Professional Documents
Culture Documents
D
D
Uploaded by
drjalalofficialCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Theme 16-2 Purulent Diseases-1Document3 pagesTheme 16-2 Purulent Diseases-1Taranbir SainiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System QuestionsDocument8 pagesRespiratory System Questionschristine_8995No ratings yet
- DDocument4 pagesDdrjalalofficialNo ratings yet
- Materi Poster PneumothoraksDocument6 pagesMateri Poster PneumothoraksDhila ThasliyahNo ratings yet
- Lung QuizDocument14 pagesLung QuizConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- 06 ChestDocument16 pages06 ChestANAS ALINo ratings yet
- Medicine-I Important BCQSDocument10 pagesMedicine-I Important BCQSShairy SohoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Ab EmpirisDocument4 pagesCeftriaxone Ab EmpirisFenyNo ratings yet
- Aku 2Document70 pagesAku 2rehan hayderNo ratings yet
- Mcqsfinalexamrespiratorysystem 181114064213Document4 pagesMcqsfinalexamrespiratorysystem 181114064213Shahzad Jawaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Quizlet LungsDocument20 pagesQuizlet LungsPrinceNo ratings yet
- Provide: Slide Adenocarcinoma ParuDocument2 pagesProvide: Slide Adenocarcinoma ParuBOONo ratings yet
- Pathophysiological Study of Chronic Necrotizing Pulmonary AspergillosisDocument5 pagesPathophysiological Study of Chronic Necrotizing Pulmonary AspergillosisSyaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Jurding Bedah MuzzamilDocument16 pagesJurding Bedah MuzzamilunknownNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (PLCH) : A Rare Cause of Chronic CoughDocument2 pagesPulmonary Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (PLCH) : A Rare Cause of Chronic CoughRaden Dicky Wirawan ListiandokoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary MedicineDocument20 pagesPulmonary Medicineد.سلمان زبيداتNo ratings yet
- Pneumonitis Ec ChemotheraphyDocument5 pagesPneumonitis Ec ChemotheraphyNurafiat AntonNo ratings yet
- Passable 350 Q&aDocument76 pagesPassable 350 Q&aDavid Yousef100% (1)
- SCERespMedSampleQs PDFDocument28 pagesSCERespMedSampleQs PDFZoya AnnamNo ratings yet
- CDocument1 pageCdrjalalofficialNo ratings yet
- A Case of Tracheal Tumor Masquerading As AsthmaDocument4 pagesA Case of Tracheal Tumor Masquerading As Asthmamastansk84No ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument3 pagesTuberculosis89qqzp4yhkNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument136 pagesMCQRahul Patil100% (1)
- Abstract PUBMEDDocument1 pageAbstract PUBMEDAlexandra MateiNo ratings yet
- Case Records: Massachusetts General HospitalDocument6 pagesCase Records: Massachusetts General HospitalRasvan Cristian StoicaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Interstitial Lung DiseasesDocument38 pagesApproach To Interstitial Lung DiseasesmeawchiNo ratings yet
- Section II - Chest Radiology: Figure 1ADocument35 pagesSection II - Chest Radiology: Figure 1AHaluk Alibazoglu100% (1)
- Mikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakDocument19 pagesMikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakVania TobingNo ratings yet
- PBL Case 2 - Lung Small Cell CarcinomaDocument19 pagesPBL Case 2 - Lung Small Cell CarcinomahalesipsumNo ratings yet
- Clase Radiología Med 1Document71 pagesClase Radiología Med 1Alejandro Elias Guzman MoreNo ratings yet
- A Case of Pulmonary Tuberculosis With Multiple Nodules Mimicking Lung MetastasesDocument4 pagesA Case of Pulmonary Tuberculosis With Multiple Nodules Mimicking Lung MetastasesKusuma IntanNo ratings yet
- Fozia Sheet 1 - ExampleDocument1 pageFozia Sheet 1 - ExamplekhurramNo ratings yet
- Chest Radiography Diagnostic Value and Interpretation: Imaging ModalitiesDocument12 pagesChest Radiography Diagnostic Value and Interpretation: Imaging Modalitiesdoctor evanNo ratings yet
- Exam Tips PDFDocument32 pagesExam Tips PDFKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- MRCP 2Document26 pagesMRCP 2riyaz414No ratings yet
- COPDDocument4 pagesCOPDomaryadak0No ratings yet
- Journal Radiologi 3Document14 pagesJournal Radiologi 3WinayNayNo ratings yet
- Hospital TherapyDocument46 pagesHospital TherapyPlutonic HeartNo ratings yet
- Pleural Thickening Mimicking With Lung Abscess and Loculated Hydropneumothorax: A Case ReportDocument1 pagePleural Thickening Mimicking With Lung Abscess and Loculated Hydropneumothorax: A Case ReportcharizardNo ratings yet
- CDocument3 pagesCdrjalalofficialNo ratings yet
- Lung CA 2012Document43 pagesLung CA 2012ulka07No ratings yet
- Med Respi T&D QuestionsDocument14 pagesMed Respi T&D QuestionsD PatelNo ratings yet
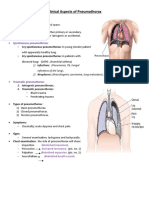
- Clinical Aspects of PneumothoraxDocument3 pagesClinical Aspects of PneumothoraxelisabethNo ratings yet
- MCQs and Cases in MedicineDocument14 pagesMCQs and Cases in Medicineyoune6No ratings yet
- Case 12749: Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Complication of TuberculosisDocument8 pagesCase 12749: Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Complication of TuberculosisSanyuki KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- TESTS "STEP-2" Full Base 2014Document57 pagesTESTS "STEP-2" Full Base 2014gauravNo ratings yet
- Cardio & Chest AnswersDocument10 pagesCardio & Chest AnswersVişiön Ac TantaNo ratings yet
- Nonresolving PF SarcoidosisDocument6 pagesNonresolving PF SarcoidosisJeansDaquinagNo ratings yet
- Chest 1-4-1-1Document7 pagesChest 1-4-1-1Kahkashan HameedNo ratings yet
- Emad Efat Chest CT BestDocument260 pagesEmad Efat Chest CT Bestdr Mohit TaylorNo ratings yet
- GC Proceedings - Docx1Document11 pagesGC Proceedings - Docx1Thejus BhaskarNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument24 pagesPneumoniaMuhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Lung MassDocument4 pagesAsthma and Lung MassAzmachamberAzmacareNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Radiology-Pathology CorrelationDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Radiology-Pathology CorrelationNetii FarhatiNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer CaseDocument13 pagesLung Cancer CaseAbdirahman Ali YabarNo ratings yet
- COC Exam 2019 For HO (1) - 250321095434Document66 pagesCOC Exam 2019 For HO (1) - 250321095434Behar Abduraheman83% (6)
- Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2019From EverandAnnual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2019No ratings yet
- ABC of Pleural DiseasesFrom EverandABC of Pleural DiseasesNajib M. RahmanNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesFrom EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo ratings yet
D
D
Uploaded by
drjalalofficialOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
D
D
Uploaded by
drjalalofficialCopyright:
Available Formats
Which of the following indicates T3 rather than T4 lung
cancer?
A. Invasion of the oesophagus
B. Invasion of the trachea
C. Invasion of the pericardium
D. Malignant pleural effusion
E. Invasion of the vertebral body
21. A 78-year-old male smoker with hospital admission 2 months
ago for a dense left Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) cerebral
infarct presents. He has a 3 week history of low grade fevers
and weight loss. Chest radiograph reveals new left lower lobe
consolidation with areas of cavitation and air fluid levels,
but no hilar lymphadenopathy. Which is the most likely
diagnosis?
A. Hospital acquired pneumonia with lung abscess
B. Bronchogenic carcinoma
C. Bronchoalveolar cell carcinoma
D. Traumatic contusion with lung cysts
E. Aspiration with anaerobic pneumonia
A 47-year-old female Caucasian smoker presents with
persistent cough and haemoptysis. CT shows a 2.2cm soft
tissue mass in the left lower lobe with coarse calcific foci
and no mediastinal, hilar or axillary lymphadenopathy. A
small endobronchial lesion is also seen in the left lower lobe
bronchus. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Bronchogenic carcinoma
B. Pulmonary TB
C. Lymphoma
D. Fibrosing mediastinits
E. Bronchial carcinoid
23. A 50-year-old builder undergoing CT of the chest has pleural
thickening and calcification along the diaphragmatic pleura.
Which is the most specific distinguishing feature to indicate
malignant rather than benign pleural disease?
A. Circumferential pleural thickening
B. Nodularity of the pleural thickening
C. Parietal pleural thickening greater than 1cm
D. Mediastinal pleural involvement
E. Pleural effusion
24. Which of the following features most favours melioidosis
rather than tuberculosis?
A. Lobar consolidation
B. Cavitation
C. Upper lobe predominance of nodular change
D. Rapid progression of clinical features
E. Lack of pleural involvement
You might also like
- Theme 16-2 Purulent Diseases-1Document3 pagesTheme 16-2 Purulent Diseases-1Taranbir SainiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System QuestionsDocument8 pagesRespiratory System Questionschristine_8995No ratings yet
- DDocument4 pagesDdrjalalofficialNo ratings yet
- Materi Poster PneumothoraksDocument6 pagesMateri Poster PneumothoraksDhila ThasliyahNo ratings yet
- Lung QuizDocument14 pagesLung QuizConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- 06 ChestDocument16 pages06 ChestANAS ALINo ratings yet
- Medicine-I Important BCQSDocument10 pagesMedicine-I Important BCQSShairy SohoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Ab EmpirisDocument4 pagesCeftriaxone Ab EmpirisFenyNo ratings yet
- Aku 2Document70 pagesAku 2rehan hayderNo ratings yet
- Mcqsfinalexamrespiratorysystem 181114064213Document4 pagesMcqsfinalexamrespiratorysystem 181114064213Shahzad Jawaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Quizlet LungsDocument20 pagesQuizlet LungsPrinceNo ratings yet
- Provide: Slide Adenocarcinoma ParuDocument2 pagesProvide: Slide Adenocarcinoma ParuBOONo ratings yet
- Pathophysiological Study of Chronic Necrotizing Pulmonary AspergillosisDocument5 pagesPathophysiological Study of Chronic Necrotizing Pulmonary AspergillosisSyaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Jurding Bedah MuzzamilDocument16 pagesJurding Bedah MuzzamilunknownNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (PLCH) : A Rare Cause of Chronic CoughDocument2 pagesPulmonary Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (PLCH) : A Rare Cause of Chronic CoughRaden Dicky Wirawan ListiandokoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary MedicineDocument20 pagesPulmonary Medicineد.سلمان زبيداتNo ratings yet
- Pneumonitis Ec ChemotheraphyDocument5 pagesPneumonitis Ec ChemotheraphyNurafiat AntonNo ratings yet
- Passable 350 Q&aDocument76 pagesPassable 350 Q&aDavid Yousef100% (1)
- SCERespMedSampleQs PDFDocument28 pagesSCERespMedSampleQs PDFZoya AnnamNo ratings yet
- CDocument1 pageCdrjalalofficialNo ratings yet
- A Case of Tracheal Tumor Masquerading As AsthmaDocument4 pagesA Case of Tracheal Tumor Masquerading As Asthmamastansk84No ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument3 pagesTuberculosis89qqzp4yhkNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument136 pagesMCQRahul Patil100% (1)
- Abstract PUBMEDDocument1 pageAbstract PUBMEDAlexandra MateiNo ratings yet
- Case Records: Massachusetts General HospitalDocument6 pagesCase Records: Massachusetts General HospitalRasvan Cristian StoicaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Interstitial Lung DiseasesDocument38 pagesApproach To Interstitial Lung DiseasesmeawchiNo ratings yet
- Section II - Chest Radiology: Figure 1ADocument35 pagesSection II - Chest Radiology: Figure 1AHaluk Alibazoglu100% (1)
- Mikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakDocument19 pagesMikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakVania TobingNo ratings yet
- PBL Case 2 - Lung Small Cell CarcinomaDocument19 pagesPBL Case 2 - Lung Small Cell CarcinomahalesipsumNo ratings yet
- Clase Radiología Med 1Document71 pagesClase Radiología Med 1Alejandro Elias Guzman MoreNo ratings yet
- A Case of Pulmonary Tuberculosis With Multiple Nodules Mimicking Lung MetastasesDocument4 pagesA Case of Pulmonary Tuberculosis With Multiple Nodules Mimicking Lung MetastasesKusuma IntanNo ratings yet
- Fozia Sheet 1 - ExampleDocument1 pageFozia Sheet 1 - ExamplekhurramNo ratings yet
- Chest Radiography Diagnostic Value and Interpretation: Imaging ModalitiesDocument12 pagesChest Radiography Diagnostic Value and Interpretation: Imaging Modalitiesdoctor evanNo ratings yet
- Exam Tips PDFDocument32 pagesExam Tips PDFKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- MRCP 2Document26 pagesMRCP 2riyaz414No ratings yet
- COPDDocument4 pagesCOPDomaryadak0No ratings yet
- Journal Radiologi 3Document14 pagesJournal Radiologi 3WinayNayNo ratings yet
- Hospital TherapyDocument46 pagesHospital TherapyPlutonic HeartNo ratings yet
- Pleural Thickening Mimicking With Lung Abscess and Loculated Hydropneumothorax: A Case ReportDocument1 pagePleural Thickening Mimicking With Lung Abscess and Loculated Hydropneumothorax: A Case ReportcharizardNo ratings yet
- CDocument3 pagesCdrjalalofficialNo ratings yet
- Lung CA 2012Document43 pagesLung CA 2012ulka07No ratings yet
- Med Respi T&D QuestionsDocument14 pagesMed Respi T&D QuestionsD PatelNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of PneumothoraxDocument3 pagesClinical Aspects of PneumothoraxelisabethNo ratings yet
- MCQs and Cases in MedicineDocument14 pagesMCQs and Cases in Medicineyoune6No ratings yet
- Case 12749: Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Complication of TuberculosisDocument8 pagesCase 12749: Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Complication of TuberculosisSanyuki KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- TESTS "STEP-2" Full Base 2014Document57 pagesTESTS "STEP-2" Full Base 2014gauravNo ratings yet
- Cardio & Chest AnswersDocument10 pagesCardio & Chest AnswersVişiön Ac TantaNo ratings yet
- Nonresolving PF SarcoidosisDocument6 pagesNonresolving PF SarcoidosisJeansDaquinagNo ratings yet
- Chest 1-4-1-1Document7 pagesChest 1-4-1-1Kahkashan HameedNo ratings yet
- Emad Efat Chest CT BestDocument260 pagesEmad Efat Chest CT Bestdr Mohit TaylorNo ratings yet
- GC Proceedings - Docx1Document11 pagesGC Proceedings - Docx1Thejus BhaskarNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument24 pagesPneumoniaMuhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Lung MassDocument4 pagesAsthma and Lung MassAzmachamberAzmacareNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Radiology-Pathology CorrelationDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Radiology-Pathology CorrelationNetii FarhatiNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer CaseDocument13 pagesLung Cancer CaseAbdirahman Ali YabarNo ratings yet
- COC Exam 2019 For HO (1) - 250321095434Document66 pagesCOC Exam 2019 For HO (1) - 250321095434Behar Abduraheman83% (6)
- Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2019From EverandAnnual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2019No ratings yet
- ABC of Pleural DiseasesFrom EverandABC of Pleural DiseasesNajib M. RahmanNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesFrom EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo ratings yet