Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsBiochem
Biochem
Uploaded by
jolibeecaldonaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cholorobenzene ProductionDocument32 pagesCholorobenzene ProductionAntarim Dutta85% (13)
- Lab Report 5 DistillationDocument6 pagesLab Report 5 DistillationMyeeka Hammond100% (1)
- 5L Super Reflux Still InstructionsDocument16 pages5L Super Reflux Still InstructionsAndréRochaNo ratings yet
- Basic Laboratory Glassware and EquipmentDocument5 pagesBasic Laboratory Glassware and EquipmentEj RafaelNo ratings yet
- Chem181: Chemistry For Engineers - Laboratory First Semester, AY 2020-2021 (Cluster 1) Activity No. 1 Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument5 pagesChem181: Chemistry For Engineers - Laboratory First Semester, AY 2020-2021 (Cluster 1) Activity No. 1 Common Laboratory ApparatusMaxine de la TorreNo ratings yet
- O'level Chemistry (Complete Notes)Document192 pagesO'level Chemistry (Complete Notes)Abdullah Ashraf83% (18)
- Genchem La 1 SantanDocument10 pagesGenchem La 1 SantanDece Andrea SantanNo ratings yet
- CHEM181 Act.-1Document8 pagesCHEM181 Act.-1villanuevazachderamaNo ratings yet
- CHM019 - Gepulango-Act 1labDocument11 pagesCHM019 - Gepulango-Act 1labKay EstelleNo ratings yet
- Mary Cris Movilla - Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument6 pagesMary Cris Movilla - Common Laboratory ApparatusMary Cris MovillaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument10 pagesLaboratory ApparatusSEAN GAVIN DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory: Chem 103 InorganicDocument11 pagesChemistry Laboratory: Chem 103 InorganicShemiah Caminos GeorsuaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusDocument9 pagesActivity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusJoaquin Angelo CortesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry IDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry IAllona de JesusNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusDocument9 pagesActivity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusSushmita LoiNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Inorganic and Organic Chemistry CHM101Document3 pagesAssignment: Inorganic and Organic Chemistry CHM101Cj DelfinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab 1Document30 pagesBiochemistry Lab 1Nereo ReoliquioNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Laboratory - Apparatus - Safety - SymbolsDocument12 pagesMODULE 3 - Laboratory - Apparatus - Safety - SymbolsgieNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Common Laboratory Apparatus and OperationsDocument9 pagesActivity 2 - Common Laboratory Apparatus and OperationsBARRY EPHRAIM PELICANONo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory Apparatus and Equipments: Engr. James L. DigolDocument7 pagesCommon Laboratory Apparatus and Equipments: Engr. James L. DigolRey Vincent RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesDocument11 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesJuliane JaynNo ratings yet
- NAMEDocument5 pagesNAMElaelia138No ratings yet
- Lab Equipment AssignmentDocument7 pagesLab Equipment AssignmentWasi IslamNo ratings yet
- Lab ApparatusesDocument8 pagesLab Apparatusesariannef092No ratings yet
- Lab ApparatusDocument4 pagesLab ApparatusArafhel AnciroNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Chemistry-Apparatus PDFDocument8 pagesIdoc - Pub Chemistry-Apparatus PDFAshrafNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ApparatusDocument8 pagesChemistry ApparatusLJ AbancoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 Familiarization of Laboratory ApparatusDocument4 pagesExercise 2 Familiarization of Laboratory ApparatusESTELLE RHINE HINDAP FRANCISCO100% (1)
- Lab Equipment Worksheet: FlameDocument6 pagesLab Equipment Worksheet: FlameSabu LazerNo ratings yet
- It Is Used For Mixing, Stirring, and Heating ChemicalsDocument7 pagesIt Is Used For Mixing, Stirring, and Heating ChemicalsDessa GuditoNo ratings yet
- GenchemDocument2 pagesGenchemChristian MorfeNo ratings yet
- Mon Lab ApparatusDocument11 pagesMon Lab ApparatusJustin MenorasNo ratings yet
- Basuel Exercise 1 Lab ApparatusDocument16 pagesBasuel Exercise 1 Lab ApparatusOrdinary GuitaristNo ratings yet
- Lab EquipmentDocument58 pagesLab EquipmentDeill UrdasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 - Laboratory Glassware and Apparatus 2021Document3 pagesAssignment 7 - Laboratory Glassware and Apparatus 2021Thanh Nguyễn XuânNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusesDocument4 pagesLaboratory ApparatusesJonsen Keon GayosaNo ratings yet
- Dissilation Apparatus Uses and PartsDocument5 pagesDissilation Apparatus Uses and PartsMa. Lilian Jem MonteroNo ratings yet
- Igoy Ukulan ChemistryDocument8 pagesIgoy Ukulan ChemistryGenesis Ducusin AguilarNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Glasswares 2Document5 pagesActivity 2 Glasswares 2EDCEL PEDRONo ratings yet
- SdfsdfsfsDocument5 pagesSdfsdfsfsmwah mwahNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument11 pagesTheoryFran Grueso CerezoNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment Worksheet: Name - PeriodDocument5 pagesLab Equipment Worksheet: Name - Periodapi-320485715No ratings yet
- Phar 205Document156 pagesPhar 205billhaddNo ratings yet
- Iligan Medical Center College: Activity 1 (Biochem)Document5 pagesIligan Medical Center College: Activity 1 (Biochem)Ronamae M. SabueroNo ratings yet
- Notes For Common ApparatusDocument6 pagesNotes For Common ApparatusCHELLA ELIN CRUZNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam Reviewer - Biology Lab: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Document7 pagesPrelim Exam Reviewer - Biology Lab: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Don'tAsK TheStupidOnesNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1-Common Lab Apparatus by Group 1 - BSMLS-1PDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1-Common Lab Apparatus by Group 1 - BSMLS-1PAnne Chelsea Ramirez OritNo ratings yet
- Mon Lab ApparatusDocument6 pagesMon Lab ApparatusGianni PillejeraNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument6 pagesCommon Laboratory ApparatusKrizia BulalacaoNo ratings yet
- 2 Lab EquipmentDocument58 pages2 Lab EquipmentaimesusonhomeworkaccNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 Common Lab ApparatusDocument6 pagesAssign 2 Common Lab ApparatusJohn Wilfred B. GarciaNo ratings yet
- CASTRO LaboratoryApparatusDocument7 pagesCASTRO LaboratoryApparatusIrene Grace A. CastroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory HW1Document2 pagesLaboratory HW1lizaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LaboratoryDocument5 pagesBiochemistry LaboratoryElvira Monica SayoNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro - BSN1-11L - Preliminary ActivitiesDocument19 pagesBarecuatro - BSN1-11L - Preliminary ActivitiesAngelica Claire BarecuatroNo ratings yet
- Name Picture Function: Jan Chrispian Mirasol Riza Mae Naria 1BSPH2Document9 pagesName Picture Function: Jan Chrispian Mirasol Riza Mae Naria 1BSPH2Jan Chrispian MirasolNo ratings yet
- ChemLab Activity #0 - JunsayP21Document17 pagesChemLab Activity #0 - JunsayP21Neldeliz Jiang JunsayNo ratings yet
- CHE1L-Exp Act - 1Document6 pagesCHE1L-Exp Act - 1Kayezel SinohinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Laboratory Equipment & ApparatusDocument12 pagesAssignment 1: Laboratory Equipment & ApparatusJAN MIKYLLA TABAMONo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument14 pagesCommon Laboratory ApparatusChristian Josh DinoyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Instruments AlbumDocument41 pagesLaboratory Instruments AlbumScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Stress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8From EverandStress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8No ratings yet
- Abhijeet Sonawane - ResumeDocument2 pagesAbhijeet Sonawane - ResumeAbhijeet SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Solution - Colligative Properties HLP PDFDocument24 pagesSolution - Colligative Properties HLP PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- New Developments in Industrial MPC Identification Yucai ZhuDocument8 pagesNew Developments in Industrial MPC Identification Yucai ZhuAlongkorn JaranchonNo ratings yet
- 2017-11-13 Liquor Price ListDocument4 pages2017-11-13 Liquor Price ListIsuru Payoe25% (4)
- Chemistry IntroDocument69 pagesChemistry IntroHasmin EniolaNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of Chemistry 19Document196 pages1 Principles of Chemistry 19LaziNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTATION FOR P&ID'sDocument50 pagesINSTRUMENTATION FOR P&ID'ssalem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nitro Alkene DerivativesDocument7 pagesNitro Alkene Derivativesgeovani2No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionNoman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Astm Pour PointDocument30 pagesAstm Pour PointMartuaHaojahanSaragihSidabutarNo ratings yet
- Crude OilDocument11 pagesCrude OildamochkaNo ratings yet
- CAGI ElectHB ch7Document259 pagesCAGI ElectHB ch7Alejandro GilNo ratings yet
- Chemical Aspects of Distilling Wines Into BrandyDocument22 pagesChemical Aspects of Distilling Wines Into Brandypana0048No ratings yet
- DSP: Seminar 2, Binary Distillation, Mccabe-Thiele Method, Column With One FeedDocument4 pagesDSP: Seminar 2, Binary Distillation, Mccabe-Thiele Method, Column With One Feedanto3harrish3fdoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For A Microscale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 6th Edition Donald L Pavia George S Kriz Gary M Lampman Randall G EngelDocument11 pagesSolution Manual For A Microscale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 6th Edition Donald L Pavia George S Kriz Gary M Lampman Randall G EngelphongphuongoifooNo ratings yet
- Global Canesugar Services Distillery Services ProfileDocument14 pagesGlobal Canesugar Services Distillery Services ProfileATUL MISRANo ratings yet
- Types of Distillation 13CH56Document25 pagesTypes of Distillation 13CH56Talal Ashraf0% (1)
- 2013 - Kick - Using Aspen Plus Resources To Model Biodiesel Production Applicable For A Senior Capstone Design Project PDFDocument16 pages2013 - Kick - Using Aspen Plus Resources To Model Biodiesel Production Applicable For A Senior Capstone Design Project PDFAdhisya Salma KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- K.golden Flower MeditationDocument6 pagesK.golden Flower Meditationamjr1001No ratings yet
- 5.-Journal of Applied Polymer Science2016Document11 pages5.-Journal of Applied Polymer Science2016sayed nasrNo ratings yet
- Midterm CaeDocument17 pagesMidterm CaeDianne AlarconNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form I IV Schemes of WorkDocument124 pagesChemistry Form I IV Schemes of WorkSamson OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- Prestons VodkaDocument1 pagePrestons VodkaTiso Blackstar GroupNo ratings yet
- Distillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationDocument4 pagesDistillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationcsandrasNo ratings yet
- Resumen CH04 FelderDocument45 pagesResumen CH04 Feldercuberbill1980No ratings yet
- Agar MediaDocument76 pagesAgar Mediafunahmed100% (1)
Biochem
Biochem
Uploaded by
jolibeecaldona0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesOriginal Title
biochem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesBiochem
Biochem
Uploaded by
jolibeecaldonaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
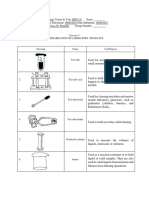
Table 2.1.
Common Laboratory Apparatuses and Instruments
Instrument Picture Function/s
(copy-paste a
downloaded picture)
1. aspirator Aspirators use a small jet pump
that creates a vacuum suction to
remove liquids. This process is done
by the Venturi effect as the fluid
flows throw a tube, the fluid
contracts and expands creating a
pressure vacuum.
2. beaker A beaker is a cylindrical glass or
plastic vessel used for holding
liquids. It is a multi- purpose piece
of equipment used for containing a
chemical reaction, measuring
liquids, heating them over a Bunsen
burner's flame or collecting them in
a titration experiment.
3. burner A burner is a device designed
to ensure that the flame is
stabilized by establishing a suitable
flow field to produce the initial
temperature rise. The flame is used
as the source of heat to preheat the
fuel/air mixture to the ignition
temperature.
4. burette A buret is used to deliver solution in
precisely-measured, variable
volumes. Burets are used primarily
for titration, to deliver one reactant
until the precise end point of the
reaction is reached. To fill a buret,
close the stopcock at the bottom
and use a funnel.
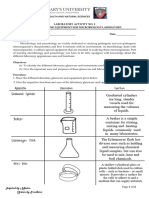
5. distillation set-up It consists of a flask
containing the liquid to be
distilled, an adapter to hold
a thermometer and to
connect the flask to a water-
cooled condenser, and a
flask to hold the condensed
liquid (the distillate).
Distillation refers to a
process involving the
vaporization of a liquid in
order to separate it from
other compounds. Once it is
separated as a vapor, it is
passed through a condenser
to cool it back into a liquid,
the distillate.
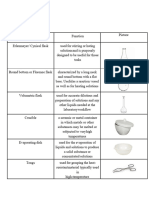
6. Erlenmeyer Flask used to contain liquids and for
mixing, heating, cooling, incubation,
filtration, storage, and other liquid-
handling processes. Their slanted
sides and narrow necks allow the
contents to be mixed by swirling
without the risk of spills, which is
useful for titrations and for boiling
liquids.
7. filter paper used to separate components from
air or liquid flow by acting as a semi-
permeable barrier. Tiny pores are
present because of that it gives a
clear solution as the particles
trapped in the pores of filter paper.
Filter paper is the process of
separating suspended solid matter
from a liquid.
8. graduated cylinder Most of the chemicals used in a
laboratory are liquid solutions and
to ensure that they are used in the
right quantities or proportions, they
need to be measured out. Function
of the cylinder is to measure liquid
volumes accurately. They are
extensively used in chemistry and
biology labs, where quantities of
accurately measured liquids need to
be used. They are purposely
designed to be long, with a shorter
diameter compared to beakers, to
facilitate accurate measurements.
Measurements made with your
naked eye, must be made carefully.
9. Iron stand Iron stand supports the iron ring
when heating substances or
mixtures in a flask or beaker (using a
Bunsen burner) clamps can also be
used to hold glasswares on the iron
ring.
10. iron ring An iron ring, sometimes referred to
as an iron support ring, is used in
chemistry labs to stabilize flasks
mounted to a ring stand and
support them over the work
area. Some iron rings also include a
clamp.
11. pipette A pipette is a laboratory instrument
used to measure out or transfer
small quantities of liquid, in volumes
of milliliters (mL), microliters (μL).
12. pH meter pH meter is an instrument used to
measure acidity or alkalinity of a
solution - also know as pH. pH is the
unit of measure that describes the
degree of acidity or alkalinity. It is
measured on a scale of 0 to 14.
13. spatula used in a wide range of laboratory
and field testing procedures and
come in five different sizes. Spatulas
are an everyday necessity in
materials testing for mixing, lifting,
and handling powders, granular
materials, and other solids, as well
as for stirring or mixing liquids and
other wet products.
14. stirring rod stirring rod is a common piece of
lab equipment used to mix or stir
liquids and chemicals. These rods
are thicker than a typical drinking
straw, have rounded ends and are
made from a special type of
laboratory glassware called
borosilicate. This glass is less
affected by thermal stress and has a
very low thermal expansion point,
so it is less affected by heat than
metals are.
15. test tube test tube is one of the most widely
used glassware apparatus. It is a
cylindrical vessel with a round
bottom that is used to hold
chemicals during the experiments.
Due to their high thermal stability,
test tubes can be used to heat or
boil chemical samples.
16, test tube brush test tube brush or spout brush is a
brush used for cleaning test tubes
and narrow mouth laboratory
glassware, such as graduated
cylinders, burettes, and Erlenmeyer
flasks.
17. test tube holder used to hold test tubes. It is used for
holding a test tube in place when
the tube is hot or should not be
touched. For example, a test tube
holder can be used to hold a test
tube while it is being heated.
18. test tube rack A test tube rack is a piece of
laboratory equipment used to hold
multiple test tubes upright at the
same time. They are especially
useful for organizing test tubes
when different solutions are being
worked on or collected at once.
19. top-loading balance A top loading balance is used
for weighing solid material when an
accuracy of 0.1 g is satisfactory. The
top loading balance is in the
precision class of balances with a
readability of 1 mg or less.
20. water-bath set up made from a container filled with
heated water. It is used to incubate
samples in water at a constant
temperature over a long period of
time. Most water baths have a
digital or an analogue interface to
allow users to set a desired
temperature, but some water baths
have their temperature controlled
by a current passing through a
reader. Utilisations include warming
of reagents, melting of substrates or
incubation of cell cultures. It is also
used to enable certain chemical
reactions to occur at high
temperature.
You might also like
- Cholorobenzene ProductionDocument32 pagesCholorobenzene ProductionAntarim Dutta85% (13)
- Lab Report 5 DistillationDocument6 pagesLab Report 5 DistillationMyeeka Hammond100% (1)
- 5L Super Reflux Still InstructionsDocument16 pages5L Super Reflux Still InstructionsAndréRochaNo ratings yet
- Basic Laboratory Glassware and EquipmentDocument5 pagesBasic Laboratory Glassware and EquipmentEj RafaelNo ratings yet
- Chem181: Chemistry For Engineers - Laboratory First Semester, AY 2020-2021 (Cluster 1) Activity No. 1 Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument5 pagesChem181: Chemistry For Engineers - Laboratory First Semester, AY 2020-2021 (Cluster 1) Activity No. 1 Common Laboratory ApparatusMaxine de la TorreNo ratings yet
- O'level Chemistry (Complete Notes)Document192 pagesO'level Chemistry (Complete Notes)Abdullah Ashraf83% (18)
- Genchem La 1 SantanDocument10 pagesGenchem La 1 SantanDece Andrea SantanNo ratings yet
- CHEM181 Act.-1Document8 pagesCHEM181 Act.-1villanuevazachderamaNo ratings yet
- CHM019 - Gepulango-Act 1labDocument11 pagesCHM019 - Gepulango-Act 1labKay EstelleNo ratings yet
- Mary Cris Movilla - Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument6 pagesMary Cris Movilla - Common Laboratory ApparatusMary Cris MovillaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument10 pagesLaboratory ApparatusSEAN GAVIN DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory: Chem 103 InorganicDocument11 pagesChemistry Laboratory: Chem 103 InorganicShemiah Caminos GeorsuaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusDocument9 pagesActivity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusJoaquin Angelo CortesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry IDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry IAllona de JesusNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusDocument9 pagesActivity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusSushmita LoiNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Inorganic and Organic Chemistry CHM101Document3 pagesAssignment: Inorganic and Organic Chemistry CHM101Cj DelfinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab 1Document30 pagesBiochemistry Lab 1Nereo ReoliquioNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Laboratory - Apparatus - Safety - SymbolsDocument12 pagesMODULE 3 - Laboratory - Apparatus - Safety - SymbolsgieNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Common Laboratory Apparatus and OperationsDocument9 pagesActivity 2 - Common Laboratory Apparatus and OperationsBARRY EPHRAIM PELICANONo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory Apparatus and Equipments: Engr. James L. DigolDocument7 pagesCommon Laboratory Apparatus and Equipments: Engr. James L. DigolRey Vincent RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesDocument11 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesJuliane JaynNo ratings yet
- NAMEDocument5 pagesNAMElaelia138No ratings yet
- Lab Equipment AssignmentDocument7 pagesLab Equipment AssignmentWasi IslamNo ratings yet
- Lab ApparatusesDocument8 pagesLab Apparatusesariannef092No ratings yet
- Lab ApparatusDocument4 pagesLab ApparatusArafhel AnciroNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Chemistry-Apparatus PDFDocument8 pagesIdoc - Pub Chemistry-Apparatus PDFAshrafNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ApparatusDocument8 pagesChemistry ApparatusLJ AbancoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 Familiarization of Laboratory ApparatusDocument4 pagesExercise 2 Familiarization of Laboratory ApparatusESTELLE RHINE HINDAP FRANCISCO100% (1)
- Lab Equipment Worksheet: FlameDocument6 pagesLab Equipment Worksheet: FlameSabu LazerNo ratings yet
- It Is Used For Mixing, Stirring, and Heating ChemicalsDocument7 pagesIt Is Used For Mixing, Stirring, and Heating ChemicalsDessa GuditoNo ratings yet
- GenchemDocument2 pagesGenchemChristian MorfeNo ratings yet
- Mon Lab ApparatusDocument11 pagesMon Lab ApparatusJustin MenorasNo ratings yet
- Basuel Exercise 1 Lab ApparatusDocument16 pagesBasuel Exercise 1 Lab ApparatusOrdinary GuitaristNo ratings yet
- Lab EquipmentDocument58 pagesLab EquipmentDeill UrdasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 - Laboratory Glassware and Apparatus 2021Document3 pagesAssignment 7 - Laboratory Glassware and Apparatus 2021Thanh Nguyễn XuânNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusesDocument4 pagesLaboratory ApparatusesJonsen Keon GayosaNo ratings yet
- Dissilation Apparatus Uses and PartsDocument5 pagesDissilation Apparatus Uses and PartsMa. Lilian Jem MonteroNo ratings yet
- Igoy Ukulan ChemistryDocument8 pagesIgoy Ukulan ChemistryGenesis Ducusin AguilarNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Glasswares 2Document5 pagesActivity 2 Glasswares 2EDCEL PEDRONo ratings yet
- SdfsdfsfsDocument5 pagesSdfsdfsfsmwah mwahNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument11 pagesTheoryFran Grueso CerezoNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment Worksheet: Name - PeriodDocument5 pagesLab Equipment Worksheet: Name - Periodapi-320485715No ratings yet
- Phar 205Document156 pagesPhar 205billhaddNo ratings yet
- Iligan Medical Center College: Activity 1 (Biochem)Document5 pagesIligan Medical Center College: Activity 1 (Biochem)Ronamae M. SabueroNo ratings yet
- Notes For Common ApparatusDocument6 pagesNotes For Common ApparatusCHELLA ELIN CRUZNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam Reviewer - Biology Lab: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Document7 pagesPrelim Exam Reviewer - Biology Lab: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Don'tAsK TheStupidOnesNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1-Common Lab Apparatus by Group 1 - BSMLS-1PDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1-Common Lab Apparatus by Group 1 - BSMLS-1PAnne Chelsea Ramirez OritNo ratings yet
- Mon Lab ApparatusDocument6 pagesMon Lab ApparatusGianni PillejeraNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument6 pagesCommon Laboratory ApparatusKrizia BulalacaoNo ratings yet
- 2 Lab EquipmentDocument58 pages2 Lab EquipmentaimesusonhomeworkaccNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 Common Lab ApparatusDocument6 pagesAssign 2 Common Lab ApparatusJohn Wilfred B. GarciaNo ratings yet
- CASTRO LaboratoryApparatusDocument7 pagesCASTRO LaboratoryApparatusIrene Grace A. CastroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory HW1Document2 pagesLaboratory HW1lizaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LaboratoryDocument5 pagesBiochemistry LaboratoryElvira Monica SayoNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro - BSN1-11L - Preliminary ActivitiesDocument19 pagesBarecuatro - BSN1-11L - Preliminary ActivitiesAngelica Claire BarecuatroNo ratings yet
- Name Picture Function: Jan Chrispian Mirasol Riza Mae Naria 1BSPH2Document9 pagesName Picture Function: Jan Chrispian Mirasol Riza Mae Naria 1BSPH2Jan Chrispian MirasolNo ratings yet
- ChemLab Activity #0 - JunsayP21Document17 pagesChemLab Activity #0 - JunsayP21Neldeliz Jiang JunsayNo ratings yet
- CHE1L-Exp Act - 1Document6 pagesCHE1L-Exp Act - 1Kayezel SinohinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Laboratory Equipment & ApparatusDocument12 pagesAssignment 1: Laboratory Equipment & ApparatusJAN MIKYLLA TABAMONo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument14 pagesCommon Laboratory ApparatusChristian Josh DinoyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Instruments AlbumDocument41 pagesLaboratory Instruments AlbumScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Stress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8From EverandStress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8No ratings yet
- Abhijeet Sonawane - ResumeDocument2 pagesAbhijeet Sonawane - ResumeAbhijeet SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Solution - Colligative Properties HLP PDFDocument24 pagesSolution - Colligative Properties HLP PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- New Developments in Industrial MPC Identification Yucai ZhuDocument8 pagesNew Developments in Industrial MPC Identification Yucai ZhuAlongkorn JaranchonNo ratings yet
- 2017-11-13 Liquor Price ListDocument4 pages2017-11-13 Liquor Price ListIsuru Payoe25% (4)
- Chemistry IntroDocument69 pagesChemistry IntroHasmin EniolaNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of Chemistry 19Document196 pages1 Principles of Chemistry 19LaziNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTATION FOR P&ID'sDocument50 pagesINSTRUMENTATION FOR P&ID'ssalem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nitro Alkene DerivativesDocument7 pagesNitro Alkene Derivativesgeovani2No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionNoman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Astm Pour PointDocument30 pagesAstm Pour PointMartuaHaojahanSaragihSidabutarNo ratings yet
- Crude OilDocument11 pagesCrude OildamochkaNo ratings yet
- CAGI ElectHB ch7Document259 pagesCAGI ElectHB ch7Alejandro GilNo ratings yet
- Chemical Aspects of Distilling Wines Into BrandyDocument22 pagesChemical Aspects of Distilling Wines Into Brandypana0048No ratings yet
- DSP: Seminar 2, Binary Distillation, Mccabe-Thiele Method, Column With One FeedDocument4 pagesDSP: Seminar 2, Binary Distillation, Mccabe-Thiele Method, Column With One Feedanto3harrish3fdoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For A Microscale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 6th Edition Donald L Pavia George S Kriz Gary M Lampman Randall G EngelDocument11 pagesSolution Manual For A Microscale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 6th Edition Donald L Pavia George S Kriz Gary M Lampman Randall G EngelphongphuongoifooNo ratings yet
- Global Canesugar Services Distillery Services ProfileDocument14 pagesGlobal Canesugar Services Distillery Services ProfileATUL MISRANo ratings yet
- Types of Distillation 13CH56Document25 pagesTypes of Distillation 13CH56Talal Ashraf0% (1)
- 2013 - Kick - Using Aspen Plus Resources To Model Biodiesel Production Applicable For A Senior Capstone Design Project PDFDocument16 pages2013 - Kick - Using Aspen Plus Resources To Model Biodiesel Production Applicable For A Senior Capstone Design Project PDFAdhisya Salma KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- K.golden Flower MeditationDocument6 pagesK.golden Flower Meditationamjr1001No ratings yet
- 5.-Journal of Applied Polymer Science2016Document11 pages5.-Journal of Applied Polymer Science2016sayed nasrNo ratings yet
- Midterm CaeDocument17 pagesMidterm CaeDianne AlarconNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form I IV Schemes of WorkDocument124 pagesChemistry Form I IV Schemes of WorkSamson OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- Prestons VodkaDocument1 pagePrestons VodkaTiso Blackstar GroupNo ratings yet
- Distillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationDocument4 pagesDistillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationcsandrasNo ratings yet
- Resumen CH04 FelderDocument45 pagesResumen CH04 Feldercuberbill1980No ratings yet
- Agar MediaDocument76 pagesAgar Mediafunahmed100% (1)