Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
The Jazz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageChemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
The JazzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
1. In a reaction, 2X → Y, the concentration of X decreases from 0.50 M to 0.38 M in 10 min.
What is the rate
of reaction in Ms-1 during this interval? (1M)
(a) 2 × 10-4 (b) 4 × 10-2 (c) 2 × 10-2 (d) 1 × 10-2
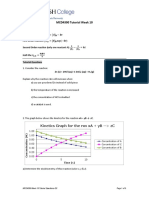
2. A plot is shown below between concentration and time t. Which of the given orders is indicated by the
graph(1M)
(a) Zero Order
(b) Second Order
(c) First Order
(d) Fractional Order
3. A reaction’s rate constant is k=3.28 × 10-4 s-1. Determine the reaction’s order(1M)
4. A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 40 min. Calculate the time required for the completion of 90% of
the reaction. (3M)
5. A first-order reaction takes 40 min for 30% decomposition. Calculate its half-life period. (2M)
6. Rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbons is 2.418 x 10 -5 s -1 at 546K. if the energy of
activation is 179.9kJ/mol, what will be the value of pre-exponential factor? (2M)
7. Explain the significance of activation energy.(3M)
8. Determine the rate equations for this reaction.(2M)
Expt [A] [B] Initial Rate (mol L-1s-1)
I 0.01 0.01 0.005
II 0.02 0.01 0.020
III 0.02 0.03 0.060
You might also like
- Main Exam SCH B302 2020 IBDocument3 pagesMain Exam SCH B302 2020 IBEzekiel MainaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4aliesyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical Kineticsnimitsigotiya2No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 7 Study Material English MediumDocument18 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 7 Study Material English MediumAakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics AssignmentDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Kinetics AssignmentHansika GidwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical KineticsakritiNo ratings yet
- 15-01-2021 Chemical & Isomerism (Autosaved)Document41 pages15-01-2021 Chemical & Isomerism (Autosaved)cric.indian.womenNo ratings yet
- ChEMICAL KINETICS - QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesChEMICAL KINETICS - QUESTIONSChhabi YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical KineticssathishNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 12th - CHEMISTRYDocument18 pagesChemical Kinetics 12th - CHEMISTRYRakesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesChemical KineticsPallabi deNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Past PapersDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics Past Papers10 A Pratyush Dubey50% (2)
- 4 BQ - Ans Chemical KineticsDocument7 pages4 BQ - Ans Chemical KineticsDawa PenjorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Maninagar-Target) Section-I (Only One Option Correct)Document4 pagesChemistry (Maninagar-Target) Section-I (Only One Option Correct)Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Chemical Kinetics HWDocument7 pagesChapter 15 Chemical Kinetics HWAlejo CardoNo ratings yet
- Long AnswersDocument2 pagesLong AnswersVehlaNo ratings yet
- GZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberDocument3 pagesGZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberSaman PanwarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 1Document103 pagesChemical Kinetics 1drvssssmcrobertganjNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics_Faculty copyDocument8 pagesChemical Kinetics_Faculty copyanshwitripathi59No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical Kineticszuhairabegum04No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical KineticsShivani VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4khalidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-I: Part - I: Subjective QuestionsDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics-I: Part - I: Subjective Questionshorn blowNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-1Document50 pagesChemical Kinetics-1telangtanushreeNo ratings yet
- H13 - Kinetics 2-SolutionsDocument4 pagesH13 - Kinetics 2-Solutionscse0909No ratings yet
- Chem Kinetics Tutorial 2024Document2 pagesChem Kinetics Tutorial 2024Sree dhathri DevaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesChemical Kineticsjayamadhavan2007No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical KineticsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Chemical KineticsSavitha ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Board Questions 2010Document5 pagesChemical Kinetics Board Questions 2010amone nNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Lec-1 NEET ChalisaDocument35 pagesKinetics Lec-1 NEET Chalisaashustarguy005No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesChemical KineticsMakbul Shaik100% (1)
- C09-NEET Chemical KineticsDocument21 pagesC09-NEET Chemical KineticsonehalfticketshowNo ratings yet
- 08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetDocument33 pages08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetVIKRANTH KUMAR JAKKOJUNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesChemical KineticsMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 12th Grade Chemical Kinetics WorhshhetDocument1 page12th Grade Chemical Kinetics WorhshhetAmen RaipurNo ratings yet
- Kinetic NCERTDocument10 pagesKinetic NCERTSionna KatiyarNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark QuestionsDocument19 pages1 Mark QuestionsSsNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8 - Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 8 - Chemical KineticsAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Org 7Document1 pageOrg 7uniquestarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemistry Chemical KineticsSurya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises Unit 6 - Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesSolutions To Exercises Unit 6 - Chemical KineticssaralvssNo ratings yet
- DPP-02 Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageDPP-02 Chemical KineticsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Reaction KineticsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Reaction KineticsDinesh RamaNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Chemical Kinetics by Shallu Jindal AggarwalDocument6 pagesMCQ On Chemical Kinetics by Shallu Jindal AggarwalNisha Miliruvani100% (4)
- Kinetics Comprehensive Review Packet - KEYDocument14 pagesKinetics Comprehensive Review Packet - KEYLuis LopezNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Chapter Test 4 Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesXII Chemistry Chapter Test 4 Chemical KineticsVishwaaNo ratings yet
- Rate (F) (Clo) 1.2X10 M/ S 0.10M 0.010M: Kinetics ProblemsDocument6 pagesRate (F) (Clo) 1.2X10 M/ S 0.10M 0.010M: Kinetics ProblemsFiyan HidayatNo ratings yet
- SOAL P13-5 (Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 4 Edition Foggler)Document31 pagesSOAL P13-5 (Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 4 Edition Foggler)Adilla PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Numericals All ChaptersDocument51 pagesNumericals All Chapterssyedafatma.109No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical KineticsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Chemical KineticsRahgul M.S.No ratings yet
- Class XII Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesClass XII Chemical KineticsvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics RevisionDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics RevisionShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 StudentDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 StudentIrsyad KamilNo ratings yet
- Ass 1Document2 pagesAss 1poorvig570No ratings yet
- HSFTXD 5Document12 pagesHSFTXD 5Adithya K SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument7 pagesChemical Kineticsthinkiit100% (1)
- CHGV 101 Tutorial 3 Questions KineticsDocument4 pagesCHGV 101 Tutorial 3 Questions KineticsOvayo TyalaNo ratings yet
- 12-04-18 Chemical Kinetics - 29Q - , Complex Compounds - 05Q - & Aryl Halides - 05QDocument4 pages12-04-18 Chemical Kinetics - 29Q - , Complex Compounds - 05Q - & Aryl Halides - 05QSHRINIDHI SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Introduction to FilesDocument17 pagesIntroduction to FilesThe JazzNo ratings yet
- English Project (MKULTRAFINAL)Document32 pagesEnglish Project (MKULTRAFINAL)The JazzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Matrices Study Module Lakshya JEE 2025Document42 pagesChapter 02 - Matrices Study Module Lakshya JEE 2025The JazzNo ratings yet
- x86 StderrDocument1 pagex86 StderrThe JazzNo ratings yet