Professional Documents
Culture Documents
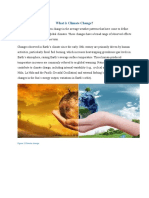
Climate Change Is Causing Five Critical Global Environmental Changes
Climate Change Is Causing Five Critical Global Environmental Changes
Uploaded by
koolkraft20Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Climate Change Is Causing Five Critical Global Environmental Changes
Climate Change Is Causing Five Critical Global Environmental Changes
Uploaded by
koolkraft20Copyright:
Available Formats
Climate change is causing five critical global environmental changes:
• Warming temperature of the earth’s surface and the oceans: The earth has warmed at a rate of
0.13° C per decade since 1957, almost twice as fast as its rate of warming during the previous
century. • Changes in the global water cycle (‘hydrologic’ cycle): Over the past century there have
been distinct geographical changes in total annual precipitation, with some areas experiencing
severe and long-term drought and others experiencing increased annual precipitation. Frequency
and intensity of storms increases as the atmosphere warms and is able to hold more water vapor. •
Declining glaciers and snowpack: Across the globe, nearly all glaciers are decreasing in area,
volume and mass. One billion people living in river watersheds fed by glaciers and snowmelt are
thus impacted. • Sea level rise: Warmer water expands, so as oceans warm the increased volume
of water is causing sea level rise. Melting glaciers and snowpack also contribute to rising seas. •
Ocean acidification: Oceans absorb about 25% of emitted CO2 from the atmosphere, leading to
acidification of seawater. These global changes result in what we experience as changes in our
local weather and climate: • Greater variability, with “wetter wets”, “drier dries” and “hotter hots” °
More frequent and severe extreme heat events ° More severe droughts ° More intense precipitation,
such as severe rains, winter storms and hurricanes • Higher average temperatures and longer frost-
free seasons • Longer wildfire seasons and worse wildfires • Loss of snowpack and earl ier spring
runoff • Recurrent coastal flooding with high tides and storm surges
You might also like
- Global WarmingDocument10 pagesGlobal WarmingYeifry AguasvivasNo ratings yet
- Impact of Climate Change's in PakistanDocument12 pagesImpact of Climate Change's in Pakistanhary1186% (7)
- 1 Nature of CCDocument36 pages1 Nature of CCJayArt Amogis TemPoralNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Global WarmingDocument7 pagesDefinition:: Global WarmingAbdul Hayee QureshiNo ratings yet
- Climatic Changes in The Ocean and What Will Happen: Melissa Wartman & Karalyn BrennanDocument17 pagesClimatic Changes in The Ocean and What Will Happen: Melissa Wartman & Karalyn BrennanKaralyn BrennanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Causes of Melting Glaciers and Ice SheetsDocument25 pagesChapter 7 - Causes of Melting Glaciers and Ice SheetsnikitaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument7 pagesGlobal WarmingPoojaNo ratings yet
- Global Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesGlobal Climate ChangeJames Hiro GeraldinoNo ratings yet
- Aecc - Evs GHG, Climate Change and Kyoto ProtocolDocument10 pagesAecc - Evs GHG, Climate Change and Kyoto ProtocolAvni ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Evidence of A Changing ClimateDocument4 pagesEvidence of A Changing ClimateNaeemah MunshiNo ratings yet
- Sea Level Change and Future ClimateDocument29 pagesSea Level Change and Future ClimateA S VermaNo ratings yet
- High School Project On Global WarmingDocument6 pagesHigh School Project On Global WarmingSam SkyeNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: By: Kenzi WaguihDocument7 pagesGlobal Warming: By: Kenzi WaguihkNo ratings yet
- Final Global WarmingDocument24 pagesFinal Global WarmingEllyn Marie PerezNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Impact On Geographical Features: Special ArticleDocument4 pagesClimate Change and Its Impact On Geographical Features: Special Articlesubhadeep sarkarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 CNRDocument41 pagesModule 5 CNRHarshith Kumar hvNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - The Global EffectsDocument7 pagesClimate Change - The Global EffectsRizwan NadeemNo ratings yet
- Climate Warming - Lect 4Document8 pagesClimate Warming - Lect 4Nishant VatsNo ratings yet
- Felix Changes in World ClimateDocument36 pagesFelix Changes in World ClimateKimberly RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Attachment Student 15Document7 pagesAttachment Student 15ShutaNo ratings yet
- Is Global Warming A Scam ?Document4 pagesIs Global Warming A Scam ?Rishabh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Calentamiento Global (En Ingles)Document4 pagesCalentamiento Global (En Ingles)Diana Flores ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Causes of Sea-Level ChangeDocument5 pagesCauses of Sea-Level ChangeRevean Esperas IINo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument1 pageGlobal Warmingshrek shrekNo ratings yet
- Global Env Issue 2021Document52 pagesGlobal Env Issue 2021Areniz ZessNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle or Greenhouse EffectDocument6 pagesWater Cycle or Greenhouse Effectapi-734660396No ratings yet
- Aside From The Rise in The Mean Temperature and CO2Document2 pagesAside From The Rise in The Mean Temperature and CO2htenywgNo ratings yet
- Unit 15Document14 pagesUnit 15Tiko BiboNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument18 pagesGlobal WarmingSargisNersisyanNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument41 pagesGreenhouse EffectKimberly Claire MaguadNo ratings yet
- Impact of Climate Change On Land Use and Environmental ChangeDocument65 pagesImpact of Climate Change On Land Use and Environmental ChangeSande Alota Boco100% (1)
- Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument46 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate ChangeTaleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Presentation (GROUP 2)Document30 pagesGlobal Warming Presentation (GROUP 2)Husni Mohd RadziNo ratings yet
- 3 - Impact of Polar RegionsDocument2 pages3 - Impact of Polar RegionsMansoor AsifNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Climate: 1.latitude 2.altitude 3.distance From The Sea 4.ocean Currents 5.land TopographyDocument54 pagesFactors Affecting Climate: 1.latitude 2.altitude 3.distance From The Sea 4.ocean Currents 5.land TopographyMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- Global Warming (33,34,35,36)Document14 pagesGlobal Warming (33,34,35,36)surajsinghNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physical OcenographyDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Physical OcenographyvenuNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Impact On HydrologyDocument51 pagesClimate Change Impact On Hydrologymohammedmahathee-2018626500No ratings yet
- Global Warming & Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming & Climate ChangekulsoomalamNo ratings yet
- AnglishtDocument4 pagesAnglishtArlinda QerajNo ratings yet
- Global Warming & Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesGlobal Warming & Climate Changeashai.daaminNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument2 pagesGeographyselbywNo ratings yet
- Unusual Properties of WaterDocument44 pagesUnusual Properties of WaterHanan ShehaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Climate Change FINAL 002Document4 pagesIntroduction To Climate Change FINAL 002adiNo ratings yet
- Drivers and Indicator of Climate Change 2Document5 pagesDrivers and Indicator of Climate Change 2Asma Rasheed Visiting TeacherNo ratings yet
- Noticia 100 InbglishDocument3 pagesNoticia 100 InbglishsantiuchihauwuxdNo ratings yet
- It's Gettin' Hot in Here!Document28 pagesIt's Gettin' Hot in Here!Dipanjan DasNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii - Types of Natural Disasters - Final - 19-Sep-2022Document72 pagesUnit-Iii - Types of Natural Disasters - Final - 19-Sep-2022Shaik Asif Ali civilNo ratings yet
- New Challenges To Human Adaptation and Social ChangesDocument20 pagesNew Challenges To Human Adaptation and Social ChangesJames RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Sts 01: Science, Technology and Society: Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesSts 01: Science, Technology and Society: Climate ChangeJayarNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect of Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesCause and Effect of Climate ChangeIndustrial ItNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - A Silent Threat To HumanityDocument8 pagesClimate Change - A Silent Threat To HumanityVignesh AukNo ratings yet
- Environment Change Over The Geological Time ScaleDocument14 pagesEnvironment Change Over The Geological Time ScaleMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- GEOG 434:climatic Change: Arid and Semi-Arid LandsDocument26 pagesGEOG 434:climatic Change: Arid and Semi-Arid LandsAdiita Agman-nyese PatrickNo ratings yet
- Sea Level ChangesDocument2 pagesSea Level ChangesPODE ADOOLNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument41 pagesClimate Changerkadyan1467No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document13 pagesUnit 4Gamer BroNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Accdg To NasaDocument12 pagesClimate Change Accdg To NasaSheenaNo ratings yet