Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry
Uploaded by
shadnawazkhanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- How To Set Up An Electrolytic CellDocument6 pagesHow To Set Up An Electrolytic CellAngel LacabaNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFDocument513 pagesA Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFClive Doyce100% (2)
- SL Chemistry Ia 4Document12 pagesSL Chemistry Ia 4api-37363504650% (2)
- Introduction To ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Electrochemistryraimasharma024No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesElectrochemistryceeptreeNo ratings yet
- Proj - Electrolytic CellDocument19 pagesProj - Electrolytic CellGeetanjali YadavNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument8 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic and Kinetic Aspects: Electrochemistry: Electrochemical CellDocument23 pagesThermodynamic and Kinetic Aspects: Electrochemistry: Electrochemical CellBasetsana MohlalaNo ratings yet
- Tioluwani Body of WorkDocument34 pagesTioluwani Body of WorkAyoolamide BoluwatifeNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Chemistry ProjectDocument26 pagesClass 12th Chemistry ProjectAarush BansalNo ratings yet
- 1Document51 pages1Moh Makhbub AlyNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument7 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Art Integration ProjectDocument10 pagesChemistry Art Integration ProjectAnsh Taneja100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument9 pagesElectrochemistryFabian AvilaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Principles and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry Principles and ApplicationsnaztrltedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lectures Week 1 and 2Document6 pagesChemistry Lectures Week 1 and 2Bliven GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry File XIIDocument34 pagesChemistry File XIITushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument2 pagesElectrochemical CellsQ202No ratings yet
- DR - MPR - ElectrochemistryDocument25 pagesDR - MPR - ElectrochemistryRishan KundetyNo ratings yet
- Chem AlokDocument19 pagesChem AlokRiya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Electrochemistryshusantochaudhary2331No ratings yet
- Unit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotespvnchemNo ratings yet
- The Transformation of Chemical Energy Into Electrical EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Transformation of Chemical Energy Into Electrical EnergyYasmin RokeyaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell - Definition, Description, Types, ApplicationsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Cell - Definition, Description, Types, ApplicationsKimberly Camacho CatubigNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry-12 2 11Document49 pagesElectrochemistry-12 2 11Vic VickyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - THE THERMODYNAMICS OF ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS 2023Document35 pagesModule 4 - THE THERMODYNAMICS OF ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS 2023andreslloydralfNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument1 pageElectrolysiszainab.fatima1150No ratings yet
- Unit-3Electrochemistry 88896Document37 pagesUnit-3Electrochemistry 88896Dhatri SriramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 EDocument1 pageChapter 12 Ehingoronaeem0No ratings yet
- Unit 7Document53 pagesUnit 7tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 3Document7 pagesChemistry 3syed waseemNo ratings yet
- SESSION (2021-22) Class-Xii (Science) SUB-Chemistry CHAPTER-Electrochemistry Notes, Activities and Assignments (2021)Document7 pagesSESSION (2021-22) Class-Xii (Science) SUB-Chemistry CHAPTER-Electrochemistry Notes, Activities and Assignments (2021)Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Module 1Document35 pagesEngineering Chemistry Module 1Audrey MendozaNo ratings yet
- K. Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of TechnologyDocument48 pagesK. Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technologyfaten emadNo ratings yet
- CHM 409 - 0Document69 pagesCHM 409 - 0tolaniogunbode52No ratings yet
- MODULE 2 ElectrochemistryDocument31 pagesMODULE 2 ElectrochemistryChristian Mark De JesusNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical EnergyDocument16 pagesElectrochemical EnergyGlecie RasNo ratings yet
- What Are Redox Reactions?Document18 pagesWhat Are Redox Reactions?Mr. Zee KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Assays and Electrophoresis 2023 MLS201Document65 pagesElectrochemical Assays and Electrophoresis 2023 MLS201Aaliyah RamogopingNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesElectrochemistryYhamNo ratings yet
- A Substance or Chemical Constituent That Is Undergoing AnalysisDocument4 pagesA Substance or Chemical Constituent That Is Undergoing AnalysisAllan ReynaNo ratings yet
- Wa0017.Document10 pagesWa0017.mishikhan1402No ratings yet
- Learning Evidence Chemistry Stage 3Document8 pagesLearning Evidence Chemistry Stage 3Fernando CamachoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document31 pagesModule 4Pragati ShindeNo ratings yet
- Cell PotentialDocument5 pagesCell PotentialHassan AliNo ratings yet
- ELECTRO ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY - NotesDocument11 pagesELECTRO ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY - NotesLAKSHMI PRIYA R B.Tech CH 2020-2024No ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellDocument11 pagesElectrochemical CellssssNo ratings yet
- 0005unit V NotesDocument33 pages0005unit V Noteskishan kumarNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsDevendraa Muniandy100% (2)
- University of Kufa - College of Science - Electrochemical cell-محولDocument13 pagesUniversity of Kufa - College of Science - Electrochemical cell-محولSASA / GAMESNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument3 pagesTerm PaperJonie MatienzoNo ratings yet
- CW 36Document15 pagesCW 36lgguillen20No ratings yet
- Chapter 1electrochemistry 16thDocument92 pagesChapter 1electrochemistry 16thHiral KoriaNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument14 pagesAcknowledgementRohaan Mohammad100% (2)
- Exploring The Wonders of ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesExploring The Wonders of Electrochemistrytamimihsan2763No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry DMDNDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry DMDNYdyfr FsytNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument21 pagesElectrochemistryhuri4648No ratings yet
- Reduction Potential Oxidation Potential and Cell PotentialDocument19 pagesReduction Potential Oxidation Potential and Cell PotentialKeanne QuicoyNo ratings yet
- The Electrochemical CellDocument41 pagesThe Electrochemical CellRaveendra GundlapalliNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: ElectrologyDocument17 pagesElectrolysis: ElectrologyFrederic WustNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesPractice Problemsanon_915449609No ratings yet
- LAS With Lectures in Gen Chem 2 4th GP School FormatDocument10 pagesLAS With Lectures in Gen Chem 2 4th GP School FormatMelanie ArangelNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3Document16 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3Kingro SimNo ratings yet
- METHODSDocument4 pagesMETHODSMa. Ruffa Mae MejiaNo ratings yet
- SPM Pecutan Kimia Berfokus t5 Cohort 2021Document28 pagesSPM Pecutan Kimia Berfokus t5 Cohort 2021Wardati Najihah MohamedNo ratings yet
- ElectrodesDocument72 pagesElectrodesSathiya MurthiNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base and RedoxDocument53 pagesAcid and Base and RedoxH M AwaisNo ratings yet
- 11 ElectrochemistryDocument26 pages11 ElectrochemistryKEVIN PALMERONo ratings yet
- Electrode PotentialDocument22 pagesElectrode PotentialSURESHNo ratings yet
- Nernst EquationDocument7 pagesNernst Equationantony2288No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and Fuels RetestDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry and Fuels RetestCorey NNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - NotesDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry - Notesn611704No ratings yet
- Electrochemical TechniquesDocument35 pagesElectrochemical Techniquesfatema100% (1)
- ElectroChemistry Slides PDFDocument44 pagesElectroChemistry Slides PDFHenry OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 1Document7 pagesProblems Set 1Mirtunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument185 pagesChemistryAshutosh Shaw100% (1)
- Electrochemistry: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument79 pagesElectrochemistry: Larry Brown Tom HolmeJJJJJNo ratings yet
- PhyChem 2 Long Quiz 1 Study GuideDocument9 pagesPhyChem 2 Long Quiz 1 Study GuideKresley GamayNo ratings yet
- 2 - Principles of CorrosionDocument31 pages2 - Principles of CorrosionEngr. KafilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 5 Part 1Document63 pagesChemistry Unit 5 Part 1Will AndyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry JEE Main Practice SheetDocument19 pagesElectrochemistry JEE Main Practice Sheetabhishekam192007No ratings yet
- Electrode Potential, Ecell, Nernst Equation and EcsDocument8 pagesElectrode Potential, Ecell, Nernst Equation and Ecssasanka shawNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Measurement and Determination of PHDocument18 pagesPotentiometric Measurement and Determination of PHSubhodip DasNo ratings yet
- C - 17 Electrochemistry JEEDocument40 pagesC - 17 Electrochemistry JEEnottchurwaifuNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument8 pagesRedox ReactionsAbhayNo ratings yet
- DP Unit 9 & 19. Redox ProcessesDocument12 pagesDP Unit 9 & 19. Redox ProcessesdeaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Document17 pagesModule 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Hazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry
Uploaded by
shadnawazkhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry
Uploaded by
shadnawazkhanCopyright:
Available Formats
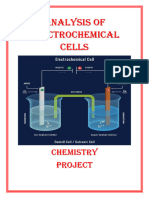
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the relationship
between electricity and chemical reactions. It involves the conversion of chemical energy
into electrical energy and vice versa. Key concepts in electrochemistry include:
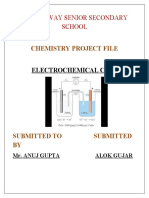
1. Electrochemical Cells:
An electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy
through redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions.
There are two main types of electrochemical cells: galvanic (voltaic) cells and electrolytic
cells.
Galvanic cells produce electrical energy from spontaneous redox reactions, generating a
voltage.
Electrolytic cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous redox reactions, often to
produce chemical changes or to facilitate electrolysis.
2. Redox Reactions:
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between reactants.
The species that loses electrons is oxidized, while the species that gains electrons is
reduced.
Redox reactions are essential in electrochemical processes, with oxidation occurring at
the anode and reduction occurring at the cathode.
3. Electrode Potentials:
Electrode potential is the measure of the tendency of an electrode to lose or gain
electrons.
Standard electrode potentials are determined relative to the standard hydrogen
electrode (SHE), which has an assigned potential of 0 volts.
The potential difference between two half-cells in an electrochemical cell determines the
cell voltage, also known as the electromotive force (EMF) or cell potential.
4. Electrolysis:
Electrolysis is the process of using electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous
chemical reaction.
It is commonly used to decompose compounds into their constituent elements or to
deposit metals onto electrodes.
Electrolysis plays a significant role in various industrial processes, including metal
refining and electroplating.
5. Applications:
Batteries: Electrochemistry is central to the functioning of batteries, which store and
release electrical energy through redox reactions.
Corrosion: Understanding electrochemical processes is crucial in studying and
preventing corrosion, which involves the degradation of materials due to
electrochemical reactions.
Sensors and Electrodes: Electrochemical sensors and electrodes are widely used in
analytical chemistry, environmental monitoring, and biomedical applications.
Overall, electrochemistry plays a vital role in various fields, including energy storage,
materials science, environmental protection, and medicine, making it a fundamental
area of study in chemistry and engineering.
You might also like
- How To Set Up An Electrolytic CellDocument6 pagesHow To Set Up An Electrolytic CellAngel LacabaNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFDocument513 pagesA Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFClive Doyce100% (2)
- SL Chemistry Ia 4Document12 pagesSL Chemistry Ia 4api-37363504650% (2)
- Introduction To ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Electrochemistryraimasharma024No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesElectrochemistryceeptreeNo ratings yet
- Proj - Electrolytic CellDocument19 pagesProj - Electrolytic CellGeetanjali YadavNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument8 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic and Kinetic Aspects: Electrochemistry: Electrochemical CellDocument23 pagesThermodynamic and Kinetic Aspects: Electrochemistry: Electrochemical CellBasetsana MohlalaNo ratings yet
- Tioluwani Body of WorkDocument34 pagesTioluwani Body of WorkAyoolamide BoluwatifeNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Chemistry ProjectDocument26 pagesClass 12th Chemistry ProjectAarush BansalNo ratings yet
- 1Document51 pages1Moh Makhbub AlyNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument7 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Art Integration ProjectDocument10 pagesChemistry Art Integration ProjectAnsh Taneja100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument9 pagesElectrochemistryFabian AvilaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Principles and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry Principles and ApplicationsnaztrltedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lectures Week 1 and 2Document6 pagesChemistry Lectures Week 1 and 2Bliven GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry File XIIDocument34 pagesChemistry File XIITushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument2 pagesElectrochemical CellsQ202No ratings yet
- DR - MPR - ElectrochemistryDocument25 pagesDR - MPR - ElectrochemistryRishan KundetyNo ratings yet
- Chem AlokDocument19 pagesChem AlokRiya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Electrochemistryshusantochaudhary2331No ratings yet
- Unit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotespvnchemNo ratings yet
- The Transformation of Chemical Energy Into Electrical EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Transformation of Chemical Energy Into Electrical EnergyYasmin RokeyaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell - Definition, Description, Types, ApplicationsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Cell - Definition, Description, Types, ApplicationsKimberly Camacho CatubigNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry-12 2 11Document49 pagesElectrochemistry-12 2 11Vic VickyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - THE THERMODYNAMICS OF ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS 2023Document35 pagesModule 4 - THE THERMODYNAMICS OF ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS 2023andreslloydralfNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument1 pageElectrolysiszainab.fatima1150No ratings yet
- Unit-3Electrochemistry 88896Document37 pagesUnit-3Electrochemistry 88896Dhatri SriramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 EDocument1 pageChapter 12 Ehingoronaeem0No ratings yet
- Unit 7Document53 pagesUnit 7tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 3Document7 pagesChemistry 3syed waseemNo ratings yet
- SESSION (2021-22) Class-Xii (Science) SUB-Chemistry CHAPTER-Electrochemistry Notes, Activities and Assignments (2021)Document7 pagesSESSION (2021-22) Class-Xii (Science) SUB-Chemistry CHAPTER-Electrochemistry Notes, Activities and Assignments (2021)Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Module 1Document35 pagesEngineering Chemistry Module 1Audrey MendozaNo ratings yet
- K. Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of TechnologyDocument48 pagesK. Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technologyfaten emadNo ratings yet
- CHM 409 - 0Document69 pagesCHM 409 - 0tolaniogunbode52No ratings yet
- MODULE 2 ElectrochemistryDocument31 pagesMODULE 2 ElectrochemistryChristian Mark De JesusNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical EnergyDocument16 pagesElectrochemical EnergyGlecie RasNo ratings yet
- What Are Redox Reactions?Document18 pagesWhat Are Redox Reactions?Mr. Zee KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Assays and Electrophoresis 2023 MLS201Document65 pagesElectrochemical Assays and Electrophoresis 2023 MLS201Aaliyah RamogopingNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesElectrochemistryYhamNo ratings yet
- A Substance or Chemical Constituent That Is Undergoing AnalysisDocument4 pagesA Substance or Chemical Constituent That Is Undergoing AnalysisAllan ReynaNo ratings yet
- Wa0017.Document10 pagesWa0017.mishikhan1402No ratings yet
- Learning Evidence Chemistry Stage 3Document8 pagesLearning Evidence Chemistry Stage 3Fernando CamachoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document31 pagesModule 4Pragati ShindeNo ratings yet
- Cell PotentialDocument5 pagesCell PotentialHassan AliNo ratings yet
- ELECTRO ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY - NotesDocument11 pagesELECTRO ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY - NotesLAKSHMI PRIYA R B.Tech CH 2020-2024No ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellDocument11 pagesElectrochemical CellssssNo ratings yet
- 0005unit V NotesDocument33 pages0005unit V Noteskishan kumarNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsDevendraa Muniandy100% (2)
- University of Kufa - College of Science - Electrochemical cell-محولDocument13 pagesUniversity of Kufa - College of Science - Electrochemical cell-محولSASA / GAMESNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument3 pagesTerm PaperJonie MatienzoNo ratings yet
- CW 36Document15 pagesCW 36lgguillen20No ratings yet
- Chapter 1electrochemistry 16thDocument92 pagesChapter 1electrochemistry 16thHiral KoriaNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument14 pagesAcknowledgementRohaan Mohammad100% (2)
- Exploring The Wonders of ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesExploring The Wonders of Electrochemistrytamimihsan2763No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry DMDNDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry DMDNYdyfr FsytNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument21 pagesElectrochemistryhuri4648No ratings yet
- Reduction Potential Oxidation Potential and Cell PotentialDocument19 pagesReduction Potential Oxidation Potential and Cell PotentialKeanne QuicoyNo ratings yet
- The Electrochemical CellDocument41 pagesThe Electrochemical CellRaveendra GundlapalliNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: ElectrologyDocument17 pagesElectrolysis: ElectrologyFrederic WustNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesPractice Problemsanon_915449609No ratings yet
- LAS With Lectures in Gen Chem 2 4th GP School FormatDocument10 pagesLAS With Lectures in Gen Chem 2 4th GP School FormatMelanie ArangelNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3Document16 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3Kingro SimNo ratings yet
- METHODSDocument4 pagesMETHODSMa. Ruffa Mae MejiaNo ratings yet
- SPM Pecutan Kimia Berfokus t5 Cohort 2021Document28 pagesSPM Pecutan Kimia Berfokus t5 Cohort 2021Wardati Najihah MohamedNo ratings yet
- ElectrodesDocument72 pagesElectrodesSathiya MurthiNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base and RedoxDocument53 pagesAcid and Base and RedoxH M AwaisNo ratings yet
- 11 ElectrochemistryDocument26 pages11 ElectrochemistryKEVIN PALMERONo ratings yet
- Electrode PotentialDocument22 pagesElectrode PotentialSURESHNo ratings yet
- Nernst EquationDocument7 pagesNernst Equationantony2288No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and Fuels RetestDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry and Fuels RetestCorey NNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - NotesDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry - Notesn611704No ratings yet
- Electrochemical TechniquesDocument35 pagesElectrochemical Techniquesfatema100% (1)
- ElectroChemistry Slides PDFDocument44 pagesElectroChemistry Slides PDFHenry OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 1Document7 pagesProblems Set 1Mirtunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument185 pagesChemistryAshutosh Shaw100% (1)
- Electrochemistry: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument79 pagesElectrochemistry: Larry Brown Tom HolmeJJJJJNo ratings yet
- PhyChem 2 Long Quiz 1 Study GuideDocument9 pagesPhyChem 2 Long Quiz 1 Study GuideKresley GamayNo ratings yet
- 2 - Principles of CorrosionDocument31 pages2 - Principles of CorrosionEngr. KafilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 5 Part 1Document63 pagesChemistry Unit 5 Part 1Will AndyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry JEE Main Practice SheetDocument19 pagesElectrochemistry JEE Main Practice Sheetabhishekam192007No ratings yet
- Electrode Potential, Ecell, Nernst Equation and EcsDocument8 pagesElectrode Potential, Ecell, Nernst Equation and Ecssasanka shawNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Measurement and Determination of PHDocument18 pagesPotentiometric Measurement and Determination of PHSubhodip DasNo ratings yet
- C - 17 Electrochemistry JEEDocument40 pagesC - 17 Electrochemistry JEEnottchurwaifuNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument8 pagesRedox ReactionsAbhayNo ratings yet
- DP Unit 9 & 19. Redox ProcessesDocument12 pagesDP Unit 9 & 19. Redox ProcessesdeaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Document17 pagesModule 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Hazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet