Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KOM Sample Report
KOM Sample Report
Uploaded by
Viraj POriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KOM Sample Report
KOM Sample Report
Uploaded by
Viraj PCopyright:
Available Formats
KINEMATICS OF MACHINES
ASSIGNMENT ON GEAR TRAINS
Submitted by:
1. VIRAJ P (B221290ME)
2. KUNAMALLA JASON RATHNAM (B220976ME)
3. INDUPALLI ABHIRAM (B220907ME)
GROUP NO 17
Department of Mechanical Engineering
National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Calicut
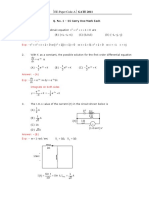
Problem 8.6
Fig. 8.6 shows an epicyclic gear train (Ferguson's paradox) in which gear A is fixed to the
frame, hence it is stationary. The arm B and gears C and D can rotate freely on the shaft S. The
PCD of all the gears is same so that the planet P meshes with all the gears. Find the revolutions
of gear C and D for one revolution of arm B.
SOLUTION:
Given data,
ZA =100 ZC =102 ZD =99
Zp =20 NB =1 rev
To find :-
(i) NC
(ii) ND
Step-1 : Calculate the revolutions of gear C and D using tabular method
Step Motion
s
Revolution of elements
Arm Gear 𝑺𝟏 Gear Gear
(output) (Input) P1 A1 -S2
P P
1 Arm fixed and give +1 0 +1 ZS ZS ZP
− ( 1) − ( 1) ( 1 )
revolution to gear A. Z P1 ZP1 ZA1
2 Multiply by + x. 0 +x ZS ZS
-x ( 1 ) -x ( 1 )
Z P1 ZA1
3 Add +y revolutions in +y +y +y +y
all elements.
4 Total motion (Adding y x+y ZS ZS
y-x ( 1 ) y-x ( 1 )
step 2 and 3). Z P1 ZA1
It is given that NB = 1 rev and NA =0
From table, NB = y = 1 rev
and NA = x + y = 0
x = -1 rev
Z 100
Speed of gear C, NC =x (ZA) +y= (-1)x102 + 1
C
1
NC = 51 rev (in the same direction of arm B)
Z 100
Speed of gear D, ND = x (ZA) + 𝑦 = (−1) ( 98 ) +1
D
1 1
∴ ND =- 49 rev. = 49 rev. (in the opposite direction of arm B)
You might also like
- PHY133 Angular MomentumDocument6 pagesPHY133 Angular MomentumAngel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PDF - Self Recorded - Lect-7 Unit - 3 Gear Trains - Problems On Epicyclic Gear TrainDocument15 pagesPDF - Self Recorded - Lect-7 Unit - 3 Gear Trains - Problems On Epicyclic Gear TrainNikhil JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chrysler Dakota Part10Document32 pagesChrysler Dakota Part10Sašo Brunšek-BrunoNo ratings yet
- KOM Sample ReportDocument3 pagesKOM Sample ReportViraj PNo ratings yet
- KOMreportDocument3 pagesKOMreportViraj PNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Gears PresentationDocument15 pagesCH 12 Gears Presentationcılem cıuNo ratings yet
- P19 IIR Filters Part2Document21 pagesP19 IIR Filters Part2Romit Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Direct Design Methods: 1 + + + + + + + + Az Az HZ B BZ BZ Az Az BZ Az ........ ...... ........Document4 pagesDirect Design Methods: 1 + + + + + + + + Az Az HZ B BZ BZ Az Az BZ Az ........ ...... ........Sajid AhmedNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. Ans.:: Module 3: Analytical Tools Tutorials (Note: Show All Workings and Explanations Clearly)Document4 pagesA. B. C. Ans.:: Module 3: Analytical Tools Tutorials (Note: Show All Workings and Explanations Clearly)Uchechi Chioma UgoNo ratings yet
- Ba'cha DSP Lab 9Document77 pagesBa'cha DSP Lab 9Time PresentsNo ratings yet
- Z - TransformDocument26 pagesZ - Transformapi-26581966No ratings yet
- Lattice and Lattice-Ladder Structures For IIR SystemsDocument12 pagesLattice and Lattice-Ladder Structures For IIR SystemsChris Oreinos50% (2)
- §4 Integration of forms: γ 2 −2 ∗ 2 −2 2 3 2 t=2 t=−2 3 t=2 t=−2Document2 pages§4 Integration of forms: γ 2 −2 ∗ 2 −2 2 3 2 t=2 t=−2 3 t=2 t=−2Gag PafNo ratings yet
- P20 IIR Filters Part3Document33 pagesP20 IIR Filters Part3Harold GealanNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Time Signals and SystemsDocument23 pagesDiscrete-Time Signals and SystemsbetagaNo ratings yet
- EngMath4 Chapter16Document11 pagesEngMath4 Chapter16Taewoo KimNo ratings yet
- Tabla Integrales-DerivadasDocument2 pagesTabla Integrales-DerivadasDuvan FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Control System Design: State SpaceDocument3 pagesFormulas For Control System Design: State SpacehanythekingNo ratings yet
- Infi Nite Impulse Response Filters: Yn BXNK AynlDocument44 pagesInfi Nite Impulse Response Filters: Yn BXNK AynlPirata kalyNo ratings yet
- 1 1 0.5z 1 1 0.3z 1 1 0.7z 1 (1 0.5z) (1 0.3z) 1 (1 0.5z) (1 0.7z) 1 1 0.5z 1 1 0.3z 1 1 0.7zDocument4 pages1 1 0.5z 1 1 0.3z 1 1 0.7z 1 (1 0.5z) (1 0.3z) 1 (1 0.5z) (1 0.7z) 1 1 0.5z 1 1 0.3z 1 1 0.7zDio Izqhaq Risky SasongkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 2 HandoutsDocument68 pagesChapter 4 2 Handoutsmeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- 10 EMI 08 System Time Response CharacteristicsDocument15 pages10 EMI 08 System Time Response Characteristicsapi-3707706No ratings yet
- EE330 Digital Signal Processing: Review of Z-TransformDocument36 pagesEE330 Digital Signal Processing: Review of Z-TransformNihal AhmadNo ratings yet
- 7 I LB 2 V VL I1 YYl SYBXSTIDocument23 pages7 I LB 2 V VL I1 YYl SYBXSTIGingka HaganeNo ratings yet
- L4 1 LTIsys AnalysisDocument11 pagesL4 1 LTIsys AnalysisMohd Shadab AlamNo ratings yet
- 6 Laurent's TheoremDocument11 pages6 Laurent's TheoremShubhi VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Solutions Ch10Document13 pagesSolutions Ch10mustafa arkanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Digital Control and State Variable MethodsDocument128 pagesSolution Manual Digital Control and State Variable MethodsAkshat Gupta75% (16)
- Formula Note Control SystemDocument9 pagesFormula Note Control SystemMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Solu of Assignment 10Document5 pagesSolu of Assignment 10dontstopmeNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document6 pagesLab 3talal pervaizNo ratings yet
- J. Hetthéssy, A. Barta, R. Bars: DeadDocument5 pagesJ. Hetthéssy, A. Barta, R. Bars: DeadArulrajNo ratings yet
- Maths Formula SheetDocument7 pagesMaths Formula SheetruchabhanapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PPT - Part 2 - HandoutDocument31 pagesChapter 4 PPT - Part 2 - Handoutmeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Ee 120 Signals and Systems, Fall 2019: Homework #1Document8 pagesEe 120 Signals and Systems, Fall 2019: Homework #1u17814No ratings yet
- Tabla de Integrales IIDocument1 pageTabla de Integrales IIJosue PorrasNo ratings yet
- Dwight SolnsDocument18 pagesDwight SolnsGarcia AlexNo ratings yet
- Arbitary Rotation ProofDocument3 pagesArbitary Rotation Proofmohamed2010526No ratings yet
- Ztransform AppDocument5 pagesZtransform AppSyed Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Block DiagramDocument23 pagesDIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Block DiagramHuy NgôNo ratings yet
- (13 - 1) Transformasi Z Dan Fourier v2Document27 pages(13 - 1) Transformasi Z Dan Fourier v2najla harzaNo ratings yet
- Controller DesignDocument116 pagesController DesignShlok MishraNo ratings yet
- 5.Z TransformDocument10 pages5.Z TransformDeepro BardhanNo ratings yet
- Rison Siregar (1615031060) + 1 3 Z +, Tentukan Nilai X (N) !: Z +2 Z Z Z X e X (Z) Z +2 Z Z Z Z eDocument3 pagesRison Siregar (1615031060) + 1 3 Z +, Tentukan Nilai X (N) !: Z +2 Z Z Z X e X (Z) Z +2 Z Z Z Z eRison SiregarNo ratings yet
- Clase31 Señales.28septiembreDocument2 pagesClase31 Señales.28septiembrekaren juliana rodriguez guerraNo ratings yet
- Where, Is A Complex Exponential Magnitude & Angle: X (Z) X N ZDocument26 pagesWhere, Is A Complex Exponential Magnitude & Angle: X (Z) X N Zanil kadleNo ratings yet
- Properties of The Z-Transform: LinearityDocument9 pagesProperties of The Z-Transform: LinearityAliNo ratings yet
- m5 Lec4Document5 pagesm5 Lec4VIKAS BHATINo ratings yet
- Tutorial in Inversion of The Z-Transform Using Partial FractionsDocument7 pagesTutorial in Inversion of The Z-Transform Using Partial FractionsRahul ChahalNo ratings yet
- CT203: Signals & Systems Tutorial 13 - Laplace Transform and SamplingDocument2 pagesCT203: Signals & Systems Tutorial 13 - Laplace Transform and SamplingKiruba KNo ratings yet
- ZT4 Appl OnlinePPTDocument20 pagesZT4 Appl OnlinePPTThato Will MongaleNo ratings yet
- EE322M Quiz-1 SolutionDocument6 pagesEE322M Quiz-1 SolutionshubhamNo ratings yet
- Expansion Into Partial FractionsDocument6 pagesExpansion Into Partial FractionsMiguel SantillanNo ratings yet
- Desig GN of Pow Wer Tra Ansmissi Ion Syst Tem: Chapte Er3Document5 pagesDesig GN of Pow Wer Tra Ansmissi Ion Syst Tem: Chapte Er3Jai SharmaNo ratings yet
- Controls Combined Lecture NotesDocument312 pagesControls Combined Lecture NotesA FNo ratings yet
- Digital Filter-3Document15 pagesDigital Filter-3Fahmi IhzaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- WBTSDocument1 pageWBTScpîndaruNo ratings yet
- Thermally Activated Absorption Chillers PDFDocument2 pagesThermally Activated Absorption Chillers PDFdalton2004No ratings yet
- E25NAFLON Expansion BellowsDocument22 pagesE25NAFLON Expansion BellowsRezza Octova GochirNo ratings yet
- SERIES 7000 Paste Slakers: Fully Automated Lime Slaking SystemsDocument4 pagesSERIES 7000 Paste Slakers: Fully Automated Lime Slaking Systemssoumyarm942No ratings yet
- ASTM A789 Stainless Steel TubingDocument6 pagesASTM A789 Stainless Steel TubingPlinio PazosNo ratings yet
- Plastic Pipes & Fittings Factory Yousif Khalid Al-Adasani EntDocument3 pagesPlastic Pipes & Fittings Factory Yousif Khalid Al-Adasani EntJoseph JoeNo ratings yet
- Marine Engineering PracticeDocument13 pagesMarine Engineering PracticeKapil Verma100% (1)
- Lecture - 5 - Tension MembersDocument67 pagesLecture - 5 - Tension Membersayoub aliousalahNo ratings yet
- M45 250 Sheeting DataDocument3 pagesM45 250 Sheeting DatamaheshbandhamNo ratings yet
- 22 HDPE Pipe Oil GasDocument2 pages22 HDPE Pipe Oil GasArunkumar SelvamNo ratings yet
- Sous Réserve de Modifications! HAWE Hydraulik München © 2003, Page 1 Sur 3, (CD1 MRZ 2019-OP)Document3 pagesSous Réserve de Modifications! HAWE Hydraulik München © 2003, Page 1 Sur 3, (CD1 MRZ 2019-OP)GERALD SIMONNo ratings yet
- (Eurocode 2) Design of Concrete Structures: Brian O'RourkeDocument20 pages(Eurocode 2) Design of Concrete Structures: Brian O'RourkeselinaNo ratings yet
- NASA-Energy Absorption Capability of Composite Tubes and BeamsDocument250 pagesNASA-Energy Absorption Capability of Composite Tubes and BeamsGiuseppeNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu Ast24 GuideDocument17 pagesFujitsu Ast24 GuideJavier García BuenoNo ratings yet
- U-Tank Stabilization SystemDocument4 pagesU-Tank Stabilization SystemBurduja IonNo ratings yet
- Dredge Sled Spec Sheet 2Document3 pagesDredge Sled Spec Sheet 2Lê Nguyễn Quang MinhNo ratings yet
- 2012 DOT Wellhead Conductor and Casing Fatigue Causes and MitigiationDocument14 pages2012 DOT Wellhead Conductor and Casing Fatigue Causes and MitigiationjoakimNo ratings yet
- MoireDocument18 pagesMoireMuhammed SulfeekNo ratings yet
- TDRDocument18 pagesTDRashish_2187No ratings yet
- Porsche MaintenanceDocument2 pagesPorsche Maintenanceke4436No ratings yet
- Ee8015 Electric Energy Generation SyllabusDocument1 pageEe8015 Electric Energy Generation SyllabusMR.R. JEBA RAJNo ratings yet
- Xp500 Tmax Technical Orientation Guide: Features and BenefitsDocument45 pagesXp500 Tmax Technical Orientation Guide: Features and BenefitsmraleNo ratings yet
- Arv Facts PDFDocument9 pagesArv Facts PDFReyNo ratings yet
- Brosur SAKAI Double Drum Atau Tandem Roller CR271Document2 pagesBrosur SAKAI Double Drum Atau Tandem Roller CR271nanapNo ratings yet
- Two Way Aqua Hand Pump: Gokul K GDocument6 pagesTwo Way Aqua Hand Pump: Gokul K GDevendrasinh PadhiyarNo ratings yet
- D1VW UkDocument8 pagesD1VW UksureshllsNo ratings yet
- 02 - G30 PowertrainDocument50 pages02 - G30 PowertrainAllan Cancino100% (1)