Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impact of AI - Demography
Impact of AI - Demography
Uploaded by
shibinantonymltrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impact of AI - Demography
Impact of AI - Demography
Uploaded by
shibinantonymltrCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
1 Demographics of the variables
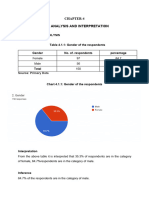
Table 4.1 Gender
Frequency Percent Cumulative
Percent
Female 66 44.0 44.0
Male 84 56.0 100.0
Total 150 100.0
Gender
Male Female
44%
56%
Figure 4.1
Source: Primary data
Interpretation:
The survey conducted to explore the effect of AI in talent acquisition among HR
professionals attracted a total of 150 respondents. Among these respondents, there was a
notable disparity in gender representation. Specifically, 84 (56%) respondents identified as
male, while 66 (44%) identified as female. The observed gender distribution within the
respondent pool holds implications for the interpretation of survey findings. Moreover,
acknowledging gender disparities in participation facilitates a more comprehensive analysis
of the survey data, allowing for insights into how gender may intersect with perceptions and
experiences related to AI in talent acquisition.
Table 4.2: Professional experience
Professional Frequency Percentage Cumulative
Experience percentage
Less than 1 20 13.33333 13.33333
1 to 2 47 31.33333 44.66667
2 to 3 41 27.33333 72
3 to 4 15 10 82
4 to 5 11 7.333333 89.33333
Above 5 16 10.66667 100
Total 150 100
Professional experience
35
30
25
20
15
10
0
Less than 1 1 to 2 2 to 3 3 to 4 4 to 5 Above 5
Professional experience
Figure 4.2
Source: Primary data
Interpretation:
From the table, it is evident that 13.33% of the respondents had less than 1 years of
professional experience, followed by 31.33% with 1-2 years, and 27.33% with 2-3 years.
Furthermore, 10% of the respondents had 3-4 years of experience, while 7.33% had 4-5
years. Additionally, 10.67% of the respondents reported having more than 5 years of
experience. Overall, the data indicates that the majority of respondents fall within the 1.1-3
years of experience range.
Table 4.3: Position in Talent Acquisition
Position in Talent Acquisition Frequency Percent Cumulative percentage
HR Director 6 4.0 4.0
HR Executive/Coordinator 50 33.3 37.3
HR Manager 38 25.3 62.6
Operation Manager 5 3.3 65.9
Talent Acquisition Specialist 41 27.3 93.2
Talent Sourcer 5 3.3 96.5
Other 5 3.3 100
Total 150 100.0
Position in Talent Acquisition
Other 3.3
Talent Sourcer 3.3
Talent Acquisition Specialist 27.3
Operation Manager 3.3
HR Manager 25.3
HR Executive/Coordinator 33.3
HR Director 4
Figure 4.3
Source: Primary data
Interpretation:
The table presents the distribution of respondents' positions in talent acquisition, indicating
their frequency and percentage within the sample. HR Executive/Coordinator represents the
highest proportion at 33.3%, followed by HR Manager at 25.3% and Talent Acquisition
Specialist at 27.3%. Other positions such as HR Director, Operation Manager, Talent Sourcer,
and those categorized as "Other" collectively account for the remaining 11.1%. This
distribution illustrates the diverse roles and responsibilities within talent acquisition, with a
notable concentration in HR-related positions.
Table 4.4: Size of Organization
Frequency Percent Cumulative Percent
Large (501+ employees) 119 79.3 79.3
Medium (101-500 employees) 26 17.3 96.7
Small (1-100 employees) 5 3.3 100.0
Total 150 100.0
Size of Organization
Small (1-100 employees)
3.3
Medium (101-500 employees)
17.3
Large (501+ employees)
79.3
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
Figure 4.4
Source: Primary source
Interpretation:
The table illustrates the distribution of companies based on their size, categorized into large
(501+ employees), medium (101-500 employees), and small (1-100 employees). The
majority of respondents, accounting for 79.3%, represent large companies, indicating a
predominant presence of organizations with over 500 employees. Medium-sized companies
constitute 17.3% of the sample, while small companies with 1-100 employees represent a
smaller proportion at 3.3%. This distribution highlights the prevalence of larger enterprises
within the surveyed sample.
You might also like
- Spss HR Analytics Assignment Employee Satisfaction 1 20162164 - Part 1Document13 pagesSpss HR Analytics Assignment Employee Satisfaction 1 20162164 - Part 1kkiiiddNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 4Document47 pages07 Chapter 4Surbhi MahendruNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Research Findings and Discussions: Table 4.1: Distribution of Total RDocument53 pagesChapter Four Research Findings and Discussions: Table 4.1: Distribution of Total RShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Presentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfileDocument5 pagesPresentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfilefgfgfNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4Document94 pagesChapter-4DR. PRASANTH.BNo ratings yet
- SPSS Results IntrepretationDocument5 pagesSPSS Results IntrepretationKhuzaima ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Analysis: Respondent Demographic ProfileDocument22 pagesDescriptive Analysis: Respondent Demographic ProfileAbygail ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Analysis and IntepretationDocument41 pagesChapter 4: Analysis and IntepretationJaya BhasinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ND 5 New 1Document12 pagesChapter 4 ND 5 New 1DebubNNPR ManagementOfficeNo ratings yet
- Math2C DocsDocument12 pagesMath2C DocsKi AngelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Lydia OdindoDocument12 pagesChapter Four Lydia OdindoRaytone Tonnie MainaNo ratings yet
- BALANDRA-CHAPTER4-5 RevisedDocument51 pagesBALANDRA-CHAPTER4-5 Revisedf.rickallen.balandraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Table 4.1 Analyzing The General Information About The RespondentsDocument16 pagesChapter Four: Table 4.1 Analyzing The General Information About The RespondentsDebubNNPR ManagementOfficeNo ratings yet
- Final Project of QTB: Submitted Too: Prof. Dr. Qasim AliDocument9 pagesFinal Project of QTB: Submitted Too: Prof. Dr. Qasim AliAlphaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Demographic Profile:: Table 1Document4 pages4.1 Demographic Profile:: Table 1AlphaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 & 5Document35 pagesChapter - 4 & 5asquareprojectcentre0120No ratings yet
- Arron Chapter 4 N 5Document16 pagesArron Chapter 4 N 5Justina Layo AgunloyeNo ratings yet
- SlidesDocument18 pagesSlidesurooj shahidNo ratings yet
- 1 Fast FoodDocument13 pages1 Fast FoodKarthikeyan ThangarajuNo ratings yet
- Analysis and FindingsDocument26 pagesAnalysis and FindingsAfzaal AliNo ratings yet
- Vat DataDocument10 pagesVat DataEdwin Okoampa BoaduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document20 pagesChapter 4Lucky MalagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Data Analysis and PresentationDocument19 pagesChapter Four Data Analysis and Presentationvictor wizvikNo ratings yet
- Employee Satisfaction & MotivationDocument13 pagesEmployee Satisfaction & Motivationpankaja shelarNo ratings yet
- Merge 014Document25 pagesMerge 014Memes tamila mareeNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 4Document65 pages10 - Chapter 4researchreportthesisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four HoseaDocument15 pagesChapter Four HoseaRaytone Tonnie MainaNo ratings yet
- 2174 Hoang Cao Bui Viet 10200581-RP-A1.1 14664 993526914-1Document32 pages2174 Hoang Cao Bui Viet 10200581-RP-A1.1 14664 993526914-1Đạt TrầnNo ratings yet
- A Study On Occupational Stress Level of Employees in Textile Shops With Special Reference To TirupurDocument9 pagesA Study On Occupational Stress Level of Employees in Textile Shops With Special Reference To TirupurMiddle East Journal of Applied Science & TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Human Resource Management Practices To The Employee Productivity As Perceived by Selected Employee of Semiconductor IndustryDocument27 pagesEffectiveness of Human Resource Management Practices To The Employee Productivity As Perceived by Selected Employee of Semiconductor IndustryAndrea TaganginNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document22 pagesChapter 4muhammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document18 pagesChapter 4skasaera76No ratings yet
- Factors Responsible For Burnout Among College StudentsDocument7 pagesFactors Responsible For Burnout Among College StudentsRaj naveenNo ratings yet
- Jyruss Regalado Mini Research 07122023Document17 pagesJyruss Regalado Mini Research 07122023JyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Iv Data Analysis and InterpretationDocument74 pagesChapter - Iv Data Analysis and InterpretationEkkala NarutteyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Iiiiv V V V: Andhra University, VisakhapatnamDocument25 pagesChapter - Iiiiv V V V: Andhra University, VisakhapatnamN Pritam DasNo ratings yet
- Research Project Study of The Impact of Reward Systems On Employee Performance of TescoDocument16 pagesResearch Project Study of The Impact of Reward Systems On Employee Performance of TescoAsif DeeproNo ratings yet
- Arcee Supsup StatisticsDocument14 pagesArcee Supsup StatisticsArcee Ardiente MondragonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Textile FirmsDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Textile FirmsMichael RopNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument18 pagesData Analysisshivam tripathiNo ratings yet
- Ghzz3083 Assignment 3 - Group 15Document31 pagesGhzz3083 Assignment 3 - Group 15miraeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 45Document12 pagesChapter 45Irish SuarezNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques of Business: Name Ibtahal Iram Roll # 32 Program MBADocument8 pagesQuantitative Techniques of Business: Name Ibtahal Iram Roll # 32 Program MBAAlphaNo ratings yet
- Penting 1Document46 pagesPenting 1Raihatul Jannah Raihatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four and FiveDocument16 pagesChapter Four and Fivemohammed musbahu shuaibuNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Table Showing Gender of Respondent: SL No Particular Respondents Percentage (%)Document18 pages1.1 Table Showing Gender of Respondent: SL No Particular Respondents Percentage (%)Sharath NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Divya DeviDocument11 pagesChapter 4 - Divya DeviSurya HariNo ratings yet
- 13 Chapter4Document81 pages13 Chapter4Being SydNo ratings yet
- Population and SamplingDocument20 pagesPopulation and SamplingAfzaal AliNo ratings yet
- Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument9 pagesPresentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataChanyeol ParkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BeginingDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Beginingahmetupdirahman37No ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument116 pagesChapter IVxetato6515No ratings yet
- Chapter III Results and DiscussionDocument10 pagesChapter III Results and DiscussionShairuz Caesar Briones DugayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document7 pagesChapter 4Hassan GandamraNo ratings yet
- 13 Chapter4Document81 pages13 Chapter4DEEPANo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 5Document78 pages08 - Chapter 5RashaNo ratings yet
- Project Report Submitted To The University of Mumbai in Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of Degree ofDocument69 pagesProject Report Submitted To The University of Mumbai in Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of Degree ofRanjitha A Dsouza100% (1)
- Chapter Four Findings and Discussion 4.1 Chapter OverviewDocument22 pagesChapter Four Findings and Discussion 4.1 Chapter OverviewronaldNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument13 pagesData AnalysisTharuka DevindiNo ratings yet
- Why Nokia FailedDocument4 pagesWhy Nokia FailedNational Star Montessori SchoolNo ratings yet
- Build Anything BookDocument267 pagesBuild Anything BookPaul C50% (2)
- Ansys Fluent Brings CFD Performance With Intel Processors and FabricsDocument8 pagesAnsys Fluent Brings CFD Performance With Intel Processors and FabricsSaid FerdjallahNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor SpecDocument10 pagesStepper Motor SpecyaserNo ratings yet
- QM.J2 Doc Ref MatrixDocument2 pagesQM.J2 Doc Ref MatrixProsenjit DasNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise No. 5 Mesh Analysis: Danica Marie Dumalagan, Kristoffer John Giganto, Jhury Kevin LastreDocument2 pagesLab Exercise No. 5 Mesh Analysis: Danica Marie Dumalagan, Kristoffer John Giganto, Jhury Kevin LastreKristoffer John GigantoNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Assessment and Financial Projection Results For A Social Health Insurance Scheme in SwazilandDocument96 pagesFeasibility Assessment and Financial Projection Results For A Social Health Insurance Scheme in SwazilandbejarhasanNo ratings yet
- BX - Cleansweep Pro ManualDocument10 pagesBX - Cleansweep Pro ManualVICTOR CHRISTIAN VASQUEZ CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Gas Kiln ManualDocument28 pagesGas Kiln ManualNenadBojovicNo ratings yet
- Blueprint: Freelance RecruitersDocument19 pagesBlueprint: Freelance RecruitersGreenCoffee 24No ratings yet
- Employment News 30 September - 06 OctoberDocument39 pagesEmployment News 30 September - 06 OctoberNishant Pratap Singh100% (1)
- Mini Habits - Smaller Habits, Bigger Results (PDFDrive) - 100-366Document267 pagesMini Habits - Smaller Habits, Bigger Results (PDFDrive) - 100-366Marlena RiveraNo ratings yet
- AnalysisofUnder reamedPilesSubjectedtoDifferentTypesofLoadinClayeySoil 1 8 PDFDocument9 pagesAnalysisofUnder reamedPilesSubjectedtoDifferentTypesofLoadinClayeySoil 1 8 PDFAkhilesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Vol-IV Approved Vendor ListDocument29 pagesVol-IV Approved Vendor ListabhishekNo ratings yet
- Physics Project of Class 11 IscDocument1 pagePhysics Project of Class 11 Iscpratima patelNo ratings yet
- 214.039 Operation of Sieve Shaker2012Document3 pages214.039 Operation of Sieve Shaker2012Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Civil AutoCAD - CVDocument3 pagesCivil AutoCAD - CVNaseef PnNo ratings yet
- Motivation: Self-Efficacy Has A Positive Impact On PerformanceDocument3 pagesMotivation: Self-Efficacy Has A Positive Impact On PerformanceVishavjeetDevganNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Grammar Reference and PracticeDocument1 pageUnit 1: Grammar Reference and PracticeLê Văn HòaNo ratings yet
- Salleh2021 Article TheEmergenceOfVeryLargeContainDocument21 pagesSalleh2021 Article TheEmergenceOfVeryLargeContainSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- 02 Kinematics Tutorial Solutions 2017Document12 pages02 Kinematics Tutorial Solutions 2017Victoria YongNo ratings yet
- What Is Text, Discourse DefinedDocument2 pagesWhat Is Text, Discourse DefinedChristine BlabagnoNo ratings yet
- An Wallis Earthing Lightning ProtectionDocument117 pagesAn Wallis Earthing Lightning Protectiongoitom01No ratings yet
- IADC Daily Drilling Report RevADocument4 pagesIADC Daily Drilling Report RevAdullahnurkalimNo ratings yet
- Magazine of Concrete ResearchDocument11 pagesMagazine of Concrete ResearchKathlene Lacosta LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Purdue Engineering 2010 PDFDocument98 pagesPurdue Engineering 2010 PDFGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Oyster Mushroom Cultivation - Ralph H. Kurtzman, JRDocument86 pagesOyster Mushroom Cultivation - Ralph H. Kurtzman, JRCaptn100% (2)
- Impacts of Economic, Cultural, Social, Individual and Environmental Factors On Demands For Cinema: Case Study of TehranDocument15 pagesImpacts of Economic, Cultural, Social, Individual and Environmental Factors On Demands For Cinema: Case Study of Tehran14-Fy arts Div A Nikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eng WEEK 3 v2Document44 pagesEng WEEK 3 v2Chel CalejaNo ratings yet
- SD220511 01Document1 pageSD220511 01Minh TranNo ratings yet