Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bartlett and Goshal Matrix
Bartlett and Goshal Matrix
Uploaded by
eshasachaniaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bartlett and Goshal Matrix
Bartlett and Goshal Matrix
Uploaded by
eshasachaniaCopyright:
Available Formats
Bartlett and Ghoshal (1991) identified four distinct
types of multinational corporations (MNCs), which are
depicted in the image at the end of this article. These
four types can be seen to illustrate, which strategic out-
look MNCs have towards managing their subsidiaries,
and how these MNCs balance the potential needs of
global integration and global differentiation. Each
MNC should ideally choose the strategic model that
satisfies the needs of the environment, and chose the
strategic model that will secure global competitiveness.
The Bartlett & Ghoshal Model indicates the strategic
‘Local responsiveness’ =
- Do customers in each country expect the product to be adapted to meet local requirements?
- Do local (domestic competitors) have an advantage based on their ability to be more responsive?
‘Global integration’ =
- How important is standardisation of the product in order to operate efficiently (e.g. economies of scale)?
- Is consistent global branding required in order to achieve international success?
1. ‘Global Strategy’ (low pressure for local responsiveness, high pressure for global integration) =
- Highly centralised
- Focus on efficiency (economies of scale)
- Little sharing of expertise locally
- Standardised products
2. ‘Transnational Strategy’ (high pressure for local responsiveness, high pressure for global integration) =
- Complex to achieve
- Aim is to maximise local responsiveness but also gain benefits from global integration
- Wide sharing of expertise (technology, staff etc.)
3. ‘International Strategy’ (low pressure for local responsiveness, low pressure for global integration) =
- Aims to achieve efficiency by focusing on domestic activities
- International operations are largely managed centrally
- Relatively little adaptation of product to local needs
4. ‘Multi-domestic Strategy’ (high pressure for local responsiveness, low pressure for global integration) =
- Aims to maximise benefits of meeting local market needs through extensive customisation
- Decision making decentralised
- Local businesses treated as separate businesses
- Strategies for each country
————— However, Bartlett and Ghoshal posits that many MNCs will have to adopt the transnational strategy, be-
cause the competitive forces of almost every industry is increasing, due, in part, to the intense globalisation occurred dur-
ing the last decades. Many modern MNCs will therefore, most likely, need to choose a transnational strategy, because
many MNCs must master both the art of cost reduction and local differentiation to maintain its competitive edge.
You might also like
- Marketing Research FINAL PROJECT REPORTDocument37 pagesMarketing Research FINAL PROJECT REPORTvaibhav100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document35 pagesChapter 5Linh Bảo BảoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Implementing and Managing A Global Entrepreneurial StrategyDocument16 pagesChapter 11 - Implementing and Managing A Global Entrepreneurial StrategyHanna Kay100% (6)
- CRH LimitedDocument16 pagesCRH LimitedAfsheen Danish Naqvi100% (1)
- I.Strategic Planning II. Organizational Structure III. Controlling Global Marketing EffortsDocument12 pagesI.Strategic Planning II. Organizational Structure III. Controlling Global Marketing Effortssudeep_rsNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Market IntegrationDocument24 pagesModule 4 - Market IntegrationJeprox MartinezNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Analysis of Strategy Development in Globalizing MarketsDocument23 pagesA Framework For Analysis of Strategy Development in Globalizing MarketsLara MaiatoNo ratings yet
- Advance Corporate Strategy 11Document2 pagesAdvance Corporate Strategy 11Passionate_to_LearnNo ratings yet
- 405 Written Assignment MrunalDocument9 pages405 Written Assignment MrunalMrunal KolteNo ratings yet
- Ib Exam FinalDocument6 pagesIb Exam FinalNeeza GautamNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Strategic Planning in Mnes: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesUnit 5 Strategic Planning in Mnes: ObjectivesManilalPNo ratings yet
- International Business Strategy: OutcomesDocument12 pagesInternational Business Strategy: OutcomesKhalil RushdiNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Topic OverviewDocument11 pagesWeek 4 - Topic OverviewmichNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategiesDocument37 pagesMarketing StrategiesLUIS FERNANDO HUMPIRI SUCARINo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 "Global Strategy: An Organizing FrameworkDocument29 pagesChapter 16 "Global Strategy: An Organizing FrameworkMohamdDerpawiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9, 10, 11 - Intl BusinessDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 9, 10, 11 - Intl BusinessAngelo Miguel BernabeNo ratings yet
- Nternational UsinessDocument4 pagesNternational UsinessNina HooperNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Analysis of Strategy Development in Globalizing Markets PDFDocument23 pagesA Framework For Analysis of Strategy Development in Globalizing Markets PDFNely PerezNo ratings yet
- Global Strategy FrameworkDocument8 pagesGlobal Strategy FrameworkRahulgoyal_88No ratings yet
- MS 29Document8 pagesMS 29Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- What Is A Multinational Corporation (MNC) ?: Key Issues in International Business StrategyDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Multinational Corporation (MNC) ?: Key Issues in International Business StrategyShubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Springer Mir: Management International ReviewDocument15 pagesSpringer Mir: Management International ReviewdawjonisNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Theory and Cases An Integrated Approach 11th Edition Hill Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesStrategic Management Theory and Cases An Integrated Approach 11th Edition Hill Solutions Manualabnormalhumble35j4i100% (31)
- International Business ExamsDocument8 pagesInternational Business ExamsGaurav MandalNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Structure in International Multi-Business GroupsDocument21 pagesStrategy and Structure in International Multi-Business GroupsShaher FuranyNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategiesDocument37 pagesMarketing StrategiesAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Global Marketing StrategiesDocument26 pagesLecture 12 Global Marketing Strategiesroadmaster_1992No ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies: January 2006Document37 pagesMarketing Strategies: January 2006dillaNo ratings yet
- Strategies of Domestic and MulDocument13 pagesStrategies of Domestic and MulJame SmithNo ratings yet
- EM 19-20 Efter The EntryDocument12 pagesEM 19-20 Efter The EntryMikkel GramNo ratings yet
- Le Liao ADynamic Viewof Global Integrationand LocalDocument10 pagesLe Liao ADynamic Viewof Global Integrationand LocalKrishnan JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategiesDocument36 pagesMarketing Strategiesjelena79100% (1)
- A1 - Individual Assignment - Emerging MarketsDocument8 pagesA1 - Individual Assignment - Emerging MarketsFawad H. KhanNo ratings yet
- Business Models in Global CompetitionDocument19 pagesBusiness Models in Global CompetitionCotton VenturaNo ratings yet
- Global Strategy - WikipediaDocument2 pagesGlobal Strategy - WikipediaFilopeNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2395277Document3 pagesSSRN Id2395277ken nguyenNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2395277Document3 pagesSSRN Id2395277ken nguyenNo ratings yet
- Accenture Emerging Markets Create Global Operating ModelsDocument37 pagesAccenture Emerging Markets Create Global Operating ModelsSandeep SianNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1 Major Strategic Issues For Multinational CorporationsDocument2 pages2.4.1 Major Strategic Issues For Multinational CorporationsJansi SonyNo ratings yet
- Four Models of Competition and Their Implications For Marketing StrategyDocument11 pagesFour Models of Competition and Their Implications For Marketing StrategyLinol P LoranceNo ratings yet
- Market IntegrationDocument2 pagesMarket IntegrationJoren PamorNo ratings yet
- Herrigel. Autoparts-OEMcompetition PDFDocument35 pagesHerrigel. Autoparts-OEMcompetition PDFmateoNo ratings yet
- International Marketing Strategies For Global CompetitivenessDocument13 pagesInternational Marketing Strategies For Global CompetitivenessFarwa Muhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Summary 8 2018Document4 pagesSummary 8 2018Stanley HoNo ratings yet
- A Dynamic View of Global Integration and Local Responsiveness FrameworkDocument10 pagesA Dynamic View of Global Integration and Local Responsiveness Frameworkviet nam duongNo ratings yet
- Class Note 11Document7 pagesClass Note 11fazlinfarhana2212No ratings yet
- Subsidiary Expansion ContractionDocument17 pagesSubsidiary Expansion Contractiondev burmanNo ratings yet
- 6.international StrategyDocument10 pages6.international Strategyphuongnhung122103No ratings yet
- International Management Managing Across Borders and Cultures Text and Cases 8th Edition Helen Deresky Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesInternational Management Managing Across Borders and Cultures Text and Cases 8th Edition Helen Deresky Solutions Manualgwynethalvaf2qroa100% (32)
- Global, Multinational International, and Transnational CompaniesDocument8 pagesGlobal, Multinational International, and Transnational CompaniesDhirendra Kumar Sharma100% (1)
- Thus, Global Strategy Is Attempting To Answer These Questions For Mnes and Other Firms AroundDocument7 pagesThus, Global Strategy Is Attempting To Answer These Questions For Mnes and Other Firms AroundPhillip James TanNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Structure of Multinational CompaniesDocument23 pagesStrategy and Structure of Multinational CompaniesM JahangirNo ratings yet
- Consumer Culture Brand Positioning Strategies: An Experimental InvestigationDocument11 pagesConsumer Culture Brand Positioning Strategies: An Experimental InvestigationShahmir ShahidNo ratings yet
- Harvard Business ReviewDocument13 pagesHarvard Business ReviewLauren RamosNo ratings yet
- Notes (Ibm Unit 8)Document6 pagesNotes (Ibm Unit 8)Chamare K WintNo ratings yet
- C 11 I S O: Hapter Nternational Trategy and Rganization L ODocument9 pagesC 11 I S O: Hapter Nternational Trategy and Rganization L OAbdirizak AbdirizakNo ratings yet
- Module 8 STRATEGIES OF FIRMS IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE PDFDocument8 pagesModule 8 STRATEGIES OF FIRMS IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE PDFRica SolanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Corporate Level Strategies-IiDocument17 pagesUnit 8: Corporate Level Strategies-IiVarunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Rationale Behind OperationalDocument25 pagesLecture 5 Rationale Behind OperationalmalakNo ratings yet
- Multinational Corporations and Emerging MarketsFrom EverandMultinational Corporations and Emerging MarketsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Concrete Construction Article PDF Strategic Planning For ContractorsDocument4 pagesConcrete Construction Article PDF Strategic Planning For ContractorsMohammed NizamNo ratings yet
- All Airtel Tariff Plans and Migration Code - List of Airtel Call PlansDocument1 pageAll Airtel Tariff Plans and Migration Code - List of Airtel Call PlansSFC FriedleyNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquision MotorolaDocument8 pagesTalent Acquision MotorolaShikha SinghNo ratings yet
- Grassroots Fundraising: Presented By: Group 2 MÙMÙ-MÖNCHDocument24 pagesGrassroots Fundraising: Presented By: Group 2 MÙMÙ-MÖNCHLovelyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- Quick Turn Marketing Exposed Interviewed by Terry Telford Proudly Brought To You by (PDFDrive)Document87 pagesQuick Turn Marketing Exposed Interviewed by Terry Telford Proudly Brought To You by (PDFDrive)Cassandra SkyNo ratings yet
- Session 1-4 Introduction To RetailingDocument48 pagesSession 1-4 Introduction To RetailingShakeeb HashmiNo ratings yet
- KARTHICK B.P (NOV '21-Time Sheet)Document3 pagesKARTHICK B.P (NOV '21-Time Sheet)SureshNo ratings yet
- Banquet and Catering Management (Tango)Document3 pagesBanquet and Catering Management (Tango)Renmar BaccayNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management AssignmentDocument10 pagesMarketing Management AssignmentkshitijNo ratings yet
- Synergy Technical PaperDocument2 pagesSynergy Technical PaperAnandmohanNo ratings yet
- Nickels10ce Enhanced PPT Ch03Document39 pagesNickels10ce Enhanced PPT Ch03Ishaan NasitNo ratings yet
- Wordpress Com Them...Document62 pagesWordpress Com Them...Semih AYBASTINo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 2008 HindiDocument32 pagesIso 9001 2008 HindiNilesh D PatilNo ratings yet
- Lipton Brand ManagementDocument34 pagesLipton Brand ManagementHassan Ali TayyabNo ratings yet
- Mumbai CST OfficeDocument8 pagesMumbai CST Officeyogesh shingareNo ratings yet
- BSCassignmentDocument4 pagesBSCassignmentBagas Wahyu LaksonoNo ratings yet
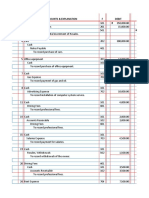
- Practice Notes For Quantity Surveyors - Cost Control and Financial Statements 202109Document12 pagesPractice Notes For Quantity Surveyors - Cost Control and Financial Statements 202109lifei2998No ratings yet
- Job Order Costing HandoutsDocument8 pagesJob Order Costing HandoutsHannah Jane Arevalo LafuenteNo ratings yet
- MBA SummaryDocument450 pagesMBA SummaryMostafa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- CardinalStone Research - Bua Cement PLC Initiation of Coverage - Unearthing Returns From Aggressive Expansions - 25 October 23Document31 pagesCardinalStone Research - Bua Cement PLC Initiation of Coverage - Unearthing Returns From Aggressive Expansions - 25 October 23OlumideNo ratings yet
- Jacopo Targa - URBAN COMMONS - 02octDocument30 pagesJacopo Targa - URBAN COMMONS - 02octLe Petit GardenNo ratings yet
- 220akm Annual Report Fy2022 23Document161 pages220akm Annual Report Fy2022 23sachinaman.2016No ratings yet
- What Not To Do When Preparing A Project ScheduleDocument2 pagesWhat Not To Do When Preparing A Project ScheduleCristian Steven SilvaNo ratings yet
- Budget Driving Institute Prob 2&3Document94 pagesBudget Driving Institute Prob 2&3Ma Sophia Mikaela EreceNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Kenyas Public Debt Dr. Abraham RugoDocument17 pages1.0 Kenyas Public Debt Dr. Abraham RugoREJAY89No ratings yet
- 4 Ways To Make Money Online ReportDocument13 pages4 Ways To Make Money Online ReportMichael IdoroNo ratings yet
- Major Influences On Pricing DecisionsDocument6 pagesMajor Influences On Pricing DecisionsAlief PramestiaNo ratings yet
- Pyramid Power. The Millennium ScienceDocument95 pagesPyramid Power. The Millennium ScienceRich McAdamNo ratings yet
- CopyofIDFM Chapter 7Document107 pagesCopyofIDFM Chapter 7Little JainNo ratings yet