Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
1
Uploaded by
johnnatividad445Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
1
Uploaded by
johnnatividad445Copyright:
Available Formats
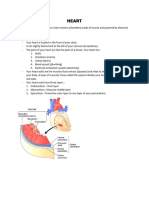
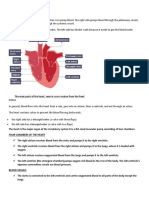
1.
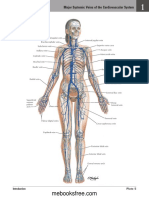
Superior vena cava - The superior vena cava and inferior vena cava have the
important function of carrying oxygen-poor blood to your heart's right atrium, where it
moves into your right ventricle and then to your lungs (through your pulmonary
artery) to trade in carbon dioxide for oxygen.
2. Aorta - The aorta is the main artery that carries blood away from your heart to the
rest of your body. The blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve. Then it travels
through the aorta, making a cane-shaped curve that allows other major arteries to
deliver oxygen-rich blood to the brain, muscles and other cells.
3. Pulmonary arteries - The pulmonary arteries carry oxygen-poor blood from your
heart to your lungs. The right pulmonary artery supplies the right lung, while the left
pulmonary artery supplies the left lung.
4. Pulmonary veins - The pulmonary veins collect oxygen-rich blood from your
lungs and carry it to your heart. The left superior pulmonary vein drains the left upper
lobe and the lingula. The left inferior pulmonary vein drains the left lower lobe. The
right superior pulmonary vein drains the right upper and middle lobes. The right
inferior pulmonary vein drains the right lower lobe.
5. Pulmonary Valve - The pulmonary valve allows blood to be pumped from the
right ventricle to the lungs (through the pulmonary artery), where it will receive
oxygen. Prevents the backflow of blood from the pulmonary artery to the right
ventricle.
6. Atriums - The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right
atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle.
The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. The left atrium
receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
7. Mitral Valve - The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart. It regulates blood
flow from the upper left chamber (left atrium) into the lower left chamber (left
ventricle). The left ventricle is the heart's main pumping chamber. A normal mitral
valve has two flaps, or leaflets.
8. Aortic Valve - The aortic valve separates the left ventricle from the aorta. Opens
to allow blood to leave the heart from the left ventricle through the aorta and the
body. Prevents the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle.
9. Ventricles - The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. The left
atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood to the body.
10. Interior vena cava - The inferior vena cava is ultimately responsible for
the transport of almost all venous blood (deoxygenated) from the abdomen and
lower extremities back to the right side of the heart for oxygenation.
You might also like
- Apostol Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesApostol Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanKaren Limpo Apostol100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentSiti Sumari HarahapNo ratings yet
- Part of The Heart and Its FunctionsDocument1 pagePart of The Heart and Its FunctionsAngelica A TultogNo ratings yet
- Research Questions-: How The Blood FlowsDocument5 pagesResearch Questions-: How The Blood FlowsAasritha SenagapallyNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument3 pagesHeartTrisha MedidasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory Systempriyamail0525No ratings yet
- Circulatory System - ScienceDocument1 pageCirculatory System - ScienceAltheaNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Structure of Heart To SendDocument12 pagesStructure of Heart To SendlaibahundekarNo ratings yet
- System Is An: ArteriesDocument4 pagesSystem Is An: ArteriesPinasti Aprilia PutriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 1Yenny YenNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument3 pagesHEARTShan ShanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Notes in Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Circulatory SystemVianney CamachoNo ratings yet
- Rat Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesRat Circulatory SystemAnkit NariyaNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument8 pagesCirculatoryKristel Faye DioNo ratings yet
- Diagram Human Heart Kel 1Document3 pagesDiagram Human Heart Kel 1Rahma SafitriNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1frenee aradanasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMuri CajucomNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Through The HeartDocument10 pagesBlood Flow Through The HeartJack MessarosNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument1 pageHeartswati singhNo ratings yet
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDocument3 pagesHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet
- CVS IDocument7 pagesCVS Itemple samNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsDocument47 pagesParts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyClint-Marie LaxaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- P.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2ADocument29 pagesP.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2AAlea Jane AranjuezNo ratings yet
- I. Anatomy and Pathophysiology: Cardiovascular System Heart Blood VesselDocument5 pagesI. Anatomy and Pathophysiology: Cardiovascular System Heart Blood VesselDibb Fabiania Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument2 pagesThe Heartmaty.visintainerNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 L 6 Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesGrade 9 L 6 Circulatory SystemJAYDEN JANSZNo ratings yet
- Question #1 Explain Femure With Structure? DefinitionDocument6 pagesQuestion #1 Explain Femure With Structure? DefinitionAmjad BhattiNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory SystemPuguh HadiNo ratings yet
- MS Wrep IIDocument51 pagesMS Wrep IIiana-almocera-6970No ratings yet
- MY CLASS NOTES - BIOLOGY Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesMY CLASS NOTES - BIOLOGY Circulatory SystemJjongNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument2 pagesThe HeartSonkapoponkaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Document10 pagesLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- BingrrisDocument1 pageBingrrisYolanda SaritaNo ratings yet
- Self Study MaterialDocument2 pagesSelf Study MaterialNisha JojanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit One Cardiovascular NursingDocument1 pageUnit One Cardiovascular Nursingapi-3729047No ratings yet
- TALLER #3 BioinstrumentacionDocument2 pagesTALLER #3 BioinstrumentacionmaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesCirculatory SystemKeyur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument16 pagesHuman HeartDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Heartrave26No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Heartkheng100% (4)
- Angelo Jhuan ScienceDocument2 pagesAngelo Jhuan ScienceGoldenaholicNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NstemiDocument3 pagesAnatomy NstemiSheana Tmpl100% (1)
- 5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2Document29 pages5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2uxdan154No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The HeartDocument3 pagesStructure and Function of The Heartuserdev987No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The HeartUfuq Azmi BasyarNo ratings yet
- Preparation Tasks - Week 6Document7 pagesPreparation Tasks - Week 6Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Circulatory SystemDocument157 pagesUnit 4 Circulatory SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- 8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pages8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMammarahn0No ratings yet
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Bolile Cerebro-Vasculare Accidentul Vascular CerebralDocument66 pagesBolile Cerebro-Vasculare Accidentul Vascular CerebralAnaSoareNo ratings yet
- Current Use and Advances in Vasopressors and Inotropes Support in ShockDocument13 pagesCurrent Use and Advances in Vasopressors and Inotropes Support in ShockJose Luis Espino MacielNo ratings yet
- Sced 3204B LDocument5 pagesSced 3204B LEllen Grace Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- CVSDocument86 pagesCVSEhsan bhuttaNo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins: A Clinical Study: Original Research ArticleDocument5 pagesVaricose Veins: A Clinical Study: Original Research ArticleAndhika DNo ratings yet
- Esmr 2Document1 pageEsmr 2Martina FitriaNo ratings yet
- Cody Michel's Blood PressureDocument4 pagesCody Michel's Blood PressureAnonymous G3r8ckbkqhNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound For Lower Extremity Deep ThrombosisDocument12 pagesUltrasound For Lower Extremity Deep ThrombosisDiego RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Sympa T Holy TicsDocument30 pagesSympa T Holy TicsAhaisibwe GordonNo ratings yet
- Patomorfologia Prezentacja - KopiaDocument14 pagesPatomorfologia Prezentacja - KopiaOlgaNo ratings yet
- COPS Cathet Cardio Intervent - 2023 - MangieriDocument9 pagesCOPS Cathet Cardio Intervent - 2023 - MangieriPraveenVeeraNo ratings yet
- Emergency Cardiovascular CareDocument56 pagesEmergency Cardiovascular CareAdit PradaNaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesPhysiology of Lymph SystemMwangi NyawiraNo ratings yet
- Aortic Arch AnomaliesDocument50 pagesAortic Arch AnomaliesROHITNo ratings yet
- Equipment and Monetring CPB PDFDocument10 pagesEquipment and Monetring CPB PDFBasantkumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment - Cardiac & PVSDocument56 pagesHealth Assessment - Cardiac & PVSclaire3230No ratings yet
- Imaging of Ventricular Septal Defect - Rizki Yuda PurnomoDocument18 pagesImaging of Ventricular Septal Defect - Rizki Yuda PurnomoRizkiYudaPurnomoNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Flex BrochureDocument6 pagesPipeline Flex Brochuretarun mathurNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Practice Questions Test Positioning Patients Nursing FundamentalsDocument3 pagesNCLEX Practice Questions Test Positioning Patients Nursing FundamentalsjhonNo ratings yet
- Circulationaha 119 034512 PDFDocument19 pagesCirculationaha 119 034512 PDFNicola MaffeiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Sistem SirkulasiDocument10 pagesLaporan Sistem SirkulasiRosa AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Jama Yang 2023 Oi 230112 1697473261.42652Document12 pagesJama Yang 2023 Oi 230112 1697473261.42652adol1018No ratings yet
- 04 - Dual Chamber TimingDocument138 pages04 - Dual Chamber TimingMihir RavalNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument7 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionRalph Emerson RatonNo ratings yet
- 114 Final Brain Dump Part 2Document8 pages114 Final Brain Dump Part 2kelsey jacksonNo ratings yet
- Netter 7-1Document1 pageNetter 7-1MateiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System AssignmentDocument8 pagesCirculatory System AssignmentMonroe P ZosaNo ratings yet
- No-Reflow Phenomenon: DR - Surinder S HansraDocument17 pagesNo-Reflow Phenomenon: DR - Surinder S HansrasshansraNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Basic InformationDocument11 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Basic InformationAnonymous cdLyeXKBNo ratings yet