Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled 1
Untitled 1
Uploaded by
macy08027Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled 1
Untitled 1
Uploaded by
macy08027Copyright:
Available Formats
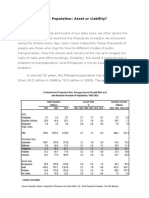
The Philippines has experienced a significant decline in its fertility rate, with the total fertility rate falling
from 2.7 children per woman in 2017 to 1.9 children per woman in 2022, according to the latest national
health demographic survey conducted by the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) 12. This decline is
attributed to various factors, including women's empowerment and easier access to family planning and
birth control. The cultural influence of Catholicism, which historically led to higher birthrates due to its
strictures against birth control and abortion, has been overshadowed by the country's economic
development.
Negative Impacts
The sharp decline in the birthrate could have several negative impacts on the country's future. One of the
most immediate concerns is the potential strain on the labor force and economic productivity. A shrinking
population could lead to a smaller workforce, which in turn could reduce the country's overall productivity
and economic growth. This could also lead to challenges in supporting an aging population, as there may
be fewer working-age individuals to support the elderly.
Positive Impacts
On the other hand, there are also potential positive effects of this demographic change. A lower birthrate
could lead to a reduction in the overall population growth rate, which could help alleviate some of the
pressures on the country's resources and infrastructure. It could also lead to improvements in the quality
of life for individuals, as there may be more resources available per capita. Additionally, a lower birthrate
could lead to improvements in women's health and empowerment, as women may have more control
over their reproductive choices and may be able to pursue education and career opportunities.
Broader Societal Implications
The decline in the birthrate could have several broader societal implications. For example, it could lead to
changes in the structure of the family, as there may be fewer children per family. This could also lead to
changes in the way that the government and other institutions provide support to families, as there may
be a greater emphasis on supporting smaller families. Additionally, the decline in the birthrate could lead
to changes in the country's political and social dynamics, as there may be shifts in the priorities and
needs of the population.
In conclusion, the sharp decline in the birthrate in the Philippines could have significant impacts on the
country's future. While there are potential negative effects, such as strain on the labor force and
economic productivity, there are also potential positive effects, such as reductions in population growth
and improvements in the quality of life. It will be important for the government and other institutions to
carefully consider the implications of this demographic change and to develop policies and programs that
can help the country adapt to these changes.
The Philippines has experienced a significant decline in its birthrate, with the fertility rate falling to 1.9
children per woman in 2022 from 2.7 children in 2017, marking the sharpest decline ever recorded12.
This trend is likely to have several implications for the country's future and broader society.
Impact on the Country's Future
The sharp decline in the birthrate is expected to have a profound impact on the country's future. One
immediate consequence is that the Philippines is now below the replacement fertility level of 2.1 children
per woman2. This means that the population may not be replaced at the current rate of reproduction,
which could lead to a shrinking and aging population in the long run. A shrinking population could have
various economic and social implications, including a smaller workforce, reduced consumer demand, and
increased fiscal pressure on the government to support an aging population.
Broader Societal Implications
The decline in the birthrate also has broader societal implications. One key implication is that it reflects
changing social and economic dynamics in the country. The drop in fertility is attributed to factors such as
women's empowerment, easier access to family planning, and the desire of many married women to
delay or forgo further childbirths12. This suggests that more women are pursuing education and careers,
and that families are increasingly prioritizing quality of life over quantity of children.
The decline in the birthrate may also have implications for the country's healthcare system. With fewer
births, there may be reduced demand for maternal and child health services, as well as for pediatric care
and education. At the same time, an aging population may place greater demand on healthcare services
for the elderly, including long-term care and treatment for age-related illnesses.
From a cultural and social perspective, the decline in the birthrate may lead to changes in family
structures and dynamics. With smaller families becoming more common, there may be a shift in the
traditional roles and responsibilities of family members. For example, there may be greater emphasis on
the care of elderly relatives, as well as on the role of women in the workforce and society more broadly.
In conclusion, the sharp decline in the birthrate in the Philippines is likely to have far-reaching
implications for the country's future and broader society. While the full extent of these implications
remains to be seen, it is clear that the trend reflects significant social, economic, and cultural changes in
the country.
The sharp decline in the birthrate in the Philippines is expected to have both positive and negative effects
on the country.
Positive Effects
Economic Opportunities: A lower birthrate can lead to a demographic dividend, where a larger proportion
of the population is in the working-age group, potentially leading to increased productivity and economic
growth.
Reduced Pressure on Resources: A lower birthrate can reduce the strain on natural resources,
infrastructure, and social services, leading to improved living standards for the population.
Women's Empowerment: The decline in birthrate may reflect greater access to education and
employment for women, leading to improved gender equality and women's empowerment.
Negative Effects
Aging Population: A lower birthrate can lead to an aging population, which may strain healthcare and
social security systems and reduce the size of the workforce2.
Economic Challenges: A shrinking working-age population and lower productivity can negatively affect
government tax revenue and create a fiscal burden, potentially leading to economic challenges2.
Social Implications: A lower birthrate can lead to changes in family structures and dynamics, potentially
impacting social norms and support systems3.
In conclusion, while a decline in the birthrate can bring about positive changes such as economic
opportunities and women's empowerment, it also poses challenges such as an aging population and
potential economic and social implications. It will be important for the government to carefully consider
and plan for the long-term effects of this demographic change.
You might also like
- Abortion - Final PaperDocument6 pagesAbortion - Final PaperShaad Kamrudeen100% (3)
- R633199 PDFDocument1 pageR633199 PDFChirag RohitNo ratings yet
- Legalizing Male Sterilization in MyanmarDocument16 pagesLegalizing Male Sterilization in MyanmarHla Myat TunNo ratings yet
- Threats To PPMPDocument5 pagesThreats To PPMPcruellaNo ratings yet
- Demographic DividendDocument38 pagesDemographic Dividendsaumyavermaa010No ratings yet
- Children - A Luxury?Document4 pagesChildren - A Luxury?jjnaseemNo ratings yet
- Old Population (C, E, S)Document2 pagesOld Population (C, E, S)Anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- ECONDocument4 pagesECONAnna ReyesNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument3 pagesFamily PlanningHanifah WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- GPAD3024 Final ProjectDocument8 pagesGPAD3024 Final ProjectiONo ratings yet
- Assigment 6573-WPS OfficeDocument23 pagesAssigment 6573-WPS OfficeTehmina HanifNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast The Population Dynamic of HICs and LICsDocument9 pagesCompare and Contrast The Population Dynamic of HICs and LICsMegharashi Rimjhim100% (1)
- Untitled DocumentDocument14 pagesUntitled Documentdua latifNo ratings yet
- Factors of Population GrowthDocument3 pagesFactors of Population GrowthSyed Hassan Raza JafryNo ratings yet
- Bus Log - 7 WhysDocument4 pagesBus Log - 7 WhysGrace CiervoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper in PovertyDocument7 pagesResearch Paper in Povertyc9kb0eszNo ratings yet
- First Draft Persuasive Writing CommentedDocument4 pagesFirst Draft Persuasive Writing CommentedMAURICIO MOLINANo ratings yet
- Population ProblemDocument5 pagesPopulation ProblemElijah MendozaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper On ChildlessnessDocument2 pagesReaction Paper On ChildlessnessAprilJoyBascosNo ratings yet
- Poverty: Eric Jason S. Diones Allyn Mae Calantas Nickle HurtadaDocument24 pagesPoverty: Eric Jason S. Diones Allyn Mae Calantas Nickle HurtadaAllyn CalantasNo ratings yet
- Alawan-ABE 159-DiscussionDocument6 pagesAlawan-ABE 159-DiscussionNathalia AlawanNo ratings yet
- When A Person or A FamilyDocument2 pagesWhen A Person or A Familyaubrey ledesmaNo ratings yet
- Philippines Undergone Demographic TransitionDocument3 pagesPhilippines Undergone Demographic TransitionNEBRIAGA, MARY S. 3-2No ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument2 pagesEconomicsTrixia Marrie RoblonNo ratings yet
- Global DemogrphyDocument6 pagesGlobal DemogrphyPring MayNo ratings yet
- Poverty and Inequality - Trixie TorresDocument5 pagesPoverty and Inequality - Trixie TorresTrixie Mendoza TorresNo ratings yet
- JosephDocument4 pagesJosephAtom GutomNo ratings yet
- Population PoliciesDocument7 pagesPopulation PoliciescruellaNo ratings yet
- New Financial Products For An Aging PopulationDocument16 pagesNew Financial Products For An Aging PopulationsaminbdNo ratings yet
- The Rampant Case of Unemployment in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesThe Rampant Case of Unemployment in The PhilippinesTomas DocaNo ratings yet
- DDDDDocument3 pagesDDDDmihir_mhkNo ratings yet
- Gelect EssayDocument2 pagesGelect EssayhavanaohvannaNo ratings yet
- Bloom e CanningDocument7 pagesBloom e Canninghel-lopesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4204Document35 pagesAssignment 4204Borshon KhanNo ratings yet
- Development Economics Chapter 2Document1 pageDevelopment Economics Chapter 2ZohaibNo ratings yet
- Problems in and Obstacles To Economic DevelopmentDocument3 pagesProblems in and Obstacles To Economic DevelopmentRomerson TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Declining Birth Rate in Developed Countries - A Radical Policy Re-Think Is RequiredDocument3 pagesDeclining Birth Rate in Developed Countries - A Radical Policy Re-Think Is RequiredxeeshannasirNo ratings yet
- TCW ActivityDocument1 pageTCW Activity2057096No ratings yet
- Focusing On HealthDocument3 pagesFocusing On HealthNiranjana HariNo ratings yet
- The Impact of The Economic Crisis On Girls and Young Women. A Review of The EvidenceDocument52 pagesThe Impact of The Economic Crisis On Girls and Young Women. A Review of The EvidenceJose Carbonell SanchezNo ratings yet
- Social PsychologyDocument2 pagesSocial Psychologyjessie james hijosNo ratings yet
- RAMISCAL-ST. MARGARET-Teenage PregnancyDocument2 pagesRAMISCAL-ST. MARGARET-Teenage PregnancyArfiele ramiscalNo ratings yet
- Poverty in PakistanDocument36 pagesPoverty in PakistanNelum Shehzade100% (1)
- Demographic DividendDocument2 pagesDemographic Dividendaddy1920No ratings yet
- An Insight On Poverty Reduction and Health Inequalities in The Philippines: Social Determinants, Constraints, and OpportunitiesDocument84 pagesAn Insight On Poverty Reduction and Health Inequalities in The Philippines: Social Determinants, Constraints, and OpportunitiesJohn Vincent Pagaddu100% (1)
- Economic Development ReportDocument10 pagesEconomic Development ReportKiran RaniNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL PERSPECTIVES Final RevisionDocument25 pagesGLOBAL PERSPECTIVES Final RevisionApparatus BoxNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Population Growth LectureDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting Population Growth LectureMuhammad AlamNo ratings yet
- Poverty EssayDocument1 pagePoverty EssaySon SonNo ratings yet
- CSS Essays PDFDocument25 pagesCSS Essays PDFAr NaseemNo ratings yet
- Effects of Population Growth On The Economic DevelopmentDocument20 pagesEffects of Population Growth On The Economic DevelopmentAMIT K SINGH100% (1)
- Gabriel-Lesson 2 - Activity 2.1 and Post-AssessmentDocument4 pagesGabriel-Lesson 2 - Activity 2.1 and Post-AssessmentLucille May GabrielNo ratings yet
- Poverty AlleviationDocument5 pagesPoverty AlleviationWaqas HabibNo ratings yet
- Ge3 Act9Document1 pageGe3 Act9clarencemagbanua2020No ratings yet
- BT TACN Week 3Document7 pagesBT TACN Week 3Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Preventing Unplanned Pregnancy 2Document36 pagesPreventing Unplanned Pregnancy 2Jhon Malo PeñaNo ratings yet
- Why You Are PoorDocument32 pagesWhy You Are PoorGuilherme MatheusNo ratings yet
- The Difficulties and Implications of Teenage Pregnancy To The Teen Age Filipino Mothers - Topic Matrix - Performance Task # 1Document5 pagesThe Difficulties and Implications of Teenage Pregnancy To The Teen Age Filipino Mothers - Topic Matrix - Performance Task # 1Maia Isabelle GuintoNo ratings yet
- Population IssuesDocument17 pagesPopulation IssuesDennis RañonNo ratings yet
- Poverty Measuring AntiPoverty Policies and The Relationship of Philippine Economy To Social InequalityDocument10 pagesPoverty Measuring AntiPoverty Policies and The Relationship of Philippine Economy To Social InequalityArrabella A. De MesaNo ratings yet
- Human CapitalDocument6 pagesHuman CapitalHARVY DAVIS CHUANo ratings yet
- Omron User ManualDocument16 pagesOmron User ManualcamonteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Reproductive HealthDocument53 pagesChapter 4 Reproductive HealthGyanendra Vikram MauryaNo ratings yet
- ContemporaryAgriculture, Vol. 62, No. 1-2, 2013.Document139 pagesContemporaryAgriculture, Vol. 62, No. 1-2, 2013.Бојана АндрићNo ratings yet
- Manji Yamada V/s Union of India (UOI) and Anr.Document6 pagesManji Yamada V/s Union of India (UOI) and Anr.DimpleChainaniNo ratings yet
- FertilityDocument38 pagesFertilityCamilla Patricia Mayugba WoolfNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 Hormones and Infertility LectureDocument48 pagesLecture 20 Hormones and Infertility LectureJoseph Stans KasiryeNo ratings yet
- FemaraDocument2 pagesFemaraMyraIntisarNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Unsafe Abortion and Postabortion Care - An OverviewDocument9 pages2011 - Unsafe Abortion and Postabortion Care - An OverviewJeremiah WestNo ratings yet
- Male SterilizationDocument19 pagesMale SterilizationEggyDsNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Through The Life Cycle 5th Edition Brown Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesNutrition Through The Life Cycle 5th Edition Brown Solutions Manualwonders.stufferlx27100% (29)
- Methods of Computing Vital StatisticsDocument38 pagesMethods of Computing Vital Statisticsvaishali TMU studentNo ratings yet
- Setting Up of IUI LabDocument23 pagesSetting Up of IUI LabSuryakant Hayatnagarkar90% (10)
- Procedure: in Vitro Fertilization (Ivf)Document7 pagesProcedure: in Vitro Fertilization (Ivf)Lovely SarangiNo ratings yet
- Mysteries Magazine U882Document41 pagesMysteries Magazine U882olav4407No ratings yet
- Acute Biologic Crisis QuizDocument1 pageAcute Biologic Crisis Quiznurse_maeNo ratings yet
- Natural Fertility GuideDocument29 pagesNatural Fertility GuideGabi100% (1)
- English Pil KBDocument4 pagesEnglish Pil KBNINING ARIESTINo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 HukKes KKIDocument12 pagesTugas 2 HukKes KKINikolasKosasihNo ratings yet
- OB Clinic ProposalDocument8 pagesOB Clinic ProposalAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- The Ultra So No Graphic Diagnosis of Pregnancy in The Dog and Cat NotesDocument8 pagesThe Ultra So No Graphic Diagnosis of Pregnancy in The Dog and Cat NotesAnur SinglaNo ratings yet
- Time Lapse PDFDocument18 pagesTime Lapse PDFFedrik Monte Kristo LimbongNo ratings yet
- KULIAH 4 - Siklus MenstruasiDocument15 pagesKULIAH 4 - Siklus MenstruasigahanNo ratings yet
- Normal LaborDocument8 pagesNormal LaborNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Ever Link Fertility Centre Brochure Translation - Lee Yoong ShinDocument13 pagesEver Link Fertility Centre Brochure Translation - Lee Yoong ShinYoong Shin LeeNo ratings yet
- Demographic Sweet Spot and Dividend in The Philippines - FINAL - DRAFT - Ver4 - OCT2015-Withcover - 0Document34 pagesDemographic Sweet Spot and Dividend in The Philippines - FINAL - DRAFT - Ver4 - OCT2015-Withcover - 0SANTOS, James Harry H.No ratings yet
- ListDocument3 pagesListFotos SotofNo ratings yet
- Definition of Family PlanningDocument4 pagesDefinition of Family PlanningKathryn Arianne CastilloNo ratings yet