Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid Rain
Acid Rain
Uploaded by
mdnaim42040Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Rain
Acid Rain
Uploaded by
mdnaim42040Copyright:
Available Formats
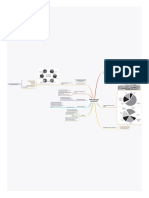
Acid rain, also known as acid deposition, is a significant environmental issue with widespread
consequences. Here's a breakdown of its key points:
Definition:
Acid rain refers to any form of precipitation (rain, snow, fog, hail) with a pH level lower than 5.6,
making it more acidic than natural precipitation.
Formation:
1. Emissions: The primary culprits are sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx)
released into the atmosphere from:
○ Power plants burning fossil fuels like coal.
○ Industrial processes like metal smelting and chemical manufacturing.
○ Vehicle emissions.
2. Chemical Reactions: These gases react with water vapor, oxygen, and other chemicals in
the atmosphere to form sulfuric and nitric acids.
3. Deposition: These acids then return to Earth's surface through:
○ Wet deposition: Acidic rain, snow, fog, etc.
○ Dry deposition: Acidic particles settling on surfaces as dust or smoke.
Environmental Impacts:
● Damage to Forests: Acid rain can weaken trees, making them more susceptible to
diseases, pests, and harsh weather conditions.
● Acidification of Lakes and Streams:Lowers pH levels, harming aquatic life, disrupting food
chains, and making it difficult for some species to reproduce.
● Soil Acidification: Alters soil chemistry, leaching essential nutrients and potentially
mobilizing toxic metals.
● Damage to Buildings and Cultural Heritage: Can accelerate the weathering of stone
structures and monuments.
Human Health Impacts:
● Respiratory Problems: Exposure to acidic particles can irritate the lungs and exacerbate
respiratory conditions like asthma.
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies:
● Reducing Emissions: Implementing stricter regulations on power plants and industries to
limit SO2 and NOx emissions.
● Switching to Cleaner Fuels: Promoting the use of renewable energy sources and
cleaner-burning technologies.
● Liming of Lakes and Streams: In some cases, adding limestone or other alkaline materials
to neutralize the acidity of affected water bodies.
Progress and Challenges:
● Significant progress has been made in reducing acid rain in many regions through stricter
emission controls.
● However, challenges remain, particularly in areas with high dependence on fossil fuels and
less stringent environmental regulations.
Overall, understanding acid rain and its impacts is crucial for promoting cleaner air and
protecting our environment from the harmful effects of this widespread pollutant.
You might also like
- Acid RainDocument17 pagesAcid RainSaif YounusNo ratings yet
- Arunima Shandilya Scienc e 10 BDocument22 pagesArunima Shandilya Scienc e 10 BHOWE CHENG TENGNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain by Zerkash SheikhDocument12 pagesAcid Rain by Zerkash Sheikhشیخ زرکاش امرتسریہNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument15 pagesAcid RainSayem Ahmmed RiponNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Assignment 1 Muhamad Amirul Aqil Bin Mat Rozali 5521311529 Azyyati Binti JohariDocument12 pagesAcid Rain: Assignment 1 Muhamad Amirul Aqil Bin Mat Rozali 5521311529 Azyyati Binti JohariSyazani HussainiNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain (Group 2)Document23 pagesAcid Rain (Group 2)Viviane O. BaylonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Acid RainDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Acid RainDevendarsingh rawatNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain OriginalDocument6 pagesAcid Rain OriginalAvikPandeyNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution & Control Water Pollution & Control Climate Change: Cause & EffectsDocument31 pagesAir Pollution & Control Water Pollution & Control Climate Change: Cause & EffectsKritikaNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain File AMOLDocument15 pagesAcid Rain File AMOLpari0000No ratings yet
- Genrated #Sytemfilescheckbatchkirii1 TempsysDocument7 pagesGenrated #Sytemfilescheckbatchkirii1 TempsysMala SinghNo ratings yet
- CE 107 - Lecture 8Document34 pagesCE 107 - Lecture 8নীল জোছনাNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument5 pagesWhat Is Acid RainEhteshamNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument4 pagesAcid RainkajalNo ratings yet
- Power Point Acid RainDocument21 pagesPower Point Acid RainBalkis Samsuddin100% (3)
- Acid RainDocument12 pagesAcid RainUmesh Gaikwad100% (3)
- Acid DepositionDocument20 pagesAcid Depositionankitsah200No ratings yet
- Enter Post Title HereDocument6 pagesEnter Post Title HereRohit ShalgarNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain and Its EffectsDocument6 pagesAcid Rain and Its Effectstamoor aliNo ratings yet
- Acid Rains, Causes and EffectsDocument12 pagesAcid Rains, Causes and EffectsIqra IjazNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityDocument20 pagesAcid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityManwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument11 pagesAcid RainTEJAS JAINNo ratings yet
- Google Form For SECDocument19 pagesGoogle Form For SECRishi DeoNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: HistoryDocument4 pagesAcid Rain: Historyrameesaali56No ratings yet
- Environmental Literacy 10Th Presentation: Assoc. Prof. Pınar Gedikkaya BALDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Literacy 10Th Presentation: Assoc. Prof. Pınar Gedikkaya BALNet FlixNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument21 pagesAcid Raintehseenmohsin6No ratings yet
- By Nischay.N B.E (CIVIL) ., M.Tech., IGBC-AP: Seminar Report OnDocument26 pagesBy Nischay.N B.E (CIVIL) ., M.Tech., IGBC-AP: Seminar Report Onravi rajamanikamNo ratings yet
- AKB M.SC - 3rd Sem Topic Acid Rain and Ozone Layer DepletionDocument20 pagesAKB M.SC - 3rd Sem Topic Acid Rain and Ozone Layer DepletionworkwithsnehhNo ratings yet
- Ankit Rana - Anuj Kumar - Ashish Sharma - Anupam Pandey - Mayank BharadwajDocument26 pagesAnkit Rana - Anuj Kumar - Ashish Sharma - Anupam Pandey - Mayank BharadwajQuyen LeNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Ms. Kathy Claire P. Ballega, RM, RN, Man, LPTDocument43 pagesAcid Rain: Ms. Kathy Claire P. Ballega, RM, RN, Man, LPTKathy Claire Pecundo BallegaNo ratings yet
- 6.3.4. Acid Deposition - GEC 007-ARCH41S2 - Science, Technology and SocietyDocument3 pages6.3.4. Acid Deposition - GEC 007-ARCH41S2 - Science, Technology and SocietyKIRSTENNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Climate Change, Acid Rain, Green-House EffectDocument19 pagesPresentation On Climate Change, Acid Rain, Green-House EffectJeevan khatryNo ratings yet
- STS Final Scope M. OlarteDocument7 pagesSTS Final Scope M. OlarteGlenn RadisNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain-The Major Cause of Pollution: Its Causes, Effects: Subodh KumarDocument6 pagesAcid Rain-The Major Cause of Pollution: Its Causes, Effects: Subodh KumarShruthi GNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument7 pagesAcid RainAnoshKhanNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument6 pagesAcid RainАнастасия МелешкоNo ratings yet
- Env Science Imp Questions For CollageDocument20 pagesEnv Science Imp Questions For Collagesolankiparth9825No ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument17 pagesAcid RainGurinder kaurNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument6 pagesAcid RainDeliaNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain Cause & Prevention: Name Student IdDocument9 pagesAcid Rain Cause & Prevention: Name Student IdNur AsyikinNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument16 pagesAcid RainSkull GamerNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number: 3: Submitted To: Muhammed Sahal Head of Chemistry Submitted By: Talha RafiqDocument6 pagesAssignment Number: 3: Submitted To: Muhammed Sahal Head of Chemistry Submitted By: Talha RafiqTalha RafiqNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument8 pagesAcid RainGerry RenaldiNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually Acidic, I.EDocument7 pagesAcid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually Acidic, I.ESarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain and Its ImpactsDocument8 pagesAcid Rain and Its ImpactsRiddhiNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: The Problem Continues: Presented by Navjot Singh Roll No. 95222454108 Bba 6 SemesterDocument38 pagesAcid Rain: The Problem Continues: Presented by Navjot Singh Roll No. 95222454108 Bba 6 SemesterlovleshrubyNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument39 pagesAcid RainSunil Shrestha100% (1)
- Thesis Statement Acid RainDocument7 pagesThesis Statement Acid Raintonichristensenaurora100% (2)
- Acid Rain: Presented byDocument13 pagesAcid Rain: Presented byAnand AsiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Air PollutionDocument15 pagesPresentation On Air PollutionVaibhav Raj PathiNo ratings yet
- Subject: Environmental Sciences - Course code:CHM-300 - Semester: 3rd - Section: EA - Topic: Chemistry of Acid Rain - Submitted By: Group #4 - Submitted To: Mam Hafiza NoreenDocument25 pagesSubject: Environmental Sciences - Course code:CHM-300 - Semester: 3rd - Section: EA - Topic: Chemistry of Acid Rain - Submitted By: Group #4 - Submitted To: Mam Hafiza NoreenLAIBA NOOR BS EnglishNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument13 pagesEnvironmental StudiesNew trend GamerzNo ratings yet
- SH2173 - Environmental Science In-Semester Exam-2 (ISE-2) : Roll Number Name Department Class DivisionDocument11 pagesSH2173 - Environmental Science In-Semester Exam-2 (ISE-2) : Roll Number Name Department Class DivisionSourabh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6Document25 pagesUnit - 6nagabhushanaatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document13 pagesLecture 7farihakanwal2021No ratings yet
- Acid Rain: For Other Uses, SeeDocument5 pagesAcid Rain: For Other Uses, SeefrancisNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Fayza Kamal Khattab: Presented To: Dr. Sayed ShalabyDocument11 pagesPresented By: Fayza Kamal Khattab: Presented To: Dr. Sayed ShalabyMohamed Maher TorkyNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Engineering:: Instructor DR Sher Jamal KhanDocument53 pagesWastewater Engineering:: Instructor DR Sher Jamal KhanZahid FarooqNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument13 pagesBiodiversity and ConservationSrividya SNo ratings yet
- 04 Activity 1 EMSDocument2 pages04 Activity 1 EMSKimNo ratings yet
- The Urgency of Environmental Conservation - Preserving Our Planet For Future GenerationsDocument2 pagesThe Urgency of Environmental Conservation - Preserving Our Planet For Future GenerationsErina NakiriNo ratings yet
- LG) Pc-Ii Formulation of Waste Management PlansDocument25 pagesLG) Pc-Ii Formulation of Waste Management PlansAhmed ButtNo ratings yet
- Conservation PlanDocument7 pagesConservation PlanHENRY PAPAGAYONo ratings yet
- No Exposure Certification For Exclusion From Npdes Stormwater Permitting (FORM 62-620.910 (17), F.A.C.)Document7 pagesNo Exposure Certification For Exclusion From Npdes Stormwater Permitting (FORM 62-620.910 (17), F.A.C.)Sean CrossNo ratings yet
- Management and Disposal of Solid WasteDocument13 pagesManagement and Disposal of Solid WasteOmar Waheed Noor ZainabNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5: Solid Waste: Generation and ManagementDocument22 pagesChapter-5: Solid Waste: Generation and ManagementAkashNo ratings yet
- DAO 2014-02 Revised Guidlines For PCO AccreditationDocument73 pagesDAO 2014-02 Revised Guidlines For PCO AccreditationPatrick Go100% (1)
- Iees 105Document31 pagesIees 105Rav NeetNo ratings yet
- IELTS Academic WritingDocument32 pagesIELTS Academic WritingInquisitor SultanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Control PlanDocument33 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Control PlanMayette Rose SarrozaNo ratings yet
- Problems of Protection of Geomorphological Monuments in The Structure of Metropolitan CityDocument10 pagesProblems of Protection of Geomorphological Monuments in The Structure of Metropolitan CityGEOLINKS International Conference 2019100% (1)
- Waste Water Report Field Visit 3Document11 pagesWaste Water Report Field Visit 3Brian LeeNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management IndiaDocument66 pagesDisaster Management IndiaAjay BaggaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay #2Document5 pagesReflective Essay #2Sarah JordanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management Action PlanDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Management Action PlansarangaNo ratings yet
- National Greening Action PlanDocument2 pagesNational Greening Action PlanAnnjon Saracia100% (1)
- Problem Proposal - Group 7 (STEM C)Document6 pagesProblem Proposal - Group 7 (STEM C)rodelio culalicNo ratings yet
- DLP 7 - Grade 7 - ASORDocument6 pagesDLP 7 - Grade 7 - ASORayanasor6100% (1)
- Jennifer Obarinde Revised WorkDocument25 pagesJennifer Obarinde Revised WorkAdetayoNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Environmental ScienceDocument31 pagesGlossary of Environmental ScienceOscar BladenNo ratings yet
- 1 Week DLL Planetary Networks OkDocument25 pages1 Week DLL Planetary Networks Okandrew100% (3)
- Chapter 3Document27 pagesChapter 3zohain sethNo ratings yet
- EVS PPT Air PollutionDocument27 pagesEVS PPT Air PollutionKajal SainiNo ratings yet
- 02 - Hammarby SjostadDocument24 pages02 - Hammarby SjostadShorbanNo ratings yet
- DOG Enchanted Unicorn F17Document10 pagesDOG Enchanted Unicorn F17Rodolfo PerezNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Environmental ManagementDocument15 pagesRisk Assessment For Environmental ManagementMOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- M1-02 Life Cycle Assessment: Chapter ObjectDocument1 pageM1-02 Life Cycle Assessment: Chapter ObjectBen ShenNo ratings yet