Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
1
Uploaded by
coomeetuser001Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
1
Uploaded by
coomeetuser001Copyright:
Available Formats
: Music Theory
Elements of Music:
Melody: The sequence of single notes that is musically satisfying.
Harmony: The combination of simultaneously sounded musical notes to produce chords
and chord progressions.
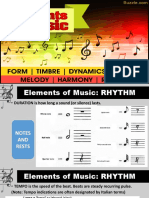
Rhythm: The pattern of sounds and silences in music, often organized into beats and
measures.
Dynamics: The varying levels of volume in music, ranging from soft (piano) to loud
(forte).
Texture: The interrelationship of musical lines and the way they interact.
Timbre: The quality or color of sound produced by a particular instrument or voice.
Notation:
Staff: Consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces on which musical notes are
written.
Clefs: Symbols placed at the beginning of the staff to indicate the pitch range of
the notes.
Notes and Rests: Represent specific durations of sound and silence respectively.
Time Signatures: Indicate the number of beats per measure and the type of note that
receives one beat.
Scales and Chords:
Major and Minor Scales: The foundation of Western music, consisting of a specific
pattern of whole and half steps.
Triads: Basic chords consisting of three notes – root, third, and fifth – stacked
in thirds.
Form and Structure:
Binary Form: Consists of two main sections, usually labeled A and B, each typically
repeated.
Ternary Form: Consists of three main sections, with the first and third sections
being similar or identical.
Theme and Variation: Involves presenting a theme followed by a series of
variations, each altering some aspect of the original theme.
You might also like
- iGCSE Music: Paper 1: Common QuestionsDocument35 pagesiGCSE Music: Paper 1: Common Questionsjosef_herman89% (9)
- Basic Music Theory For BeginnersDocument13 pagesBasic Music Theory For BeginnersgreetingspkNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Music Revision NotesDocument61 pagesIGCSE Music Revision Notesbujustin100% (14)
- Music Theory and Notation: SparkChartsDocument8 pagesMusic Theory and Notation: SparkChartsElizabeth Alarcón-Gaxiola100% (2)
- Basic Music Theory For BeginnersDocument18 pagesBasic Music Theory For BeginnersJenna Marie Tolosa0% (1)
- Music TermsDocument2 pagesMusic TermsMiffie101No ratings yet
- Glossary - Elementary MusicDocument2 pagesGlossary - Elementary MusicDANA100% (1)
- Strategic Intervention Material MusicDocument48 pagesStrategic Intervention Material MusicCarol GelbolingoNo ratings yet
- Elements of MusicDocument4 pagesElements of MusicMaryFifiNo ratings yet
- Elements of MusicDocument23 pagesElements of MusicJowel RespicioNo ratings yet
- Survey of Music Literature: Click Here and Press PlayDocument47 pagesSurvey of Music Literature: Click Here and Press PlayBlake BishopNo ratings yet
- Music: Music Terminologies, Types of Music/ Music GenresDocument91 pagesMusic: Music Terminologies, Types of Music/ Music GenresChristopher TorlaoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Music 1. Rhythm: TH TH THDocument3 pagesElements of Music 1. Rhythm: TH TH THKmerylE100% (1)
- Lesson 6 MusicDocument9 pagesLesson 6 MusicJesusNo ratings yet
- Elements of MusicDocument3 pagesElements of MusicAndrea B.No ratings yet
- Thailand MusicDocument3 pagesThailand MusicAndrey Cabrera0% (1)
- Parametres of Music (2024)Document33 pagesParametres of Music (2024)simsek.hakan.2003No ratings yet
- MA Test Study OutlineDocument2 pagesMA Test Study Outlinejack wootenNo ratings yet
- VerybasicelementsofmusicDocument1 pageVerybasicelementsofmusicapi-326325979No ratings yet
- Musical Parameters: Main Elements of MusicDocument3 pagesMusical Parameters: Main Elements of MusicPascal BleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document2 pagesChapter 10Michael Racelis100% (1)
- Music Lessons For KidsDocument5 pagesMusic Lessons For KidsRomeo Mana100% (2)
- Music 7Document31 pagesMusic 7johbaguilatNo ratings yet
- Music Vocabulary PDFDocument3 pagesMusic Vocabulary PDFJairo MezaNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 5 - MUSIC PPT Q3 - The Elements and Organization of MusicDocument38 pagesMAPEH 5 - MUSIC PPT Q3 - The Elements and Organization of MusicRowena Rañoco GalangNo ratings yet
- Elements of MusicDocument23 pagesElements of Musicbv123bv100% (3)
- Mus 210Document124 pagesMus 210Marie BtaichNo ratings yet
- 2019 MU Music Aural Analysis Notes Madison BersikhDocument18 pages2019 MU Music Aural Analysis Notes Madison BersikhKhanh HoNo ratings yet
- Elements of MusicDocument27 pagesElements of MusicLaarni Torres100% (1)
- The Elements of MusicDocument4 pagesThe Elements of MusicKerry TapdasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Pitch, Dynamics, and Tone ColourDocument6 pagesChapter 1: Pitch, Dynamics, and Tone ColourIinda IinNo ratings yet
- Indiana Academic Standards For Music: Glossary and Vocabulary WordsDocument5 pagesIndiana Academic Standards For Music: Glossary and Vocabulary WordsIsadora SobredoNo ratings yet
- Music Theory and NotationDocument13 pagesMusic Theory and NotationElizabeth Alarcón-GaxiolaNo ratings yet
- Basic Music TheoryDocument15 pagesBasic Music TheoryCasa FantiNo ratings yet
- Music ElementsDocument16 pagesMusic ElementsRauven Jean Erodias FadriquelaNo ratings yet
- Simbulan k12 MERGEDocument116 pagesSimbulan k12 MERGERenato Roa SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Music ReviewerDocument37 pagesMusic Reviewerjepte smurfNo ratings yet
- Components AssignmentDocument5 pagesComponents AssignmentDaniel Emmanuel AyomideNo ratings yet
- W HH QQ Ee Ry Ry S S DFFG Q Q H W Eqe H H.: 5 Grade Music VocabularyDocument3 pagesW HH QQ Ee Ry Ry S S DFFG Q Q H W Eqe H H.: 5 Grade Music VocabularyJ Nay SasNo ratings yet
- Music PowerPoint LectureDocument132 pagesMusic PowerPoint LectureResonationNo ratings yet
- MUSICDocument21 pagesMUSICSyrill PortugalNo ratings yet
- Basic Music Theory NotesDocument2 pagesBasic Music Theory NotesCharlotte Dolders100% (1)
- Chord of Tonic Is Modal or Minor Key Dynamic Accent: (Crescendo/diminuendo)Document1 pageChord of Tonic Is Modal or Minor Key Dynamic Accent: (Crescendo/diminuendo)Stephanie ChenNo ratings yet
- Elements of MusicDocument10 pagesElements of MusicEden Martirez-VillalonNo ratings yet
- Elements of MusicDocument2 pagesElements of MusicJamie MonckNo ratings yet
- MUSIC Seventh Eighth Ninth GradeDocument67 pagesMUSIC Seventh Eighth Ninth GradeScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Music Theory - Note ReadingDocument4 pagesMusic Theory - Note ReadingKimberly Bao RamosNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Musical TermsDocument13 pagesGlossary of Musical TermshistealangNo ratings yet
- Elements of Music For Mapeh ..Document2 pagesElements of Music For Mapeh ..Beatingo JoveleeneNo ratings yet
- Glosario 1Document5 pagesGlosario 1Leo zcNo ratings yet
- Musical Signs and Their MeaningDocument5 pagesMusical Signs and Their MeaningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Day1-Plenary-Session2-Application-of-Music-Elements - Jezreel LastraDocument56 pagesDay1-Plenary-Session2-Application-of-Music-Elements - Jezreel LastraHector Gocila ConcillesNo ratings yet
- Music Lessons q1Document3 pagesMusic Lessons q1Jordaine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Art AppreciationDocument2 pagesGroup 7 Art AppreciationJennelyn Saupi BantalaNo ratings yet
- Review: Note, Scale, and StaffDocument35 pagesReview: Note, Scale, and StaffRescher Kim GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Armonía - Acordes (Cifrado Americano) PDFDocument26 pagesArmonía - Acordes (Cifrado Americano) PDFHernán Ballesteros100% (1)
- The Fundamentals of Music Composition: Learn Music Composition Step by Step: MusicFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Music Composition: Learn Music Composition Step by Step: MusicNo ratings yet
- Intro to Music Theory: The Nuts and Bolts of MusicFrom EverandIntro to Music Theory: The Nuts and Bolts of MusicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)