Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHOBIA
PHOBIA
Uploaded by
Nonie Castro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesPHOBIA
PHOBIA
Uploaded by
Nonie CastroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
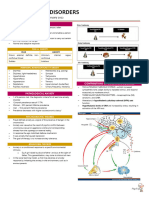
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
PHOBIA Cognitive theorists believe that some
Persistent avoidance behavior individuals engage in negative and
secondary to irrational feel of a irrational thinking that produces
specific object, activity, or situation. anxiety reactions.
Excessive irrational fear of a specific The individual begins to seek out
object, circumstance, or situation. avoidance behaviors to prevent the
PHOBIA CLASSIFICATION anxiety reactions, and phobias result.
Agoraphobia BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS
Social Phobia Temperament
Specific Phobia Life experience
Other phobic anxiety disorder CLINICAL FEATURES
Phobic anxiety disorder, unspecified Cannot be explained the reason away.
PRE DISPOSING FACTORS OF PHOBIA Fear leads to an avoidance of the
PSYCHO ANALYTICAL THEORY feared situations.
Freud believed that phobias develop TYPES OF PHOBIA
when a child experiences normal SIMPLE PHOBIA (SPECIFIC PHOBIA)
incestuous feeling toward the irrational fear of a specific object or
opposite sex parent (Oedipal/Electra stimulus.
complex) and fears aggression from Commonly seen in children.
the same-sex parent (castration Exposure to phobic object result in
anxiety) panic attacks.
LEARNING THEORY TERM
Classic conditioning in the case of Ailurophobia – Cats
phobias may be explained as follows: Alophobia – Pain
stressful stimulus produces an Anthophobia – Flowers
“unconditioned” response of fear. Anthropophobia – People
COGNITIVE THEORY Aquaphobia – Water
Arachnophobia – Spider
Astraphobia – Lightning SOCIAL PHOBIA
Belonephobia – Needles Irrational fear of performing activities
Brontophobia – Thunder in the presence of other people or
Claustrophobia – Closed spaces interacting with others.
Cynophobia – Dogs AGORAPHOBIA
Dementophia – Insanity Irrational fear of being places away
Equinophobia – Horses from the familiar setting of home, in
Gamophobia – Marriage crowds, or the situations in which the
Herpetophobia – Lizard, Reptiles patients cannot leave easily.
Homophobia – Homosexuality COURSE
Murophobia – Mice Phobia are more common in women.
Mysophobia – Dirt, germs, Onset is sudden without any cause.
contamination The course is usually chronic.
Numerophobia – Numbers MANAGEMENT
Nyctophobia – Darkness Supportive therapy
Ochophobia – Riding a car Individual psychotherapy
Ophidiophobia – Snakes
Pyrophobia – Fire BEHAVIORAL THERAPY
Scoleciphobia – Worms Systematic desensitization
Siderodromophobia – Railroads or Implosion therapy (flooding)
Train travel Regroup/family therapy
Taphophobia – Being buried alive PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
Thanatophobia – Death ANXIOLITICS – Benzodiazepines
Trichophobia – Hair ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS – Beta
Xenophobia – Strangers blockers, propranolol and atenolol,
Zoophobia – Animal have been tried with success in clients
experiencing anticipatory
performance anxiety or “stage fright”
ANTIDEPRESSANTS – Tricyclic
imipramine and the monoamine
oxidaze (MAO) inhibitor phenelzine
have been effective in diminishing
symptoms of agoraphobia and social
phobia and the SSRI’s have become
the first-line treatment of choice for
social phobia.
NSG DIAGNOSIS
Fear related to causing
embarrassment to self in front of
others; to being in a place from which
one is unable to escape.
Social isolation related to fears of
being in a place from which one is
unable to escape, evidenced by
staying alone, refusing to leave room
or home.
You might also like
- Exposure Therapy For Anxiety - Principles and PracticeDocument511 pagesExposure Therapy For Anxiety - Principles and PracticeTrang NGUYEN100% (1)
- Textbook Anxiety Disorders Second EditionDocument823 pagesTextbook Anxiety Disorders Second EditionMauricio Harker100% (6)
- 2021 Drills-MergedDocument58 pages2021 Drills-MergedPJBautistaMadduma100% (1)
- The Encyclopedia of Phobias, Fears, and AnxietiesDocument643 pagesThe Encyclopedia of Phobias, Fears, and Anxietiescharlotte_avignon100% (1)
- Phobias LectureDocument28 pagesPhobias Lectureanon_473291823100% (1)
- 317 Revalida ReviewerDocument13 pages317 Revalida ReviewerSOPHIA PILLENANo ratings yet
- Topic-3 Disorders in Human BehaviorDocument7 pagesTopic-3 Disorders in Human BehaviorKYLA STEFANIE MATULACNo ratings yet
- Neurotic (Psychoneurotic) BehaviorsDocument2 pagesNeurotic (Psychoneurotic) BehaviorsNoelyn Natarte LuadNo ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument27 pagesPhobiasuresh patilNo ratings yet
- Neurotic DisorderDocument180 pagesNeurotic DisordertendolsmithNo ratings yet
- Phobia - Introduction & Kinds (Psyche)Document4 pagesPhobia - Introduction & Kinds (Psyche)Jonas914No ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument43 pagesPhobiaastha singhNo ratings yet
- Module in Chapter 3Document21 pagesModule in Chapter 3Laiza Mae Autor100% (1)
- Anxiety and Stress-Related IllnessDocument58 pagesAnxiety and Stress-Related IllnessQuennie Rose Arobo EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Phobias BookletDocument16 pagesPhobias Bookletnaiksushil87No ratings yet
- Anxiety-Related Disorders: by Joan SinghDocument41 pagesAnxiety-Related Disorders: by Joan SinghJoan SinghNo ratings yet
- Phobias and Its Types: Group Members Tanishq, Lakshya, Samarth & ChetanDocument40 pagesPhobias and Its Types: Group Members Tanishq, Lakshya, Samarth & Chetanlakshya rautelaNo ratings yet
- Activity On PhobiasDocument1 pageActivity On PhobiasMingoy, CarlosNo ratings yet
- Common Phobias GK Notes in PDFDocument4 pagesCommon Phobias GK Notes in PDFMagesh MagiNo ratings yet
- Phobias: Students: Cruz Palacios David Gómez Pérez Angel Eduardo Ruperto Monroy Bernardo Ventura Ochoa YeseniaDocument9 pagesPhobias: Students: Cruz Palacios David Gómez Pérez Angel Eduardo Ruperto Monroy Bernardo Ventura Ochoa YeseniaEduardo GomezNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument14 pagesPhobiasLaura CampolinoNo ratings yet
- Do You Suffer From A PhobiaDocument4 pagesDo You Suffer From A PhobiaNavinYattiNo ratings yet
- 1) Phobic Anxiety DisordersDocument12 pages1) Phobic Anxiety DisordersAzrina KhanNo ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument41 pagesPhobiaRujuta BaramateNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument10 pagesPhobiasapi-276690632No ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument10 pagesPhobiasuganogkevinNo ratings yet
- Salinan Dari Scary Stories by SlidesgoDocument6 pagesSalinan Dari Scary Stories by SlidesgoBetrand SkullNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument17 pagesEnglishMery MeryemNo ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument24 pagesPhobiaLany Cardente PascuaNo ratings yet
- Phobias - Causes, Types, Treatment, Symptoms & MoreDocument5 pagesPhobias - Causes, Types, Treatment, Symptoms & MoreLone SaithaNo ratings yet
- Ronnie Report 2Document133 pagesRonnie Report 2s8dtt2dxcqNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders - Phobias - Blog PsychologyDocument7 pagesAnxiety Disorders - Phobias - Blog PsychologyDamayanthi RajasekarNo ratings yet
- Phobia: IntroductionDocument7 pagesPhobia: IntroductionRachel SepthyNo ratings yet
- Common and Unique Fears ExplainedDocument10 pagesCommon and Unique Fears ExplainedMark DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- ქეთევან რაქვიაშვილიDocument12 pagesქეთევან რაქვიაშვილიKetevan RakviashviliNo ratings yet
- Phobias b1 PDFDocument2 pagesPhobias b1 PDFkailukahsuNo ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument11 pagesPhobiaLegal Affairs OfficeNo ratings yet
- Salinan Dari Scary Stories by SlidesgoDocument6 pagesSalinan Dari Scary Stories by SlidesgoBetrand SkullNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument22 pagesPhobiasSharizal SaklinNo ratings yet
- All About PhobiasDocument13 pagesAll About PhobiasJharna MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- List of Common Phobias, Manias and PhiliasDocument4 pagesList of Common Phobias, Manias and PhiliasKhalid MushtaqueNo ratings yet
- Phobias Group PresentationDocument11 pagesPhobias Group PresentationHafsa MarufNo ratings yet
- ქეთევან რაქვიაშვილიDocument8 pagesქეთევან რაქვიაშვილიKetevan RakviashviliNo ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument4 pagesPhobiaZeba QuadiriNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument52 pagesPhobiassc2ghrc9kqNo ratings yet
- AgoraphobiaDocument12 pagesAgoraphobiaKanchan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Psycho 4Document15 pagesPsycho 4Basma AlwindawiNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument10 pagesPhobiasHafiza Rija ShahidNo ratings yet
- Al G. DavenDocument2 pagesAl G. DaventhecutealNo ratings yet
- Past Life Regression PDFDocument38 pagesPast Life Regression PDFVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument17 pagesPhobiaastha singhNo ratings yet
- PsycjopatholoyDocument7 pagesPsycjopatholoyamnaNo ratings yet
- Psychological Conditions, Non-Psychological Conditions & Animal PhobiasDocument3 pagesPsychological Conditions, Non-Psychological Conditions & Animal PhobiasJyuKyuNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument6 pagesAnxietylyleNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Based DisordersDocument111 pagesAnxiety Based DisordersVinaya KrithikaNo ratings yet
- Human BehaviorDocument5 pagesHuman Behaviorjetlee estacionNo ratings yet
- Psych 1 Phobia ProjectDocument3 pagesPsych 1 Phobia ProjectalexlaneNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggrisDocument2 pagesTugas B.inggrisdian_purwandiNo ratings yet
- (Presentation) PhobiaDocument40 pages(Presentation) PhobiaJajaMeowNo ratings yet
- Eng 3Document3 pagesEng 3groverdrishti3124No ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disordersallen cabasagNo ratings yet
- Ghost PhobiaDocument3 pagesGhost PhobiaHamza yusuf100% (1)
- Understanding Phobias: Symptoms; Causes; Treatment; PreventionFrom EverandUnderstanding Phobias: Symptoms; Causes; Treatment; PreventionNo ratings yet
- Negative Affect Erasing MethodDocument2 pagesNegative Affect Erasing MethodmirkjhaelNo ratings yet
- Hypnosis and Behavior Therapy A ReviewDocument25 pagesHypnosis and Behavior Therapy A ReviewGeorgios LeriosNo ratings yet
- Case Note Question Sem 2-2022 (Official Version)Document9 pagesCase Note Question Sem 2-2022 (Official Version)Thảo ThanhNo ratings yet
- Kring Abnormal Psychology Chapter 6 Anxiety NotesDocument16 pagesKring Abnormal Psychology Chapter 6 Anxiety NotesAnn Ross Fernandez50% (2)
- Imtiaz Manji Trust and Value EbookDocument16 pagesImtiaz Manji Trust and Value EbookLoreen DionicioNo ratings yet
- Psych NotesDocument24 pagesPsych NotesMae Ann Flores Mahinay100% (2)
- Order 6352675 - Skinner's Legacy and The Modern Day Applications of TheoriesDocument8 pagesOrder 6352675 - Skinner's Legacy and The Modern Day Applications of Theoriesmidgetpopstar1998No ratings yet
- TT Lib Breath 2.0 PDFDocument0 pagesTT Lib Breath 2.0 PDFKristijan IvankovicNo ratings yet
- Phobias - Skimming and Scanning ExerciseDocument4 pagesPhobias - Skimming and Scanning ExerciseJuan ArizaNo ratings yet
- FINAL History of Psychiatric ClassificationDocument89 pagesFINAL History of Psychiatric ClassificationAli B. SafadiNo ratings yet
- Techno PhobiaDocument1 pageTechno Phobiaabdel2121No ratings yet
- Neurotic DisordersDocument13 pagesNeurotic DisordersSushmita BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- Overcome ShynessDocument3 pagesOvercome ShynessLM CuestaNo ratings yet
- Appetite Volume 25 Issue 2 1995 (Doi 10.1006/appe.1995.0046) KAREN HOBDEN PATRICIA PLINER - Effects of A Model On Food Neophobia in HumansDocument13 pagesAppetite Volume 25 Issue 2 1995 (Doi 10.1006/appe.1995.0046) KAREN HOBDEN PATRICIA PLINER - Effects of A Model On Food Neophobia in HumansRodrigo Alejandro Romo MuñozNo ratings yet
- Abbott (2004) - Post-Event Rumination and Negative Self-Appraisal in Social Phobia Before and After TreatmentDocument9 pagesAbbott (2004) - Post-Event Rumination and Negative Self-Appraisal in Social Phobia Before and After TreatmentAnahi CopatiNo ratings yet
- ListeningsDocument4 pagesListeningscvinglesNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Its Impact On Students Performance at University Level University of Peshawar (Ayesha Irfan)Document77 pagesAnxiety and Its Impact On Students Performance at University Level University of Peshawar (Ayesha Irfan)Muhammad Nawaz Khan Abbasi100% (2)
- Theories of Personality MidtermDocument18 pagesTheories of Personality MidtermJesabel AycoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Psycho Class 12Document15 pagesChapter 4 Psycho Class 12Shreya JainNo ratings yet
- Unturned Stones PsychologyDocument8 pagesUnturned Stones PsychologyartycraftsocialNo ratings yet
- Phobias: What Is Your Problem ?! Hippopotomonstro-Sesquipedaliophobia ?!Document4 pagesPhobias: What Is Your Problem ?! Hippopotomonstro-Sesquipedaliophobia ?!MarNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument36 pagesResearch Paperjamaicapascual590No ratings yet
- Specific Phobias: Moderator: Dr. Navkiran S. MahajanDocument26 pagesSpecific Phobias: Moderator: Dr. Navkiran S. MahajanaartiNo ratings yet
- Modelul Lui Claire WeekesDocument11 pagesModelul Lui Claire WeekesDiana Alexandru-DolghiiNo ratings yet
- The Paradox of Being A Probationer Tales of Joy and SorrowDocument10 pagesThe Paradox of Being A Probationer Tales of Joy and SorrowInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet