Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1997 850 TCM Electronic Controls
1997 850 TCM Electronic Controls
Uploaded by
matthis.flamant00 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pageselectronic control of AW42-50le
Original Title
1997 850 TCM electronic controls
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentelectronic control of AW42-50le
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pages1997 850 TCM Electronic Controls
1997 850 TCM Electronic Controls
Uploaded by
matthis.flamant0electronic control of AW42-50le
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
"VCC-024484 EN 2010-05-08"
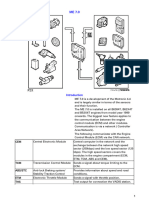
Electronic Control System
To permit exact determination of the gear-
change and lock–up engagement points based
on the selected driving mode, the
transmission control module (TCM) receives
information about the following:
- Selected gear – from gear-shift position
sensor (8).
- Selected driving mode – from the mode
selector (11).
- Road speed – from the vehicle speed sensor
(VSS) (17).
- Transmission input shaft rpm – from
transmission speed sensor (5).
- Engine rpm and load – the fuel injection
system control module (18).
- Throttle opening – from the fuel injection
system control module (18).
- Brake pedal operation – from the stop
(brake) light switch (19).
- Fully depressed accelerator pedal (AP) –
from the kickdown switch (20) on the
throttle cable.
- Transmission oil temperature – from a
temperature sensor (6) in the transmission.
All of this information is processed by the
transmission control module (TCM) (21),
which calculates which gear will provide the
best driving performance based on the
selected driving mode. The transmission
control module (TCM) orders gear-shifts by
sending shift signals to two shift solenoid
valves (S1, S2) in the transmission. Depending
on the input signals, the control module
decides if and when torque converter lock–up,
which is engaged with the help of a special
solenoid (SL), should be activated.
During gear-change, the transmission control
module (TCM) modulates the transmission oil
pressure via a system pressure solenoid valve
(STH), while simultaneously sending a signal
to the ignition system (22) so that the engine
torque is limited as gear-changing occurs.
The transmission control module (TCM) is also
connected to the data link connector (DLC)
(23). Faults occurring in the electronic system
are recorded in the transmission control
module (TCM) memory for subsequent display
© Copyright 2004 Volvo Car Corporation. All rights reserved. 1(2)
"VCC-024484 EN 2010-05-08"
as diagnostic trouble codes (DTC). If a fault is
serious enough to require immediate
attention, the warning lamp (24) in the
combined instrument panel.
In some markets where an on-board
diagnostics system OBD II is a statutory
requirement the transmission control module
(TCM) can also activate the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) (25). The malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) is controlled by the
engine control module (ECM). A transmission
malfunction that affects exhaust emissions will
cause a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) to be
posted and the transmission control module
(TCM) sends a request to the engine control
module (ECM) to activate the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL).
The gear-shift position sensor (8) provides the
transmission control module (TCM) with
information about the selected gear.
The vehicle speed signal (VS) is sent from the
vehicle speed sensor (VSS) (17) which
received pulses from a pulse wheel, locking
wheel for the shift-lock on the output shaft.
Transmission speed information is sent from
the transmission speed sensor (5).
Information about engine rpm and load comes
from the fuel injection system control module
which also provides information about the
throttle opening.
If the brake pedal is depressed, the stop
(brake) light switch closes and transmits a
signal to the transmission control module
(TCM).
When the accelerator pedal (AP) is fully
depressed, the kickdown switch (20) closes.
The transmission control module (TCM) uses
the above signals to calculate the following:
- The control module determines the engine
power output by comparing information
about the throttle opening with the values
for engine load and rpm. This forms the
basis for calculating gear-shift engagement
pressure.
- Signals from the brake light switch are used
to disengage lock–up during braking in
order to avoid jolts in the transmission.
© Copyright 2004 Volvo Car Corporation. All rights reserved. 2(2)
You might also like
- Chapter 23 - Engine Control System WECS 3000Document59 pagesChapter 23 - Engine Control System WECS 3000sezar100% (1)
- Immobilizer System: - System Features & Control SystemDocument50 pagesImmobilizer System: - System Features & Control SystemChanakaAnuruddha100% (12)
- Isuzu 07TF Immobilizer Training Ver1Document50 pagesIsuzu 07TF Immobilizer Training Ver1Teddy KhantNo ratings yet
- Seikitech HW User Manual, T SeriesDocument12 pagesSeikitech HW User Manual, T SeriesKen Dizzeru0% (1)
- Dokumen - Tips Isuzu 07tf Immobilizer Training Ver1Document50 pagesDokumen - Tips Isuzu 07tf Immobilizer Training Ver1Chamila tharanga madushanNo ratings yet
- 320D-336D Excavator Elec. Control SysDocument38 pages320D-336D Excavator Elec. Control Sysjlrodriguezma91% (47)
- 2233000-100 Rev 18 MINItrace Service Manual - MaintenanceDocument760 pages2233000-100 Rev 18 MINItrace Service Manual - MaintenanceNick BNo ratings yet
- Starting SystemDocument84 pagesStarting SystemautoscanningNo ratings yet
- Sitema de Funcionamento AP300DpdfDocument5 pagesSitema de Funcionamento AP300DpdfFrancisco Vitor Mesquita da SilvaNo ratings yet
- 326D Main Electrical System (M0077068Document3 pages326D Main Electrical System (M0077068Baron KasoziNo ratings yet
- v850 Fenix OversiktDocument14 pagesv850 Fenix Oversiktpapaki2No ratings yet
- 777G Off-Highway Power TrainDocument37 pages777G Off-Highway Power TrainMedard OBOUMOUNo ratings yet
- C140/145 Service Training Manual: Body Control ModuleDocument34 pagesC140/145 Service Training Manual: Body Control ModuleJOSE JOSENo ratings yet
- Sis 2.0Document3 pagesSis 2.0sjh14No ratings yet
- Electronic Control Module (Power Train) Inout OutputDocument7 pagesElectronic Control Module (Power Train) Inout OutputSayed Younis Sadaat100% (1)
- Maxiim Vehicle Diagnostic ReportDocument3 pagesMaxiim Vehicle Diagnostic ReportimuxesNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Control SystemsDocument89 pagesVehicle Control SystemsNguyễn Thanh Nhàn100% (1)
- Ecs Service Technical Handbook: Publ. No. 923862-0014 00-08Document31 pagesEcs Service Technical Handbook: Publ. No. 923862-0014 00-08Trần Quốc ĐôngNo ratings yet
- 096transm - Diagnostic ProcedureDocument82 pages096transm - Diagnostic ProcedureCristian Eugen BarburNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM)Document2 pagesComprehensive Component Monitor (CCM)rodrigo alexis aravena ponceNo ratings yet
- Electronic Engine Control (EEC) SystemDocument2 pagesElectronic Engine Control (EEC) SystemJosé AntonioNo ratings yet
- 1574744335252-Je Ldce2Document44 pages1574744335252-Je Ldce2Ponnurangam VeluNo ratings yet
- Section 55 - Electrical System - Chapter 1Document46 pagesSection 55 - Electrical System - Chapter 1Cristian SterieNo ratings yet
- Electronic Transmission Control System Electronic System Description Power Train Control ModuleDocument6 pagesElectronic Transmission Control System Electronic System Description Power Train Control ModuleScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Input Components 326DDocument7 pagesElectrical Input Components 326DBaron KasoziNo ratings yet
- ATA 70 CFM56 B2: A318/19/20/21 Single Aisle FamilyDocument86 pagesATA 70 CFM56 B2: A318/19/20/21 Single Aisle FamilyZbor ZborNo ratings yet
- Cruise ControlDocument10 pagesCruise ControlChandu 143No ratings yet
- System Overview Wiring Harnesses: Harness For The Left RailDocument15 pagesSystem Overview Wiring Harnesses: Harness For The Left RailGleynder Irarica100% (1)
- 320D System OperationDocument13 pages320D System Operationardan fadilahNo ratings yet
- SSP - 250 W12 Engine ManagmentDocument68 pagesSSP - 250 W12 Engine ManagmentBernardNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Control and Monitoring Plat-Form (CAMP)Document16 pages9.3 Control and Monitoring Plat-Form (CAMP)Edwin Alfonso Hernandez MontesNo ratings yet
- Control de Velocidad Del Motor: 30/11/2015 Operación Del Sistema (RENR9848)Document13 pagesControl de Velocidad Del Motor: 30/11/2015 Operación Del Sistema (RENR9848)WalterNo ratings yet
- Case IH Maxxum Calibration, Configuration, Fault Code & H-Menu GuideDocument146 pagesCase IH Maxxum Calibration, Configuration, Fault Code & H-Menu GuideRepairman88No ratings yet
- C32 Engine ControlDocument8 pagesC32 Engine Controlbilmon selvianto100% (1)
- RLO4 Control SystemsDocument36 pagesRLO4 Control SystemsАндрей АндреевичNo ratings yet
- Volvo - My05 07B5254T S40V50C70C30Document30 pagesVolvo - My05 07B5254T S40V50C70C30sharck04100% (1)
- ME7 0-CommsViaNetworkDocument2 pagesME7 0-CommsViaNetworkHumberto ClaudinoNo ratings yet
- Fuel System: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDocument9 pagesFuel System: Shutdown SIS Previous Screenjames foxNo ratings yet
- Introduction To System ArchitectureDocument11 pagesIntroduction To System ArchitectureHakim SabRiNo ratings yet
- Mustang 2005Document40 pagesMustang 2005Ramon SanchezNo ratings yet
- ME7 0-IgnitionDocument2 pagesME7 0-IgnitionHumberto ClaudinoNo ratings yet
- Steering ElectronicDocument18 pagesSteering ElectronicpricopdanielNo ratings yet
- 4001 PDFDocument42 pages4001 PDFlungu mihaiNo ratings yet
- 324e329e m02 Eleccntsysmont en SLDDocument43 pages324e329e m02 Eleccntsysmont en SLDpop67% (3)
- Caf Salidas ElectrónicasDocument6 pagesCaf Salidas ElectrónicasMiguel Angel Garrido CardenasNo ratings yet
- Cat Error ConrollerDocument74 pagesCat Error ConrollerДмитро СелютінNo ratings yet
- Cid Mid FmiDocument11 pagesCid Mid FmiLuis Enrique Castro Manzaneda100% (1)
- 5 EML IIIs - pdf2Document20 pages5 EML IIIs - pdf2NO,NO,NO 2 status QUONo ratings yet
- Auto 3Document40 pagesAuto 3mohamed A.abdeltwabNo ratings yet
- Steering GeneralDocument10 pagesSteering GeneralpricopdanielNo ratings yet
- 140H DAWI Systems OperationDocument18 pages140H DAWI Systems OperationDaniel TekleNo ratings yet
- System Block DiagramDocument2 pagesSystem Block DiagramSüleyman KiliçaslanNo ratings yet
- Bosch ME 7 PDFDocument3 pagesBosch ME 7 PDFBagrinNo ratings yet
- Electronic Engine ControlDocument19 pagesElectronic Engine ControlSohail Bashir97% (31)
- Ram 2014Document3 pagesRam 2014rashidmax111No ratings yet
- 08 Engine Control SystemDocument15 pages08 Engine Control Systemmicudan100% (2)
- FGE30N ControllerDocument80 pagesFGE30N ControllerHai DuyNo ratings yet
- The NAG1 (5-Speed) Automatic TransmissionDocument4 pagesThe NAG1 (5-Speed) Automatic TransmissionEdBunge100% (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Robot Mechanisms and Mechanical Devices IllustratedFrom EverandRobot Mechanisms and Mechanical Devices IllustratedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- An Adaptive I-V Curve Detecting Method For Photovoltaic ModulesDocument6 pagesAn Adaptive I-V Curve Detecting Method For Photovoltaic ModulesKORAKRIT ANANTA-AUOYPORNNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram O F Digital Vo Ltmeter: SwitchDocument1 pageCircuit Diagram O F Digital Vo Ltmeter: SwitchAnil TandonNo ratings yet
- Lecture #8 Operational Amplifiers: J-601-1448 Electronic PrincipalsDocument16 pagesLecture #8 Operational Amplifiers: J-601-1448 Electronic PrincipalschiranjibaviNo ratings yet
- FL-2100B AMP Operators ManualDocument7 pagesFL-2100B AMP Operators Manualoctavian barbuNo ratings yet
- NTE Electronics NTE4049 DatasheetDocument2 pagesNTE Electronics NTE4049 DatasheetalejandrosaumethNo ratings yet
- HT648LDocument14 pagesHT648LHarshit DuaNo ratings yet
- 336E M03 ElecCtrlSysMntr en STUDocument5 pages336E M03 ElecCtrlSysMntr en STUKJDNKJZEFNo ratings yet
- Supertex MOSFETX RefDocument1 pageSupertex MOSFETX RefjuampicNo ratings yet
- Talk Back SystemDocument2 pagesTalk Back SystemkamranNo ratings yet
- Dimensionnement'une Antenne Patch A Frequence FixeDocument4 pagesDimensionnement'une Antenne Patch A Frequence FixeTASONA DOKO JOCELYN TANGUYNo ratings yet
- NAMM20 Exhibitor List 05-02-2024Document76 pagesNAMM20 Exhibitor List 05-02-2024nenamishevskaNo ratings yet
- Soil Monitoring - Report 1Document13 pagesSoil Monitoring - Report 1Bisma MuhammadNo ratings yet
- TAS6XX - Install Manual - 2011Document102 pagesTAS6XX - Install Manual - 2011Hozya100% (1)
- Localized Commercial Leaflet 929002998002 en AADocument4 pagesLocalized Commercial Leaflet 929002998002 en AAandrejacvetkovic7No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-1Document24 pagesChapter 1-1Ashraf YusofNo ratings yet
- Motherboards and Power SupplyDocument6 pagesMotherboards and Power SupplyThairu KamauNo ratings yet
- Product Information Oticon Safari SP 900, 600 and 300: Fitting RangeDocument2 pagesProduct Information Oticon Safari SP 900, 600 and 300: Fitting RangeSulaNo ratings yet
- 9 30783 62576 en AdminDocument2 pages9 30783 62576 en AdminAlek Freire DíazNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety TestDocument1 pageElectrical Safety TestCollins OtienoNo ratings yet
- 3SU11000AB401FA0 Datasheet enDocument4 pages3SU11000AB401FA0 Datasheet enpatrykk11195No ratings yet
- Intelia Rysunki MechanikiDocument8 pagesIntelia Rysunki MechanikiJan GumskiNo ratings yet
- DT50 Accessory Brochure en - 20190926Document10 pagesDT50 Accessory Brochure en - 20190926yashavanta shettyNo ratings yet
- Multistage Coil Gun Project ProposalDocument8 pagesMultistage Coil Gun Project ProposalAbdullah ArifNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineers 02-2024 - List of Qualified ExamineesDocument23 pagesMechanical Engineers 02-2024 - List of Qualified ExamineesPRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- 210 (645 665) ASTRO 6 Twins - CHSM66M (DG) F-BH - 2384x1303x35 - EN - 20220616Document2 pages210 (645 665) ASTRO 6 Twins - CHSM66M (DG) F-BH - 2384x1303x35 - EN - 20220616RichardNo ratings yet
- Corruption Exposed Between Spic Drdo Lab & Bel Bangalore PDFDocument7 pagesCorruption Exposed Between Spic Drdo Lab & Bel Bangalore PDFNathaniel WareNo ratings yet
- Apl-12 12 2022Document33 pagesApl-12 12 2022Cristina SubirNo ratings yet
- Mistake Proofing: See If You Can Find The Poka-Yokes!Document8 pagesMistake Proofing: See If You Can Find The Poka-Yokes!Balachandar SNo ratings yet