Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit-12 Carbonyl Compounds 2021
Unit-12 Carbonyl Compounds 2021
Uploaded by
jagannathanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit-12 Carbonyl Compounds 2021
Unit-12 Carbonyl Compounds 2021
Uploaded by
jagannathanCopyright:
Available Formats
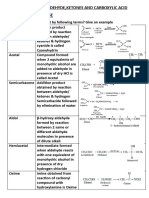
Compound IUPAC name Common name
Methanal Formaldehyde
Ethanal Acetaldehyde
Prop-2-enal Acrolein
But-2-enal Crotonaldehyde
Phenylmethanal Benzaldehyde
Propanone Acetone
1-phenylethan-1-one acetophenone
Diphenylmethanone Benzophenone
What is Ozonolysis? Give an example.
Alkenes react with ozone to form Ozonide and it is cleaved by Zn/H2O to form smaller
molecules.
What happens when 1-butene subjected for Ozonolysis?
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 1
What is Rosenmund reduction?
In this reaction BaSO4 is used as a Catalytic Poison
Formaldehyde cannot be prepared by this method, since formylchloride is unstable at
room temperature.
What is Stephen’s reaction?
Aldehydes can be prepared by the reduction of alkyl cyanides by SnCl 2/HCl.
Discuss the selective reduction of alkyl cyanides by DIBAL-H
Diisobutyl aluminium hydride (DIBAL –H) selectively reduces the alkyl cyanides to form
imines which on hydrolysis gives aldehydes.
What is Gattermann –Koch reaction?
When benzene is treated with a mixture of CO + HCl, it generates an intermediate which
reacts like formyl chloride to give benzaldehyde.
What is Urotropine? How is it prepared? Give its structure and use.
Formaldehyde reacts with ammonia to give Urotropine (hexa methylene tetramine)
Uses:
Urotropine is used to treat urinary infection.
Nitration of Urotropine under controlled condition
gives an explosive RDX. It is also called cyclonite (or)
cyclotrimethylene trinitramine.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 2
What is Popoff’s rule? Explain with an example.
When an unsymmetrical ketones is oxidised, a (C–CO) bond is cleaved in such a way that the
keto group stays with the smaller alkyl group.
What is Clemmenson reduction?
Aldehydes and Ketones when heated with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid
gives hydrocarbons.
What is Wolf kishner reduction?
Aldehydes and Ketones when heated with hydrazine and sodium ethoxide, hydrocarbons are
formed Hydrazine acts as a reducing agent and sodium ethoxide as a catalyst.
What is pinacol ? How is it prepared?
2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diol is known as Pinacol. It is prepared by the reduction of acetone
with magnesium amalgam and water.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 3
What is Iodoform (Haloform ) reaction ?
The carbonyl compounds having Methyl Keto group, undergoes Haloform reaction with
halogen and alkali to form an haloform.
What is crossed aldol condensation?
If aldol condensation takes place between two different aldehydes (or) ketones (or)
between one aldehyde and one ketone, it is called as crossed aldol condensation.
What is Claisen-Schmidt condensation?
Benzaldehyde condenses with aliphatic aldehyde or methyl ketone in the presence of
dil.alkali at room temperature to form unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 4
Explain the mechanism of aldol condensation.
When acetaldehyde is warmed with dil NaOH it gives acetaldol.
Mechanism:
Step-I :
The carbanion is formed by the removal of α hydrogen atom by a base.
Step-II:
Nucleophilic attack of carbonyl carbon by a carbanion to form an alkoxide ion.
Step-III:
protonation of alkoxide ion leads to an aldol.
This aldol rapidly undergoes dehydration on heating to form an
.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 5
Explain the mechanism of Cannizaro reaction.
Aldehydes which do not have α - hydrogen atom undergo disproportionation reaction to give
a mixture of alcohol and a salt of carboxylic acid.
Benzaldehyde on treatment with concentrated NaOH (50%) gives benzyl alcohol and
sodium benzoate.
Mechanism:
Step-1: Nucleophilic attack by OH- ion on carbonyl carbon
Step-2: Transfer of hydride ion.
Step-3: Transfer of proton:
What is crossed Cannizaro reaction?
When Cannizaro reaction takes place between two different aldehyde containing no α
hydrogen atom, the reaction is called as cross Cannizaro reaction. In this, more reactive
aldehyde is oxidized and less reactive aldehyde is reduced.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 6
What is Benzoin condensation?
When benzaldehyde is refluxed with aqueous alcoholic KCN solution, an α-hydroxy ketone
called Benzoin is formed.
What is Perkin reaction?
When benzaldehyde is heated with an acetic anhydride in the presence of
the sodium acetate, an cinnamic acid (α, β unsaturated acid) is obtained.
What is Knoevenagal reaction?
Benzaldehyde condenses with malonic acid in presence of pyridine to form Cinnamic
acid.
How will you convert benzaldehyde into Schiff’s base?
Benzaldehyde react with primary amines in the presence of an acid to form schiff ’s base.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 7
How will you convert Benzaldehyde into Malachite green?
Benzaldehyde condenses with N, N – dimethyl aniline in the presence of conc H 2SO4 to from
triphenyl methane dye.
Tollen’s Reagent Test (silver mirror test.)
Tollen’s reagent is an ammoniacal silver nitrate solution.
When an aldehyde is warmed with Tollen’s reagent a bright silver mirror is produced due
to the formation of silver metal.
Fehling’s solution Test
Fehling's solution is prepared by mixing equal volumes of Fehling-A ( CuSO 4) and Fehling-
B (alkaline solution of sodium potassium tartrate-Rochelle salt).
When an aldehyde is warmed with Fehling’s solution deep blue colour solution is
changed to red precipitate of cuprous oxide.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 8
Molecular formula Common name IUPAC name
HCOOH Formic acid Methanoic acid
CH3COOH Acetic acid Ethanoic acid
C3H7 COOH Butyric acid Butanoic acid
C6H5 COOH Benzoic acid Benzene carboxylic acid
How will you convert CO2 and CH3COOH?
Methyl magnesium bromide reacts with carbon di oxide (dry ice) followed by acidification
gives acetic acid.
Formic acid cannot be prepared by Grignard reagent since acid contains only one carbon
atom
How will you prepare benzoic acid prepared using Grignard reagent?
How is benzoic acid prepared from toluene?
Benzoic acid can be prepared by vigorous oxidation of alkyl benzene with
chromic acid (or) acidic (or) alkaline potassium permanganate.
What is glacial acetic acid?
Pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid.
Vinegar is 6 to 8% solution of acetic acid in water.
When aqueous acetic acid is cooled at 289.5 K (16.350C), acetic acid solidifies and forms
ice like crystals, whereas water remains in liquid state and removed by filtration. This
process is repeated to obtain glacial acetic acid.
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 9
Give any three tests for carboxylic acids.
Aqueous solution of carboxylic acids turns Blue litmus into Red.
When carboxylic acid is warmed with alcohol and Con H 2SO4 it forms an ester, which is
detected by its fruity odour.
Carboxylic acids give brisk effervescence with sodium bi carbonate solution due to
evolution of carbon di oxide.
Explain the mechanism of esterification reaction.
When carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of conc. H 2SO4 (or dry HCl)
esters are formed. This reaction is reversible.
Mechanism:
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 10
1. The correct structure of the product ‘A’ formed in the reaction
a) b)
c) d)
2. The formation of cyanohydrin from acetone is an example of
a) Nucleophilic substitution b) electrophilic substitution
c) Electrophilic addition d) Nucleophilic addition
3. Reaction of acetone with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition
followed by elimination of water. The reagent is
a) Grignard reagent
b) Sn / HCl
c) Hydrazine in presence of slightly acidic solution
d) hydrocyanic acid
4. the final product ‘Y’ is
a) Formaldehyde b) diacetoneammonia
c) Hexamethylenetetramine d) oxime
5. Predict the product Z in the following series of reactions
a) ( C H 3 ) 2 C ( OH ) C 6 H 5 b) CH 3 CH ( OH ) C 6 H 5
c) C H 3 CH ( OH ) C H 2 C H 3 d) C 6 H 5 C H 2 OH
6. the compound ‘C’ is
a) Anilinium chloride b) O – nitro aniline
c) Benzene diazonium chloride d) m – nitro benzoic acid
7. . This reaction is called
a) Finkelstein reaction b) Haloform reaction
c) Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction d) none of these
8. . The product (c) is
a) Acetyl chloride b) Chloro acetic acid
c) α- Chlorocyano ethanoic acid d) none of these
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 11
9. Which one of the following reduces Tollen’s reagent
a) Formic acid b) acetic acid
c) Benzophenone d) none of these
10. the product B is
a) b)
c) d)
11. The IUPAC name of
a) but – 3- enoicacid b) but – 1- ene-4-oicacid
c) but – 2- ene-1-oic acid d) but -3-ene-1-oicacid
12. Identify the product formed in the reaction
a) b)
c) d)
13. Assertion : p – N, N – dimethyl amino benzaldehyde undergoes benzoin condensation
Reason : The aldehyde (-CHO) group is meta directing
a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion.
c) assertion is true but reason is false
d) both assertion and reason are false.
14. Which one of the following reaction is an example of disproportionation reaction?
a) Aldol condensation b) cannizaro reaction
c) Benzoin condensation d) none of these
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 12
15. Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% sodium hydroxide solution to give
the corresponding alcohol and acid
a) Phenyl Methanal b) Ethanal c) Ethanol d) methanol
16. Phenyl Methanal is reacted with concentrated NaOH to give two products X and Y. X reacts
with metallic sodium to liberate hydrogen X and Y are
a) sodiumbenzoate and phenol
b) Sodium benzoate and phenyl methanol
c) Phenyl methanol and sodium benzoate
d) None of these
17. In which of the following reactions new carbon – carbon bond is not formed?
a) Aldol condensation b) Friedel craft reaction
c) Kolbe’s reaction d) Wolf kishner reduction
18. An alkene “A” on reaction with O 3 and Zn – H2O gives propanone and ethanol in equimolar
ratio. Addition of HCl to alkene “A” gives “B” as the major product. The structure of product
“B” is
a) b)
c) d)
19. Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of
comparable molecular mass. It is due to their
a) more extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals force of attraction
b) formation of carboxylate ion
c) formation of intramolecular H-bonding
d) formation of intermolecular H – bonding
20. Of the following, which is the product formed when cyclohexanone undergoes aldol
condensation followed by heating?
a) b)
c) d)
UNIT –12 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS The Turning Point 13
You might also like
- All Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFDocument11 pagesAll Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFprabs2006917882% (152)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 2015 JC2 H2 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Part 1 Tutorial (Teachers) UpdatedDocument18 pages2015 JC2 H2 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Part 1 Tutorial (Teachers) UpdatedJohnNo ratings yet
- Prodew 400: Amino Acid Based Humectant For Skin CareDocument26 pagesProdew 400: Amino Acid Based Humectant For Skin CareKlara Miliktrisa KirbitievnaNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisecse.220840131017No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument19 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidPraneel BhattNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument119 pagesAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsKashvi KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds TVVDocument13 pagesCarbonyl Compounds TVVjyothi sai sriNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument50 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acidssukaina fatima100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationTiya KapoorNo ratings yet
- 1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument117 pages1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsKRISHNARJUNA NNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds: A2 Chemistry Unit 4Document45 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: A2 Chemistry Unit 4Faddy Oraha100% (1)
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesDocument58 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument40 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsMiguelNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetonesDocument45 pagesAldehyde and KetonesShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Named RXNDocument10 pagesNamed RXNssatechies62No ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionsDocument5 pagesNamed ReactionsJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Aldehydes and KetonesDocument11 pagesPreparation of Aldehydes and KetonesJyoti Gaba -ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Namedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Document11 pagesNamedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Vishant SinghNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compound-2Document20 pagesCarbonyl Compound-2fishindasea00No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 3Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3GundanNo ratings yet
- Project On Name Reaction PDFDocument10 pagesProject On Name Reaction PDFAbhinav SaxenaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument40 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Name ReactionsDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Name ReactionspiyashnathNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Organic Chemistry ReactionsDocument6 pagesUnit 4 Organic Chemistry ReactionsRobbing_Hood100% (1)
- Theory of The Aldol Condensation ReactionDocument9 pagesTheory of The Aldol Condensation ReactionaizatNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationAtif AteeqNo ratings yet
- Updated Grade 12 Organic Name Reactions-Units 10,11,12,13Document10 pagesUpdated Grade 12 Organic Name Reactions-Units 10,11,12,13Tanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsDocument64 pagesChapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactionsaggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- All Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFDocument11 pagesAll Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFzakiya100% (2)
- NotesDocument10 pagesNotespovikanimathiNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionsDocument10 pagesName ReactionsParam SoniNo ratings yet
- F334 - What's in A Medicine?Document11 pagesF334 - What's in A Medicine?Becky Tenney100% (1)
- Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsDocument20 pagesReduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsDhewi LayNo ratings yet
- 20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFDocument21 pages20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFJoshua VincentNo ratings yet
- All Named Reactions of ChemistryDocument11 pagesAll Named Reactions of ChemistryAbhay Narayan Mishra0% (1)
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument20 pagesAldehydes and KetonesA BeheraNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions YhcDocument5 pagesName Reactions Yhcpcyathish37100% (1)
- AldolDocument7 pagesAldolGindo Baroes WanNo ratings yet
- Important Name Reactions of Chemistry in Class 12th CBSE and ISC BoardDocument11 pagesImportant Name Reactions of Chemistry in Class 12th CBSE and ISC BoardGudia kumari100% (1)
- Naming Reactions Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesNaming Reactions Organic Chemistrysaapldesign1 1No ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 1Document12 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers 1kumar.gammer07ayushNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocument104 pagesAldehydes & KetonesCharin Kadian75% (4)
- NamereactionorganicDocument13 pagesNamereactionorganicdeykrishna654100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Important Reagents-EditDocument19 pagesOrganic Chemistry Important Reagents-Edit10C 27 SAI VISHWA JETHNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY FORM 6 SEM 3 Chapter 6 PDFDocument32 pagesCHEMISTRY FORM 6 SEM 3 Chapter 6 PDFYuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- Notes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIDocument52 pagesNotes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIMahesh AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocument5 pagesAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiNo ratings yet
- Akash & Priyanshu XIIDocument24 pagesAkash & Priyanshu XIIAnindya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- C C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CDocument5 pagesC C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CShan TiNo ratings yet
- Organic Nitrogen CompoundsDocument9 pagesOrganic Nitrogen CompoundsSaranga BuwanekaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSC Board Important Reactions PDFDocument47 pagesChemistry HSC Board Important Reactions PDFNutzie YNo ratings yet
- Done By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDocument10 pagesDone By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim Papersdiejunqs sNo ratings yet
- Kap 5 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral CentersDocument102 pagesKap 5 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral CentersHemen ZebariNo ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Unit-14 BiomoleculesDocument25 pagesUnit-14 BiomoleculesjagannathanNo ratings yet
- 7 Thermodynamics 2023Document18 pages7 Thermodynamics 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Unit-7 Chemical Kinetics 2021Document12 pagesUnit-7 Chemical Kinetics 2021jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Unit-12 Carbonyl Compounds 2023Document20 pagesUnit-12 Carbonyl Compounds 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 P-Block Elements-Ii 2021Document9 pagesUnit-3 P-Block Elements-Ii 2021jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Metallurgy 2023Document12 pagesUnit-1 Metallurgy 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Activity 6Document4 pagesPost Lab Activity 6Shaira Soriano CincoNo ratings yet
- H BR H H 1 2 1 2 (A, E) Cis-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR H H BR H BR 1 2 1 2 (A, A) Trans-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR BR BR HDocument19 pagesH BR H H 1 2 1 2 (A, E) Cis-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR H H BR H BR 1 2 1 2 (A, A) Trans-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR BR BR HVIGHNESH BALKRISHNA LOKARENo ratings yet
- DFGHJKLDocument102 pagesDFGHJKLLucas MarchiniNo ratings yet
- Soap and DetergentDocument24 pagesSoap and DetergentCik Tiem Ngagiman80% (10)
- Org Chem Lesson Plan Tuliao Alleah Eunice CDocument6 pagesOrg Chem Lesson Plan Tuliao Alleah Eunice Calleaheunice29No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds 1654147338445Document33 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 1654147338445Harsh VardhanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesCarboxylic Acidsapi-3734333100% (1)
- Chemistry: 13. S-And P - Block ElementsDocument8 pagesChemistry: 13. S-And P - Block ElementsAimen AmjadNo ratings yet
- Pyrrolo (1,2 A) Quinoxalines BasedDocument24 pagesPyrrolo (1,2 A) Quinoxalines BasededwquimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Drug Design: Topic 7.2Document38 pagesIntroduction To Drug Design: Topic 7.2detki007No ratings yet
- Alkohol Dari Senyawa KarbonilDocument31 pagesAlkohol Dari Senyawa KarbonilAshfie MarwaNo ratings yet
- Part XI - CHEMISTRY OF CARBON COMPOUNDS (Part 1)Document67 pagesPart XI - CHEMISTRY OF CARBON COMPOUNDS (Part 1)yana LAUNo ratings yet
- B.pharmacy SyllabusDocument74 pagesB.pharmacy SyllabusPraveen Johnny AlugojuNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Monitoring The Environment: Stage 2 Chemistry Must Know ListDocument40 pagesTopic 1: Monitoring The Environment: Stage 2 Chemistry Must Know ListThalia MaesNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument50 pagesExerciseAbhiNo ratings yet
- Low Water Permeability Through Hydrophobicity: COIN Project Report 1 - 2008Document36 pagesLow Water Permeability Through Hydrophobicity: COIN Project Report 1 - 2008Alejandro Camargo SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BDocument18 pagesTutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- C11 Alcohol, Phenol & EthersDocument1 pageC11 Alcohol, Phenol & EthersRonak kadamNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Organic Synthesis: Formation of An Ester Lab ReportDocument11 pagesTable of Content: Organic Synthesis: Formation of An Ester Lab ReportMuhammad Irfan Malik100% (1)
- NJ SirDocument5 pagesNJ SirAyush shuklaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Organic ChemDocument5 pagesModule 6 - Organic Chemangelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- OCR F324 MS Chemistry - Rings, Polymers and Analysis January 2011 MARK SCHEMEDocument18 pagesOCR F324 MS Chemistry - Rings, Polymers and Analysis January 2011 MARK SCHEMEDNo ratings yet
- Terms I Should Remember BiochemDocument1 pageTerms I Should Remember BiochemAmyNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Answers To ProblemsDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Answers To ProblemsKshitij BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Methods of Lead OptimizationDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Methods of Lead Optimizationمها عقديNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles & TechniquesDocument22 pagesOrganic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles & TechniquesBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- Notes C16 121Document13 pagesNotes C16 121Amir HussainNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Isoprenyl Ether Polymer Molecular Structure On Cementitious CompositesDocument11 pagesThe Effect of Isoprenyl Ether Polymer Molecular Structure On Cementitious Compositessantosh mhetreNo ratings yet