Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2310-8783 - Traumatic Brain Injury Infographics
2310-8783 - Traumatic Brain Injury Infographics
Uploaded by
Sheema RahmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2310-8783 - Traumatic Brain Injury Infographics
2310-8783 - Traumatic Brain Injury Infographics
Uploaded by
Sheema RahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
WHAT IS TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY ?
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) as a disruption in the normal function of the brain that can be
caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head, or penetrating head injury.
CAUSES
PREVALANCE
Cases per year - 27.16 Million Malaysia:
168,222 cases per year
Male : Female - 2 : 1
Age Range : 0 -19 & 75+
TYPES
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
Brief or no loss of Unconsciousness (>30 Prolonged unconsciousness
consciousness (<30 mins). (>24 hours).
mins).
Serious side effects: cognitive Severe symptoms: profound
Usually resolve with time impairments, physical cognitive deficits, physical
and management. disabilities, mood changes, disabilities, sensory
behavioral difficulties. impairments, emotional
Symptoms: headaches, disturbances.
confusion, dizziness,
Often requires extensive Often leads to permanent
memory issues.
rehabilitation. disabilities, requiring
comprehensive medical care
and long term support. High
mortality rate in young adults.
SYMPTOMS
PHYSICAL COGNITIVE BEHAVIOURAL
Headache Difficulty Imbalance Concentration Attention Forgetfulness
speaking deficit Anger
Acting Frustration
reckless issues
Hearing Vsion Taste Repeating things Indecisive
Acceptance and Self-Awareness
COPING Regular exercise
Recognize personal
limitations and
STARTERGIES Boosts oxygen supply to
the brain and reduces
strengths. brain inflammation.
Develop a positive attitude
towards rehabilitation and
recovery. Support Network
Seek support from family,
Self-Care and Healthy Habits friends, and healthcare
professional.
Adequate sleep,
nutrition, and Join support groups or
hydration. connect with other
individuals with TBI for
Avoid substance mutual support and
abuse and prioritize understanding.
mental health.
Adaptive Techniques Stress Management:
Use memory aids such as Practice relaxation
calendars, lists, and techniques such as deep
reminders. breathing, meditation, or
yoga.
Break tasks into smaller
steps and prioritise
activities.
ASSESSMENT
GLASSGOW COMA SCALE CT/MRI SCAN
Evaluates eye, verbal, and motor responses.
CT Scan: MRI Scan:
Consciousness Gauge
Initial imaging for TBI emergencies. Detailed brain tissue assessment.
Measures level of consciousness (3 to 15 scoring range).
Detects acute injuries like bleeding or fractures. High-resolution images using magnetic fields.
Severity Indication: Lower scores signal more severe impairment.
Quick and widely available. Detects subtle damage or abnormalities.
Critical Guidance: Essential for treatment decisions and prognosis.
Ideal for detecting acute hemorrhages.
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION THE GALVESTON ORIENTATION AND AMNESIA
TEST (GOAT)
Mental Status Evaluation: Assess orientation, Sensory Function Examination: Test sensation,
memory, attention, language, and confusion signs. proprioception, and discrimination of sensory stimuli. Widely used
Cranial Nerve Exam: Evaluate sensory and motor Reflex Testing: Evaluate deep tendon and plantar It evaluates orientation (person, place, time) and short-term memory.
functions of the twelve cranial nerves. reflexes for neurological function. Crucial for understanding cognitive function Guides treatment and
Motor Function Assessment: Check muscle strength, Gait Assessment: Examine walking pattern and rehabilitation planning.
coordination, balance, and detect abnormalities. balance for signs of ataxia or abnormalities.
TREATMENTS
1 Emergency care
Enquiry regarding the injury
How did the injury occur? Did the person lose consciousness?
2 Imaging tests
CT SCAN / M RI SCAN
Visualising the injury and analysising the degree of the injury - mild, moderate and sever
3 Intracranial pressure monitor
Tissue swelling from a traumatic brain injury can increase pressure inside the skull and cause additional damage to the brain
4 Medications
Diuretics: Reduce Anticonvulsants: Prevent seizures Analgesics: Reduce pain during TBI
the fluids and further damage. treatment.
5 Surgery
Removing clotted blood Repairing skull Bleeding in the Opening a window in
(hematomas) fractures brain the skull
6 Rehabilitation
Brain injury often requires rehabilitation for Rehabilitation aims to improve daily activity
relearning basic skills. abilities.
Therapy starts in the hospital, then may Rehabilitation type and duration vary based
continue in various settings. on injury severity and affected brain areas.
You might also like
- BMW 3 Series E46 1997 2006 Workshop ManualDocument1,257 pagesBMW 3 Series E46 1997 2006 Workshop ManualTakács Dániel100% (4)
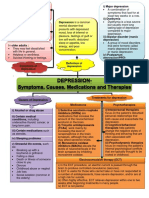
- Depression Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesDepression Lesson PlanManisha Samson60% (5)
- Load Bank Catalog (ComRent)Document59 pagesLoad Bank Catalog (ComRent)ccorp0089No ratings yet
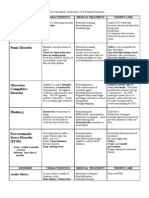
- Anxiety & Personality DisordersDocument4 pagesAnxiety & Personality Disordersdlneisha61No ratings yet
- Mental Health High School Curriculum Guide Teacher Knowledge UpdateDocument25 pagesMental Health High School Curriculum Guide Teacher Knowledge Updateapi-356243627No ratings yet
- ITT Mackay Instruction Manual For Model 3030A-3030AR Synthesized Receiver Issue 3 June 1982Document110 pagesITT Mackay Instruction Manual For Model 3030A-3030AR Synthesized Receiver Issue 3 June 1982antoniNo ratings yet
- Tae Evo 015 - 351 EnglDocument39 pagesTae Evo 015 - 351 EnglMantenimientoValdezGutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chicken's MoltingDocument11 pagesChicken's MoltingKhaira Fani100% (1)
- BuspironeDocument2 pagesBuspironeFatima Diane S. MondejarNo ratings yet
- Mind Your Mind BrochureDocument2 pagesMind Your Mind BrochureMarylendra PenetranteNo ratings yet
- Delirium, Dementia, PsychosisDocument1 pageDelirium, Dementia, PsychosisLana LocoNo ratings yet
- A Combination of Symptoms That Last For at Least Two Weeks in A RowDocument1 pageA Combination of Symptoms That Last For at Least Two Weeks in A RowadlinNo ratings yet
- Go 3Document1 pageGo 3adlinNo ratings yet
- Brochure - INHALANT PreviewDocument2 pagesBrochure - INHALANT PreviewBarangay Guinayang San MateoNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesAlzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and SymptomsMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- Sketchpad Chapter 8Document9 pagesSketchpad Chapter 8Matt JumawanNo ratings yet
- Concepts of StressDocument9 pagesConcepts of Stressdexter100% (4)
- Mood Disorders: Mental Health Nursing-NUR 417Document44 pagesMood Disorders: Mental Health Nursing-NUR 417preeti vermaNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 5Document5 pagesNCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 5Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Dissociative DisordersDocument1 pageDissociative DisordersRedgie G. GabaneNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Psychological DisordersDocument1 pageCH 4 Psychological DisordersKshitij DasariNo ratings yet
- 1-01 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination Appendix CIC v1Document5 pages1-01 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination Appendix CIC v1Dane Mikhael CalicaNo ratings yet
- Recreational NCD Grade 12Document30 pagesRecreational NCD Grade 12Rafael AnianoNo ratings yet
- Mental Health: What To Do When Someone Is Suicidal?Document1 pageMental Health: What To Do When Someone Is Suicidal?Gabriel RelayoNo ratings yet
- What Is Mental Health?: "Caring For Your Mental Health Amidst The Challenges and Change"Document23 pagesWhat Is Mental Health?: "Caring For Your Mental Health Amidst The Challenges and Change"amelito m. lingaNo ratings yet
- PerDev ReviewerDocument6 pagesPerDev ReviewerChristian CalauadNo ratings yet
- STRESSDocument19 pagesSTRESScherrymaemidoriNo ratings yet
- Uts (Module1) - FinalsDocument1 pageUts (Module1) - FinalslovelyNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument3 pagesCognitive DisordersCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Depressive DisorderDocument59 pagesDepressive DisorderJoshua RingorNo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping 10.2020Document22 pagesStress and Coping 10.2020Anonymous cKLSPQfNo ratings yet
- OBM255 NEWSLETTErDocument2 pagesOBM255 NEWSLETTErFreddy Msc100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 Added InfosDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 2 Added InfosRins BanalNo ratings yet
- Stress Management WorkshopDocument45 pagesStress Management WorkshopEdenmay VerNo ratings yet
- Caregiver Manual 8st - JosephDocument51 pagesCaregiver Manual 8st - Josephcarlo penidoNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitasi Medis Untuk GSA - Dr. LuhDocument32 pagesRehabilitasi Medis Untuk GSA - Dr. LuhDoc HadiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Health 7 I. Content Standard: Teacher's Activity Students' ActivityDocument10 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Health 7 I. Content Standard: Teacher's Activity Students' ActivityGladys Javier PatoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder HandoutDocument3 pagesBipolar Disorder Handoutapi-548175940No ratings yet
- Medical Cannabis For Traumatic Brain InjuriesDocument1 pageMedical Cannabis For Traumatic Brain InjuriesSantiago IbarraNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryDocument18 pagesPsychiatryWorld MedclickzNo ratings yet
- Mental Retardation Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesMental Retardation Lesson Plansp2056251No ratings yet
- Pe NotesDocument20 pagesPe NotesHim SharNo ratings yet
- Understanding Stress, Anxiety, and Depression & Making Mental Health Your PriorityDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Stress, Anxiety, and Depression & Making Mental Health Your PriorityDanicaNo ratings yet
- Neouropsychiatric AssessmentDocument21 pagesNeouropsychiatric AssessmentKopano'Gucci'ModisenyaneNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument5 pagesPsychiatric NursingcelestineNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIATRIC NURSING - Level of AnxietyDocument1 pagePSYCHIATRIC NURSING - Level of AnxietyZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Counselling PTSD Treatment IssuesDocument2 pagesCounselling PTSD Treatment IssuesJoseph PrestiNo ratings yet
- Psy202-2021 Dissociative DisordersDocument4 pagesPsy202-2021 Dissociative DisordersJustin TayabanNo ratings yet
- SARP (Skin Anesthesia Radiology Psychiatry) Review 2010Document4 pagesSARP (Skin Anesthesia Radiology Psychiatry) Review 2010QworldNo ratings yet
- Post Concussion SyndromeDocument2 pagesPost Concussion SyndromeCeleborn021100% (2)
- Biofeedback Neurofeedback and Cognitive RehabDocument29 pagesBiofeedback Neurofeedback and Cognitive RehabDr Nader KorhaniNo ratings yet
- Infografía de La DepresiónDocument1 pageInfografía de La DepresiónAndreaNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Mouse PartyDocument2 pagesActivity 4 Mouse PartyKolynNo ratings yet
- Amnesia DemensiaDocument2 pagesAmnesia DemensiaAlexander TegarNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) : Presented By: Joseph Rafael B. MasingDocument15 pagesDissociative Identity Disorder (DID) : Presented By: Joseph Rafael B. MasingIan Francis RojasNo ratings yet
- Brochure About Mental HealthDocument2 pagesBrochure About Mental HealthAron PholleNo ratings yet
- Recovery TheropyDocument17 pagesRecovery Theropysifft.stevenNo ratings yet
- Delirum Vs DementiaDocument1 pageDelirum Vs Dementiaapi-577583685No ratings yet
- Promoting Professional Relationships and Fostering Social SupportDocument14 pagesPromoting Professional Relationships and Fostering Social SupportuhapartmentNo ratings yet
- Y10 PDHPE NotesDocument14 pagesY10 PDHPE NotesOscar ReinitzNo ratings yet
- DBT Skills Workbook for Women with Anxiety and Negative EmotionsFrom EverandDBT Skills Workbook for Women with Anxiety and Negative EmotionsNo ratings yet
- Easy Giantess CalculatorDocument1 pageEasy Giantess CalculatorArthur Dutra ReccoNo ratings yet
- Oishi GroupDocument20 pagesOishi GroupCamilleJoyceAdrianoNo ratings yet
- Crochet A Deer Pattern in 20 Minutes.Document17 pagesCrochet A Deer Pattern in 20 Minutes.Maria Elisa BalestriniNo ratings yet
- GrundfosDocument16 pagesGrundfosKarthick SarathyNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemDocument75 pagesEmbedded SystemDnyaneshwar KarhaleNo ratings yet
- HMI Design Process ENDocument2 pagesHMI Design Process ENSHNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia of Popular Science (Steven N.shore)Document353 pagesEncyclopaedia of Popular Science (Steven N.shore)Muhammad Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P2 Grade 10 Nov 2017 EngDocument15 pagesPhysical Sciences P2 Grade 10 Nov 2017 EngSesanda SibiyaNo ratings yet
- Aerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw MaterialsDocument5 pagesAerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw Materialskinley dorjee100% (1)
- P1-F Revision For Midyear - Listening - The Sydney Opera HouseDocument4 pagesP1-F Revision For Midyear - Listening - The Sydney Opera HouseYusuf Can SözerNo ratings yet
- Module-8 - Hydrocyclone AdjustmentsDocument184 pagesModule-8 - Hydrocyclone AdjustmentsizotreyNo ratings yet
- Piling - Good Practice GuideDocument2 pagesPiling - Good Practice GuideRachel IngramNo ratings yet
- SINAMICS SL150 Cyclo Converters: Highest Marks in Robustness and ReliablilityDocument12 pagesSINAMICS SL150 Cyclo Converters: Highest Marks in Robustness and ReliablilityEdgardNo ratings yet
- Urine Examination# DivyaDocument69 pagesUrine Examination# DivyaMedicine 0786No ratings yet
- Gillies Main MenuDocument2 pagesGillies Main MenugalgormNo ratings yet
- Vortec Lh6 5.3l v8 MT OrgDocument837 pagesVortec Lh6 5.3l v8 MT Orggabriel megaNo ratings yet
- Proposed Philippine Games: Title of The Game: Venue/Facility: Plan ADocument2 pagesProposed Philippine Games: Title of The Game: Venue/Facility: Plan AJane DizonNo ratings yet
- My Project SatarliteDocument33 pagesMy Project SatarlitesarjoonNo ratings yet
- 15.1. Kitzes, J. - An Introduction To Environmentally-Extended Input-Output AnalysisDocument27 pages15.1. Kitzes, J. - An Introduction To Environmentally-Extended Input-Output AnalysisDiana Toro HernandezNo ratings yet
- Steeple Analysis in ParaguayDocument64 pagesSteeple Analysis in ParaguayVijay GohilNo ratings yet
- The Fascinating World of AnimalsDocument2 pagesThe Fascinating World of AnimalsdilaydurmazNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology - Exercises. Gaetano MarroneDocument4 pagesEpidemiology - Exercises. Gaetano Marronemillion assefaNo ratings yet
- Bioisosterismo - RevisãoDocument27 pagesBioisosterismo - RevisãoCLARA VITORIA CAVALCANTE CARVALHONo ratings yet
- Tanks DesignDocument8 pagesTanks DesignAhmed EnnehriNo ratings yet
- RKS IFC 2015 Solar CellDocument23 pagesRKS IFC 2015 Solar CellAnugrah PangeranNo ratings yet