Professional Documents
Culture Documents
29 Follow-Up NCU Patients
29 Follow-Up NCU Patients
Uploaded by
SAMWEL JOSIA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 page29 Follow-Up NCU Patients
29 Follow-Up NCU Patients
Uploaded by
SAMWEL JOSIACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
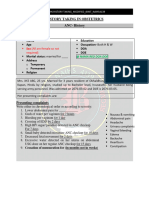
SOP 29: NCU
Follow-Up of NCU Patients
Indications for Follow-Up What do we assess?
All NCU patients: History:
- Prematurity and LBW ✓ Feeding problems?
- Asphyxia ✓ Supplements given?
- Sepsis ✓ Stool? Urine? Excessive crying?
- Congenital malformations ✓ KMC practiced?
✓ Maternal problems?
(depending on the management)
✓ Any other problems?
- Complications in neonatal period
- Birth injury Physical examination:
✓ Complete physical examination
Location and Timing ✓ Specific examinations (e.g. neurologic in
HIE patients)
Clinic close to NCU or RCH
Temperature:
First visit: 2-7 days after
✓ If > 37.5 °C: Admit the baby, examine
discharge depending on thoroughly, inform the doctor to
the condition review, and treat for sepsis
Following visits: ✓ If < 36 °C: Examine thoroughly. If no
Depending on the obvious reasons (e.g. sepsis), rewarm
findings on the actual visit baby on KMC and check temperature
(usually weekly) again
Clinician Consult if: Weight:
✓ Compare actual weight with last ones
- Fever or hypothermia ✓ Aim: Weight gain of about 200g/week
- Feeding problems (If not, search for reason)
- Weight loss or inadequate weight Investigations:
gain ✓ According to findings
- Fast breathing /difficulty breathing
- Convulsions Information to caretakers:
- Jaundice ✓ Findings, progress
- Skin lesions or rashes ✓ Explanations on further management
✓ Encourage communication and play
- Malformations
with baby
- Any unclear symptoms or signs
✓ Encourage asking questions
Ending Follow-Up Visits
- Prematurity/LBW: Graduation at 2500 g, if no other complaints
- Other conditions: If no pathological findings, no need for further management
- HIE, other neurological and chronic conditions: Long-term follow-up required
- Encourage the mother to attend the routine RCH visits
MoHCDGEC (2019) National Guideline for Neonatal Care and Establishment of Neonatal Care Unit, p 230-231
You might also like
- This Is The Complete Set of PDF Study Guides 2023Document4,356 pagesThis Is The Complete Set of PDF Study Guides 2023learn exams50% (2)
- Koenig and Schultz's Disaster Medicine - Comprehensive Principles and PracticesDocument2,738 pagesKoenig and Schultz's Disaster Medicine - Comprehensive Principles and Practicesjhbvf kmmgg67% (3)
- 2014 AAAHC Accreditation HandbookDocument195 pages2014 AAAHC Accreditation Handbooksapna78No ratings yet
- Perspective in PharmacyDocument3 pagesPerspective in PharmacyAgniez Hannah Permites100% (4)
- Case Presentation: Group 3-BDocument39 pagesCase Presentation: Group 3-BKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- Patient Admission Centre (Pac) (HRPZ Houseman Guide) : O&G HO Guide @thechayondeducationDocument25 pagesPatient Admission Centre (Pac) (HRPZ Houseman Guide) : O&G HO Guide @thechayondeducationNurulain HamzahNo ratings yet
- GynaeBoxanswer PDFDocument99 pagesGynaeBoxanswer PDFViktor Charles KDNo ratings yet
- 3B2 Preceptorial Nov 17 - D in PediPatientsDocument59 pages3B2 Preceptorial Nov 17 - D in PediPatientsAbigail PaasaNo ratings yet
- NCM-107 1Document3 pagesNCM-107 1Althea Jean RaplizaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain (Uncomplicated Cystitis)Document1 pageAbdominal Pain (Uncomplicated Cystitis)GhulamMemonNo ratings yet
- OB - History, Physical Examination AND Plan of ManagementDocument10 pagesOB - History, Physical Examination AND Plan of ManagementCarl LeeNo ratings yet
- DR Skills LabDocument14 pagesDR Skills LabHameda MangulamasNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Morning RoundsDocument3 pagesPost-Partum Morning RoundsMaya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- Dercetus SlidesCarnivalDocument54 pagesDercetus SlidesCarnivalGil Sunpayco Jr.No ratings yet
- PROM ApproachDocument3 pagesPROM Approachعبد الله الحربيNo ratings yet
- PaedsDocument10 pagesPaedsOsman Bin SaifNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument72 pagesObstetrics and GynecologyLaura GranadosNo ratings yet
- 1B-Antenatal Care Case Protocol-1Document3 pages1B-Antenatal Care Case Protocol-1Mario EspinoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Case.Document47 pagesGestational Diabetes Case.Saivenkat KumbhamNo ratings yet
- Morning Report: Rabu, 19 Januari 2022Document41 pagesMorning Report: Rabu, 19 Januari 2022fabian arassiNo ratings yet
- CMC Pedia Batch 2Document43 pagesCMC Pedia Batch 2Marrione CalinawanNo ratings yet
- Permohonan Kredensial Indah KurniatiDocument5 pagesPermohonan Kredensial Indah KurniatiRehand ChandraNo ratings yet
- Grand-Rounds AbortionDocument30 pagesGrand-Rounds AbortionRoselle Joy D. RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Konfrens RS Stella Maris 6092022-2Document21 pagesKonfrens RS Stella Maris 6092022-2Maya Rosmaria PNo ratings yet
- Sibayan - Health Assessment FormDocument1 pageSibayan - Health Assessment FormAlberlee SibayanNo ratings yet
- 2023.aug.29 IMCI FormDocument5 pages2023.aug.29 IMCI FormHanna Fritch LariosaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics and Gynecology NotesDocument73 pagesObstetrics and Gynecology NotesHaspreet GillNo ratings yet
- Intern Obs Hx-1Document6 pagesIntern Obs Hx-1essasam12No ratings yet
- Ob Gyn History TakingDocument24 pagesOb Gyn History TakingBishal SigdelNo ratings yet
- Pedia Final Case 3Document37 pagesPedia Final Case 3Arun RaviNo ratings yet
- SPUP School of Medicine: Smyle/MABCDocument9 pagesSPUP School of Medicine: Smyle/MABCJOnapz Santos UnisTaNo ratings yet
- Case Title: PreeclampsiaDocument6 pagesCase Title: PreeclampsiaLanaNo ratings yet
- Konfrens RS Stella Maris 6092022Document21 pagesKonfrens RS Stella Maris 6092022Maya Rosmaria PNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis With Moderate DehydrationDocument59 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis With Moderate DehydrationCharisse Aser Flores AquinoNo ratings yet
- Mid Trimester DisorderDocument33 pagesMid Trimester DisorderdhivyadiyaNo ratings yet
- HISTORY TAKING - obsDocument16 pagesHISTORY TAKING - obsAlex XanderNo ratings yet
- HAF StudentDocument1 pageHAF StudentsheenacgacitaNo ratings yet
- OPD Orientation (July 26, 2021)Document7 pagesOPD Orientation (July 26, 2021)Jennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Case No. 5 Rle - PernitoDocument4 pagesCase No. 5 Rle - PernitoAlecxia Nicole PernitoNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CareDocument29 pagesAntenatal Caresanmaisingh130No ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Aakriti Shankar Ganesh 4 Year, MBBSDocument42 pagesCase Presentation: Aakriti Shankar Ganesh 4 Year, MBBSAakriti GNo ratings yet
- PrenatalDocument6 pagesPrenatalMaricar EustaquioNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child - Pre IntensiveDocument24 pagesMaternal and Child - Pre IntensiveLizaNo ratings yet
- Soap 2 Neale ClinicalDocument9 pagesSoap 2 Neale Clinicalapi-726948535No ratings yet
- Management of Neonatal SepsisDocument30 pagesManagement of Neonatal SepsisRam krishnaNo ratings yet
- 3 CH 19 20 High Risk PregnancyDocument20 pages3 CH 19 20 High Risk PregnancyabyNo ratings yet
- Medical Examination Form 2022-2023Document5 pagesMedical Examination Form 2022-2023Linh ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Maternal Tachycardia Management Pathway at Health Clinic in Pahang 2022Document2 pagesMaternal Tachycardia Management Pathway at Health Clinic in Pahang 2022Yash atri100% (1)
- ObsGyn - OSCE NotesDocument69 pagesObsGyn - OSCE NotesMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- C. PROM and PRETERM LABORDocument34 pagesC. PROM and PRETERM LABORMay MayNo ratings yet
- BlankDocument2 pagesBlankShyica SalacNo ratings yet
- My Case StudyDocument17 pagesMy Case StudymaramNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument34 pagesObstetricshassanwejdan1No ratings yet
- Audit Tool IOLDocument6 pagesAudit Tool IOLRosa ValenteNo ratings yet
- Management of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDDocument30 pagesManagement of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDiniidzniNo ratings yet
- GE in ChildrenDocument23 pagesGE in ChildrensamiNo ratings yet
- Obstric History Taking, CasesDocument151 pagesObstric History Taking, CasesljilffbNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Postnatal AssessmentDocument114 pagesAntenatal Postnatal AssessmentWendell Gian GolezNo ratings yet
- Case Study Male MSW 1Document27 pagesCase Study Male MSW 1JONAMAY RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- SFD PresentationDocument9 pagesSFD PresentationMena HashemNo ratings yet
- Cmca Trans AntenatalDocument4 pagesCmca Trans Antenatal2xy79knkmyNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics: Topic OutlineDocument5 pagesObstetrics: Topic OutlineRea Dominique CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Newborn ExaminationDocument13 pagesNewborn ExaminationAniq Zahran MasomNo ratings yet
- Chronic Diseases - Lymes, Hpv, Hsv Mis-Diagnosis and Mistreatment: A New Approach to the EpidemicFrom EverandChronic Diseases - Lymes, Hpv, Hsv Mis-Diagnosis and Mistreatment: A New Approach to the EpidemicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Meditec Clinika 2008Document23 pagesMeditec Clinika 2008api-26938677100% (2)
- Covid 19 Daily Reporting DasDocument6 pagesCovid 19 Daily Reporting DasRuhayati88gmail.com EyeshieldNo ratings yet
- Rural Health Care System in IndiaDocument22 pagesRural Health Care System in IndiaSumit Singhal62% (13)
- הפרעות אכילה מתוך הפרעות אחרות h1Document29 pagesהפרעות אכילה מתוך הפרעות אחרות h1Nina BravermanNo ratings yet
- Rural Review ReportDocument181 pagesRural Review ReportMorning StarNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6610 Assessment 1 Comprehensive Needs AssessmentDocument6 pagesNURS FPX 6610 Assessment 1 Comprehensive Needs Assessmentzadem5266No ratings yet
- The Do's of Patient Before SurgeryDocument8 pagesThe Do's of Patient Before SurgeryMENARDNo ratings yet
- 4 High Alert Medication FinalDocument4 pages4 High Alert Medication Finalrini setyawatiNo ratings yet
- WCECS2015 pp297-301Document299 pagesWCECS2015 pp297-301Sivakumar RajarathinamNo ratings yet
- Curing The Silent Epidemic: Caries Management in The 21st Century and BeyondDocument5 pagesCuring The Silent Epidemic: Caries Management in The 21st Century and BeyondghinaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Rehabilitation Principle and Practise PDFDocument292 pagesNeuro Rehabilitation Principle and Practise PDFIonela Arustei100% (1)
- List of Chapters - EULAR Textbook On Rheumatic DiseasesDocument3 pagesList of Chapters - EULAR Textbook On Rheumatic DiseasesOana CristeaNo ratings yet
- Reporting & Documenting Client Care: A Communication Skills ModuleDocument13 pagesReporting & Documenting Client Care: A Communication Skills Modulefarhan anwarNo ratings yet
- Preventive Orthodontics Canadian Children PDFDocument6 pagesPreventive Orthodontics Canadian Children PDFDragomir LarisaNo ratings yet
- Association Between Low Back Pain and Various Everyday PerformancesDocument9 pagesAssociation Between Low Back Pain and Various Everyday Performancesshaik chandiniNo ratings yet
- Ambulance Response Protocol DraftDocument3 pagesAmbulance Response Protocol DraftCommand CenterNo ratings yet
- Journal of Medical - Clinical Research & Reviews: Dermatology and Mental Wellbeing in The Era of COVID-19 PandemicDocument4 pagesJournal of Medical - Clinical Research & Reviews: Dermatology and Mental Wellbeing in The Era of COVID-19 PandemicSally EzzNo ratings yet
- Quizlet PDFDocument4 pagesQuizlet PDFsgkismetNo ratings yet
- HiMAS National Trainers' Profile May 2012Document6 pagesHiMAS National Trainers' Profile May 2012Benjie EugenioNo ratings yet
- Advances in Psychological and Social Support After DisastersDocument149 pagesAdvances in Psychological and Social Support After DisastersjprewittdiazNo ratings yet
- Telepharmacy and Home Delivery Program in SpainDocument4 pagesTelepharmacy and Home Delivery Program in SpainAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Diet Module 5 - 2019Document94 pagesDiet Module 5 - 2019Nithya NagrajNo ratings yet
- ORDINANCE TEMPLATE - First 1000 DaysDocument15 pagesORDINANCE TEMPLATE - First 1000 DaysGiezlRamos-PolcaNo ratings yet
- Common Proposal FormDocument4 pagesCommon Proposal Formsamknight2009No ratings yet
- Clinical PathwayDocument15 pagesClinical Pathwaygehad mohamed100% (1)
- Calvert, Carboplatin Dosage Based On Renal Function, JCO, 1989Document9 pagesCalvert, Carboplatin Dosage Based On Renal Function, JCO, 1989Valentina BenavidezNo ratings yet