Professional Documents
Culture Documents
555 Timer Astable
555 Timer Astable
Uploaded by
Abel SeifuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MR366X8488B000Document16 pagesMR366X8488B000Mislav GudeljNo ratings yet
- Measuring T1 and T2Document25 pagesMeasuring T1 and T2drnmrdrnmrNo ratings yet
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay SettingDocument2 pagesCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Settingsaran100% (2)
- Jungheinrich Ejc112 & E1202Document184 pagesJungheinrich Ejc112 & E1202Thomas Hansen80% (10)
- Modularis Service PDFDocument63 pagesModularis Service PDFVictor ZambranoNo ratings yet
- How To Configure A 555 Timer ICijDocument2 pagesHow To Configure A 555 Timer ICijJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- How To Configure A 555 Timer ICijDocument2 pagesHow To Configure A 555 Timer ICijJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- 555 TimersDocument29 pages555 TimersSatchit PrabhuNo ratings yet
- ES Assignment: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesES Assignment: ObjectiveLekhraj PariharNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9Nixon GamingNo ratings yet
- ELE302 - Lab 2-092021Document17 pagesELE302 - Lab 2-092021hughjass39.99No ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Instrumentation Lab EE-702Document5 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Instrumentation Lab EE-702Saurav SumanNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Maximum Sampling Rate of An Analog MuxDocument4 pagesHow To Calculate Maximum Sampling Rate of An Analog MuxmaysquaredNo ratings yet
- Beginning Time T Time To Half Value of V: TheoreticalDocument6 pagesBeginning Time T Time To Half Value of V: TheoreticalAli Amir ShreifNo ratings yet
- Measurement Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesMeasurement Literature Reviewuam22No ratings yet
- DC To DC Two Quadrant ConverterDocument7 pagesDC To DC Two Quadrant Converterhamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Dwarkadas. J. Sanghvi College of EngineeringDocument8 pagesDwarkadas. J. Sanghvi College of EngineeringAbir DeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3ARUN KUMAR PNo ratings yet
- APSC 1299 Test 2 - Spring 2011 AnswersDocument7 pagesAPSC 1299 Test 2 - Spring 2011 AnswersJonathan WongNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 PDFDocument4 pagesLab 1 PDFTanmay KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- Dealing With PLL Clock Jitter in Advanced Processor DesignsDocument5 pagesDealing With PLL Clock Jitter in Advanced Processor DesignsrobduronNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 6 - Sinusoidal Responses Self Assessment Exercise No.1Document1 pageControl Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 6 - Sinusoidal Responses Self Assessment Exercise No.1cataiceNo ratings yet
- Iv TimersDocument48 pagesIv TimersanishthNo ratings yet
- An550 PDFDocument8 pagesAn550 PDFCarlos RamirezNo ratings yet
- Sequential Logic and Memory ComponentsDocument9 pagesSequential Logic and Memory ComponentsShashank MishraNo ratings yet
- PLC Laboratory Activity 1Document4 pagesPLC Laboratory Activity 1Kate AlindajaoNo ratings yet
- 8051-CH9-TimePmg in Assem & CDocument101 pages8051-CH9-TimePmg in Assem & CshivaspyNo ratings yet
- A Multi Vibrator Is An Electronic Circuit Used To Implement ADocument5 pagesA Multi Vibrator Is An Electronic Circuit Used To Implement AbulkSoftNo ratings yet
- 1 Analog SignalsDocument25 pages1 Analog SignalsseenusoftNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document9 pagesChapter 22lotex77No ratings yet
- Sdic 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 2)Document4 pagesSdic 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 2)Ganapathy RamadossNo ratings yet
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) : Square WaveDocument23 pagesPulse Width Modulation (PWM) : Square WavepaulinaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 4 - System Response Self Assessment Exercise No.1Document3 pagesControl Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 4 - System Response Self Assessment Exercise No.1cataiceNo ratings yet
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)Document8 pagesCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)Aslam kathat100% (2)
- Microcontrollers and Its Applications: Shivaum Heranjal L27+28 17BEC0315 Padmini T NDocument6 pagesMicrocontrollers and Its Applications: Shivaum Heranjal L27+28 17BEC0315 Padmini T NShivaum Heranjal100% (1)
- Chapter 22 General Purpose PID ControlDocument10 pagesChapter 22 General Purpose PID ControlEduardo AlvearNo ratings yet
- Study and Evaluation of Performances of The Digital MultimeterDocument10 pagesStudy and Evaluation of Performances of The Digital Multimetermihaela0chiorescuNo ratings yet
- DMM PPTDocument17 pagesDMM PPTShah Najmus SaqibNo ratings yet
- Calculate Setting of IdmtDocument2 pagesCalculate Setting of IdmtsakthivelduraiNo ratings yet
- Digital Control System-1Document47 pagesDigital Control System-1Makesh MäKzNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 7 - Stability Analysis Self Assessment Exercise No.1Document4 pagesControl Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 7 - Stability Analysis Self Assessment Exercise No.1cataiceNo ratings yet
- AstableDocument6 pagesAstablemanthan NaikNo ratings yet
- IdmtDocument3 pagesIdmtAdeel RazaNo ratings yet
- Large Amplitude Pendulum With PC InterfaceDocument8 pagesLarge Amplitude Pendulum With PC InterfaceKarl KaiNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller TimersDocument42 pagesMicrocontroller TimersPatel NeelNo ratings yet
- m4Document46 pagesm4sunilgj123No ratings yet
- Sample IDMT SettingDocument4 pagesSample IDMT SettingMesias John FedericoNo ratings yet
- Setting Calculation of Oc and Ef RealyDocument1 pageSetting Calculation of Oc and Ef RealyManishPandya67% (3)
- Ec6504 MPMC Unit 5Document192 pagesEc6504 MPMC Unit 5Gomathi PsNo ratings yet
- CT303: Digital Communication Lab1 and Lab2 Report: TOPIC 1: PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation)Document8 pagesCT303: Digital Communication Lab1 and Lab2 Report: TOPIC 1: PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation)LAKSHYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument43 pagesElectric DrivesDigital AlarmNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ExxonMobilDocument30 pagesHeat Transfer ExxonMobilHernan CobaNo ratings yet
- Real Timer ControlDocument94 pagesReal Timer ControlSai Krishna KodaliNo ratings yet
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)Document11 pagesCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)robertovm2002No ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Wein-Bridge OscillatorDocument8 pagesAssignment 3: Wein-Bridge OscillatorDeepal PrasankaNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 Ultrashort Pulses 01Document33 pagesLecture03 Ultrashort Pulses 01Yeong Gyu KimNo ratings yet
- Working With IC555: : Astable MultivibratorDocument5 pagesWorking With IC555: : Astable Multivibrator9909552136No ratings yet
- The Dual-Slope Conversion Improvement: Radojle Radetić, Marijana Pavlov-Kagadejev, Nikola MilivojevićDocument13 pagesThe Dual-Slope Conversion Improvement: Radojle Radetić, Marijana Pavlov-Kagadejev, Nikola MilivojevićasprillaNo ratings yet
- Ger3973 (Calculo de TC para Proteccion)Document16 pagesGer3973 (Calculo de TC para Proteccion)Erick Daniel Toyo MarinNo ratings yet
- Allen J Wood Power Generation Operation OstDocument33 pagesAllen J Wood Power Generation Operation OstDhoviar M. AliNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesAbaid UllahNo ratings yet
- Extra: Battery Chargers and Expansion ModulesDocument2 pagesExtra: Battery Chargers and Expansion Modulessammy muisyoNo ratings yet
- Different Types of LightsDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of LightsAnusha SawhneyNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodsDocument2 pagesPartial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodskashifNo ratings yet
- UT593 595 Data SheetDocument1 pageUT593 595 Data SheetqaqcmepteamNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Systems-Variation of Efficiency With Band-Gap and TemperatureDocument9 pagesPhotovoltaic Systems-Variation of Efficiency With Band-Gap and TemperatureRaja SekaranNo ratings yet
- ) Mets: Iqdilution BookDocument106 pages) Mets: Iqdilution BookDanilNo ratings yet
- LAB 12-PE-LabDocument9 pagesLAB 12-PE-LabLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Ropex Res 403 - eDocument42 pagesRopex Res 403 - eАлександр Колосов100% (1)
- Advanced Switching Solutions: FeaturesDocument4 pagesAdvanced Switching Solutions: Featuresraza239No ratings yet
- Treadtronics ProfileDocument31 pagesTreadtronics ProfileEhtisham BhattiNo ratings yet
- Networked Option Pods Operating Instructions July 2023 v1.3Document17 pagesNetworked Option Pods Operating Instructions July 2023 v1.3Ariel Horta LoeraNo ratings yet
- Mos Inverters: Static CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesMos Inverters: Static Characteristicskeshav guptaNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument11 pagesCourseIvan ElisioNo ratings yet
- Study On The Effects of ElectromagnetsDocument6 pagesStudy On The Effects of ElectromagnetsDrake Athenaeus CaminongNo ratings yet
- Led Based Scrolling Message DisplayDocument125 pagesLed Based Scrolling Message DisplayVikas Choudhary100% (3)
- Etos TD and Etos ED Innovative Motor-Drive Solutions With Integrated MonitoringDocument12 pagesEtos TD and Etos ED Innovative Motor-Drive Solutions With Integrated Monitoringrichardt999No ratings yet
- Marshall 'Blues Breaker': Manual & Assembly GuideDocument27 pagesMarshall 'Blues Breaker': Manual & Assembly GuideAndre OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Logic Gates & Boolean AlgebraDocument32 pagesChapter 2 Logic Gates & Boolean AlgebraAmita PalNo ratings yet
- Ahuja SSA-250M Specifications & FeaturesDocument1 pageAhuja SSA-250M Specifications & Featuressecurekart50% (2)
- Audio StandardsDocument8 pagesAudio Standardsyomama3100% (1)
- Solis 3P-8K-4GDocument2 pagesSolis 3P-8K-4GBanjaran SolarNo ratings yet
- Arduino Base Over Voltage and Under Voltage Protection Circuit LITERATURE REVIEWDocument23 pagesArduino Base Over Voltage and Under Voltage Protection Circuit LITERATURE REVIEWOlasupo IyaboNo ratings yet
- Datasheet DL50-P1123 1047361 enDocument6 pagesDatasheet DL50-P1123 1047361 enFaiz BajwaNo ratings yet
- Electrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing Level - II: TVET Institution Training TheoryDocument4 pagesElectrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing Level - II: TVET Institution Training Theorybelacheweshetu222100% (3)
- 15p0072b1 Sinus N en r00Document142 pages15p0072b1 Sinus N en r00Maher JarrarNo ratings yet
- 7PA30321AA001 Datasheet enDocument2 pages7PA30321AA001 Datasheet enptepartheepan.sNo ratings yet
555 Timer Astable
555 Timer Astable
Uploaded by
Abel SeifuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
555 Timer Astable
555 Timer Astable
Uploaded by
Abel SeifuCopyright:
Available Formats
555 Timer Astable Calculator Description
When a 555 timer is operating in Astable mode we obtain a pulse on the output pin
whose ON time (Time high) and OFF time (Time low) can be controlled. This
controlling can be done by selecting the appropriate values for the Resistor R1,R2 and
capacitor C1. The circuit diagram to operate the 555 IC in Astable mode is shown be
The circuit can be used to produce a square wave in which the high time (T1) and low
time (T2) can be calculated. This method can be used to generate clock pulses for
Microcontrollers/Digital IC’s or blink an LED or any other applications where
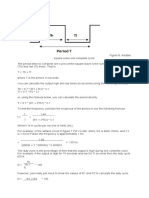
specific time intervals are needed. The output wave obtained from pin 3 is shown with
markings below
The time axis T is measured in seconds and the Voltage axis is measured in Volts. As
said earlier how long the pulse stays high, how long the pulse stays low and the
frequency of the pulse can be calculated using the value of components R1,R2 and C1
shown on the circuit diagram above.
The above 555 timer Astable calculator can be used to calculate these values, but to
understand its working we need to know the following formulas based on which the
calculator works.
Parameter Formulae Unit
Time
0.693 × (R1+R2) × C1 Seconds
High (T1)
Time
0.693 × R2 × C1 Seconds
Low (T2)
Time 0.693 × (R1+2×R2) × Seconds
Period (T) C1
1.44 / (R1+2×R2) ×
Frequency (F) Hertz (Hz)
C1
Duty Cycle (T1/T)×100 Percentage (%)
Note: These units are applicable only when R1 and R2 is in ohms and Capacitor is in
Farads
It might be hectic to try different values of Resistor and capacitors to arrive at you
desired Time interval and Frequency. So, always keep these below tips in head while
selecting your values
TIPS:
Period(T) and Frequency(F) are inversely proportional
Increase in C1 will decrease Frequency (F)
Increase in R1 will increase High Time (T1) but will not alter low Time (T2)
Increase in R2 will increase High Time (T1) and also increase low Time (T2)
So, always set T2 first and then T1
Increase in R2 will decrease duty cycle
Once we have all these details, we can get to know the complete properties of the
output wave. To get used to the formulas lets calculate the value for parameters using
these formulas for the circuit diagram given above.
Model Calculation
In our circuit diagram the value of Resistors R1 and R2 is 1K and 100K respectively,
the value of capacitor C1 is 10uf.
So, R1 = 1K; R2 = 100K and 10uF
Or can be written as R1=1000 Ohms; R2=100000 Ohms, C1=0.00001 Farads
The Time high (T1) is the amount of time during which the pulse stays high (5V) in
the output wave. This can be calculated as
Time high (T1) = 0.693 × (R1+R2) × C1
= 0.693 × (1000 +100000) × 0.00001
= 0.699 seconds
T1 = 699 milliseconds
The Time low (T2) is the amount of time during which the pulse stays low(0v) in the
output wave. It can be calculated as
Time low (T2) = 0.693 × R2 × C1
= 0.693 × 100000 × 0.00001
= 0.693 seconds
T2 = 693 milliseconds
The time Period (T) is the sum of Time low and Time high. Changing wither Time
high or time low will affect the Total time period T
Time Period (T) = 0.693 × (R1+2×R2) × C1 or (T1+T2)
= 0.693 × (1000 +2×100000) × 0.00001 or (0.699+0.693)
T = 1.393 seconds
As we all know frequency is just the inverse of time. There are certain applications
like a servo motor control where the pulse has to be in a certain frequency for the
driver circuit to respond. The frequency can be calculated as
Frequency (F) = 1.44 / (R1+2×R2) × C1 or (1/T)
= 1.44 / (1000 +2×100000) × 0.00001 or (1/1.393)
F = 0.718 Hertz
Duty Cycle is always given in terms of percentage, if high time is equal to low time
then the pulse has 50% duty cycle and if the off time is zero then it has 100% duty
cycle. We can calculate the duty cycle as.
Duty Cycle = (T1/T) × 100
= (0.966/1.393) × 100
DC = 50.249 %
You might also like
- MR366X8488B000Document16 pagesMR366X8488B000Mislav GudeljNo ratings yet
- Measuring T1 and T2Document25 pagesMeasuring T1 and T2drnmrdrnmrNo ratings yet
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay SettingDocument2 pagesCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Settingsaran100% (2)
- Jungheinrich Ejc112 & E1202Document184 pagesJungheinrich Ejc112 & E1202Thomas Hansen80% (10)
- Modularis Service PDFDocument63 pagesModularis Service PDFVictor ZambranoNo ratings yet
- How To Configure A 555 Timer ICijDocument2 pagesHow To Configure A 555 Timer ICijJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- How To Configure A 555 Timer ICijDocument2 pagesHow To Configure A 555 Timer ICijJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- 555 TimersDocument29 pages555 TimersSatchit PrabhuNo ratings yet
- ES Assignment: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesES Assignment: ObjectiveLekhraj PariharNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9Nixon GamingNo ratings yet
- ELE302 - Lab 2-092021Document17 pagesELE302 - Lab 2-092021hughjass39.99No ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Instrumentation Lab EE-702Document5 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Instrumentation Lab EE-702Saurav SumanNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Maximum Sampling Rate of An Analog MuxDocument4 pagesHow To Calculate Maximum Sampling Rate of An Analog MuxmaysquaredNo ratings yet
- Beginning Time T Time To Half Value of V: TheoreticalDocument6 pagesBeginning Time T Time To Half Value of V: TheoreticalAli Amir ShreifNo ratings yet
- Measurement Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesMeasurement Literature Reviewuam22No ratings yet
- DC To DC Two Quadrant ConverterDocument7 pagesDC To DC Two Quadrant Converterhamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Dwarkadas. J. Sanghvi College of EngineeringDocument8 pagesDwarkadas. J. Sanghvi College of EngineeringAbir DeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3ARUN KUMAR PNo ratings yet
- APSC 1299 Test 2 - Spring 2011 AnswersDocument7 pagesAPSC 1299 Test 2 - Spring 2011 AnswersJonathan WongNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 PDFDocument4 pagesLab 1 PDFTanmay KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- Dealing With PLL Clock Jitter in Advanced Processor DesignsDocument5 pagesDealing With PLL Clock Jitter in Advanced Processor DesignsrobduronNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 6 - Sinusoidal Responses Self Assessment Exercise No.1Document1 pageControl Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 6 - Sinusoidal Responses Self Assessment Exercise No.1cataiceNo ratings yet
- Iv TimersDocument48 pagesIv TimersanishthNo ratings yet
- An550 PDFDocument8 pagesAn550 PDFCarlos RamirezNo ratings yet
- Sequential Logic and Memory ComponentsDocument9 pagesSequential Logic and Memory ComponentsShashank MishraNo ratings yet
- PLC Laboratory Activity 1Document4 pagesPLC Laboratory Activity 1Kate AlindajaoNo ratings yet
- 8051-CH9-TimePmg in Assem & CDocument101 pages8051-CH9-TimePmg in Assem & CshivaspyNo ratings yet
- A Multi Vibrator Is An Electronic Circuit Used To Implement ADocument5 pagesA Multi Vibrator Is An Electronic Circuit Used To Implement AbulkSoftNo ratings yet
- 1 Analog SignalsDocument25 pages1 Analog SignalsseenusoftNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document9 pagesChapter 22lotex77No ratings yet
- Sdic 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 2)Document4 pagesSdic 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 2)Ganapathy RamadossNo ratings yet
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) : Square WaveDocument23 pagesPulse Width Modulation (PWM) : Square WavepaulinaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 4 - System Response Self Assessment Exercise No.1Document3 pagesControl Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 4 - System Response Self Assessment Exercise No.1cataiceNo ratings yet
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)Document8 pagesCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)Aslam kathat100% (2)
- Microcontrollers and Its Applications: Shivaum Heranjal L27+28 17BEC0315 Padmini T NDocument6 pagesMicrocontrollers and Its Applications: Shivaum Heranjal L27+28 17BEC0315 Padmini T NShivaum Heranjal100% (1)
- Chapter 22 General Purpose PID ControlDocument10 pagesChapter 22 General Purpose PID ControlEduardo AlvearNo ratings yet
- Study and Evaluation of Performances of The Digital MultimeterDocument10 pagesStudy and Evaluation of Performances of The Digital Multimetermihaela0chiorescuNo ratings yet
- DMM PPTDocument17 pagesDMM PPTShah Najmus SaqibNo ratings yet
- Calculate Setting of IdmtDocument2 pagesCalculate Setting of IdmtsakthivelduraiNo ratings yet
- Digital Control System-1Document47 pagesDigital Control System-1Makesh MäKzNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 7 - Stability Analysis Self Assessment Exercise No.1Document4 pagesControl Systems Engineering D227 S.A.E. Solutions Tutorial 7 - Stability Analysis Self Assessment Exercise No.1cataiceNo ratings yet
- AstableDocument6 pagesAstablemanthan NaikNo ratings yet
- IdmtDocument3 pagesIdmtAdeel RazaNo ratings yet
- Large Amplitude Pendulum With PC InterfaceDocument8 pagesLarge Amplitude Pendulum With PC InterfaceKarl KaiNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller TimersDocument42 pagesMicrocontroller TimersPatel NeelNo ratings yet
- m4Document46 pagesm4sunilgj123No ratings yet
- Sample IDMT SettingDocument4 pagesSample IDMT SettingMesias John FedericoNo ratings yet
- Setting Calculation of Oc and Ef RealyDocument1 pageSetting Calculation of Oc and Ef RealyManishPandya67% (3)
- Ec6504 MPMC Unit 5Document192 pagesEc6504 MPMC Unit 5Gomathi PsNo ratings yet
- CT303: Digital Communication Lab1 and Lab2 Report: TOPIC 1: PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation)Document8 pagesCT303: Digital Communication Lab1 and Lab2 Report: TOPIC 1: PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation)LAKSHYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument43 pagesElectric DrivesDigital AlarmNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ExxonMobilDocument30 pagesHeat Transfer ExxonMobilHernan CobaNo ratings yet
- Real Timer ControlDocument94 pagesReal Timer ControlSai Krishna KodaliNo ratings yet
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)Document11 pagesCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50/51)robertovm2002No ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Wein-Bridge OscillatorDocument8 pagesAssignment 3: Wein-Bridge OscillatorDeepal PrasankaNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 Ultrashort Pulses 01Document33 pagesLecture03 Ultrashort Pulses 01Yeong Gyu KimNo ratings yet
- Working With IC555: : Astable MultivibratorDocument5 pagesWorking With IC555: : Astable Multivibrator9909552136No ratings yet
- The Dual-Slope Conversion Improvement: Radojle Radetić, Marijana Pavlov-Kagadejev, Nikola MilivojevićDocument13 pagesThe Dual-Slope Conversion Improvement: Radojle Radetić, Marijana Pavlov-Kagadejev, Nikola MilivojevićasprillaNo ratings yet
- Ger3973 (Calculo de TC para Proteccion)Document16 pagesGer3973 (Calculo de TC para Proteccion)Erick Daniel Toyo MarinNo ratings yet
- Allen J Wood Power Generation Operation OstDocument33 pagesAllen J Wood Power Generation Operation OstDhoviar M. AliNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesAbaid UllahNo ratings yet
- Extra: Battery Chargers and Expansion ModulesDocument2 pagesExtra: Battery Chargers and Expansion Modulessammy muisyoNo ratings yet
- Different Types of LightsDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of LightsAnusha SawhneyNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodsDocument2 pagesPartial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodskashifNo ratings yet
- UT593 595 Data SheetDocument1 pageUT593 595 Data SheetqaqcmepteamNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Systems-Variation of Efficiency With Band-Gap and TemperatureDocument9 pagesPhotovoltaic Systems-Variation of Efficiency With Band-Gap and TemperatureRaja SekaranNo ratings yet
- ) Mets: Iqdilution BookDocument106 pages) Mets: Iqdilution BookDanilNo ratings yet
- LAB 12-PE-LabDocument9 pagesLAB 12-PE-LabLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Ropex Res 403 - eDocument42 pagesRopex Res 403 - eАлександр Колосов100% (1)
- Advanced Switching Solutions: FeaturesDocument4 pagesAdvanced Switching Solutions: Featuresraza239No ratings yet
- Treadtronics ProfileDocument31 pagesTreadtronics ProfileEhtisham BhattiNo ratings yet
- Networked Option Pods Operating Instructions July 2023 v1.3Document17 pagesNetworked Option Pods Operating Instructions July 2023 v1.3Ariel Horta LoeraNo ratings yet
- Mos Inverters: Static CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesMos Inverters: Static Characteristicskeshav guptaNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument11 pagesCourseIvan ElisioNo ratings yet
- Study On The Effects of ElectromagnetsDocument6 pagesStudy On The Effects of ElectromagnetsDrake Athenaeus CaminongNo ratings yet
- Led Based Scrolling Message DisplayDocument125 pagesLed Based Scrolling Message DisplayVikas Choudhary100% (3)
- Etos TD and Etos ED Innovative Motor-Drive Solutions With Integrated MonitoringDocument12 pagesEtos TD and Etos ED Innovative Motor-Drive Solutions With Integrated Monitoringrichardt999No ratings yet
- Marshall 'Blues Breaker': Manual & Assembly GuideDocument27 pagesMarshall 'Blues Breaker': Manual & Assembly GuideAndre OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Logic Gates & Boolean AlgebraDocument32 pagesChapter 2 Logic Gates & Boolean AlgebraAmita PalNo ratings yet
- Ahuja SSA-250M Specifications & FeaturesDocument1 pageAhuja SSA-250M Specifications & Featuressecurekart50% (2)
- Audio StandardsDocument8 pagesAudio Standardsyomama3100% (1)
- Solis 3P-8K-4GDocument2 pagesSolis 3P-8K-4GBanjaran SolarNo ratings yet
- Arduino Base Over Voltage and Under Voltage Protection Circuit LITERATURE REVIEWDocument23 pagesArduino Base Over Voltage and Under Voltage Protection Circuit LITERATURE REVIEWOlasupo IyaboNo ratings yet
- Datasheet DL50-P1123 1047361 enDocument6 pagesDatasheet DL50-P1123 1047361 enFaiz BajwaNo ratings yet
- Electrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing Level - II: TVET Institution Training TheoryDocument4 pagesElectrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing Level - II: TVET Institution Training Theorybelacheweshetu222100% (3)
- 15p0072b1 Sinus N en r00Document142 pages15p0072b1 Sinus N en r00Maher JarrarNo ratings yet
- 7PA30321AA001 Datasheet enDocument2 pages7PA30321AA001 Datasheet enptepartheepan.sNo ratings yet