➢ 1st law of thermodynamics: Is the principle of conservation of
energy, which states that energy is an isolated system that can
be transformed but cannot be created or destroyed.
➢ 2nd law of thermodynamics (Entropy): Refers to the energy
being transformed through energy transfers.
Entropy: Is a measure of the amount of disorder in a system.
Entropy ↑ Energy↓. Al menos que tengamos que poner energía para
ordenarlo.Pero todo tiende al desorden
★ Equilibria:
➔ Equilibrium: Static, does not exist as we live in an environment. All the time
all the same
➔ Steady state: We are going to have the same ups and downs but we are going
to be constant with the steady state equilibrium. It breaks when a tipping
point can go up or down.
➔ Feedback: - or + feedback
➢ Negative feedback: Is the one that returns to the equilibrium state,
example: I'm cold i put something on)
➢ Positive feedback: Something that disturbs the equilibrium and you
end up having a new equilibrium.
➔ Resilience: The ability for a system to return to an equilibrium.
★ Sustainability:
❖ When a system or a model can return to normal equilibrium, we are always
going to have more than that. Water will not be sustainable anymore as we
contaminate the water from the rivers
➔ Sustainability indicators: The biotic (from the living things) and abiotic factors
(ph, good temperature, good air).
➔ Natural capital: The resources that you can sell, or purchase.
➔ EIA(Environmental impact assessment): A previous investigation we are
going to do before damaging the abiotic or biotic factors of the environment.
➔ Footprint: The things that we do to the environment will leave a mark in the
environment.
➔ Humans and pollutions.
Type of Pollutants:
- Matter
- Energy
- Living Organisms
Point source: The release from one indefinite site.
Non Point source: May have many sources, it is virtually impossible to detect exactly where
it is coming from.
Persistent: Are the ones that cannot be degraded by living organisms. And those desechos
leaves in the environment which can creates biomagnification or bioaccumulation (El pajarito
come una planta con DDT insecticida, entonces el insecticida queda dentro de los tejidos del
pajarito.)
Biodegradable Can be degraded by living organisims.
Greenhouse effect: The layer of gasses that allows us to leave the earth. The layer of gasses
can lead to global warming.
Chronic pollution: All the time is happening, example cars as they are always releasing
carbon dioxide
Acute pollution: Is the one that happens in a short period of time and contaminantes a lot of
pollution, example: Nuclear bomb.
● Measurements of pollution:
➔ Indirect pollution: Taking the measurement of the abiotic or biotic factors. If
there are lignans
➔ Strategies:
1. By changing the human activity which produces it.
2. By regulating or preventing the release of pollutants.
3. By working to clean up or restore damaged ecosystems.
You might also like
- AP Environmental Science - Chapter 1 NotesDocument8 pagesAP Environmental Science - Chapter 1 NotesRECON_iND100% (2)
- ESS - Topic 1 - Foundations To EssDocument36 pagesESS - Topic 1 - Foundations To EssRAGINI RAMACHANDRANNo ratings yet
- IB ESS Notes of CH #1 & CH #2Document24 pagesIB ESS Notes of CH #1 & CH #2zwslpoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Environmental ScienceEljhon Satsat100% (1)
- Calgary Green Infrastructure Mobility Corridors SecDocument129 pagesCalgary Green Infrastructure Mobility Corridors SecSzeleczky OlivérNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document6 pagesUnit 1Valerio CastelliniNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Topic 1 2 1Document22 pagesRevision Notes Topic 1 2 1Rafael REVERTER CUSTODIONo ratings yet
- ESS Revision Session 1 - Topics 1-4 & ConceptsDocument112 pagesESS Revision Session 1 - Topics 1-4 & ConceptsjinLNo ratings yet
- Environmental Summary 2021Document37 pagesEnvironmental Summary 2021martina hirschenNo ratings yet
- ESS NoteDocument7 pagesESS NoteYi Qi NieNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1-3Document10 pagesChapters 1-3ElsaNo ratings yet
- Ess - 1.3Document3 pagesEss - 1.3Maidhani OjhaNo ratings yet
- ESS DuckDocument37 pagesESS DuckValerio CastelliniNo ratings yet
- SL Environmental and Social Systems Duck: Good LuckDocument36 pagesSL Environmental and Social Systems Duck: Good LuckNishitaNo ratings yet
- PolienvironDocument3 pagesPolienvironAndrew LeaheyNo ratings yet
- LAWS and PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGYDocument2 pagesLAWS and PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGYMarie FeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems and Societies Mock Summary W:o Case StudiesDocument140 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Mock Summary W:o Case Studiesmartina hirschenNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems and Societies Complete SummaryDocument161 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Complete Summarymartina hirschenNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument10 pagesChemEricka ArceNo ratings yet
- L10 ThermodynamicsDocument39 pagesL10 ThermodynamicsfaresNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Living World Part ADocument22 pagesUnit 1 The Living World Part ALama DebanyNo ratings yet
- BIOL101 Ch6 Pt1Document26 pagesBIOL101 Ch6 Pt1marwa haribNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-3 ReviewDocument36 pagesUnit 1-3 Reviewapi-282611325No ratings yet
- Integrated Science (CXC) NotesDocument4 pagesIntegrated Science (CXC) Notesjoelwillie252No ratings yet
- Topic 2 Sub-Topic 1.3Document21 pagesTopic 2 Sub-Topic 1.3Syazwan KhirudinNo ratings yet
- ESS Notebook Topic 1Document11 pagesESS Notebook Topic 1yansisay00No ratings yet
- ESS NotebookDocument97 pagesESS Notebookyansisay00No ratings yet
- Week 2 Basic Concepts and Principles in Ecology and Environmental ScienceDocument33 pagesWeek 2 Basic Concepts and Principles in Ecology and Environmental SciencejamaellajaneNo ratings yet
- 1.3 LessonDocument22 pages1.3 LessonViolet XuNo ratings yet
- Apes Chapter 3Document3 pagesApes Chapter 3api-235959158No ratings yet
- Topic 1 NotesDocument11 pagesTopic 1 NotesRaviNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics Lesson Pert 1Document67 pagesChemical Thermodynamics Lesson Pert 1GLUSITANIO, DIANA YSABELA JOHANA T.No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Organism and Thier Environment - PPTDocument35 pagesChapter 6 - Organism and Thier Environment - PPTmisganamarcos10No ratings yet
- Ess - Notes May 24Document59 pagesEss - Notes May 24martipineiro2006No ratings yet
- Ess Yr 5 NotesDocument11 pagesEss Yr 5 Notesbelle jokyNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Energy and EquilibriaDocument30 pages1.3 Energy and EquilibriaYasser Khairy AbdelghaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument43 pagesChemical Thermodynamics: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenChery-an PletNo ratings yet
- LiaschapteroutlinesDocument18 pagesLiaschapteroutlinesapi-276507313No ratings yet
- Power Point - ThermodynamicsDocument71 pagesPower Point - ThermodynamicsAsad AzizNo ratings yet
- Apbio CHP 8 DetaillectoutDocument12 pagesApbio CHP 8 DetaillectoutJohn Reiner BacusNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 1Document5 pagesEnvironmental Science 1BONNA FAYE CHRISZEL HUI YING TANNo ratings yet
- What Are SystemsDocument2 pagesWhat Are SystemsMichael SmithNo ratings yet
- DiffrencesDocument23 pagesDiffrencessajidhussainjatoiNo ratings yet
- Ess Topic 1Document4 pagesEss Topic 1erikadeabrilNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Chemistry - A Molecular Approach, 1Document58 pagesThermochemistry: Chemistry - A Molecular Approach, 1John Matthew GicomNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q4 M2Document35 pagesGen Chem 2 Q4 M2Jake Aldred CabelaNo ratings yet
- Environmental IssuesDocument39 pagesEnvironmental IssuesKoshy VaidyanNo ratings yet
- Primer Cuatri Ess 2023Document32 pagesPrimer Cuatri Ess 2023pacitatimeNo ratings yet
- Ibdp Ess Notes Topic 1Document8 pagesIbdp Ess Notes Topic 1chaitanya anandNo ratings yet
- IB ESS Topic 1.3 NotesDocument5 pagesIB ESS Topic 1.3 NotesZiwei DongNo ratings yet
- Ap EsDocument37 pagesAp EsChae ChaeNo ratings yet
- Introducing Environmental Science and StabilityDocument19 pagesIntroducing Environmental Science and StabilityMarj Jermaine M. FernandoNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Project - Kinetics and EquilibriumDocument32 pagesAP Chemistry Project - Kinetics and EquilibriumSyarifahNo ratings yet
- 19 - Lecture To My KidsDocument70 pages19 - Lecture To My Kids焦尚鴻No ratings yet
- 1.1 Environmental Value SystemsDocument38 pages1.1 Environmental Value SystemsBhaswati BharNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science Set 2 SolutionDocument7 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science Set 2 SolutionNarayanamurthy AmirapuNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Honors Biology Study Guide: Chapters 1-8Document13 pagesSemester 1 Honors Biology Study Guide: Chapters 1-8Jessica LeeNo ratings yet
- Ess Sstudy GuideDocument60 pagesEss Sstudy GuideDanna AyalaNo ratings yet
- GC2 - 03 Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument42 pagesGC2 - 03 Chemical Thermodynamicsalthea villanuevaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Systems and ModelsDocument34 pages1.2 Systems and Modelsgiada.guzzardiNo ratings yet
- Data InterpretationDocument8 pagesData InterpretationshivambedarNo ratings yet
- Affordable Housing Site AnalysisDocument4 pagesAffordable Housing Site AnalysisAlekhya DeviNo ratings yet
- The Vancouver Action PlanDocument51 pagesThe Vancouver Action PlanRobert PollardNo ratings yet
- Interview With Urban FarmsDocument6 pagesInterview With Urban FarmsAlfyanNo ratings yet
- Related Lit. of NPK SoilDocument17 pagesRelated Lit. of NPK SoilVeejay Soriano CuevasNo ratings yet
- Senior EssayDocument8 pagesSenior Essayapi-457335360No ratings yet
- Green Wall Capstone PosterDocument1 pageGreen Wall Capstone Posterapi-614692220No ratings yet
- Oil Palm CultivationDocument59 pagesOil Palm Cultivationshini1308100% (23)
- PD 705Document26 pagesPD 705Jane CA100% (6)
- Green Warriors of Norway ECHA REACH Bisphenol Comments and EvidenceDocument18 pagesGreen Warriors of Norway ECHA REACH Bisphenol Comments and EvidenceMassimiliano Zocchi100% (1)
- Kindergarten UnpackDocument12 pagesKindergarten Unpackapi-399215392No ratings yet
- Difficulties of Prosecuting Environmental CrimesDocument6 pagesDifficulties of Prosecuting Environmental CrimesKyle louisNo ratings yet
- Brochure For MapehDocument4 pagesBrochure For MapehKarl Anthony SuarezNo ratings yet
- Modified Rational Method For Sizing Infiltration StructuresDocument5 pagesModified Rational Method For Sizing Infiltration Structuresthedevilsdue9420No ratings yet
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh 6 Bai 11Document14 pagesBai Tap Tieng Anh 6 Bai 11buitrucquynh2003No ratings yet
- Pesticides.: English ThursdayDocument10 pagesPesticides.: English ThursdayJuliana Mercedes Negrete BarraganNo ratings yet
- TQ ES 2ndDocument4 pagesTQ ES 2ndAldrin SahurdaNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Civil Engineering MCQ QuestionsDocument6 pagesEmerging Trends in Civil Engineering MCQ QuestionsPratik BatemanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Geography ResourcesDocument31 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 8 Geography ResourcesGirish JethwaNo ratings yet
- Earth's SpheresDocument9 pagesEarth's SpheresSajad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Town PlanningDocument13 pagesTown Planningasif hakeemNo ratings yet
- Uba OrganogramDocument1 pageUba OrganogramPrecious KadiriNo ratings yet
- Panel Discussion: The New Face (Environment) Duration: Maximum of 15-20 MinutesDocument5 pagesPanel Discussion: The New Face (Environment) Duration: Maximum of 15-20 MinutesQuize Manriquez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Minerals and PowerDocument4 pagesMinerals and PowerSrishti kashyapNo ratings yet
- Soil Salinity and AlkalinityDocument19 pagesSoil Salinity and AlkalinityFazeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Close-Up B1+ Progress Test 3Document4 pagesClose-Up B1+ Progress Test 3Aline Morais50% (4)
- 08 Chapter-5Document114 pages08 Chapter-5Lamico Dellavvoltoio100% (1)
- Status and Conservation of Marsh or Mugger Crocodile: A ReviewDocument4 pagesStatus and Conservation of Marsh or Mugger Crocodile: A ReviewMayida ZehraNo ratings yet
- An Urgent Need For Sustainable Thinking in Agriculture - An Indian ScenarioDocument3 pagesAn Urgent Need For Sustainable Thinking in Agriculture - An Indian ScenarioRafael GarcíaNo ratings yet