Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Passing Physics
Science Passing Physics
Uploaded by
revathishetty340Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Abc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesFrom EverandAbc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesWürth ElektronikNo ratings yet
- Experiment Details Physics (Class 10)Document13 pagesExperiment Details Physics (Class 10)8311 Mirza Muhammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- PS12 Week3 Las1Document2 pagesPS12 Week3 Las1Jeffry Centeno PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Activity - 24-25 DAVCPSDocument12 pagesActivity - 24-25 DAVCPSAnujNo ratings yet
- Phy Rev MaterialDocument15 pagesPhy Rev Materiald.tharun37No ratings yet
- Part 2 2nd PU GBJCDocument94 pagesPart 2 2nd PU GBJCJhenkarNo ratings yet
- Must Revision Topics (From Board Analysis) : Book 2 Chap 9Document2 pagesMust Revision Topics (From Board Analysis) : Book 2 Chap 9Harsh SolankiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Important Question Xiith PhysicsDocument5 pagesChapter Wise Important Question Xiith PhysicsTamanna SahuNo ratings yet
- Summer Holiday Homework - 22Document19 pagesSummer Holiday Homework - 22Ananya DashNo ratings yet
- Important Derivations 12 PhysicsDocument6 pagesImportant Derivations 12 PhysicsSanjay Kumar SheoranNo ratings yet
- Physics 25 Days Schedule 1Document3 pagesPhysics 25 Days Schedule 1anandiangel123No ratings yet
- EPHY105L LabManualDocument49 pagesEPHY105L LabManualaryanNo ratings yet
- SR Physics Fast LearnerDocument7 pagesSR Physics Fast LearnerShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Class 10thDocument3 pagesRevision Worksheet Class 10thSamarth KhatorNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 2024-25Document22 pagesPhysics Assignment 2024-25mandaarapucollege123No ratings yet
- SECOND For UkDocument8 pagesSECOND For UkyellaiahNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument4 pagesLAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightJose RizalNo ratings yet
- Physics 2nd Yr BDocument3 pagesPhysics 2nd Yr BShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Important Questions XII PHYSICSDocument8 pagesChapter Wise Important Questions XII PHYSICSsavitridevi9668No ratings yet
- PhysicsX PDFDocument124 pagesPhysicsX PDFcitsNo ratings yet
- Resistance and TemperatureDocument11 pagesResistance and TemperatureUkoima Kelvin NkaloNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - Physics: Other Educational PortalsDocument7 pagesSample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - Physics: Other Educational PortalsSourabh SirradhanaNo ratings yet
- 2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan RasheedDocument73 pages2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan RasheedAmroz AfzalNo ratings yet
- Xii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseDocument4 pagesXii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseSharulathaNo ratings yet
- Physics II Year - 121754Document5 pagesPhysics II Year - 121754Quran The MercyNo ratings yet
- Archivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavDocument8 pagesArchivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavChess ManNo ratings yet
- Imp. Derivations For XII PhysicsDocument3 pagesImp. Derivations For XII PhysicsJethiya SyckoNo ratings yet
- The Impedance Plane and Probes PDFDocument2 pagesThe Impedance Plane and Probes PDFanas dwiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-IInd YEAR (Board List)Document2 pagesPHYSICS-IInd YEAR (Board List)cherukunavaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics (Theory)Document20 pagesRay Optics (Theory)Kumar Rohit100% (1)
- CLASS X PHYSICS chapter 2 CONTENTDocument10 pagesCLASS X PHYSICS chapter 2 CONTENTmishalrayna2712No ratings yet
- Physics-2 Practical HandoutDocument82 pagesPhysics-2 Practical Handoutملهم الخصيبيNo ratings yet
- Light-STD X-PHY NOTESDocument15 pagesLight-STD X-PHY NOTESFakhruddin PocketwalaNo ratings yet
- Geometric OpticsDocument34 pagesGeometric OpticsLadymie MantoNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics - ManualDocument9 pagesGeometrical Optics - ManualfarehaNo ratings yet
- 12 Optics AssignmentDocument4 pages12 Optics AssignmentKeerthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument1 pagePHYSICSMun AhmedNo ratings yet
- SSLC Phy Viq24Document12 pagesSSLC Phy Viq24jyothibhovi29No ratings yet
- Re Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesRe Exam Questionsabuthahir1.mcaNo ratings yet
- WorkSheet PHYSICS 2287docDocument3 pagesWorkSheet PHYSICS 2287docKshitij BichaveNo ratings yet
- Physics Important Derivations QuestionDocument3 pagesPhysics Important Derivations QuestionsumitNo ratings yet
- 102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionDocument9 pages102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments: Chapter NineDocument42 pagesRay Optics and Optical Instruments: Chapter NineAsh LeyNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument11 pagesRay OpticsTatvamasiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Phy Imp QuestionsDocument5 pagesClass 12 Phy Imp Questionsrajeshsharma4121No ratings yet
- Lab ActivityDocument9 pagesLab ActivityAnvi MantriNo ratings yet
- Vol. 5 No. 1 JUNE 2019 11Document12 pagesVol. 5 No. 1 JUNE 2019 11João TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- SR Physics IPE Imp QuestionsDocument6 pagesSR Physics IPE Imp QuestionsHemanth MindhiNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics NCERTDocument42 pagesRay Optics NCERTsohamNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter LightDocument25 pagesPhysics Chapter LightNurliyana Zairul AfendiNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions 2023 XiiDocument4 pagesFrequently Asked Questions 2023 XiiBala MugeshNo ratings yet
- Phy Set-6Document4 pagesPhy Set-6Saeeda IftikharNo ratings yet
- Optics Sena PeoblemsDocument11 pagesOptics Sena PeoblemsAndre Aleksandrov CherenkovskiNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics English Theory HvxcmX8Document67 pagesGeometrical Optics English Theory HvxcmX8Emad ElsehlyNo ratings yet
- TWOTERMDocument3 pagesTWOTERMnavyashreehegde28No ratings yet
- Efek Pockel p5451 - e PDFDocument4 pagesEfek Pockel p5451 - e PDFBayuPermanagagNo ratings yet
- T LensDocument8 pagesT LensGan Hock KiamNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument26 pagesImportant QuestionsAyush TomarNo ratings yet
- 01ADMModule - S11 12PS IIIa 1 EDITED LatestDocument40 pages01ADMModule - S11 12PS IIIa 1 EDITED LatestDharyn CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Nuclei: One Mark QuestionsDocument8 pagesNuclei: One Mark QuestionsBrittany GreenNo ratings yet
- SAP Exercises 4 2018 CommentedDocument3 pagesSAP Exercises 4 2018 CommentedIgnacio Fernandez GrañaNo ratings yet
- Direct Nuclear Reactions and Compound Nucleus ReactionsDocument5 pagesDirect Nuclear Reactions and Compound Nucleus ReactionsKishore GujjarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Neutron Physics: Carlo CazzanigaDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Neutron Physics: Carlo CazzanigaRiska MulyaniNo ratings yet
- (Ronald A. Knief) - Nuclear Reactor Theory (Booklet)Document19 pages(Ronald A. Knief) - Nuclear Reactor Theory (Booklet)sina sanatiNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question Bank-6Document34 pagesPhysics: Question Bank-6MUSIC WORLDNo ratings yet
- Gacan Qabad Chemistry Book With AnswersDocument32 pagesGacan Qabad Chemistry Book With Answerscazmi Andirahman100% (1)
- Shs Daily Lesson Log Physical ScienceDocument33 pagesShs Daily Lesson Log Physical ScienceJaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- Major 09Document48 pagesMajor 09Vipranshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Nuclear - Physics - WebquestDocument6 pagesChemistry - Nuclear - Physics - Webquesto18.makiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Cie Nuclear MCQ 1,2Document14 pagesIGCSE Cie Nuclear MCQ 1,2Payail Parineeta PalNo ratings yet
- Che 131 Final Study GuideDocument23 pagesChe 131 Final Study GuideVictoria SteinbergNo ratings yet
- Basic Radiation Physics: This Set of 194 Slides Is Based On Chapter 1 Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA PublicationDocument97 pagesBasic Radiation Physics: This Set of 194 Slides Is Based On Chapter 1 Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA PublicationStephen AveryNo ratings yet
- 4-Electric Power GenerationDocument31 pages4-Electric Power GenerationCaribNo ratings yet
- Ford f150 2015 Electrical Wiring DiagramsDocument22 pagesFord f150 2015 Electrical Wiring Diagramsshaunthomas011196cbg100% (76)
- MathematicalDocument31 pagesMathematicalmohammed1998No ratings yet
- Physics Capsule Watermark (1) .PDF 22Document12 pagesPhysics Capsule Watermark (1) .PDF 22ChandreshDharDubeyNo ratings yet
- Trs468 WebDocument279 pagesTrs468 WebВладимир ФроловNo ratings yet
- Particle QuestionsDocument14 pagesParticle QuestionsSaginskyNo ratings yet
- SL Paper1Document21 pagesSL Paper1Patrick PrakasaNo ratings yet
- Quipper Lecture Physical ScienceDocument279 pagesQuipper Lecture Physical ScienceLoren Marie Lemana AceboNo ratings yet
- Makalah FismodDocument19 pagesMakalah FismodRirinNo ratings yet
- Nucleus (Stability and Reaction) : Nuclear ChemistryDocument22 pagesNucleus (Stability and Reaction) : Nuclear ChemistryANSHUNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Physics Paper-1 Question Paper Solutions 2018Document14 pagesICSE Class 10 Physics Paper-1 Question Paper Solutions 2018Venu MaheshNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactions LecDocument32 pagesNuclear Reactions Lecjon alex100% (1)
- FT - HR: G V 15 Knots V 15 Knots West GDocument11 pagesFT - HR: G V 15 Knots V 15 Knots West Gtsania nkdNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission Vs Nuclear FusionDocument17 pagesNuclear Fission Vs Nuclear FusionJinky Marie Abunan100% (1)
- The Los Alamos ProjectDocument16 pagesThe Los Alamos ProjectDavid MolinattoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument25 pagesNuclear ChemistryLeeza Servidad100% (1)
Science Passing Physics
Science Passing Physics
Uploaded by
revathishetty340Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Passing Physics
Science Passing Physics
Uploaded by
revathishetty340Copyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE PASSING PACKAGE
PHYSICS
3 MARKS RAY DIAGRAM
1 Draw the ray diagram for the image formation by a convex lens, when
the object is placed at 2F1. With the help of the ray diagram mention
the position and the nature of the image formed.
2 Draw the ray diagram for the image formation in a convex lens when
the object is placed beyond 2F1 . With the help of the ray diagram
mention the position and the nature of the image formed.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 1
3 Draw the ray diagram when the object is kept between F1 and 2F1 of
the convex lens. With the help of the diagram mention the position
and nature of the image formed.
4 Draw the ray diagrams for the image formation in a convex lens when
an object is placed at focus F1
5 Draw the ray diagram when the object is kept between F1 and O
(optical centre) of the convex lens. With the help of the diagram
mention the position and nature of the image formed.
Position of the image : same side of the object
Nature of the image : virtual and erect
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 2
6 Draw the ray diagram for the image formation in a concave lens when
the object is placed between F1 and 2F1.
7 Draw the ray diagram of image formation when the object is kept
between C and F of the concave mirror. With the help of the ray
diagram mention the position and the nature of the image formed.
8 Draw the ray diagram of image formation when the object is kept at C
of the concave mirror. With the help of the ray diagram mention the
position and the nature of the image formed.
position : at C
Nature of the Image : Real and inverted
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 3
9 Draw the ray diagram of image formation when the object is kept
beyond C of the concave mirror. With the help of the ray diagram
mention the position and the nature of the image formed.
10 Draw the ray diagram of image formation when the object is kept at F
of the concave mirror. With the help of the ray diagram mention the
position and the nature of the image formed.
11 A SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF AN ELECTRIC CIRCUIT.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 4
12 S.N Component Circuit symbol
1 an electric cell
a battery or a
2
combination of cells
3 plug key or switch (open)
plug key or switch
4
(closed)
5 a wire joint
wires crossing without
6
joining
7 electric bulb
8 a resistor
variable resistance or
9
rheostat
10 Ammeter / Voltmeter
/
13 RESISTORS IN SERIES
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 5
14 RESISTOR IN PARALLEL
15 Electric circuit for studying Ohm’s law
16 Draw the diagram of a simple electric generator.
Label the following parts: i) Brushes ii) Rings.
17 DRAW THE DIAGRAM OF A SIMPLE ELECTRIC MOTOR.
LABEL THE FOLLOWING PARTS : (I) BRUSHES (II) BATTERY.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 6
18 The field lines of a magnetic field around a straight conducting wire.
The arrows in the circles show the direction of the field lines.
19 Draw the diagram to represent the recombination of the spectrum of
white light.
20 Draw a neat diagram of bio gas plant and label the parts.
21 Draw the diagram of myopic eye and its correction.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 7
22 Draw the diagram of hypermetric eye and its corrections.
IMPORTANT LAWS
23 State Ohm’s law?
Potential difference across the ends of a metallic conductor is
directly proportional to current passing through the circuit
provided that temperature remains same.
24 State Joule’s law of heating.
The heat produced in a resistor is
i) directly proportional to the square of current for a given resistance
ii) directly proportional to the resistance for a given current
iii) directly proportional to the time for which the current flows through the
resistor. H = I2Rt
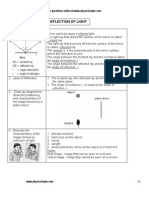
25 State the law of reflection.
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray, all lie in the
same plane.
26 State the law of refraction.
The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal all lie in the
same plane.
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of
refraction is a constant.
27 State Snell’s law of refraction.
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of
refraction is a constant for the given color and media.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 8
IMPORTANT RULE
28 Explain the right hand thumb rule?
Hold a current carrying straight conductor in a right hand such that the
thumb shows the direction of current and wrapped fingers shows the
direction of magnetic field lines.
29 State Fleming’s left hand rule? ( State Motor rule)
Stretch the thumb, fore finger and middle finger of left hand at right
angle.
fore finger indicates magnetic field,
Middle finger indicates direction of current
Thumb will point the direction of motion.
30 State Fleming’s right hand rule? (GENERATOR RULE)
Stretch the thumb, fore finger and middle finger of right hand at right
angle.
fore finger Indicates magnetic field,
thumb shows the direction of motion of The conductor
Middle finger shows the direction of Induced current.
IMPORTANT S.I UNITS
31 Electric Current Ampere
Charge Coulomb
Potential difference Volt
Resistance Ohm
Resistivity Ohm meter
Power Watt
Commercial unit of power Kilowatt hour Or unit
Power of lens dioptre
IMPORTANT DEVICES AND ITS FUNCTION
32 Ammeter: Ammeter measures electric current in a circuit.
Connection: It is always connected in series.
33 Voltmeter: The voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference.
Connection: The voltmeter is always connected in parallel.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 9
34 Variable resistance: It is used to regulate current without changing the
voltage.
35 Rheostat: It is used to change the resistance in the circuit.
36 Fuse : It protects circuits and appliances by stopping the flow Of
any unduly high electric current
Connection: the fuse is connected in series.
37 Commutator: A device that reverses the direction of flow of current
through a circuit
38 Split rings : it reverses the direction of flow of current through a circuit
39 Galvanometer: it is used to detect the presence of current.
40 Motor: it converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
41 Generator: it converts mechanical energy to electrical energy.
42 Earth wire: This is used as a safety measure for appliances have a metallic
body in domestic circuit.
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS
43 What is the meaning of the statement “The potential difference
between two points is 1 V”.
1 Volt =
44 Define Ohm.
1 ohm =
45 Define watt.
46 Define I ampere.
1Amphere =
47 Define 1 Dioptre.
The power of lens is I dioptre when its focal length is 1m.
IMPORTANT TERMS RELATED TO MIRROR
48 focal length The distance between the centre of mirror and
the principal focus.
Aperture The diameter of the spherical mirror is called
aperture.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 10
Principle focus The point on principal axis at which the parallel
rays after reflection actually meets.
Pole The centre of the reflecting surface of the mirror is
called pole.
centre of The Centre of the reflecting surface of a
curvature spherical mirror.
radius of The radius of the sphere of which the reflecting
curvature surface of a spherical mirror forms a part.
Principal axis A straight line passing through the pole and the
centre of curvature of a spherical mirror
IMPORTANT TERMS RELATED TO LENS
49 principal focus The point on principal axis at which the parallel
rays after refraction actually meets.
Optic centre The central point of a lens is called optical centre.
principal axis An imaginary straight line passing through the two centres
of curvature of a lens is called its principal axis
50 WRITE THE FUNCTIONS OF PARTS OF HUMAN EYES.
N Parts Function
1 Retina The part of eye where the image is formed.
2 Cornea Part of eye where the light rays get refracted.
3 Crystalline Focuses the light that enters the eye .
lens
4 Iris Irish controls the size of the pupil.
5 Pupil It controls the amount of light entering into the eye.
6 Optic nerves The signals are sent to the brain via optic nerves.
7 Ciliary It helps in the adjustment of its focal length.
muscles
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 11
HUMAN EYE DISORDERS
51 What is myopia (near-sigtness)? Write causes and remedies for myopia.
A person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects
distinctly.
Causes (reason)
excessive curvature of the eye lens
Elongation of the eyeball.
Remedies.
using a concave lens of suitable power
52 What is Hypermetropia(far-sightedness)Write its causes and remidies.
A person can see distant objects clearly but cannot see nearby objects
distinctly.
Causes (reason)
the focal length of the eye lens is too long,
The eyeball has become too small.
Remedies.
using a convex lens of appropriate power.
89 What is presbyopia? Write its causes and remedies?
The power of accommodation of the eye usually decreases with ageing.
Causes (reason)
Diminishing flexibility of the eye lens.
Gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles
Remedies.
Using bi-focal lenses consists of both concave and convex lenses.
53 What is cataract? Write its effects and Remedies?
The crystalline lens of people at old age becomes milky and cloudy. This
condition is called cataract.
This causes partial or complete loss of vision.
It is possible to restore vision through a cataract surgery.
NATURAL PHENOMENON
54 What is dispersion of light?
The splitting of light into its component colours is called dispersion.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 12
55 Name the colour that bends the least and the colour that bends the
most when white light is dispersed by a prism
Red colour bends the least and Violet colour bends the most
56 Explain the formation of the rainbow:
The water droplets act like small prisms
They refract and disperse the incident sunlight
Then reflect internally
Finally refract again while coming out of water droplets.
Due to the dispersion of light in this manner the rainbow is formed.
57 Why don’t the planets twinkle?
The planets are much closer to the earth, and are thus seen as extended
sources.
58 Why do stars twinkle?
Starlight gets refracted in the atmosphere.
This changes the apparent position of the stars.
Path of light rays coming from the stars is too far
Point sized apparent position keeps changing continuously
therefore they blink
59 What is the reason for Advance sunrise and delayed sunset?
Answer: because of atmospheric refraction.
60 Why is the colour of the clear Sky Blue?
When sunlight passes through the atmosphere, it scatters the blue colour
more strongly than red.
61 The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitudes. Give
reason? OR
Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Due to the absence of molecules in air, the scattering of light does not
take place.
Thus, sky appears dark in the absence of scattering.
62 Danger signals are red in colour why?
The red is least scattered by fog or smoke. Therefore, it can be seen in the
same colour at a distance.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 13
63 Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Most of the part of blue light and light of small wavelength gets scattered
near the horizon. So, the light reaching our eyes is of large wavelength.
IMPORTANT QUETIONS
64 What is electric current?
The rate of flow of electric charge is called electric current.
65 What is Potential Difference?
Work done to move a unit charge from one point to another.
66 What is Resistance?
It is the property of a conductor to resist the flow of charges.
67 How does a bulb work based on joules law?
Tungsten metal is used in the bulb.
It is filled with nitrogen and argon gases.
The most part of electric energy converted in to heat and small part
produced as light.
68 Write the Factors on which the Resistance of a Conductor
depends.
length of Conductor
area of cross-Section,
nature of material
69 “Connecting electrical appliances in parallel is advantageous over
connecting them in series” in a circuit. Justify. (advantages of series
connection)
If one component fails the circuit will not break.
It offers low resistance.
70 In domestic electric circuit electrical appliances are not connected in
series. Why? (disadvantages of series connection)
When one component fails, the circuit is broken.
It offers high resistance.
71 What is heating effect of electric current?
The energy continually gets dissipated entirely in the form of heat. This is
known as the heating effect of electric current.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 14
72 Why are the alloys like nichrome used in electrical heating devices?
Why tungsten is used in the filament of bulb.
Alloys do not oxidise (burn) readily at high temperature.
Alloys have high melting point.
73 Name the metal used in the filament and the gas filled in electric bulb.
Tungsten
Nitrogen OR Argon
74 What is electric power?
The rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in an electric
circuit is called electric power.
75 Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across
conductor. Answer : Battery or AC source
76 What is Electric circuit?
The continues and closed path of electric current.
77 Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar
magnet? Answer: Because of the magnetic fields.
78 What is a magnetic field line?
The lines along which iron fillings align themselves called magnetic field
lines.
79 Write the characteristics of field lines. Or List the properties of
magnetic lines of force?
Field lines are closed curves.
Field lines are never intersecting each other
80 Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
Because magnets cannot show two same direction at once.
81 What is solenoid?
A coil of many circular turns of copper wire wrapped in the shape of a
cylinder is called solenoid
82 Write the properties of the magnetic field lines formed around a
current carrying solenoid
At the ends of a solenoid, the magnetic field lines are appear in the form
of concentric circles.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 15
At the centre inside the solenoid the magnetic field lines are appear in
the form of parallel straight lines.
83 How does a solenoid behave like a magnet?
When current is passed through a solenoid magnetic field is
produced.
The magnetic field is very strong and uniform
84 Name the Commutator used in motor? Split rings
85 Write the components used by the motor?
(i) An electro magnet
(ii) Large number of turns in the coil
(iii) Soft iron core
86 What is electromagnetic Induction?
OR state the principle of generator.
The changing magnetic field in a conductor induces a current in another
conductor is called electromagnetic Induction.
87 Write the principle of electric generator?
Electromagnetic Induction
88 What is alternate current?
The current which reverse its direction periodically.
89 What is direct current? The current which flows always in one direction
90 What is the frequency of alternate current? 50 Hz
91 What are the advantages AC over DC.
The electric energy can be transmitted over long distances without much
loss of energy.
92 It is necessary to connect the electric appliances having metallic body
to earth wire in domestic electric circuit. Why? Explain.
This provides a low resistance conducting path for the current
If any leakage of current in the appliances the user may not get a severe
electric shock.
93 What are the reasons for occurring overload in an electric circuit?
Connecting too many appliances to a single socket
When live wire and neutral wire come into direct contact.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 16
94 Suggest any two measures to avoid overloading in domestic circuits.
Live and neutral wires should not come into direct contact.
Too many appliances should not be connected to a single socket.
95 List the uses of concave mirror.
used in torches
Used as shaving mirrors
The dentists use to see large images of the teeth.
Used in solar furnaces.
96 Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
It enables the driver to see traffic behind him/her to facilitate safe driving.
97 Write the difference between concave mirror and convex mirror?
Concave mirror Convex mirror
Both real and virtual images are Images are always virtual and
formed very small
Both inverted and erect images Images are always erect
are formed
98 Write the relationship between the radius of curvature R, and
focal length f, of a spherical mirror?
R = 2f
99 Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of
an object.
Concave mirror.
100 If the focal length of spherical mirror is 15cm find the radius
of curvature.
𝑓 = 15𝑐𝑚
= 2𝑓 = 2 × 15 = 30𝑐m
101 The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal
length?
Focal length = x Radius of curvature
= ½ x 20 cm = 10 cm
102 Write mirror formula.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 17
103 What is magnification?
The ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object.
104 What is Refraction of light?
When light travelling from one medium to another, the direction of
light in the second medium changes. This phenomenon is called
Refraction of light.
105 A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the
light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
The light-ray bends towards the normal
Due to change in velocity.
106 Define refractive index of a medium.
It is the ratio of speed of light in the air to the speed of light in the
medium.
107 The refractive index of water, nw = 1.33.what does it means?
This means that the ratio of the speed of light in air and the speed of light
in water is equal to 1.33.
108 Write lens formula.
𝑓
109 What is power of lens? Write its formula.
The power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal
length.
110 Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
111 Opticians prescribe corrective lenses indicating their power equal to +
2.0 D. what does it mean.
This means the lens prescribed is convex.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 18
112 What is Power of Accommodation?
The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length accordingly as the
distances is called power of accommodation.
113 What is near point of the eye?
the near point of the eye is 25cm for normal eye.
114 What is far-point of the eye?
The far point of the eye is infinity for a normal eye.
115 A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last
row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it
be corrected?
Answer: The child is suffering from myopia.
The child should use concave lens of suitable focal length.
116 What is angle of prism?
The angle between its two lateral faces is called the angle of the prism.
117 What is Tyndall effect?
The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particles is called
Tyndall effect.
118 What are the qualities of good source of energy? OR Idle source of
energy.
Give more heat per unit mass.
Burn without smoke
Cheap and easily available.
Safe to transport.
119 Name any two fossil fuels and mention any two disadvantages of using
fossil fuels.
Fossile fules are: Natural gas , Petroleum and Coal.
disadvantages
Air pollution
Acid rain
120 What is thermal power plant? Write its advantages.
A power plant which uses heat energy to generate electricity.
• Transmission of electricity is more efficient.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 19
121 Write the advantages of hydro power plants.
(i) No environmental pollution.
(ii) It is a renewable source of electric energy.
122 Bio-gas is an excellent fuel. Why? OR write the advantages of bio fuel.
Burns without smoke
Leaves no residue like ash
Heating capacity is high
Contains 75% of methane
123 What are the advantages of wind energy?
(i) Eco-friendly.
(ii) Efficient source of renewable energy.
124 What are the disadvantages of wind energy?
(i) It needs large area of land.
(ii) The wind speed should be 15-20 KmPH.
125 Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
(i) Present energy sources are getting exhausted soon.
(ii) To reduce the pollution level and to save the environment
126 Name the gas generated by bio gas plant.
Methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
127 Name the major constituent of biogas. Answer :Methane
128 The inner wall of the solar cooker is painted black. Why?
Because black colour absorbs more heat
129 What kind of mirror – concave, convex or plain – would be best suited
for use in a solar cooker? Why?
concave mirrors
Solar cookers achieve a higher temperature.
130 What is Solar cell? Write the range of its potential difference (Voltage)
and power?
Solar cells convert solar energy into electricity.
voltage : 0.5-1 V and power is 0.7W
131 What are the advantages of Solar cell?
Have no moving parts.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 20
Require little maintenance.
Can work without any focusing device.
Can be set up in remote and inaccessible area
132 What are the Disadvantages of solar cell?
Availability of special grade silicon for making solar cells is limited.
Their efficiency is low.
133 Name the element which used to make solar cell. Answer: Silicon.
134 What is solar panel?
A large number of solar cells are, combined in an arrangement called solar
cell panel.
135 What is nuclear energy? Name the two types of nuclear reactions.
The energy released during a nuclear reaction is called nuclear energy.
It can be obtained by two types of nuclear reactions :
(i) Nuclear fission (ii) Nuclear fusion
136 List the hazards of nuclear power generation. (Limitations)
Improper nuclear-waste storage and disposal result in environmental
contamination
There is a risk of accidental leakage of nuclear radiation.
137 Explain how nuclear energy is generated in power reactors. How is
electricity produced from nuclear energy?
By the process of Nuclear fission reaction.
The nucleus of heavy atom bombarded with low-energy neutrons, can be
split apart into lighter nuclei.
When this is done, a huge amount of energy is released at a controlled
rate.
The released energy is used to produce steam and further generate
electricity.
138 Note
A negative sign in the value of the magnification indicates that the image is real.
A positive sign in the value of the magnification indicates that the image is
virtual
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 21
139 The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean?
(i) m = 1 indicates the size of image is same as that of object.
(ii) Positive sign of m indicates that an erect image is formed.
140 A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray
bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
The light-ray bends towards the normal because the ray of light goes from a rarer
medium to a denser medium.
141 You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the
light travel fastest?
kerosene, n = 1.44 turpentine, n = 1.47 water, n = 1.33
water has the lowest refractive index, therefore light travels fastest in this optically
rarer medium than kerosene and turpentine oil.
142 Note :
The power of a convex lens is positive and that of a concave lens is negative.
IMPORTANT CALCULATIONS
143 A current of 0.5 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb for 10 minutes.
Find the amount of electric charge that flows through the circuit.
Solution
I = 0.5 A; t = 10 min = 600 s.
Q = It
= 0.5 A × 600 s
= 300 C
144 How much work is done in moving a charge of 2 C across two points having a
potential difference 12 V?
W = VQ
= 12 V × 2 C
= 24 J.
145 How much current will an electric bulb draw from a 220 V source, if the
resistance of the bulb filament is 1200 Ω?
V = 220 V; R = 1200 Ω.
146 100 J of heat are produced each second in a 4 Ω resistance. Find the
potential difference across the resistor.
Solution H = 100 J, R = 4 Ω, t = 1 s, V = ?
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 22
√
Thus the potential difference across the resistor is
V = IR
=5A×4Ω
= 20 V.
147 An electric bulb is connected to a 220 V generator. The current is 0.50 A.
What is the power of the bulb? Solution
P = VI
= 220 V × 0.50 A
= 110 J/s
= 110 W.
RASUL KHAN HAZRATH SEYYID MADANI ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL,ULLAL Page 23
You might also like
- Abc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesFrom EverandAbc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesWürth ElektronikNo ratings yet
- Experiment Details Physics (Class 10)Document13 pagesExperiment Details Physics (Class 10)8311 Mirza Muhammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- PS12 Week3 Las1Document2 pagesPS12 Week3 Las1Jeffry Centeno PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Activity - 24-25 DAVCPSDocument12 pagesActivity - 24-25 DAVCPSAnujNo ratings yet
- Phy Rev MaterialDocument15 pagesPhy Rev Materiald.tharun37No ratings yet
- Part 2 2nd PU GBJCDocument94 pagesPart 2 2nd PU GBJCJhenkarNo ratings yet
- Must Revision Topics (From Board Analysis) : Book 2 Chap 9Document2 pagesMust Revision Topics (From Board Analysis) : Book 2 Chap 9Harsh SolankiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Important Question Xiith PhysicsDocument5 pagesChapter Wise Important Question Xiith PhysicsTamanna SahuNo ratings yet
- Summer Holiday Homework - 22Document19 pagesSummer Holiday Homework - 22Ananya DashNo ratings yet
- Important Derivations 12 PhysicsDocument6 pagesImportant Derivations 12 PhysicsSanjay Kumar SheoranNo ratings yet
- Physics 25 Days Schedule 1Document3 pagesPhysics 25 Days Schedule 1anandiangel123No ratings yet
- EPHY105L LabManualDocument49 pagesEPHY105L LabManualaryanNo ratings yet
- SR Physics Fast LearnerDocument7 pagesSR Physics Fast LearnerShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Class 10thDocument3 pagesRevision Worksheet Class 10thSamarth KhatorNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 2024-25Document22 pagesPhysics Assignment 2024-25mandaarapucollege123No ratings yet
- SECOND For UkDocument8 pagesSECOND For UkyellaiahNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument4 pagesLAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightJose RizalNo ratings yet
- Physics 2nd Yr BDocument3 pagesPhysics 2nd Yr BShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Important Questions XII PHYSICSDocument8 pagesChapter Wise Important Questions XII PHYSICSsavitridevi9668No ratings yet
- PhysicsX PDFDocument124 pagesPhysicsX PDFcitsNo ratings yet
- Resistance and TemperatureDocument11 pagesResistance and TemperatureUkoima Kelvin NkaloNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - Physics: Other Educational PortalsDocument7 pagesSample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - Physics: Other Educational PortalsSourabh SirradhanaNo ratings yet
- 2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan RasheedDocument73 pages2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan RasheedAmroz AfzalNo ratings yet
- Xii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseDocument4 pagesXii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseSharulathaNo ratings yet
- Physics II Year - 121754Document5 pagesPhysics II Year - 121754Quran The MercyNo ratings yet
- Archivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavDocument8 pagesArchivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavChess ManNo ratings yet
- Imp. Derivations For XII PhysicsDocument3 pagesImp. Derivations For XII PhysicsJethiya SyckoNo ratings yet
- The Impedance Plane and Probes PDFDocument2 pagesThe Impedance Plane and Probes PDFanas dwiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-IInd YEAR (Board List)Document2 pagesPHYSICS-IInd YEAR (Board List)cherukunavaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics (Theory)Document20 pagesRay Optics (Theory)Kumar Rohit100% (1)
- CLASS X PHYSICS chapter 2 CONTENTDocument10 pagesCLASS X PHYSICS chapter 2 CONTENTmishalrayna2712No ratings yet
- Physics-2 Practical HandoutDocument82 pagesPhysics-2 Practical Handoutملهم الخصيبيNo ratings yet
- Light-STD X-PHY NOTESDocument15 pagesLight-STD X-PHY NOTESFakhruddin PocketwalaNo ratings yet
- Geometric OpticsDocument34 pagesGeometric OpticsLadymie MantoNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics - ManualDocument9 pagesGeometrical Optics - ManualfarehaNo ratings yet
- 12 Optics AssignmentDocument4 pages12 Optics AssignmentKeerthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument1 pagePHYSICSMun AhmedNo ratings yet
- SSLC Phy Viq24Document12 pagesSSLC Phy Viq24jyothibhovi29No ratings yet
- Re Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesRe Exam Questionsabuthahir1.mcaNo ratings yet
- WorkSheet PHYSICS 2287docDocument3 pagesWorkSheet PHYSICS 2287docKshitij BichaveNo ratings yet
- Physics Important Derivations QuestionDocument3 pagesPhysics Important Derivations QuestionsumitNo ratings yet
- 102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionDocument9 pages102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments: Chapter NineDocument42 pagesRay Optics and Optical Instruments: Chapter NineAsh LeyNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument11 pagesRay OpticsTatvamasiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Phy Imp QuestionsDocument5 pagesClass 12 Phy Imp Questionsrajeshsharma4121No ratings yet
- Lab ActivityDocument9 pagesLab ActivityAnvi MantriNo ratings yet
- Vol. 5 No. 1 JUNE 2019 11Document12 pagesVol. 5 No. 1 JUNE 2019 11João TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- SR Physics IPE Imp QuestionsDocument6 pagesSR Physics IPE Imp QuestionsHemanth MindhiNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics NCERTDocument42 pagesRay Optics NCERTsohamNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter LightDocument25 pagesPhysics Chapter LightNurliyana Zairul AfendiNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions 2023 XiiDocument4 pagesFrequently Asked Questions 2023 XiiBala MugeshNo ratings yet
- Phy Set-6Document4 pagesPhy Set-6Saeeda IftikharNo ratings yet
- Optics Sena PeoblemsDocument11 pagesOptics Sena PeoblemsAndre Aleksandrov CherenkovskiNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics English Theory HvxcmX8Document67 pagesGeometrical Optics English Theory HvxcmX8Emad ElsehlyNo ratings yet
- TWOTERMDocument3 pagesTWOTERMnavyashreehegde28No ratings yet
- Efek Pockel p5451 - e PDFDocument4 pagesEfek Pockel p5451 - e PDFBayuPermanagagNo ratings yet
- T LensDocument8 pagesT LensGan Hock KiamNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument26 pagesImportant QuestionsAyush TomarNo ratings yet
- 01ADMModule - S11 12PS IIIa 1 EDITED LatestDocument40 pages01ADMModule - S11 12PS IIIa 1 EDITED LatestDharyn CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Nuclei: One Mark QuestionsDocument8 pagesNuclei: One Mark QuestionsBrittany GreenNo ratings yet
- SAP Exercises 4 2018 CommentedDocument3 pagesSAP Exercises 4 2018 CommentedIgnacio Fernandez GrañaNo ratings yet
- Direct Nuclear Reactions and Compound Nucleus ReactionsDocument5 pagesDirect Nuclear Reactions and Compound Nucleus ReactionsKishore GujjarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Neutron Physics: Carlo CazzanigaDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Neutron Physics: Carlo CazzanigaRiska MulyaniNo ratings yet
- (Ronald A. Knief) - Nuclear Reactor Theory (Booklet)Document19 pages(Ronald A. Knief) - Nuclear Reactor Theory (Booklet)sina sanatiNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question Bank-6Document34 pagesPhysics: Question Bank-6MUSIC WORLDNo ratings yet
- Gacan Qabad Chemistry Book With AnswersDocument32 pagesGacan Qabad Chemistry Book With Answerscazmi Andirahman100% (1)
- Shs Daily Lesson Log Physical ScienceDocument33 pagesShs Daily Lesson Log Physical ScienceJaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- Major 09Document48 pagesMajor 09Vipranshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Nuclear - Physics - WebquestDocument6 pagesChemistry - Nuclear - Physics - Webquesto18.makiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Cie Nuclear MCQ 1,2Document14 pagesIGCSE Cie Nuclear MCQ 1,2Payail Parineeta PalNo ratings yet
- Che 131 Final Study GuideDocument23 pagesChe 131 Final Study GuideVictoria SteinbergNo ratings yet
- Basic Radiation Physics: This Set of 194 Slides Is Based On Chapter 1 Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA PublicationDocument97 pagesBasic Radiation Physics: This Set of 194 Slides Is Based On Chapter 1 Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA PublicationStephen AveryNo ratings yet
- 4-Electric Power GenerationDocument31 pages4-Electric Power GenerationCaribNo ratings yet
- Ford f150 2015 Electrical Wiring DiagramsDocument22 pagesFord f150 2015 Electrical Wiring Diagramsshaunthomas011196cbg100% (76)
- MathematicalDocument31 pagesMathematicalmohammed1998No ratings yet
- Physics Capsule Watermark (1) .PDF 22Document12 pagesPhysics Capsule Watermark (1) .PDF 22ChandreshDharDubeyNo ratings yet
- Trs468 WebDocument279 pagesTrs468 WebВладимир ФроловNo ratings yet
- Particle QuestionsDocument14 pagesParticle QuestionsSaginskyNo ratings yet
- SL Paper1Document21 pagesSL Paper1Patrick PrakasaNo ratings yet
- Quipper Lecture Physical ScienceDocument279 pagesQuipper Lecture Physical ScienceLoren Marie Lemana AceboNo ratings yet
- Makalah FismodDocument19 pagesMakalah FismodRirinNo ratings yet
- Nucleus (Stability and Reaction) : Nuclear ChemistryDocument22 pagesNucleus (Stability and Reaction) : Nuclear ChemistryANSHUNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Physics Paper-1 Question Paper Solutions 2018Document14 pagesICSE Class 10 Physics Paper-1 Question Paper Solutions 2018Venu MaheshNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactions LecDocument32 pagesNuclear Reactions Lecjon alex100% (1)
- FT - HR: G V 15 Knots V 15 Knots West GDocument11 pagesFT - HR: G V 15 Knots V 15 Knots West Gtsania nkdNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission Vs Nuclear FusionDocument17 pagesNuclear Fission Vs Nuclear FusionJinky Marie Abunan100% (1)
- The Los Alamos ProjectDocument16 pagesThe Los Alamos ProjectDavid MolinattoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument25 pagesNuclear ChemistryLeeza Servidad100% (1)