Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsENZYMES
ENZYMES
Uploaded by
jcpacate1178qcCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Testbank 4e CH14Document19 pagesTestbank 4e CH14somasudeshna100% (5)
- Biochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismDocument6 pagesBiochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismSchat ZiNo ratings yet
- CC-LEC-NOTES-1Document4 pagesCC-LEC-NOTES-1CDNo ratings yet
- CCHM 312: Week 2: EnzymesDocument10 pagesCCHM 312: Week 2: EnzymesJanine Alicia VargasNo ratings yet
- CC Lab M1 7Document99 pagesCC Lab M1 7CDNo ratings yet
- MEDT 19 (Lec)Document17 pagesMEDT 19 (Lec)Erick PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 12 5 19Document113 pagesEnzymes 12 5 19Arshad Mehmood MinhasNo ratings yet
- Biochem Term 2Document28 pagesBiochem Term 2Michelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Proteins-Enzymes Part 1Document12 pagesCatalytic Proteins-Enzymes Part 1Mohammed HassounNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Kamisha L. Johnson-DavisDocument29 pagesEnzymes: Kamisha L. Johnson-DavisWho KnowsNo ratings yet
- Bisgop EnxymeDocument28 pagesBisgop EnxymefjkgldjfNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Document30 pagesBiological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Mohammed shaffiqueNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LectureDocument115 pagesEnzymes LectureJane Tai100% (1)
- EnzymologyDocument13 pagesEnzymologyRane MandapatNo ratings yet
- 6 EnzymesDocument3 pages6 EnzymesIYA LABAONo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument7 pagesEnzymesDANIKA JADE INFIESTONo ratings yet
- Unit 3 EnzymesDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Enzymeskamsjain6802No ratings yet
- $RLW3VJ1Document3 pages$RLW3VJ1Crow LordNo ratings yet
- Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDDocument46 pagesGly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDketakeeNo ratings yet
- Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDDocument46 pagesGly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDAlexander LotukhovNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesAstro KeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 2 ENZYMES. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry 2 ENZYMES. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGYBib imbapNo ratings yet
- Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman: Smt. Sharadchandrika Suresh Patil College of Pharmacy, Chopda, Maharashtra, IndiaDocument20 pagesDr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman: Smt. Sharadchandrika Suresh Patil College of Pharmacy, Chopda, Maharashtra, IndiaAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- C5 EnzymesDocument19 pagesC5 EnzymesSoraya D. Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry EnzymesDocument88 pagesBiochemistry EnzymesLama QaimariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - EnzymesDocument19 pagesLecture 3 - EnzymesEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- Michael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi - Bioprocess Engineering - Basic Concepts-Prentice Hall (2001) (077-113)Document37 pagesMichael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi - Bioprocess Engineering - Basic Concepts-Prentice Hall (2001) (077-113)Dome VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LEC Enzymes OutlineDocument6 pagesBiochemistry LEC Enzymes OutlineShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- 4A. Cellular RespirationDocument5 pages4A. Cellular RespirationIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Part 1Document5 pagesEnzymes Part 1Mar LagmayNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Enzymes Review NotesDocument4 pagesBiochemistry - Enzymes Review NotesKenneth100% (1)
- Biochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureDocument4 pagesBiochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureJohn Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- New EnzymesDocument64 pagesNew Enzymeslovi bahunNo ratings yet
- Biochem (Finals)Document5 pagesBiochem (Finals)cjyulo99710No ratings yet
- Enzymology To Kreb's CycleDocument34 pagesEnzymology To Kreb's Cycleferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- $RZ2YE8ODocument2 pages$RZ2YE8OCrow LordNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LectureDocument16 pagesEnzymes Lectureglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument52 pagesBiochem NotesAnonymous 4Ib1ByFC100% (2)
- Enzymes BN 2019Document67 pagesEnzymes BN 2019Rezan ThapaNo ratings yet
- 2C Enzyme SpecificityDocument8 pages2C Enzyme SpecificityqueyrhiaNo ratings yet
- 05 EnzymesDocument35 pages05 EnzymesFrances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - IntroDocument17 pagesEnzymes - IntroFatima MendozaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ShortDocument83 pagesEnzymes ShortWaleed ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Chem 113 - Week 2 - EnzymesDocument5 pagesChem 113 - Week 2 - EnzymesFormosa G.No ratings yet
- (Module) Lesson 4 Basic Concepts of Enzyme ActionDocument9 pages(Module) Lesson 4 Basic Concepts of Enzyme Actionkmiboy976No ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsAGENT M.DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesChapter 16 Cellular RespirationLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Reactions That Produce and Consume ATP - 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesGen Bio - Reactions That Produce and Consume ATP - 2nd QuarterChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Notes - SathyanarayanaDocument32 pagesEnzyme Notes - SathyanarayanaSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Semifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and VitaminsDocument4 pagesSemifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and Vitaminsino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Quiz Let 22Document3 pagesQuiz Let 22Hazel LopezNo ratings yet
- CHY 47 EnzymesDocument143 pagesCHY 47 EnzymesElle BuhisanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LectureDocument120 pagesEnzymes LectureHERSEY MIAYONo ratings yet
- EnzyDocument33 pagesEnzyPranaliNo ratings yet
- Enzyme 2016Document50 pagesEnzyme 2016igus696No ratings yet
- Food Chemistry - Activity 2Document3 pagesFood Chemistry - Activity 2Leda PeñaNo ratings yet
- (BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymesDocument9 pages(BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymeshellokrisjaejoongNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyDocument8 pagesEnzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyStefanie LucresiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Microbial MetabolismDocument48 pagesUnit 3 Microbial MetabolismNICOLE ANGELIQUE M. DINOYNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument16 pagesENZYMESWiza MulengaNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up: List Any Facts You Know About The Molecule ShownDocument30 pagesWarm-Up: List Any Facts You Know About The Molecule ShownZhiyong HuangNo ratings yet
- Product List Vet PDFDocument6 pagesProduct List Vet PDFNilamdeen Mohamed Zamil75% (4)
- S28JUNDocument4 pagesS28JUNTri CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4secondary Metabolites FinalDocument29 pagesChapter 4secondary Metabolites FinalDhruv KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 AnticholinesterasesDocument55 pages2 AnticholinesterasesSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Kimi FarmaceutikeDocument64 pagesKimi FarmaceutikeHabib Berisha100% (1)
- Biomolecules: Chemical Compounds of The Living SystemDocument89 pagesBiomolecules: Chemical Compounds of The Living SystemAriane DionisioNo ratings yet
- Esterification and ProductsDocument7 pagesEsterification and Productsdevraj raikarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Synthetic and Natural Organic PolymersDocument10 pagesChapter 25: Synthetic and Natural Organic PolymersChristian BareraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Notes ProteinsRegine Chua100% (1)
- Identification of PTH-Amino Acids by HPLC: Gregory A. Grant and Mark W. CrankshawDocument22 pagesIdentification of PTH-Amino Acids by HPLC: Gregory A. Grant and Mark W. CrankshawJe RivasNo ratings yet
- Fats & Oils IntroductionDocument12 pagesFats & Oils IntroductionShibbu GangwarNo ratings yet
- Acetophenone Uses: Acute EffectsDocument3 pagesAcetophenone Uses: Acute EffectsRahul JadhavNo ratings yet
- Daftar Dosis Dan Sediaan Obat AnakDocument5 pagesDaftar Dosis Dan Sediaan Obat AnakDaman Gregorius ManikNo ratings yet
- A Review On Finger Millet Properties, Processing, Health Benefits, and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesA Review On Finger Millet Properties, Processing, Health Benefits, and Applicationsjsbska88No ratings yet
- Pharam GuideDocument4,386 pagesPharam Guideابُوالبَتُول ڈاکٹر صفدر علی قادری رضوی100% (1)
- ShrinkageDocument2 pagesShrinkageAgusPurwantoNo ratings yet
- Alkane and CycloalkanesDocument59 pagesAlkane and CycloalkanesS JNo ratings yet
- Section B and C: Volume-02Document5 pagesSection B and C: Volume-02lovelylover_17No ratings yet
- MCQ Chapter 9 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesMCQ Chapter 9 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesNinaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Fix So Ranap Apr-Mei 2023Document432 pagesLaporan Fix So Ranap Apr-Mei 2023hefikurniasariNo ratings yet
- Word Sarcina TermicaDocument3 pagesWord Sarcina TermicaSergiu AlupoaeNo ratings yet
- AS LEVEL BIOLOGY Paper 1 EnzymesDocument54 pagesAS LEVEL BIOLOGY Paper 1 EnzymesADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- C34 Pepaña Drill2Document5 pagesC34 Pepaña Drill2Ruth Stephanie P. PepañaNo ratings yet
- Execises - Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 Part 1Document2 pagesExecises - Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 Part 1Michelle ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- MIMS PharCareDocument5 pagesMIMS PharCareKimgenesis TuazonNo ratings yet
- Pump Sizing Calculation (Photo)Document25 pagesPump Sizing Calculation (Photo)anto3harrish3fdoNo ratings yet
- Price List 09.08.2021Document7 pagesPrice List 09.08.2021A Abhishek Ludo KingNo ratings yet
- Wade 18 PowerpointDocument55 pagesWade 18 PowerpointIwanNo ratings yet
ENZYMES
ENZYMES
Uploaded by
jcpacate1178qc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageENZYMES
ENZYMES
Uploaded by
jcpacate1178qcCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
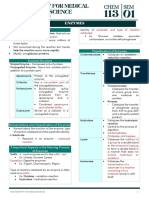
ENZYMES Apoenzyme - protein portion of the classified according to:
- hastens chemical reactions in organic enzyme - biochemical function
matter - Subject to denaturation, in which - substrate catalyzed
- catalyzes single or limited number of enzyme losses its activity - class of reaction catalyzed
chemical reactions - individual identification numbers
- large molecules confined in cells Holoenzyme - an active substance ex. AMS EC 3.2.1.1
- increase membrane permeability formed by combination of a co-enzyme
allows them to enter the blood and an apoenzyme. ENZYME ABBREVIATION IDENTIFICATIO
- measured in terms of their activity N NUMBER
Proenzyme or ZymogensAn inactive 1. Acid ACP 3.1.3.2
and not of their absolute values phosphatase
- appear in serum after cellular injury, enzyme precursor 2. Aldolase ALD 4.1.2.13
degradation of cells or from storage Eg. Coagulation factors and 3. Alkaline ALP 3.1.3.1
areas Digestive enzymes phosphatase
4. Amylase AMS 3.2.1.1
- used clinically as evidence of organ 5. Alanine ALT 2.6.1.2
damage Classification & Nomenclature aminotransfera
- specific for a substrate that it converts Oxidoreductases se
to a defined product Catalyze redox rxn. between 2 6. Aspartate AST 2.6.1.1
aminotransfera
substrates se
Function A-+ B →A + B- 7. Aldolase ALD 4.1.2.13
i. Hydration of CO2 (respiration) – E.g: Dehydrogenase (LD) 8. Angiotensin ACE 3.4.15.1
converting
Carbonic Anhydrase enzyme
ii. Nerve induction –Choline Transferases 9. Creatine CK 2.7.3.2
acetyltransferase (Cholinergic enzymes) Catalyze the transfer of a group kinase
iii. Muscle contraction -AChE between 2 substrates (A-X+ B →A + B- 10. True / ACHE 3.1.1.7
Acetyl
iv. Nutrient degradation (digestion): X)
cholinesterase
Pepsin, Amylase, Lipase Eg: Transferase (ALT, AST, GGT), Kinase 11. PCHE 3.1.1.8
v. Growth and reproduction: Helicase Pseudocholines
Hydrolases terase
(Cell division) 12. Gamma GGT 2.3.2.2
vi. Energy storage and use: LDH, PPK1 & Catalyze hydrolysis of various bonds glutamyl
PPK2 (Conversion and conservation of A–B + H2O→A–OH+ B–H transferase
ATP) Eg: Amylase (AMY), Lipase(LPS), 13. Glucose-6- G-6-PD 1.1.1.49
Phosphatase (ACP) phosphate
dehydrogenase
A. Components of an Enzyme 14. Lactic LD 1.1.1.27
Active Site - cavity of an enzyme Lyases dehydrogenase
where substrates bind and undergo a Removal of groups from substrates 15. Leukocyte LAP 3.4.11.1
alkaline
chemical reaction without hydrolysis; product remain
phosphatase
double bonds ATP → cAMP + PPi 16. Lipase LPS 3.1.1.3
Allosteric Site - cavity other than the Fructose biphosphate aldolase (ALS) 17. 5’N 3.1.3.5
5’Nucleotidase
active site that binds regulatory
molecules . Isomerases
. Interconversion of geometric, optical,
B. Terms associated with an enzyme or positional isomersA →B
Substrates - substances acted upon by . Triphosphate isomerase (TPI)
enzymes .
Specific for their particular enzyme . Isomerases
. Interconversion of geometric, optical or
Cofactors - substance added in the positional isomersA →B
enzyme substrate complex to manifest . Triphosphate isomerase (TPI)
the enzyme activity .
a. Coenzyme or Prosthetic group . Ligases
Organic: Nucleotide (NADP) &Vitamins . Joins 2 substrate molecules, coupled
b. Activator Inorganic: Metal ion (Cl, with breaking of pyrophosphate bond
Mg, Cu) in ATPAb + C →A–C + b
. Glutathione Synthetase (GSH-S)
Isoenzyme - similar enzymatic activity .
but differ in physical, biochemical, and ENZYME NOMENCLATURE
immunologic characteristics. standardized by Enzyme Commission
(EC) in 1961 and revised in 1972 and
1978
You might also like
- Testbank 4e CH14Document19 pagesTestbank 4e CH14somasudeshna100% (5)
- Biochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismDocument6 pagesBiochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismSchat ZiNo ratings yet
- CC-LEC-NOTES-1Document4 pagesCC-LEC-NOTES-1CDNo ratings yet
- CCHM 312: Week 2: EnzymesDocument10 pagesCCHM 312: Week 2: EnzymesJanine Alicia VargasNo ratings yet
- CC Lab M1 7Document99 pagesCC Lab M1 7CDNo ratings yet
- MEDT 19 (Lec)Document17 pagesMEDT 19 (Lec)Erick PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 12 5 19Document113 pagesEnzymes 12 5 19Arshad Mehmood MinhasNo ratings yet
- Biochem Term 2Document28 pagesBiochem Term 2Michelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Proteins-Enzymes Part 1Document12 pagesCatalytic Proteins-Enzymes Part 1Mohammed HassounNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Kamisha L. Johnson-DavisDocument29 pagesEnzymes: Kamisha L. Johnson-DavisWho KnowsNo ratings yet
- Bisgop EnxymeDocument28 pagesBisgop EnxymefjkgldjfNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Document30 pagesBiological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Mohammed shaffiqueNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LectureDocument115 pagesEnzymes LectureJane Tai100% (1)
- EnzymologyDocument13 pagesEnzymologyRane MandapatNo ratings yet
- 6 EnzymesDocument3 pages6 EnzymesIYA LABAONo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument7 pagesEnzymesDANIKA JADE INFIESTONo ratings yet
- Unit 3 EnzymesDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Enzymeskamsjain6802No ratings yet
- $RLW3VJ1Document3 pages$RLW3VJ1Crow LordNo ratings yet
- Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDDocument46 pagesGly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDketakeeNo ratings yet
- Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDDocument46 pagesGly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDAlexander LotukhovNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesAstro KeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 2 ENZYMES. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry 2 ENZYMES. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGYBib imbapNo ratings yet
- Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman: Smt. Sharadchandrika Suresh Patil College of Pharmacy, Chopda, Maharashtra, IndiaDocument20 pagesDr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman: Smt. Sharadchandrika Suresh Patil College of Pharmacy, Chopda, Maharashtra, IndiaAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- C5 EnzymesDocument19 pagesC5 EnzymesSoraya D. Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry EnzymesDocument88 pagesBiochemistry EnzymesLama QaimariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - EnzymesDocument19 pagesLecture 3 - EnzymesEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- Michael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi - Bioprocess Engineering - Basic Concepts-Prentice Hall (2001) (077-113)Document37 pagesMichael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi - Bioprocess Engineering - Basic Concepts-Prentice Hall (2001) (077-113)Dome VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LEC Enzymes OutlineDocument6 pagesBiochemistry LEC Enzymes OutlineShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- 4A. Cellular RespirationDocument5 pages4A. Cellular RespirationIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Part 1Document5 pagesEnzymes Part 1Mar LagmayNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Enzymes Review NotesDocument4 pagesBiochemistry - Enzymes Review NotesKenneth100% (1)
- Biochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureDocument4 pagesBiochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureJohn Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- New EnzymesDocument64 pagesNew Enzymeslovi bahunNo ratings yet
- Biochem (Finals)Document5 pagesBiochem (Finals)cjyulo99710No ratings yet
- Enzymology To Kreb's CycleDocument34 pagesEnzymology To Kreb's Cycleferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- $RZ2YE8ODocument2 pages$RZ2YE8OCrow LordNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LectureDocument16 pagesEnzymes Lectureglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument52 pagesBiochem NotesAnonymous 4Ib1ByFC100% (2)
- Enzymes BN 2019Document67 pagesEnzymes BN 2019Rezan ThapaNo ratings yet
- 2C Enzyme SpecificityDocument8 pages2C Enzyme SpecificityqueyrhiaNo ratings yet
- 05 EnzymesDocument35 pages05 EnzymesFrances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - IntroDocument17 pagesEnzymes - IntroFatima MendozaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ShortDocument83 pagesEnzymes ShortWaleed ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Chem 113 - Week 2 - EnzymesDocument5 pagesChem 113 - Week 2 - EnzymesFormosa G.No ratings yet
- (Module) Lesson 4 Basic Concepts of Enzyme ActionDocument9 pages(Module) Lesson 4 Basic Concepts of Enzyme Actionkmiboy976No ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsAGENT M.DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesChapter 16 Cellular RespirationLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Reactions That Produce and Consume ATP - 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesGen Bio - Reactions That Produce and Consume ATP - 2nd QuarterChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Notes - SathyanarayanaDocument32 pagesEnzyme Notes - SathyanarayanaSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Semifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and VitaminsDocument4 pagesSemifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and Vitaminsino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Quiz Let 22Document3 pagesQuiz Let 22Hazel LopezNo ratings yet
- CHY 47 EnzymesDocument143 pagesCHY 47 EnzymesElle BuhisanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LectureDocument120 pagesEnzymes LectureHERSEY MIAYONo ratings yet
- EnzyDocument33 pagesEnzyPranaliNo ratings yet
- Enzyme 2016Document50 pagesEnzyme 2016igus696No ratings yet
- Food Chemistry - Activity 2Document3 pagesFood Chemistry - Activity 2Leda PeñaNo ratings yet
- (BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymesDocument9 pages(BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymeshellokrisjaejoongNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyDocument8 pagesEnzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyStefanie LucresiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Microbial MetabolismDocument48 pagesUnit 3 Microbial MetabolismNICOLE ANGELIQUE M. DINOYNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument16 pagesENZYMESWiza MulengaNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up: List Any Facts You Know About The Molecule ShownDocument30 pagesWarm-Up: List Any Facts You Know About The Molecule ShownZhiyong HuangNo ratings yet
- Product List Vet PDFDocument6 pagesProduct List Vet PDFNilamdeen Mohamed Zamil75% (4)
- S28JUNDocument4 pagesS28JUNTri CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4secondary Metabolites FinalDocument29 pagesChapter 4secondary Metabolites FinalDhruv KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 AnticholinesterasesDocument55 pages2 AnticholinesterasesSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Kimi FarmaceutikeDocument64 pagesKimi FarmaceutikeHabib Berisha100% (1)
- Biomolecules: Chemical Compounds of The Living SystemDocument89 pagesBiomolecules: Chemical Compounds of The Living SystemAriane DionisioNo ratings yet
- Esterification and ProductsDocument7 pagesEsterification and Productsdevraj raikarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Synthetic and Natural Organic PolymersDocument10 pagesChapter 25: Synthetic and Natural Organic PolymersChristian BareraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Notes ProteinsRegine Chua100% (1)
- Identification of PTH-Amino Acids by HPLC: Gregory A. Grant and Mark W. CrankshawDocument22 pagesIdentification of PTH-Amino Acids by HPLC: Gregory A. Grant and Mark W. CrankshawJe RivasNo ratings yet
- Fats & Oils IntroductionDocument12 pagesFats & Oils IntroductionShibbu GangwarNo ratings yet
- Acetophenone Uses: Acute EffectsDocument3 pagesAcetophenone Uses: Acute EffectsRahul JadhavNo ratings yet
- Daftar Dosis Dan Sediaan Obat AnakDocument5 pagesDaftar Dosis Dan Sediaan Obat AnakDaman Gregorius ManikNo ratings yet
- A Review On Finger Millet Properties, Processing, Health Benefits, and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesA Review On Finger Millet Properties, Processing, Health Benefits, and Applicationsjsbska88No ratings yet
- Pharam GuideDocument4,386 pagesPharam Guideابُوالبَتُول ڈاکٹر صفدر علی قادری رضوی100% (1)
- ShrinkageDocument2 pagesShrinkageAgusPurwantoNo ratings yet
- Alkane and CycloalkanesDocument59 pagesAlkane and CycloalkanesS JNo ratings yet
- Section B and C: Volume-02Document5 pagesSection B and C: Volume-02lovelylover_17No ratings yet
- MCQ Chapter 9 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesMCQ Chapter 9 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesNinaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Fix So Ranap Apr-Mei 2023Document432 pagesLaporan Fix So Ranap Apr-Mei 2023hefikurniasariNo ratings yet
- Word Sarcina TermicaDocument3 pagesWord Sarcina TermicaSergiu AlupoaeNo ratings yet
- AS LEVEL BIOLOGY Paper 1 EnzymesDocument54 pagesAS LEVEL BIOLOGY Paper 1 EnzymesADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- C34 Pepaña Drill2Document5 pagesC34 Pepaña Drill2Ruth Stephanie P. PepañaNo ratings yet
- Execises - Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 Part 1Document2 pagesExecises - Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 Part 1Michelle ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- MIMS PharCareDocument5 pagesMIMS PharCareKimgenesis TuazonNo ratings yet
- Pump Sizing Calculation (Photo)Document25 pagesPump Sizing Calculation (Photo)anto3harrish3fdoNo ratings yet
- Price List 09.08.2021Document7 pagesPrice List 09.08.2021A Abhishek Ludo KingNo ratings yet
- Wade 18 PowerpointDocument55 pagesWade 18 PowerpointIwanNo ratings yet